Deck 6: Optimization Models With Integer Variables
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/28
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Optimization Models With Integer Variables
1
Rounding the solution of a linear programming to the nearest integer values provides an:
A) integer solution that is optimal
B) integer solution that is not optimal
C) integer solution that might be optimal
D) infeasible solution
A) integer solution that is optimal
B) integer solution that is not optimal
C) integer solution that might be optimal
D) infeasible solution
C
2
An algorithm which uses implicit enumeration:
A) is impractical
B) examines all possible solutions
C) does not guarantee that some of the solutions not examined could be optimal
D) excludes many possible solutions that guaranteed to be suboptimal
A) is impractical
B) examines all possible solutions
C) does not guarantee that some of the solutions not examined could be optimal
D) excludes many possible solutions that guaranteed to be suboptimal
D
3
In a set-covering model,each member of a given set (set 1)must be "covered" by all members of another set (set 2).
False
4
Exhibit 6-1
A recent college graduate is planning to move cross country from her college town to the city where her first job is located.She has rented a truck that can haul up to 1100 cubic feet of furniture.The volume and value of each item she is considering moving on the truck are given below.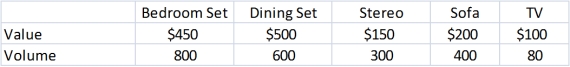
Refer to Exhibit 6-1.This problem is an example of what type of integer programming model?
A recent college graduate is planning to move cross country from her college town to the city where her first job is located.She has rented a truck that can haul up to 1100 cubic feet of furniture.The volume and value of each item she is considering moving on the truck are given below.

Refer to Exhibit 6-1.This problem is an example of what type of integer programming model?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Complete enumeration of all possible solutions in many integer programming problems is impractical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The branch and bound algorithm uses:
A) lower bounds
B) upper bounds
C) both upper and lower bounds
D) neither upper or lower bounds
A) lower bounds
B) upper bounds
C) both upper and lower bounds
D) neither upper or lower bounds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Exhibit 6-1
A recent college graduate is planning to move cross country from her college town to the city where her first job is located.She has rented a truck that can haul up to 1100 cubic feet of furniture.The volume and value of each item she is considering moving on the truck are given below.
Refer to Exhibit 6-1.Which items should she take with her to her new home? What is the value of these items?
A recent college graduate is planning to move cross country from her college town to the city where her first job is located.She has rented a truck that can haul up to 1100 cubic feet of furniture.The volume and value of each item she is considering moving on the truck are given below.

Refer to Exhibit 6-1.Which items should she take with her to her new home? What is the value of these items?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The binary variables in the fixed cost models correspond to:
A) the number of units or products produced
B) the total profit
C) the amount of labor hours
D) a process for which a fixed cost occurs
A) the number of units or products produced
B) the total profit
C) the amount of labor hours
D) a process for which a fixed cost occurs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In a linear model,the target cell and constraints are ultimately:
A) a product of changing cells
B) a sum of products of changing cells
C) a product of constants and changing cells
D) a sum of products of constants and changing cells
A) a product of changing cells
B) a sum of products of changing cells
C) a product of constants and changing cells
D) a sum of products of constants and changing cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The branching part of the branch and bound algorithm that Solver uses to solve integer programming models means that the algorithm:
A) creates subsets of solutions through which to search
B) searches through only a limited set of feasible integer solutions
C) identifies an incumbent solution which is optimal
D) uses a decision tree to find the optimal solution
A) creates subsets of solutions through which to search
B) searches through only a limited set of feasible integer solutions
C) identifies an incumbent solution which is optimal
D) uses a decision tree to find the optimal solution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In a model with 8 changing cells,all of which are constrained to be binary,the number of potentially feasible solutions is:
A) 4
B) 8
C) 64
D) 256
A) 4
B) 8
C) 64
D) 256

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Optimization software,including Solver,typically has more difficulty solving an integer programming problem,relative to a linear programming problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Problems with a fixed cost that is incurred only if an activity is undertaken at a positive level are inherently nonlinear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Solver may be unable to solve some integer programming problems,even when they have an optimal solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
During the solution of a problem with the branch and bound algorithm,an incumbent solution represents an upper bound on the solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The higher the upper bound produced in the branch and bound solution process,the faster the algorithm will be.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Many inherently nonlinear problems can be transformed into linear models with the use of:
A) integer variables
B) integer constraints
C) binary variables
D) binary constraints
A) integer variables
B) integer constraints
C) binary variables
D) binary constraints

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If Solver fails to find an optimal solution to an integer programming problem,we might be able to find a near optimal solution by decreasing the tolerance setting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Fixed costs imply that the divisibility assumption of linear models no longer holds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The LP relaxation of an integer programming (IP)problem is typically easy to solve and provides a bound for the IP model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Exhibit 6-2
Sinclair Plastics operates two chemical plants which produce polyethylene; the Ohio Valley plant which can produce up to 10,000 tons per month and the Lakeview plant which can produce up to 7,000 tons per month.Sinclair sells its polyethylene to three different auto manufacturing plants,Grand Rapids (demand = 3000 tons per month),Blue Ridge (demand = 5000 tons per month),and Sunset (demand = 4000 tons per month).The variable unit costs of shipping between the respective plants are shown in the table below:
 In addition to the variable unit costs of shipping,Sinclair incurs a fixed handling cost (of pickup and delivery)for any shipping routes it uses.These costs are discounted for longer routes,as shown below:
In addition to the variable unit costs of shipping,Sinclair incurs a fixed handling cost (of pickup and delivery)for any shipping routes it uses.These costs are discounted for longer routes,as shown below: 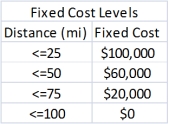
Refer to Exhibit 6-2.This problem is an example of what type of integer programming model?
Sinclair Plastics operates two chemical plants which produce polyethylene; the Ohio Valley plant which can produce up to 10,000 tons per month and the Lakeview plant which can produce up to 7,000 tons per month.Sinclair sells its polyethylene to three different auto manufacturing plants,Grand Rapids (demand = 3000 tons per month),Blue Ridge (demand = 5000 tons per month),and Sunset (demand = 4000 tons per month).The variable unit costs of shipping between the respective plants are shown in the table below:
 In addition to the variable unit costs of shipping,Sinclair incurs a fixed handling cost (of pickup and delivery)for any shipping routes it uses.These costs are discounted for longer routes,as shown below:
In addition to the variable unit costs of shipping,Sinclair incurs a fixed handling cost (of pickup and delivery)for any shipping routes it uses.These costs are discounted for longer routes,as shown below: 
Refer to Exhibit 6-2.This problem is an example of what type of integer programming model?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Exhibit 6-2
Sinclair Plastics operates two chemical plants which produce polyethylene; the Ohio Valley plant which can produce up to 10,000 tons per month and the Lakeview plant which can produce up to 7,000 tons per month.Sinclair sells its polyethylene to three different auto manufacturing plants,Grand Rapids (demand = 3000 tons per month),Blue Ridge (demand = 5000 tons per month),and Sunset (demand = 4000 tons per month).The variable unit costs of shipping between the respective plants are shown in the table below:
 In addition to the variable unit costs of shipping,Sinclair incurs a fixed handling cost (of pickup and delivery)for any shipping routes it uses.These costs are discounted for longer routes,as shown below:
In addition to the variable unit costs of shipping,Sinclair incurs a fixed handling cost (of pickup and delivery)for any shipping routes it uses.These costs are discounted for longer routes,as shown below: 
Refer to Exhibit 6-2.Suppose the shipping capacity for all routes is 3000 tons per month.What is Sinclair's optimal shipping plan in that case? What is the total cost in that case?
Sinclair Plastics operates two chemical plants which produce polyethylene; the Ohio Valley plant which can produce up to 10,000 tons per month and the Lakeview plant which can produce up to 7,000 tons per month.Sinclair sells its polyethylene to three different auto manufacturing plants,Grand Rapids (demand = 3000 tons per month),Blue Ridge (demand = 5000 tons per month),and Sunset (demand = 4000 tons per month).The variable unit costs of shipping between the respective plants are shown in the table below:
 In addition to the variable unit costs of shipping,Sinclair incurs a fixed handling cost (of pickup and delivery)for any shipping routes it uses.These costs are discounted for longer routes,as shown below:
In addition to the variable unit costs of shipping,Sinclair incurs a fixed handling cost (of pickup and delivery)for any shipping routes it uses.These costs are discounted for longer routes,as shown below: 
Refer to Exhibit 6-2.Suppose the shipping capacity for all routes is 3000 tons per month.What is Sinclair's optimal shipping plan in that case? What is the total cost in that case?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Exhibit 6-3
PharmaCo wants to determine how to deploy sales representatives across its Western U.S.region to support a new drug for obesity.Sales representatives will be located in a "home city",which they serve,in addition to cities with feasible commuting distance,with the objective that all cities must be served by at least one sales representative.The feasible connections between each city in the region are listed below (1 indicates a feasible connection):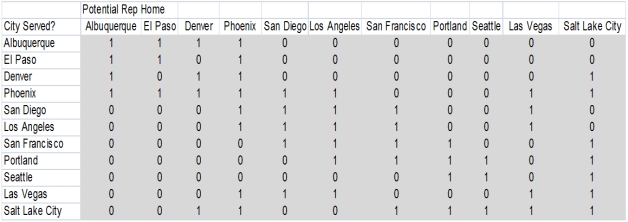
Refer to Exhibit 6-3.Suppose PharmaCo wants to have a backup for each city.What is the minimum number of representatives that can cover this region in that case? What are their home cities?
PharmaCo wants to determine how to deploy sales representatives across its Western U.S.region to support a new drug for obesity.Sales representatives will be located in a "home city",which they serve,in addition to cities with feasible commuting distance,with the objective that all cities must be served by at least one sales representative.The feasible connections between each city in the region are listed below (1 indicates a feasible connection):

Refer to Exhibit 6-3.Suppose PharmaCo wants to have a backup for each city.What is the minimum number of representatives that can cover this region in that case? What are their home cities?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Exhibit 6-3
PharmaCo wants to determine how to deploy sales representatives across its Western U.S.region to support a new drug for obesity.Sales representatives will be located in a "home city",which they serve,in addition to cities with feasible commuting distance,with the objective that all cities must be served by at least one sales representative.The feasible connections between each city in the region are listed below (1 indicates a feasible connection):
Refer to Exhibit 6-3.Formulate an integer programming model to identify a feasible deployment plan to the sales representatives.What is the minimum number of representatives that can cover this region? What are their home cities?
PharmaCo wants to determine how to deploy sales representatives across its Western U.S.region to support a new drug for obesity.Sales representatives will be located in a "home city",which they serve,in addition to cities with feasible commuting distance,with the objective that all cities must be served by at least one sales representative.The feasible connections between each city in the region are listed below (1 indicates a feasible connection):

Refer to Exhibit 6-3.Formulate an integer programming model to identify a feasible deployment plan to the sales representatives.What is the minimum number of representatives that can cover this region? What are their home cities?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Exhibit 6-1
A recent college graduate is planning to move cross country from her college town to the city where her first job is located.She has rented a truck that can haul up to 1100 cubic feet of furniture.The volume and value of each item she is considering moving on the truck are given below.
Refer to Exhibit 6-1.Suppose she can save $400 by renting a smaller truck,which has only 800 cubic feed of capacity.Would she be better off with the smaller truck?
A recent college graduate is planning to move cross country from her college town to the city where her first job is located.She has rented a truck that can haul up to 1100 cubic feet of furniture.The volume and value of each item she is considering moving on the truck are given below.

Refer to Exhibit 6-1.Suppose she can save $400 by renting a smaller truck,which has only 800 cubic feed of capacity.Would she be better off with the smaller truck?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Exhibit 6-3
PharmaCo wants to determine how to deploy sales representatives across its Western U.S.region to support a new drug for obesity.Sales representatives will be located in a "home city",which they serve,in addition to cities with feasible commuting distance,with the objective that all cities must be served by at least one sales representative.The feasible connections between each city in the region are listed below (1 indicates a feasible connection):
Refer to Exhibit 6-3.This problem is an example of what type of integer programming model?
PharmaCo wants to determine how to deploy sales representatives across its Western U.S.region to support a new drug for obesity.Sales representatives will be located in a "home city",which they serve,in addition to cities with feasible commuting distance,with the objective that all cities must be served by at least one sales representative.The feasible connections between each city in the region are listed below (1 indicates a feasible connection):

Refer to Exhibit 6-3.This problem is an example of what type of integer programming model?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Exhibit 6-2
Sinclair Plastics operates two chemical plants which produce polyethylene; the Ohio Valley plant which can produce up to 10,000 tons per month and the Lakeview plant which can produce up to 7,000 tons per month.Sinclair sells its polyethylene to three different auto manufacturing plants,Grand Rapids (demand = 3000 tons per month),Blue Ridge (demand = 5000 tons per month),and Sunset (demand = 4000 tons per month).The variable unit costs of shipping between the respective plants are shown in the table below:
 In addition to the variable unit costs of shipping,Sinclair incurs a fixed handling cost (of pickup and delivery)for any shipping routes it uses.These costs are discounted for longer routes,as shown below:
In addition to the variable unit costs of shipping,Sinclair incurs a fixed handling cost (of pickup and delivery)for any shipping routes it uses.These costs are discounted for longer routes,as shown below: 
Refer to Exhibit 6-2.What problem will occur if we use an IF statement to model the fixed handling costs?
Sinclair Plastics operates two chemical plants which produce polyethylene; the Ohio Valley plant which can produce up to 10,000 tons per month and the Lakeview plant which can produce up to 7,000 tons per month.Sinclair sells its polyethylene to three different auto manufacturing plants,Grand Rapids (demand = 3000 tons per month),Blue Ridge (demand = 5000 tons per month),and Sunset (demand = 4000 tons per month).The variable unit costs of shipping between the respective plants are shown in the table below:
 In addition to the variable unit costs of shipping,Sinclair incurs a fixed handling cost (of pickup and delivery)for any shipping routes it uses.These costs are discounted for longer routes,as shown below:
In addition to the variable unit costs of shipping,Sinclair incurs a fixed handling cost (of pickup and delivery)for any shipping routes it uses.These costs are discounted for longer routes,as shown below: 
Refer to Exhibit 6-2.What problem will occur if we use an IF statement to model the fixed handling costs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Exhibit 6-2
Sinclair Plastics operates two chemical plants which produce polyethylene; the Ohio Valley plant which can produce up to 10,000 tons per month and the Lakeview plant which can produce up to 7,000 tons per month.Sinclair sells its polyethylene to three different auto manufacturing plants,Grand Rapids (demand = 3000 tons per month),Blue Ridge (demand = 5000 tons per month),and Sunset (demand = 4000 tons per month).The variable unit costs of shipping between the respective plants are shown in the table below:
 In addition to the variable unit costs of shipping,Sinclair incurs a fixed handling cost (of pickup and delivery)for any shipping routes it uses.These costs are discounted for longer routes,as shown below:
In addition to the variable unit costs of shipping,Sinclair incurs a fixed handling cost (of pickup and delivery)for any shipping routes it uses.These costs are discounted for longer routes,as shown below: 
Refer to Exhibit 6-2.What is Sinclair's optimal shipping plan? What is the total cost in that case?
Sinclair Plastics operates two chemical plants which produce polyethylene; the Ohio Valley plant which can produce up to 10,000 tons per month and the Lakeview plant which can produce up to 7,000 tons per month.Sinclair sells its polyethylene to three different auto manufacturing plants,Grand Rapids (demand = 3000 tons per month),Blue Ridge (demand = 5000 tons per month),and Sunset (demand = 4000 tons per month).The variable unit costs of shipping between the respective plants are shown in the table below:
 In addition to the variable unit costs of shipping,Sinclair incurs a fixed handling cost (of pickup and delivery)for any shipping routes it uses.These costs are discounted for longer routes,as shown below:
In addition to the variable unit costs of shipping,Sinclair incurs a fixed handling cost (of pickup and delivery)for any shipping routes it uses.These costs are discounted for longer routes,as shown below: 
Refer to Exhibit 6-2.What is Sinclair's optimal shipping plan? What is the total cost in that case?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



