
Basic Nursing 1st Edition by Judith Wilkinson, Leslie Treas
Edition 1ISBN: 9780803627789
Basic Nursing 1st Edition by Judith Wilkinson, Leslie Treas
Edition 1ISBN: 9780803627789 Exercise 13
M., McGinnis, M.A., Hudson, L R., et al. (2006).A focused telephonic nursing intervention delivers improved adherence to A lc testing. Disease Management 9(5), 277-283.
This 6-month study investigated whether a focused telephone intervention would improve patient adherence to hemoglobin A I c testing (a test of diabetes control). Subjects were already enrolled in a diabetes disease management program and were receiving various types of phone calls and educational materials. During the study, when a routine call was made to a member of the program, the clinician determined whether the A I c had been tested in the past 6 months. If not, a specific goal was created with the member during the conversation (e.g., "I will make an appointment to follow up on my A I c test"); a copy was mailed to the member. Phone calls were repeated every 2 weeks to check on the person's progress in meeting the goal. Patient records were examined for evidence that an Alc test had been done. At the end of the 6 months, quantitative analysis of data was done. The number of group members who received an A I c test increased significantly, by 12%. Gender did not affect adherence to A I c testing, but age did. The greatest improvement was observed in the 0- to 19-year age group (14.9%), those ages 50 to 59 (12.7%), and those ages 60 to 69 years (I 3.4%). All other age categories showed increases ranging from 8.1% to 10.6%. Increases in the number of phone calls made to a member were associated with subsequent increases in Alc testing adherence.
Duhamel, F., Dupuis, F., Reidy, M., et al. (2007).A qualitative evaluation of a family nursing intervention. Clinical Nurse Specialist, 2I (1 ), 43-49.
In this qualitative study, a clinical nurse specialist met with each of four couples for four 60-minute therapeutic meetings. Meetings were also audiotaped. The patients were retired men with congestive heart failure (CHF), whose wives were their caregivers. Researchers used semi structured interviews before and after the intervention and analyzed them qualitatively. Results showed that both spouses were experiencing a high level of suffering, which was relieved through a family nursing meeting that allowed them to obtain a better understanding of each other's experience.
How are these two studies similar (if you need to do so read about research in Chpater8.)
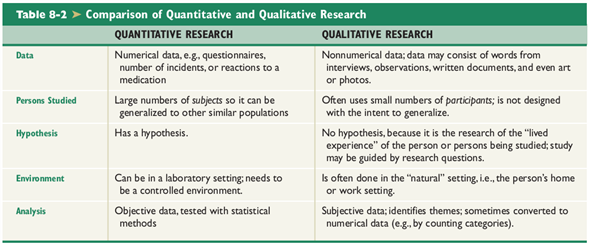
Quantitative Research
The main purpose of quantitative research is to gather data from enough subjects (people being studied) to be able to generalize the results to a similar population. Generalizing results means that you think, "What I found to be so for this sample group of people will probably be the same for all people who are similar" (e.g., "My findings for this group of women over age 40 in the United States will probably be useful for all women over age 40 in the United States"). In quantitative research, researchers carefully control data collection and are careful to maintain the objectivity of the process. Quantitative data are reported as numbers. The Framingham studies are a classic example of a quantitative study-actually of several quantitative studies. To read more about this landmark research,
Another classic example of quantitative nursing research is the Conduct and Utilization of Research in Nursing (CURN) project, which was intended to increase the use of research by direct-care nurses (Horsley, 1983). Many of the protocols (procedures) developed from these studies are used today with some modification. The following are some CURN protocol examples:
Clean intermittent catheterization
Intravenous cannula change
Distress reduction through sensory preparation
Preventing decubitus ulcers
Qualitative Research
Qualitative research focuses on the lived experience of people. The purpose is not to generalize the data, but to share the experience of the person or persons in the study. There is no need for large numbers. A case study of one person can examine the lived experience, for example, of a 19-year-old single mother of triplets or a middle-aged woman with HIV. Qualitative research uses words, quotations from persons interviewed, observations, and other nonnumeric sources of data. The Nun Study, a long-term, multidisciplinary project involving a convent of Catholic nuns in Minnesota, included some qualitative research (e.g., data obtained by interviews
This 6-month study investigated whether a focused telephone intervention would improve patient adherence to hemoglobin A I c testing (a test of diabetes control). Subjects were already enrolled in a diabetes disease management program and were receiving various types of phone calls and educational materials. During the study, when a routine call was made to a member of the program, the clinician determined whether the A I c had been tested in the past 6 months. If not, a specific goal was created with the member during the conversation (e.g., "I will make an appointment to follow up on my A I c test"); a copy was mailed to the member. Phone calls were repeated every 2 weeks to check on the person's progress in meeting the goal. Patient records were examined for evidence that an Alc test had been done. At the end of the 6 months, quantitative analysis of data was done. The number of group members who received an A I c test increased significantly, by 12%. Gender did not affect adherence to A I c testing, but age did. The greatest improvement was observed in the 0- to 19-year age group (14.9%), those ages 50 to 59 (12.7%), and those ages 60 to 69 years (I 3.4%). All other age categories showed increases ranging from 8.1% to 10.6%. Increases in the number of phone calls made to a member were associated with subsequent increases in Alc testing adherence.
Duhamel, F., Dupuis, F., Reidy, M., et al. (2007).A qualitative evaluation of a family nursing intervention. Clinical Nurse Specialist, 2I (1 ), 43-49.
In this qualitative study, a clinical nurse specialist met with each of four couples for four 60-minute therapeutic meetings. Meetings were also audiotaped. The patients were retired men with congestive heart failure (CHF), whose wives were their caregivers. Researchers used semi structured interviews before and after the intervention and analyzed them qualitatively. Results showed that both spouses were experiencing a high level of suffering, which was relieved through a family nursing meeting that allowed them to obtain a better understanding of each other's experience.
How are these two studies similar (if you need to do so read about research in Chpater8.)
Quantitative Research
The main purpose of quantitative research is to gather data from enough subjects (people being studied) to be able to generalize the results to a similar population. Generalizing results means that you think, "What I found to be so for this sample group of people will probably be the same for all people who are similar" (e.g., "My findings for this group of women over age 40 in the United States will probably be useful for all women over age 40 in the United States"). In quantitative research, researchers carefully control data collection and are careful to maintain the objectivity of the process. Quantitative data are reported as numbers. The Framingham studies are a classic example of a quantitative study-actually of several quantitative studies. To read more about this landmark research,
Another classic example of quantitative nursing research is the Conduct and Utilization of Research in Nursing (CURN) project, which was intended to increase the use of research by direct-care nurses (Horsley, 1983). Many of the protocols (procedures) developed from these studies are used today with some modification. The following are some CURN protocol examples:
Clean intermittent catheterization
Intravenous cannula change
Distress reduction through sensory preparation
Preventing decubitus ulcers
Qualitative Research
Qualitative research focuses on the lived experience of people. The purpose is not to generalize the data, but to share the experience of the person or persons in the study. There is no need for large numbers. A case study of one person can examine the lived experience, for example, of a 19-year-old single mother of triplets or a middle-aged woman with HIV. Qualitative research uses words, quotations from persons interviewed, observations, and other nonnumeric sources of data. The Nun Study, a long-term, multidisciplinary project involving a convent of Catholic nuns in Minnesota, included some qualitative research (e.g., data obtained by interviews

Explanation
Study 1 :
This study examined a telephon...
Basic Nursing 1st Edition by Judith Wilkinson, Leslie Treas
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



