Deck 7: Cost and Industry Structure
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/244
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Cost and Industry Structure
1
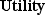


(Exhibit: Utility) The law of diminishing marginal utility is first observed at the _______ unit.
A) second
B) third
C) fifth
D) sixth
second
2
The amount by which an additional unit of a good or service increases a consumer's total utility, all other things unchanged, is:
A) marginal utility.
B) maximum utility.
C) average utility.
D) required utility.
A) marginal utility.
B) maximum utility.
C) average utility.
D) required utility.
marginal utility.
3
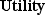


(Exhibit: Utility) The marginal utility for the fifth unit is:
A) 15.
B) 10.
C) 5.
D) 0.
0.
4
Marginal utility is best computed as the:
A) change in total utility from an additional unit consumed.
B) total utility divided by the total quantity consumed.
C) change in total utility divided by the total quantity consumed.
D) total utility divided by the change in quantity consumed.
A) change in total utility from an additional unit consumed.
B) total utility divided by the total quantity consumed.
C) change in total utility divided by the total quantity consumed.
D) total utility divided by the change in quantity consumed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Assume that the total utilities corresponding to the first five units of a product consumed are 10, 15, 19, 22, and 24, respectively. The marginal utility of the third unit is:
A) 19.
B) 15.
C) 4.
D) 3.
A) 19.
B) 15.
C) 4.
D) 3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements is true regarding utility?
A) Utility can be measured.
B) Utility cannot be measured.
C) Utility, at the margin, eventually increases as more of a good is consumed.
D) A and C are true.
A) Utility can be measured.
B) Utility cannot be measured.
C) Utility, at the margin, eventually increases as more of a good is consumed.
D) A and C are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The amount by which total utility increases when an additional unit of a good is consumed is called ________ utility.
A) average
B) additional
C) maximum
D) marginal
A) average
B) additional
C) maximum
D) marginal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Assume that the total utilities for the fifth and sixth units of a good consumed are 83 and 97, respectively. The marginal utility for the sixth unit is:
A) -14.
B) 14.
C) 83.
D) 97.
A) -14.
B) 14.
C) 83.
D) 97.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
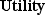


(Exhibit: Utility.) Marginal utility is zero for the _______ unit.
A) first
B) second
C) third
D) fifth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
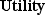


(Exhibit: Utility) Marginal utility first becomes negative at the _______ unit.
A) first
B) second
C) fifth
D) sixth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The utility of a good is determined by how much _______ a particular consumer obtains from it.
A) satisfaction
B) usefulness
C) cost
D) need fulfillment
A) satisfaction
B) usefulness
C) cost
D) need fulfillment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Assume that the marginal utilities for the first three units of a good consumed are 200, 150, and 125, respectively. The total utility when 2 units are consumed is:
A) 150.
B) 200.
C) 350.
D) 475.
A) 150.
B) 200.
C) 350.
D) 475.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The conceptual measure of the satisfaction a person obtains by consuming a given quantity of a good or service during a given time period is:
A) average product.
B) marginal cost.
C) marginal revenue.
D) total utility.
A) average product.
B) marginal cost.
C) marginal revenue.
D) total utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14


(Exhibit: Utility) Total utility is maximized at the _______ unit.
A) first
B) second
C) fourth
D) sixth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The ability of a good to satisfy a want refers to its:
A) utility.
B) usefulness.
C) worthiness.
D) necessity.
A) utility.
B) usefulness.
C) worthiness.
D) necessity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16


(Exhibit: Utility) The marginal utility for the sixth unit is:
A) -5.
B) 0.
C) 5.
D) -10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17


(Exhibit: Utility) The marginal utility for the second unit is:
A) 35.
B) 15.
C) 10.
D) 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Utility is most closely related to the term:
A) usefulness.
B) satisfaction.
C) requirement.
D) necessity.
A) usefulness.
B) satisfaction.
C) requirement.
D) necessity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Assume that the marginal utilities for the first three units of a good consumed are 200, 150, and 125, respectively. The total utility for the first unit is:
A) 125.
B) 150.
C) 200.
D) 350.
A) 125.
B) 150.
C) 200.
D) 350.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Economists identify the satisfaction a person derives from the consumption of goods and services as:
A) happiness.
B) usefulness.
C) utility.
D) pleasure.
A) happiness.
B) usefulness.
C) utility.
D) pleasure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If the first four units of a good consumed have marginal utilities of 60, 50, 40, and 30, respectively, this trend is an indication of the:
A) maximization of utility.
B) law of diminishing marginal utility.
C) law of consumer equilibrium.
D) minimization of utility.
A) maximization of utility.
B) law of diminishing marginal utility.
C) law of consumer equilibrium.
D) minimization of utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Total Utility and Marginal Utility from Consumption of Good A
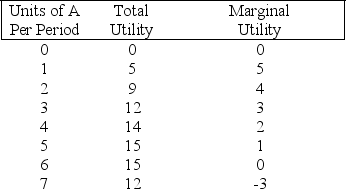
(Exhibit: Total Utility and Marginal Utility from Consumption of Good A) Marginal utility eventually decreases with the consumption of additional units of good A because of the law of:
A) increasing costs.
B) decreasing total returns.
C) diminishing average returns.
D) diminishing marginal utility.

(Exhibit: Total Utility and Marginal Utility from Consumption of Good A) Marginal utility eventually decreases with the consumption of additional units of good A because of the law of:
A) increasing costs.
B) decreasing total returns.
C) diminishing average returns.
D) diminishing marginal utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The law of diminishing marginal utility indicates that the slope of the marginal utility curve eventually becomes:
A) negative.
B) vertical.
C) horizontal.
D) positive.
A) negative.
B) vertical.
C) horizontal.
D) positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Assume that the total utilities corresponding to the first five units of a product consumed are 14, 20, 25, 29, and 32, respectively. The marginal utility of the third unit is:
A) 5.
B) 6.
C) 20.
D) 25.
A) 5.
B) 6.
C) 20.
D) 25.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The law of diminishing marginal utility exists for the first three units of a good if they have total utilities of:
A) 8, 17, 27.
B) 9, 17, 27.
C) 9, 19, 30.
D) 10, 19, 27.
A) 8, 17, 27.
B) 9, 17, 27.
C) 9, 19, 30.
D) 10, 19, 27.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Total Utility and Marginal Utility from Consumption of Good A

(Exhibit: Total Utility and Marginal Utility from Consumption of Good A) If 4 units of good A are consumed, the total utility received is _______ and the marginal utility of the 4th unit is _______ .
A) 26; 5
B) 14; 2
C) 12; 3
D) None of the above is correct.

(Exhibit: Total Utility and Marginal Utility from Consumption of Good A) If 4 units of good A are consumed, the total utility received is _______ and the marginal utility of the 4th unit is _______ .
A) 26; 5
B) 14; 2
C) 12; 3
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Total Utility and Marginal Utility from Consumption of Good A

(Exhibit: Total Utility and Marginal Utility from Consumption of Good A) Marginal utility of good A is found by:
A) dividing total utility by the number of units consumed of good A.
B) dividing the change in the number of units of A by the change in total utility of A.
C) computing the change in total utility of A resulting from the consumption of one more unit of A.
D) doing none of the above.

(Exhibit: Total Utility and Marginal Utility from Consumption of Good A) Marginal utility of good A is found by:
A) dividing total utility by the number of units consumed of good A.
B) dividing the change in the number of units of A by the change in total utility of A.
C) computing the change in total utility of A resulting from the consumption of one more unit of A.
D) doing none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The amount by which total utility rises when an additional unit of a good is consumed is called:
A) average utility.
B) the law of diminishing returns.
C) incremental utility.
D) marginal utility.
A) average utility.
B) the law of diminishing returns.
C) incremental utility.
D) marginal utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The law of diminishing marginal utility indicates that the marginal utility curve eventually becomes:
A) vertical.
B) U-shaped.
C) upward sloping.
D) downward sloping.
A) vertical.
B) U-shaped.
C) upward sloping.
D) downward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The law of diminishing marginal utility exists for the first three units of a good if they have marginal utilities, respectively, of:
A) 8, 9, 10.
B) 9, 8, 10.
C) 9, 10, 8.
D) 10, 9, 8.
A) 8, 9, 10.
B) 9, 8, 10.
C) 9, 10, 8.
D) 10, 9, 8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the first four units of a good consumed have marginal utilities of 10, 9, 8, and 7, respectively, this trend is an indication of the:
A) law of diminishing marginal utility.
B) minimization of utility.
C) law of consumer equilibrium.
D) law of diminishing consumer surplus.
A) law of diminishing marginal utility.
B) minimization of utility.
C) law of consumer equilibrium.
D) law of diminishing consumer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
As you consume more of good A relative to another good B, the _______ of good A eventually decreases.
A) total utility
B) usefulness
C) marginal utility
D) demand
A) total utility
B) usefulness
C) marginal utility
D) demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When supply and demand are in equilibrium, the price of a good is:
A) greater than the marginal utility of the good.
B) equal to the marginal utility of the good.
C) less than the marginal utility of the good.
D) not necessarily any of the above.
A) greater than the marginal utility of the good.
B) equal to the marginal utility of the good.
C) less than the marginal utility of the good.
D) not necessarily any of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following statements is true because of the law of diminishing marginal utility?
A) When a customer continues to eat more pie at the Pie Palace, each additional piece of pie gives a larger amount of marginal utility.
B) When a customer continues to eat more pie at the Pie Palace, each additional piece of pie gives a smaller amount of marginal utility.
C) The marginal utility of a piece of pie is maximum when the total utility of pie is zero.
D) The total utility of pie is at a maximum while the marginal utility of pie is still increasing.
A) When a customer continues to eat more pie at the Pie Palace, each additional piece of pie gives a larger amount of marginal utility.
B) When a customer continues to eat more pie at the Pie Palace, each additional piece of pie gives a smaller amount of marginal utility.
C) The marginal utility of a piece of pie is maximum when the total utility of pie is zero.
D) The total utility of pie is at a maximum while the marginal utility of pie is still increasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The law of diminishing marginal utility:
A) is the tendency of total utility to increase until an individual's budget is no longer constrained.
B) refers to the tendency of marginal utility to decline beyond some level of consumption during a period.
C) indicates that, if a good is inferior, less of it will be purchased when income falls during a period.
D) assumes all goods are normal.
A) is the tendency of total utility to increase until an individual's budget is no longer constrained.
B) refers to the tendency of marginal utility to decline beyond some level of consumption during a period.
C) indicates that, if a good is inferior, less of it will be purchased when income falls during a period.
D) assumes all goods are normal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Total Utility and Marginal Utility from Consumption of Good A

(Exhibit: Total Utility and Marginal Utility from Consumption of Good A) If the total utility curve of good A is plotted on a graph, the slope of TU between 3 units consumed and 4 units consumed is:
A) 1.
B) 2.
C) 3.
D) 4.

(Exhibit: Total Utility and Marginal Utility from Consumption of Good A) If the total utility curve of good A is plotted on a graph, the slope of TU between 3 units consumed and 4 units consumed is:
A) 1.
B) 2.
C) 3.
D) 4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In using the concept of marginal utility as an argument for a downward-sloping demand curve, economists:
A) are ignoring the law of diminishing marginal utility.
B) invoke the law of diminishing marginal utility.
C) are denying the law of diminishing marginal utility.
D) are doing none of the above.
A) are ignoring the law of diminishing marginal utility.
B) invoke the law of diminishing marginal utility.
C) are denying the law of diminishing marginal utility.
D) are doing none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Total Utility and Marginal Utility from Consumption of Good A

(Exhibit: Total Utility and Marginal Utility from Consumption of Good A) If 2 units of A are consumed, the total utility received is _______ , and the marginal utility of the second unit is _______ .
A) 4; 9
B) 9; 4
C) 12; 3
D) 14; 9

(Exhibit: Total Utility and Marginal Utility from Consumption of Good A) If 2 units of A are consumed, the total utility received is _______ , and the marginal utility of the second unit is _______ .
A) 4; 9
B) 9; 4
C) 12; 3
D) 14; 9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When total utility is at a maximum, marginal utility is:
A) rising.
B) at its average value.
C) at a maximum.
D) zero.
A) rising.
B) at its average value.
C) at a maximum.
D) zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements is (are) true?
A) As a consumer consumes more and more of a good or service, its marginal utility eventually falls.
B) Utility is a quality inherent in the good or service itself.
C) Marginal utility is the change in total utility resulting from consuming one more or one less unit of a good.
D) Both A and C are true.
A) As a consumer consumes more and more of a good or service, its marginal utility eventually falls.
B) Utility is a quality inherent in the good or service itself.
C) Marginal utility is the change in total utility resulting from consuming one more or one less unit of a good.
D) Both A and C are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The Case in Point on Changing Lanes and Raising Utility, indicated that the government's decision to allow single-occupancy-vehicle to use former HOV lanes for a fee resulted in:
A) only wealthy drivers using these lanes.
B) only poor drivers using these lanes.
C) drivers of all income levels using these lanes.
D) no statistical evidence on who uses these lanes most frequently.
A) only wealthy drivers using these lanes.
B) only poor drivers using these lanes.
C) drivers of all income levels using these lanes.
D) no statistical evidence on who uses these lanes most frequently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If a consumer purchases a combination of commodities a and b such that MUa/Pa = 40 and MUb/Pb = 60, to maximize utility, the consumer should buy:
A) less of both a and b.
B) less of a and more of b.
C) more of both a and b.
D) more of a and less of b.
A) less of both a and b.
B) less of a and more of b.
C) more of both a and b.
D) more of a and less of b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In dealing with utility, we assume that the ability of consumers to purchase goods and services is:
A) infinite.
B) irrelevant.
C) limited.
D) infinitesimal.
A) infinite.
B) irrelevant.
C) limited.
D) infinitesimal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following statements most fully explains a driver's decision, as discussed in the Case in Point on Changing Lane and Raising Utility, to pay to use a highway express lane?
A) The total utility of using the lane must be greater than zero.
B) The marginal utility per dollar on using the lane must be greater than zero.
C) The marginal utility per dollar spent on the lane must be equal to the price per gallon of gasoline plus associated driving costs.
D) The marginal utility per dollar spent on the lane must be greater than the marginal utility per dollar spent on the next best alternative.
A) The total utility of using the lane must be greater than zero.
B) The marginal utility per dollar on using the lane must be greater than zero.
C) The marginal utility per dollar spent on the lane must be equal to the price per gallon of gasoline plus associated driving costs.
D) The marginal utility per dollar spent on the lane must be greater than the marginal utility per dollar spent on the next best alternative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Economists assume that consumers behave in a manner consistent with the _______ of utility.
A) maintenance
B) minimization
C) maximization
D) final degree
A) maintenance
B) minimization
C) maximization
D) final degree

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If a consumer purchases a combination of commodities a and b such that MUa/Pa = 50 and MUb/Pb = 30, to maximize utility, the consumer should buy:
A) less of both a and b.
B) more of both a and b.
C) more of a and less of b.
D) less of a and more of b.
A) less of both a and b.
B) more of both a and b.
C) more of a and less of b.
D) less of a and more of b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The utility-maximization condition for two goods is achieved by equating the:
A) prices of both goods.
B) marginal utilities of both goods.
C) ratios of total utility to price of both goods.
D) ratios of marginal utility to price of both goods.
A) prices of both goods.
B) marginal utilities of both goods.
C) ratios of total utility to price of both goods.
D) ratios of marginal utility to price of both goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is (are) true?
A) A budget constraint limits what a poor consumer can spend, but there is no similar constraint on rich people.
B) Utility maximization requires seeking the greatest utility from a given budget.
C) In consumer choice theory, we assume all goods and services are normal.
D) All of the above are true.
A) A budget constraint limits what a poor consumer can spend, but there is no similar constraint on rich people.
B) Utility maximization requires seeking the greatest utility from a given budget.
C) In consumer choice theory, we assume all goods and services are normal.
D) All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If a consumer purchases a combination of commodities x and y such that MUx/Px = 30 and MUy/Py = 40, to maximize utility, the consumers should buy.
A) less of x and more of y.
B) more of x and less of y.
C) more of both x and y.
D) less of both x and y.
A) less of x and more of y.
B) more of x and less of y.
C) more of both x and y.
D) less of both x and y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If a consumer purchases a combination of commodities x and y such that MUx/Px = 20 and MUy/Py = 10, to maximize utility, the consumers should buy.
A) less of x and more of y.
B) more of x and less of y.
C) more of both x and y.
D) less of both x and y.
A) less of x and more of y.
B) more of x and less of y.
C) more of both x and y.
D) less of both x and y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is (are) true?
A) The goal of a consumer is to maximize utility.
B) A consumer will consume each good at a level that yields the maximum utility possible.
C) Rich consumers are not constrained by income or budget constraints.
D) A and C are true.
A) The goal of a consumer is to maximize utility.
B) A consumer will consume each good at a level that yields the maximum utility possible.
C) Rich consumers are not constrained by income or budget constraints.
D) A and C are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If a consumer purchases a combination of commodities a and b such that MUa/Pa = 100
And MUb/Pb = 80, to maximize utility, the consumer should buy:
A) less of both a and b.
B) more of a and less of b.
C) less of a and more of b.
D) more of both a and b.
And MUb/Pb = 80, to maximize utility, the consumer should buy:
A) less of both a and b.
B) more of a and less of b.
C) less of a and more of b.
D) more of both a and b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If a consumer purchases a combination of commodities x and y such that MUx/Px = 20 and MUy/Py = 5, to maximize utility, the consumers should buy.
A) more of x and less of y.
B) less of x and less of y.
C) more of both x and y.
D) less of both x and y.
A) more of x and less of y.
B) less of x and less of y.
C) more of both x and y.
D) less of both x and y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following statements is (are) true?
A) Consumers are constrained by a budget.
B) If a consumer decides to spend more on one good, he or she must decide to spend less on another good to satisfy the budget constraint.
C) The marginal decision rule states that an activity should be expanded if its marginal benefit exceeds its marginal cost.
D) All of the above statements are true.
A) Consumers are constrained by a budget.
B) If a consumer decides to spend more on one good, he or she must decide to spend less on another good to satisfy the budget constraint.
C) The marginal decision rule states that an activity should be expanded if its marginal benefit exceeds its marginal cost.
D) All of the above statements are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A consumer's spending is restricted because of:
A) marginal utility.
B) total utility.
C) a budget constraint.
D) utility maximization.
A) marginal utility.
B) total utility.
C) a budget constraint.
D) utility maximization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is true regarding a budget constraint?
A) The budget constraint indicates that consumers desire more income.
B) The budget constraint indicates that there are limits on the consumption possibilities for a consumer.
C) The budget constraint is based on some, but not all of the prices for goods that consumers may want to buy.
D) All of the above statements describe the budget constraint.
A) The budget constraint indicates that consumers desire more income.
B) The budget constraint indicates that there are limits on the consumption possibilities for a consumer.
C) The budget constraint is based on some, but not all of the prices for goods that consumers may want to buy.
D) All of the above statements describe the budget constraint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Utility is maximized in the consumption of two goods by equating the:
A) marginal utility of one good to the price of the other.
B) ratios of marginal utility to price for both goods.
C) ratios of total utility to price of both goods.
D) marginal utilities of both goods.
A) marginal utility of one good to the price of the other.
B) ratios of marginal utility to price for both goods.
C) ratios of total utility to price of both goods.
D) marginal utilities of both goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Whatever the time period involved, a consumer's spending will be _______ by his or her _______ .
A) unlimited; marginal utility
B) limited; marginal utility
C) limited; budget
D) unlimited; budget
A) unlimited; marginal utility
B) limited; marginal utility
C) limited; budget
D) unlimited; budget

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A budget constraint is:
A) a consumer's restriction on spending.
B) a consumer's total utility.
C) a consumer's marginal utility.
D) the income effect.
A) a consumer's restriction on spending.
B) a consumer's total utility.
C) a consumer's marginal utility.
D) the income effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If a consumer purchases a combination of commodities x and y such that MUx/Px = 50 and MUy/Py = 40, to maximize utility, the consumers should buy.
A) more of x and less of y.
B) more of both x and y.
C) less of x and more of y.
D) less of both x and y.
A) more of x and less of y.
B) more of both x and y.
C) less of x and more of y.
D) less of both x and y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Utility maximization for all goods requires that:
A) the marginal utilities of all goods consumed divided by their prices are equal to the budget constraint.
B) the marginal utilities of all goods exceed the total utility of all goods.
C) the marginal utilities of all goods divided by their respective prices are equal.
D) all of the above be true.
A) the marginal utilities of all goods consumed divided by their prices are equal to the budget constraint.
B) the marginal utilities of all goods exceed the total utility of all goods.
C) the marginal utilities of all goods divided by their respective prices are equal.
D) all of the above be true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If a consumer buys more of good X and less of good Y, the _______ of good X will _______ , and the ________ of good Y will _______ .
A) marginal utility; fall; marginal utility; rise
B) marginal utility; rise; marginal utility; fall
C) total utility; fall; marginal utility; rise
D) marginal utility; rise; total utility; rise
A) marginal utility; fall; marginal utility; rise
B) marginal utility; rise; marginal utility; fall
C) total utility; fall; marginal utility; rise
D) marginal utility; rise; total utility; rise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If a consumer derives more utility by spending an additional $1 on good X rather than on good Y, then:
A) MUx/Px > MUy/Py.
B) MUx/Px = MUy/Py.
C) MUx/Px < MUy/Py.
D) Px/MUx > Py/MUy.
A) MUx/Px > MUy/Py.
B) MUx/Px = MUy/Py.
C) MUx/Px < MUy/Py.
D) Px/MUx > Py/MUy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Utility is maximized when:
A) the marginal utility of every good consumed times its price is everywhere equal.
B) total outlays equal a varying budget and when the ratios of marginal utilities to prices are equal for all goods and services.
C) total outlays equal a given budget and the ratios of marginal utilities to prices are equal for all goods and services.
D) A and C occur.
A) the marginal utility of every good consumed times its price is everywhere equal.
B) total outlays equal a varying budget and when the ratios of marginal utilities to prices are equal for all goods and services.
C) total outlays equal a given budget and the ratios of marginal utilities to prices are equal for all goods and services.
D) A and C occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
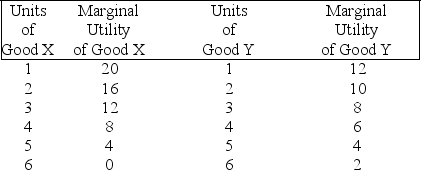
(Exhibit: Consumer Equilibrium 1) Assume that the price of good X is $2 per unit and the price of good Y is $1 per unit, and you consume 3 units of good X and 3 units of good Y. To maximize utility, assuming that the goods are divisible, you would consume:
A) less of both X and Y.
B) more of both X and Y.
C) less of X and more of Y.
D) more of X and less of Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66

(Exhibit: Consumer Equilibrium 1) Assume that the price of good X is $1 per unit and the price of good Y is $2 per unit, and you consume 4 units of good X and 2 units of good Y. To maximize utility, assuming that the goods are divisible, you would consume:
A) less of both X and Y.
B) more of both X and Y.
C) less of X and more of Y.
D) more of X and less of Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67

(Exhibit: Consumer Equilibrium 1) Assume that the price of good X is $2 per unit, the price of good Y is $1 per unit, and you have $10 of income to spend on both goods. To maximize utility, you would consume _______ units of X and _______ units of Y.
A) 3; 4
B) 4; 3
C) 4; 6
D) 5; 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Sally Garcia devotes all of her income to the consumption of two goods, apples and Reese's Peanut Butter Cups. She has just discovered that at her current level of consumption the marginal utility of an apple is 6 and the marginal utility of a Reese's Peanut Butter Cup is 8. To maximize her total utility, she would:
A) consume more of both goods.
B) consume less of both goods.
C) consume more apples and fewer Reese's Butter Cups.
D) there is not enough information to justify a change in her current level of consumption.
A) consume more of both goods.
B) consume less of both goods.
C) consume more apples and fewer Reese's Butter Cups.
D) there is not enough information to justify a change in her current level of consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
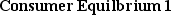

(Exhibit: Consumer Equilibrium 1) Assume that the price of both goods X and Y is $1 per unit, and you have $7 of income to spend on both goods. To maximize utility, you would consume ________ units of X and _______ units of Y.
A) 2; 5
B) 3; 4
C) 4; 3
D) 5; 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If a consumer purchases a combination of commodities a and b such that MUa/Pa = 50 and MUb/Pb = 40, to maximize utility, the consumer should buy:
A) less of both a and b.
B) more of both a and b.
C) more of a and less of b.
D) less of a and more of b.
A) less of both a and b.
B) more of both a and b.
C) more of a and less of b.
D) less of a and more of b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Sally Garcia devotes all of her income to the consumption of two goods, apples and Reese's Peanut Butter Cups. She has just discovered that at her current level of consumption the marginal utility of an apple is 6 and the marginal utility of a Reese's Peanut Butter Cup is 8. Suppose the price of an apple is $0.20, while the price of a Reese's Peanut Butter Cup is $0.25. To maximize her total utility, assuming that the goods are divisible, she would:
A) consume more Reese's Butter Cups and fewer apples.
B) consume less of both goods.
C) consume more apples and fewer Reese's Butter Cups.
D) there is not enough information to justify a change in her current level of consumption.
A) consume more Reese's Butter Cups and fewer apples.
B) consume less of both goods.
C) consume more apples and fewer Reese's Butter Cups.
D) there is not enough information to justify a change in her current level of consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
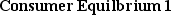

(Exhibit: Consumer Equilibrium 1) Assume that the price of both goods X and Y is $1 per unit, and you have $4 of income to spend on both goods. To maximize utility, you would consume ______ units of X and _______ units of Y.
A) 0; 4
B) 1; 3
C) 2; 2
D) 3; 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
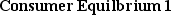

(Exhibit: Consumer Equilibrium 1) Assume that the price of both goods is $1 per unit, and you consume 4 units of good X and 2 units of good Y. To maximize utility, assuming that the goods are divisible, you would consume:
A) less of X and more of Y.
B) more of both X and Y.
C) less of both X and Y.
D) more of X and less of Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Sally Garcia devotes all of her income to the consumption of two goods, apples and Reese's Peanut Butter Cups. She has just discovered that at her current level of consumption the marginal utility of an apple is 6 and the marginal utility of a Reese's Peanut Butter Cup is 8. Suppose the price of an apple is $0.10, while the price of a Reese's Peanut Butter Cup is $0.25. To maximize her total utility, assuming that the goods are divisible, she would:
A) consume more Reese's Butter Cups and fewer apples.
B) consume less of both goods.
C) consume more apples and fewer Reese's Butter Cups.
D) there is not enough information to justify a change in her current level of consumption.
A) consume more Reese's Butter Cups and fewer apples.
B) consume less of both goods.
C) consume more apples and fewer Reese's Butter Cups.
D) there is not enough information to justify a change in her current level of consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
How much utility is gained by spending an additional dollar on good X?
A) It is the average utility of good X divided by the price of good X.
B) MUx/Px
C) TUx/Px
D) None of the above are correct.
A) It is the average utility of good X divided by the price of good X.
B) MUx/Px
C) TUx/Px
D) None of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Faced with two goods to buy, good 1 and good 2, a utility-maximizing individual will buy according to which of the following statements?
A) price of good 1 = price of good 2
B) MU of good 1 = MU of good 2
C) price of good 1 divided by MU of good 2 = price of good 2 divided by MU of good 1
D) MU of good 1 divided by price of good 1 = MU of good 2 divided by price of good 2
A) price of good 1 = price of good 2
B) MU of good 1 = MU of good 2
C) price of good 1 divided by MU of good 2 = price of good 2 divided by MU of good 1
D) MU of good 1 divided by price of good 1 = MU of good 2 divided by price of good 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
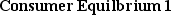

(Exhibit: Consumer Equilibrium 1) Assume that the price of good X is $5 per unit, the price of good Y is $1 per unit, and you have $10 of income to spend on both goods. To maximize utility, you would consume _______ units of X and _______ units of Y.
A) 0; 1
B) 1; 5
C) 4; 6
D) 5; 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78

(Exhibit: Consumer Equilibrium 1) Assume that the price of both goods is $1 per unit, and you consume 3 units of good X and 3 units of good Y. To maximize utility, assuming that the goods are divisible, you would consume:
A) less of both X and Y.
B) more of both X and Y.
C) less of X and more of Y.
D) more of X and less of Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79

(Exhibit: Consumer Equilibrium 1) Assume that the price of both goods X and Y is $1 per unit, and you have $10 of income to spend on both goods. To maximize utility, you would consume ________ units of X and _______ units of Y.
A) 3; 4
B) 4; 3
C) 4; 6
D) 5; 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If, for a particular consumer, the marginal utility of ties is greater than the marginal utility of shirts, this consumer should:
A) buy more ties and fewer shirts.
B) buy more shirts and fewer ties.
C) buy the same amount of each.
D) not do anything until more information is available.
A) buy more ties and fewer shirts.
B) buy more shirts and fewer ties.
C) buy the same amount of each.
D) not do anything until more information is available.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



