Deck 13: Risk and Capital Budgeting
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/97
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Risk and Capital Budgeting
1
In determining the appropriate discount rate for an individual project, the financial manager will be most influenced by the:
A) expected value.
B) internal rate of return.
C) standard deviation.
D) coefficient of variation.
A) expected value.
B) internal rate of return.
C) standard deviation.
D) coefficient of variation.
D
2
Which of the following is a false statement?
A) Risky investments may produce large losses.
B) Risky investments may produce large gains.
C) The coefficient of variation is a risk measure.
D) Risk-averse investors cannot be induced to invest in risky assets.
A) Risky investments may produce large losses.
B) Risky investments may produce large gains.
C) The coefficient of variation is a risk measure.
D) Risk-averse investors cannot be induced to invest in risky assets.
D
3
The firm's highest risk-adjusted discount should be applied to:
A) the repair of old machinery.
B) a new product in a related field.
C) a new product in a foreign market.
D) the purchase of new equipment.
A) the repair of old machinery.
B) a new product in a related field.
C) a new product in a foreign market.
D) the purchase of new equipment.
C
4
Risk is usually measured as the:
A) potential loss.
B) variability of outcomes around some expected value.
C) probability of expected values.
D) potential expected loss.
A) potential loss.
B) variability of outcomes around some expected value.
C) probability of expected values.
D) potential expected loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In order to evaluate risk, management may also set qualitative risk classes. Rank these four projects from the least to the most risky. 1. Completely new market in Canada
2) Completely new market in South America
3) Addition to normal product line
4) Repair to old machinery
A) 4, 3, 1, 2
B) 1, 2, 3, 4
C) 3, 4, 1, 2
D) 2, 3, 4, 1
2) Completely new market in South America
3) Addition to normal product line
4) Repair to old machinery
A) 4, 3, 1, 2
B) 1, 2, 3, 4
C) 3, 4, 1, 2
D) 2, 3, 4, 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A correlation coefficient of zero indicates:
A) the projects have the same expected value.
B) there is no correlation and no risk reduction between combined projects.
C) there is no correlation, but some risk reduction when the projects are combined.
D) the projects have the same standard deviation.
A) the projects have the same expected value.
B) there is no correlation and no risk reduction between combined projects.
C) there is no correlation, but some risk reduction when the projects are combined.
D) the projects have the same standard deviation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Projects that are negatively correlated:
A) cut down the maximum profit potential for the firm.
B) increase the possible losses of the firm.
C) are generally in the same industry.
D) have an equal amount of risk.
A) cut down the maximum profit potential for the firm.
B) increase the possible losses of the firm.
C) are generally in the same industry.
D) have an equal amount of risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which investment has the least amount of risk?
A) Standard deviation = $500, expected return = $5,000
B) Standard deviation = $700, expected return = $500
C) Standard deviation = $900, expected return = $800
D) Standard deviation = $400, expected return = $350
A) Standard deviation = $500, expected return = $5,000
B) Standard deviation = $700, expected return = $500
C) Standard deviation = $900, expected return = $800
D) Standard deviation = $400, expected return = $350

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The "efficient frontier" indicates:
A) alternatives with neutral combinations of risk and return.
B) alternatives with the highest returns.
C) alternatives with the best combination of risk and return.
D) alternatives with no risk.
A) alternatives with neutral combinations of risk and return.
B) alternatives with the highest returns.
C) alternatives with the best combination of risk and return.
D) alternatives with no risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If one project has a higher standard deviation than another:
A) it has a greater risk.
B) it has a higher expected value.
C) it has more possible outcomes.
D) it may be riskier, but this can only be determined by the coefficient of variation.
A) it has a greater risk.
B) it has a higher expected value.
C) it has more possible outcomes.
D) it may be riskier, but this can only be determined by the coefficient of variation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The standard deviation can be defined as the:
A) square root of the sum (D-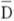 )2P.
)2P.
B) square root of the sum (D-)P.
C) square root of (D-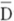 )2P.
)2P.
D) square root of (D-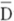 )P.
)P.
A) square root of the sum (D-
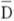 )2P.
)2P.B) square root of the sum (D-)P.
C) square root of (D-
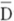 )2P.
)2P.D) square root of (D-
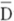 )P.
)P.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The portfolio effect in capital budgeting refers to:
A) the relationship of stocks to bonds.
B) the degree of correlation between various investments.
C) the coefficient of variation.
D) the risk-adjusted discount rate.
A) the relationship of stocks to bonds.
B) the degree of correlation between various investments.
C) the coefficient of variation.
D) the risk-adjusted discount rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Risk may be integrated into capital budgeting decisions by:
A) adjusting the standard deviation of possible outcomes.
B) determining the expected value.
C) adjusting the discount rate.
D) adjusting the time horizon.
A) adjusting the standard deviation of possible outcomes.
B) determining the expected value.
C) adjusting the discount rate.
D) adjusting the time horizon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If three investment alternatives all have some degree of risk and different expected returns, which of the following measures could best be used to rank the risk levels of the projects?
A) Coefficient of correlation
B) Coefficient of variation
C) Standard deviation of returns
D) Net present value
A) Coefficient of correlation
B) Coefficient of variation
C) Standard deviation of returns
D) Net present value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The term "risk averse" means that:
A) an individual refuses to take risks.
B) most investors and businesspersons seek risk.
C) an individual will seek to avoid risk or be compensated with a higher return.
D) only investment proposals with no risk should be accepted.
A) an individual refuses to take risks.
B) most investors and businesspersons seek risk.
C) an individual will seek to avoid risk or be compensated with a higher return.
D) only investment proposals with no risk should be accepted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The concept of being risk averse means:
A) for a given situation investors would prefer relative uncertainty to certainty.
B) investors would prefer investments with high standard deviations and greater opportunity for gain.
C) that the lower the volatility the higher the standard deviation must be.
D) that the greater the risk the higher the expected return must be.
A) for a given situation investors would prefer relative uncertainty to certainty.
B) investors would prefer investments with high standard deviations and greater opportunity for gain.
C) that the lower the volatility the higher the standard deviation must be.
D) that the greater the risk the higher the expected return must be.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In order to reduce risk in a firm, the firm would seek to enter a business that:
A) has high positive correlation with its present business.
B) has zero correlation with its present business.
C) has high negative correlation with its present business.
D) has high negative variation with its present business.
A) has high positive correlation with its present business.
B) has zero correlation with its present business.
C) has high negative correlation with its present business.
D) has high negative variation with its present business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The coefficient of variation (V) can be defined as the:
A) expected value multiplied by the standard deviation.
B) standard deviation divided by the mean (expected value).
C) mean (expected value) divided by the standard deviation.
D) standard deviation squared, divided by the expected value.
A) expected value multiplied by the standard deviation.
B) standard deviation divided by the mean (expected value).
C) mean (expected value) divided by the standard deviation.
D) standard deviation squared, divided by the expected value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The coefficient of correlation:
A) takes on values anywhere from 0 to + 1.
B) takes on values anywhere from - 1 to 0.
C) takes on values anywhere from - 1 to + 1.
D) takes on values of 0 or larger.
A) takes on values anywhere from 0 to + 1.
B) takes on values anywhere from - 1 to 0.
C) takes on values anywhere from - 1 to + 1.
D) takes on values of 0 or larger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An example of negative correlation may exist between the:
A) forest products and housing industries.
B) jewellery and discount furniture industries.
C) steel and aluminum industries.
D) oil and auto industries.
A) forest products and housing industries.
B) jewellery and discount furniture industries.
C) steel and aluminum industries.
D) oil and auto industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Simulation models allow the planner to:
A) consider unknown risks of mutually exclusive projects.
B) test possible changes in each variable.
C) generate a unique value for consideration.
D) determine the risk in a Government of Canada Treasury Bill.
A) consider unknown risks of mutually exclusive projects.
B) test possible changes in each variable.
C) generate a unique value for consideration.
D) determine the risk in a Government of Canada Treasury Bill.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A coefficient of _____ provides the greatest risk reduction.
A) 0
B) -1
C) +1
D) +.5
A) 0
B) -1
C) +1
D) +.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A project has the following projected outcomes in dollars: $250, $350, and $500. The probabilities of their outcomes are 25%, 50%, and 25% respectively. What is the standard deviation of these outcomes?
A) $363
B) $89
C) $94
D) $178
A) $363
B) $89
C) $94
D) $178

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An analytical tool which helps to organize the decision process by presenting a graphical comparison of investment choices is called a(an):
A) module hierarchy diagram.
B) "what if" simulation.
C) decision tree.
D) random simulation.
A) module hierarchy diagram.
B) "what if" simulation.
C) decision tree.
D) random simulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Projects that are totally uncorrelated provide:
A) no risk reduction.
B) some risk reduction.
C) extreme risk reduction.
D) Need more information.
A) no risk reduction.
B) some risk reduction.
C) extreme risk reduction.
D) Need more information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is a characteristic of beta?
A) Beta measures only the volatility of returns on an individual bond relative to a bond market index.
B) A beta of 1.0 is of equal risk with the market.
C) A beta of greater than 1.0 has less risk than the market.
D) Beta measures the correlation between the risk free rate and the market rate of risk.
A) Beta measures only the volatility of returns on an individual bond relative to a bond market index.
B) A beta of 1.0 is of equal risk with the market.
C) A beta of greater than 1.0 has less risk than the market.
D) Beta measures the correlation between the risk free rate and the market rate of risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The certainty equivalent approach:
A) is only appropriate for analyzing cash flows with risk similar government securities.
B) adjusts each cash flow based on a probability distribution.
C) adjusts the discount to suit the risk of each cash flow.
D) models the sequence of decisions required over time.
A) is only appropriate for analyzing cash flows with risk similar government securities.
B) adjusts each cash flow based on a probability distribution.
C) adjusts the discount to suit the risk of each cash flow.
D) models the sequence of decisions required over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Beta is a better risk measure than standard deviation when the firm:
A) is effectively diversified.
B) focused on total risk.
C) uses the CAPM in its cost of capital calculation.
D) has a beta that is close to 1.0.
A) is effectively diversified.
B) focused on total risk.
C) uses the CAPM in its cost of capital calculation.
D) has a beta that is close to 1.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Using the risk-adjusted discount rate approach, the firm's cost of capital is applied to projects with:
A) normal risk.
B) high risk.
C) no risk.
D) low risk.
A) normal risk.
B) high risk.
C) no risk.
D) low risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
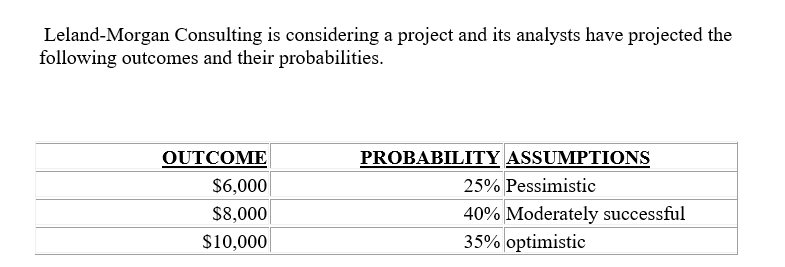
Firm X is considering a project and its analysts have projected the following outcomes and their probabilities. 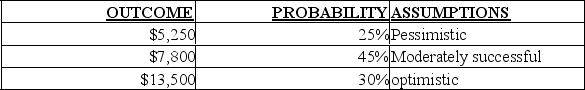 What is the expected value of the outcomes?
What is the expected value of the outcomes?
A) $3,123
B) $8,460
C) $8,873
D) Cannot be determined/depends upon which prediction is correct
 What is the expected value of the outcomes?
What is the expected value of the outcomes?A) $3,123
B) $8,460
C) $8,873
D) Cannot be determined/depends upon which prediction is correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Using progressively higher discount rates:
A) tends to reduce early and late cash flows equally.
B) tends to penalize early flows more than late flows.
C) tends to lower net present value.
D) reflects the decreasing nature of risk in the discount rate.
A) tends to reduce early and late cash flows equally.
B) tends to penalize early flows more than late flows.
C) tends to lower net present value.
D) reflects the decreasing nature of risk in the discount rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The "efficient frontier" indicates:
A) alternatives with neutral combinations of risk and return.
B) alternatives with the highest returns.
C) alternatives with no risk.
D) the best risk return line for a firm.
A) alternatives with neutral combinations of risk and return.
B) alternatives with the highest returns.
C) alternatives with no risk.
D) the best risk return line for a firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A "what if" simulation using a computer helps to:
A) reduce the risk associated with a particular investment.
B) determine the effects of changes in certain variables.
C) increase the accuracy of the inputs.
D) none of these answer options are true.
A) reduce the risk associated with a particular investment.
B) determine the effects of changes in certain variables.
C) increase the accuracy of the inputs.
D) none of these answer options are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A Monte Carlo simulation model uses:
A) random variables as inputs.
B) a point estimate.
C) the cost of capital.
D) portfolio risk.
A) random variables as inputs.
B) a point estimate.
C) the cost of capital.
D) portfolio risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The lower the coefficient of correlation the greater the:
A) risk when projects are combined.
B) risk reduction when projects are combined.
C) return when projects are combined.
D) standard deviation when projects are combined.
A) risk when projects are combined.
B) risk reduction when projects are combined.
C) return when projects are combined.
D) standard deviation when projects are combined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Using the risk-adjusted discount rate approach, projects with high coefficients of variation will have ______ net present values than projects with low coefficients of variation.
A) somewhat higher
B) substantially higher
C) lower
D) no change on
A) somewhat higher
B) substantially higher
C) lower
D) no change on

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In a portfolio, risk is evaluated in a different way than with an individual project. In evaluating portfolio risk we:
A) don't need to consider the impact of a given project on the overall risk of the firm.
B) recognize that a risky investment will not create a portfolio with less risk.
C) consider the risk of the project with the highest beta only.
D) need to consider how the returns of the projects in the portfolio are correlated.
A) don't need to consider the impact of a given project on the overall risk of the firm.
B) recognize that a risky investment will not create a portfolio with less risk.
C) consider the risk of the project with the highest beta only.
D) need to consider how the returns of the projects in the portfolio are correlated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A project's coefficient of variation is 0.40. The project has a positive coefficient of correlation of 0.20. The expected value is $2,000. What is one standard deviation?
A) $400.00
B) $500.00
C) $800.00
D) $1,000.00
A) $400.00
B) $500.00
C) $800.00
D) $1,000.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A coefficient correlation of _____ provides no risk reduction.
A) 0
B) -1
C) +1
D) +.5
A) 0
B) -1
C) +1
D) +.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is a common approach in dealing with uncertainty?
A) Monte Carlo simulation
B) Internal rate of return
C) Net present value
D) Beta analysis
A) Monte Carlo simulation
B) Internal rate of return
C) Net present value
D) Beta analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In order to reduce risk, one should diversify into areas that are positively correlated with current areas of involvement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
-What is the expected value of the outcomes?
A) $8,200
B) $6,400
C) $8,500
D) Cannot be determined until we know the actual outcome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A project has the following projected outcomes: $100, $500, and $800. The probabilities of their outcomes are 10%, 50%, and 40% respectively. What is the standard deviation of these outcomes?
A) $124
B) $214
C) $546
D) $580
A) $124
B) $214
C) $546
D) $580

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The concept of being risk averse means:
A) for a given situation investors would prefer relative uncertainty to certainty.
B) investors would prefer investments with high standard deviations and greater opportunity for gain.
C) that the higher the risk the lower the expected return must be.
D) investors prefer low risk to high risk investments.
A) for a given situation investors would prefer relative uncertainty to certainty.
B) investors would prefer investments with high standard deviations and greater opportunity for gain.
C) that the higher the risk the lower the expected return must be.
D) investors prefer low risk to high risk investments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is a true statement?
A) Risky investments may produce large losses.
B) Risky investments will not produce large gains.
C) The coefficient of variation is not a risk measure.
D) All risky investments have a high probability of succeeding.
A) Risky investments may produce large losses.
B) Risky investments will not produce large gains.
C) The coefficient of variation is not a risk measure.
D) All risky investments have a high probability of succeeding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which investment has the least amount of risk?
A) Standard deviation = $800, expected return = $400
B) Standard deviation = $700, expected return = $3,000
C) Standard deviation = $1,000, expected return = $8,000
D) Standard deviation = $1,000, expected return = $7,000
A) Standard deviation = $800, expected return = $400
B) Standard deviation = $700, expected return = $3,000
C) Standard deviation = $1,000, expected return = $8,000
D) Standard deviation = $1,000, expected return = $7,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47

-This project's coefficient of variation is ______.
A) 0.80
B) 0.90
C) 1.67
D) 2.30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48

-This project's expected profit is ________.
A) $5,000
B) $5,499
C) $8,250
D) $12,890

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49

-What is the standard deviation of the outcomes?
A) $2,850
B) $4,200
C) $1,536
D) Cannot be determined with the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Simulation models allow the planner to:
A) reduce the standard deviations of projects.
B) test possible changes in each variable.
C) deal with all uncertainty in forecasting outcomes.
D) increase the standard deviations of projects.
A) reduce the standard deviations of projects.
B) test possible changes in each variable.
C) deal with all uncertainty in forecasting outcomes.
D) increase the standard deviations of projects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51

-A project's total risk is measured by _________________________.
A) Beta
B) Sharpe Ratio
C) Chi Square
D) coefficient of variation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The W Equity portfolio has a standard deviation of returns of 8. The R Bond portfolio has a standard deviation of returns of 6. If the Covariance of these portfolio is 5 what is this portfolio's coefficient of correlation?
A) 0.1042
B) 0.889
C) 0.43
D) -0.1042
A) 0.1042
B) 0.889
C) 0.43
D) -0.1042

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In a portfolio, risk is evaluated in a different way than with an individual project. In evaluating portfolio risk we:
A) need to consider the impact of a given project on the overall risk of the firm.
B) recognize that a risky investment always creates a portfolio with less risk.
C) need to ensure all the projects in the portfolio are positively correlated.
D) only consider the average beta.
A) need to consider the impact of a given project on the overall risk of the firm.
B) recognize that a risky investment always creates a portfolio with less risk.
C) need to ensure all the projects in the portfolio are positively correlated.
D) only consider the average beta.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A project's coefficient of variation is 0.50. The project has a positive coefficient of correlation of 0.20. The expected value is $3,000. What is the standard deviation?
A) $600
B) $300
C) $1,200
D) $1,500
A) $600
B) $300
C) $1,200
D) $1,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55

-This project's standard deviation is ___________.
A) $5,626
B) $8,254
C) $7,462
D) $2,597

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Generally, because of the unpredictability of earnings, cyclical stocks are given higher price-earnings multiples than growth stocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Using progressively higher discount rates:
A) tends to penalize late flows more than early flows.
B) tends to penalize early flows more than late flows.
C) tends to increase net present value.
D) is not reflective of risk expectations.
A) tends to penalize late flows more than early flows.
B) tends to penalize early flows more than late flows.
C) tends to increase net present value.
D) is not reflective of risk expectations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Projects that are negatively correlated:
A) increase the maximum profit potential for the firm.
B) increase the possible losses of the firm.
C) are generally in the same industry.
D) provide a degree of risk reduction.
A) increase the maximum profit potential for the firm.
B) increase the possible losses of the firm.
C) are generally in the same industry.
D) provide a degree of risk reduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A basic assumption in financial theory is that most investors and managers are risk seekers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60

-What is the coefficient of variation of the outcomes?
A) 1.29
B) 0.19
C) 0.44
D) Cannot be determined with the information given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Generally, the higher the coefficient of variation a project has, the higher the discount rate it should be assigned.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A common stock with a beta of 1.0 is said to be of equal risk with the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The efficient frontier is always along the left-most portion of the risk-return tradeoff diagram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Projects with high positive correlation are sometimes valuable because they allow us to smooth out the overall performance of the firm during a business cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Risk is not only measured in terms of losses, but also in terms of variability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When choosing portfolios of assets, management should try to achieve the highest possible return at a given level of risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Projects that are totally uncorrelated provide some overall reduction in portfolio risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A firm might be willing to accept high risk in a given investment if the portfolio effect (for the whole firm) were beneficial.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The investor's portfolio should always be on the efficient frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The capital budgeting decisions of a firm will have no effect on the share price of the common stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Combining assets with highly correlated returns will reduce portfolio risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Choosing projects with returns equal to the company norm but having a higher level of risk will most likely lower the company's share price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The cost of capital is assumed to contain no risk for the firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The highest possible value for positive correlation is +1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Selection of portfolio combinations from the efficient frontier will depend upon our willingness to assume risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The coefficient of correlation represents the standard deviation divided by the expected value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The expected value is a weighted average of the outcomes multiplied by their probabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Investment A may have a higher standard deviation than investment B and still have less risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If we are risk-averse, a risky investment with an 8% return will be preferred over a 10% risk-free investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In considering the share price effect on risk-return trade-offs, our goal should always be to earn the highest return possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



