Deck 19: International Trade
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/139
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: International Trade
1
Wealth is measured as
A) A flow only.
B) A stock only.
C) Both a flow and a stock.
D) Neither a flow nor a stock.
A) A flow only.
B) A stock only.
C) Both a flow and a stock.
D) Neither a flow nor a stock.
B
2
Which of the following statements regarding the distribution of money income is most correct?
A) The distribution of money income is synonymous with the distribution of goods and services.
B) The distribution of money income includes the monetary value of in-kind benefits.
C) Statistics on the distribution of money income include the underground economy.
D) The distribution of money income overstates the extent of poverty in the United States.
A) The distribution of money income is synonymous with the distribution of goods and services.
B) The distribution of money income includes the monetary value of in-kind benefits.
C) Statistics on the distribution of money income include the underground economy.
D) The distribution of money income overstates the extent of poverty in the United States.
D
3
If a greater portion of income is distributed to those in the highest income quintile, the
A) Lorenz curve is a straight line.
B) Line of equality sags below the Lorenz curve.
C) Lorenz curve sags below the diagonal line of absolute equality.
D) Gini coefficient is less than zero.
A) Lorenz curve is a straight line.
B) Line of equality sags below the Lorenz curve.
C) Lorenz curve sags below the diagonal line of absolute equality.
D) Gini coefficient is less than zero.
C
4
Wealth refers to
A) The way personal income is divided among households.
B) The purchasing power this year.
C) A flow of money over time.
D) The market value of assets people own.
A) The way personal income is divided among households.
B) The purchasing power this year.
C) A flow of money over time.
D) The market value of assets people own.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If income is distributed equally, the
A) Lorenz curve is a straight line.
B) Line of equality sags below the Lorenz curve.
C) Lorenz curve sags below the line of equality.
D) Gini coefficient is greater than zero.
A) Lorenz curve is a straight line.
B) Line of equality sags below the Lorenz curve.
C) Lorenz curve sags below the line of equality.
D) Gini coefficient is greater than zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Income is measured as
A) A flow only.
B) A stock only.
C) Both a flow and a stock.
D) Neither a flow nor a stock.
A) A flow only.
B) A stock only.
C) Both a flow and a stock.
D) Neither a flow nor a stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Personal income is
A) The sum of wealth and in-kind income.
B) The sum of taxes, in-kind income, and personal consumption.
C) A good measure of the distribution of output.
D) The income received by households before payment of personal taxes.
A) The sum of wealth and in-kind income.
B) The sum of taxes, in-kind income, and personal consumption.
C) A good measure of the distribution of output.
D) The income received by households before payment of personal taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A mathematical summary of inequality based on the Lorenz curve is known as the
A) Okun coefficient.
B) Income distribution share.
C) Gini coefficient.
D) Lorenz coefficient.
A) Okun coefficient.
B) Income distribution share.
C) Gini coefficient.
D) Lorenz coefficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The federal income tax is designed to
A) Shift the Lorenz curve inward.
B) Shift the Lorenz curve outward.
C) Raise the Gini coefficient.
D) Decrease vertical equity.
A) Shift the Lorenz curve inward.
B) Shift the Lorenz curve outward.
C) Raise the Gini coefficient.
D) Decrease vertical equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
How income is distributed is typically measured using
A) In-kind income.
B) Personal income.
C) Wealth.
D) The production of goods and services.
A) In-kind income.
B) Personal income.
C) Wealth.
D) The production of goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The size distribution of income
A) Is the same thing as the functional distribution of income.
B) Tells how personal income is divided up among households or income classes.
C) Focuses on the distribution of income to different factors of production.
D) Reflects the distribution of financial assets.
A) Is the same thing as the functional distribution of income.
B) Tells how personal income is divided up among households or income classes.
C) Focuses on the distribution of income to different factors of production.
D) Reflects the distribution of financial assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The proportion of total income received by a particular group is called the group's
A) Market share.
B) Income share.
C) Gini coefficient.
D) Functional distribution of income.
A) Market share.
B) Income share.
C) Gini coefficient.
D) Functional distribution of income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If the area between the diagonal line of absolute equality and the Lorenz curve is greater for China than for the United States, we can conclude that the
A) Distribution of income in China is closer to being equal than in the United States.
B) Distribution of income in China is as equal as in the United States.
C) Distribution of income in China is less equal than in the United States.
D) Relative distributions of income in the two countries are the same.
A) Distribution of income in China is closer to being equal than in the United States.
B) Distribution of income in China is as equal as in the United States.
C) Distribution of income in China is less equal than in the United States.
D) Relative distributions of income in the two countries are the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In-kind benefits are a way of correcting
A) Market power.
B) Government failure.
C) Natural monopoly.
D) Inequity.
A) Market power.
B) Government failure.
C) Natural monopoly.
D) Inequity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Public housing is an example of
A) In-kind income.
B) Free goods.
C) Money income.
D) Personal expenditure.
A) In-kind income.
B) Free goods.
C) Money income.
D) Personal expenditure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
According to the Census Bureau, in 2010 nearly _____________ Americans were counted as poor.
A) 1 million
B) 9 million
C) 20 million
D) 45 million
A) 1 million
B) 9 million
C) 20 million
D) 45 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Medicare is an example of
A) Free goods.
B) Personal income.
C) In-kind income.
D) A direct cash transfer payment.
A) Free goods.
B) Personal income.
C) In-kind income.
D) A direct cash transfer payment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If the area between the diagonal line of absolute equality and the Lorenz curve is greater for the United States than for Japan, we can conclude that the
A) Distribution of income in Japan is closer to being equal than in the United States.
B) Distribution of income in Japan is as equal as in the United States.
C) Distribution of income in Japan is less equal than in the United States.
D) Relative distributions of income in the two countries are the same.
A) Distribution of income in Japan is closer to being equal than in the United States.
B) Distribution of income in Japan is as equal as in the United States.
C) Distribution of income in Japan is less equal than in the United States.
D) Relative distributions of income in the two countries are the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A graphic illustration of the cumulative size distribution of income is known as the
A) Size distribution of income.
B) Okun curve.
C) Lorenz curve.
D) Gini coefficient.
A) Size distribution of income.
B) Okun curve.
C) Lorenz curve.
D) Gini coefficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When the Census Bureau counts the number of poor Americans, it counts
A) Only in-kind income.
B) Both in-kind and money income.
C) Only money income.
D) Personal income plus transfer payments.
A) Only in-kind income.
B) Both in-kind and money income.
C) Only money income.
D) Personal income plus transfer payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
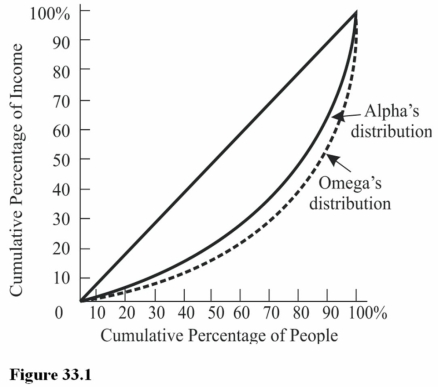 The bottom 80 percent of families in Alpha receive approximately what percentage of total income? (See Figure 33.1.)
The bottom 80 percent of families in Alpha receive approximately what percentage of total income? (See Figure 33.1.)A) 80 percent.
B) 60 percent.
C) 50 percent.
D) 40 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is a progressive tax?
A) The federal income tax.
B) The Social Security tax.
C) Local sales taxes.
D) Local property taxes.
A) The federal income tax.
B) The Social Security tax.
C) Local sales taxes.
D) Local property taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
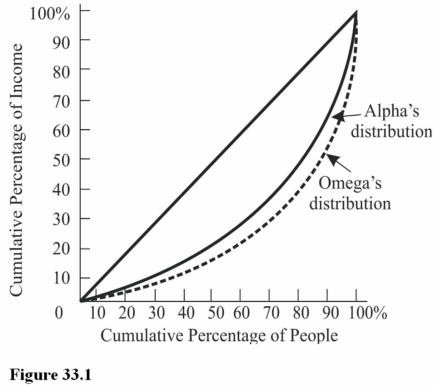 The size distribution of income in Figure 33.1 reveals that
The size distribution of income in Figure 33.1 reveals thatA) Incomes are more equally distributed in Alpha than in Omega.
B) Incomes are more equally distributed in Omega than in Alpha.
C) The Gini coefficient for Alpha is larger than for Omega.
D) People are wealthier in Alpha than in Omega.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
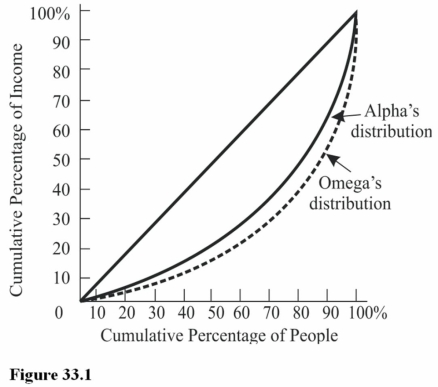 In Omega the lowest 40 percent of families receive approximately what percentage of income? (See Figure 33.1)
In Omega the lowest 40 percent of families receive approximately what percentage of income? (See Figure 33.1)A) 20 percent.
B) 40 percent.
C) 10 percent.
D) 17 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If the Gini coefficient is greater for Zambia than for the Netherlands, we can conclude that the
A) Relative distributions of income in the two countries are the same.
B) Distribution of income in the Netherlands is less equal than in Zambia.
C) Distribution of income in the Netherlands is as equal as it is in Zambia.
D) Distribution of income in the Netherlands is closer to being equal than in Zambia.
A) Relative distributions of income in the two countries are the same.
B) Distribution of income in the Netherlands is less equal than in Zambia.
C) Distribution of income in the Netherlands is as equal as it is in Zambia.
D) Distribution of income in the Netherlands is closer to being equal than in Zambia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
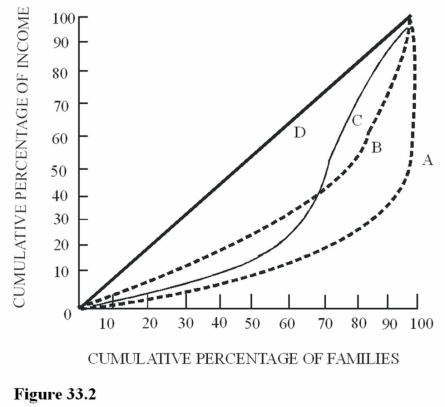 Figure 33.2 illustrates Lorenz curves for four different economies. For which economy would lower-income families receive the largest share of total income?
Figure 33.2 illustrates Lorenz curves for four different economies. For which economy would lower-income families receive the largest share of total income?A)A.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following taxes is most likely to reduce inequity?
A) A local property tax.
B) The federal income tax.
C) A gasoline tax.
D) A sales tax.
A) A local property tax.
B) The federal income tax.
C) A gasoline tax.
D) A sales tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
As the ________ becomes larger, the distance between the line of absolute equality and the ________ becomes greater.
A) Gini coefficient; Lorenz curve
B) Gini coefficient; production possibilities curve
C) Lorenz curve; Gini curve
D) Income distribution size; Lorenz curve
A) Gini coefficient; Lorenz curve
B) Gini coefficient; production possibilities curve
C) Lorenz curve; Gini curve
D) Income distribution size; Lorenz curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Market failure exists whenever
A) Income distribution is unequal.
B) The market generates a suboptimal outcome of income distribution.
C) The government intervenes in the market.
D) Government intervention makes the income distribution worse.
A) Income distribution is unequal.
B) The market generates a suboptimal outcome of income distribution.
C) The government intervenes in the market.
D) Government intervention makes the income distribution worse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A tax is progressive if it takes a
A) Larger number of dollars as income rises.
B) Larger number of dollars as income falls.
C) Smaller fraction of income as income falls.
D) Smaller fraction of income as income rises.
A) Larger number of dollars as income rises.
B) Larger number of dollars as income falls.
C) Smaller fraction of income as income falls.
D) Smaller fraction of income as income rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the Gini coefficient is greater for the United Kingdom than for Japan, we can conclude that the
A) Relative distributions of income in the two countries are the same.
B) Distribution of income in the United Kingdom is less equal than in Japan.
C) Distribution of income in the United Kingdom is as equal as it is in Japan.
D) Distribution of income in the United Kingdom is closer to being equal than in Japan.
A) Relative distributions of income in the two countries are the same.
B) Distribution of income in the United Kingdom is less equal than in Japan.
C) Distribution of income in the United Kingdom is as equal as it is in Japan.
D) Distribution of income in the United Kingdom is closer to being equal than in Japan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
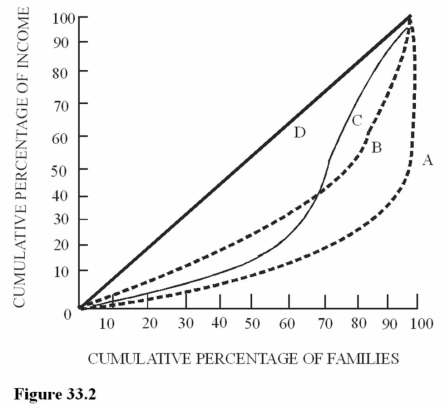 Figure 33.2 illustrates Lorenz curves for four different economies. Which economy should have a Gini coefficient of zero?
Figure 33.2 illustrates Lorenz curves for four different economies. Which economy should have a Gini coefficient of zero?A)A.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The U.S. federal income tax is classified as a
A) Regressive tax only.
B) Flat tax only.
C) Progressive tax only.
D) Regressive or flat tax, but not a progressive tax.
A) Regressive tax only.
B) Flat tax only.
C) Progressive tax only.
D) Regressive or flat tax, but not a progressive tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
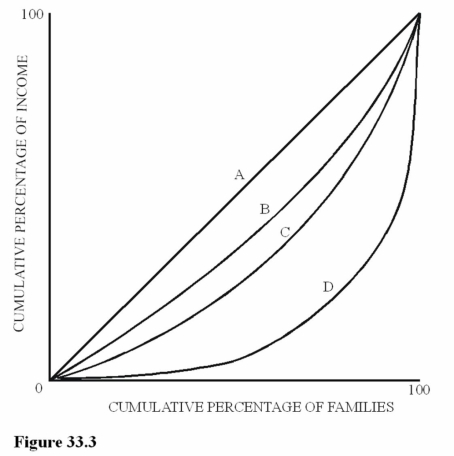 Figure 33.3 illustrates Lorenz curves for four different economies. For which economy would the lowest 20 percent of families receive the smallest share of total income?
Figure 33.3 illustrates Lorenz curves for four different economies. For which economy would the lowest 20 percent of families receive the smallest share of total income?A)A.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
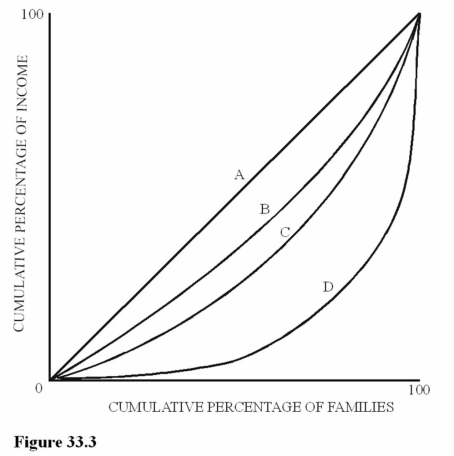 Figure 33.3 illustrate Lorenz curves for four different economies. Which economy will have a Gini coefficient of zero?
Figure 33.3 illustrate Lorenz curves for four different economies. Which economy will have a Gini coefficient of zero?A)A.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
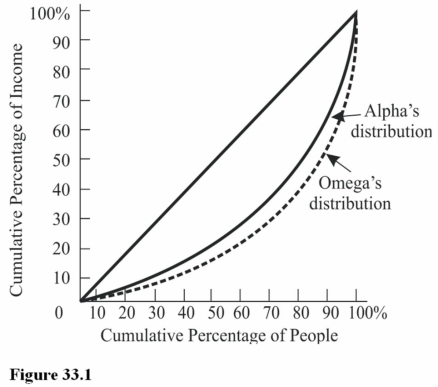 In Alpha the lowest 20 percent of families receive approximately what percentage of income? (See Figure 33.1)
In Alpha the lowest 20 percent of families receive approximately what percentage of income? (See Figure 33.1)A) 10 percent.
B) 5 percent.
C) 20 percent.
D) 80 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In the United States between 1980 and 2009, the Gini coefficient
A) Increased, indicating greater income inequality.
B) Increased, indicating less income inequality.
C) Decreased, indicating greater income inequality.
D) Decreased, indicating less income inequality.
A) Increased, indicating greater income inequality.
B) Increased, indicating less income inequality.
C) Decreased, indicating greater income inequality.
D) Decreased, indicating less income inequality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the percentage of income paid in taxes increases as income rises, then the tax system is
A) Regressive.
B) Progressive.
C) Marginal.
D) Nominal.
A) Regressive.
B) Progressive.
C) Marginal.
D) Nominal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
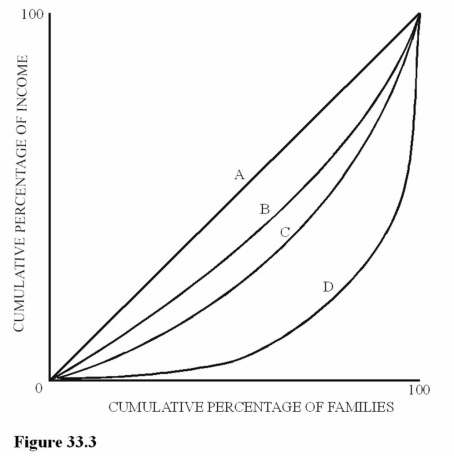 Figure 33.3 illustrate four different Lorenz curves. Assume Brazil has a larger Gini coefficient than the United States. If the income distribution for the United States is represented by curve C, which curve would most likely represent the income distribution for Brazil?
Figure 33.3 illustrate four different Lorenz curves. Assume Brazil has a larger Gini coefficient than the United States. If the income distribution for the United States is represented by curve C, which curve would most likely represent the income distribution for Brazil?A)A.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
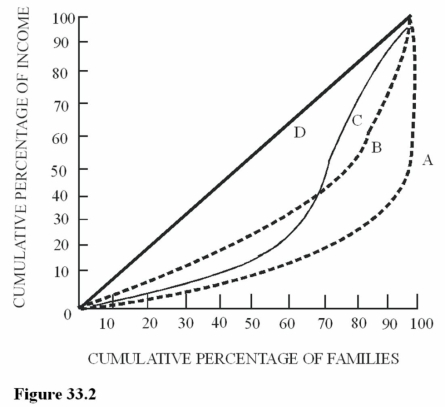 Figure 33.2 illustrates Lorenz curves for four different economies. For which economy would the lowest 20 percent of families receive the smallest share of total income?
Figure 33.2 illustrates Lorenz curves for four different economies. For which economy would the lowest 20 percent of families receive the smallest share of total income?A)A.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Assume the marginal tax rate is 12 percent for the first $40,000 of income, 28 percent for income between $40,000 and $100,000, and 30 percent for any income over $100,000. If Sarah has taxable income equal to $120,000 for the year, what is her tax bill?
A) $27,600.
B) $33,600.
C) $34,000.
D) $36,000.
A) $27,600.
B) $33,600.
C) $34,000.
D) $36,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If the marginal tax rate is too high, it can cause all of the following except
A) Businesses to produce more.
B) Government tax receipts to decline.
C) The rate of saving to decline.
D) Work effort to decrease.
A) Businesses to produce more.
B) Government tax receipts to decline.
C) The rate of saving to decline.
D) Work effort to decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In general, lower marginal tax rates provide incentives to
A) Work less.
B) Produce more output.
C) Invest less.
D) Find more tax loopholes.
A) Work less.
B) Produce more output.
C) Invest less.
D) Find more tax loopholes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Government attempts to create a more equitable income distribution by increasing marginal tax rates may do all of the following except
A) Reduce output.
B) Increase unemployment.
C) Reduce government tax receipts.
D) Increase work effort.
A) Reduce output.
B) Increase unemployment.
C) Reduce government tax receipts.
D) Increase work effort.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A tax elasticity of supply equal to .21 indicates that
A) Employers will not hire any workers if tax rates increase.
B) Employers will hire more workers if tax rates increase.
C) Workers will not cut back on the number of hours worked if tax rates increase.
D) Workers will cut back on the number of hours worked if tax rates increase.
A) Employers will not hire any workers if tax rates increase.
B) Employers will hire more workers if tax rates increase.
C) Workers will not cut back on the number of hours worked if tax rates increase.
D) Workers will cut back on the number of hours worked if tax rates increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Assume that the marginal tax rate is 10 percent for the first $10,000 of income, 20 percent for income between $10,000 and $40,000, and 30 percent for any income over $40,000. If Aaron has taxable income equal to $60,000 for the year, what is his tax bill?
A) $6,000.
B) $13,000.
C) $15,000.
D) $18,000.
A) $6,000.
B) $13,000.
C) $15,000.
D) $18,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If an individual is taxed at a 17 percent rate for each extra dollar earned, the reference is to the
A) Marginal tax rate.
B) Nominal tax rate.
C) Average tax rate.
D) Effective tax rate.
A) Marginal tax rate.
B) Nominal tax rate.
C) Average tax rate.
D) Effective tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The tax elasticity of supply measures the
A) Response of workers to a change in the tax rate.
B) Response of workers to a change in prices.
C) Change in the amount of taxes workers must pay when tax rates change.
D) Response of employers to a change in the tax rate.
A) Response of workers to a change in the tax rate.
B) Response of workers to a change in prices.
C) Change in the amount of taxes workers must pay when tax rates change.
D) Response of employers to a change in the tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
To make a tax system more progressive, policy makers could
A) Raise marginal tax rates for higher incomes.
B) Narrow the tax base.
C) Allow all interest expenses to be deductible, not just interest on mortgages.
D) Raise sales taxes on commonly purchased items.
A) Raise marginal tax rates for higher incomes.
B) Narrow the tax base.
C) Allow all interest expenses to be deductible, not just interest on mortgages.
D) Raise sales taxes on commonly purchased items.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Exemptions and deductions included in the tax laws
A) Are designed to encourage specific economic activities.
B) Reduce vertical inequities.
C) Make the tax structure more progressive.
D) Reduce horizontal inequities.
A) Are designed to encourage specific economic activities.
B) Reduce vertical inequities.
C) Make the tax structure more progressive.
D) Reduce horizontal inequities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Assume the marginal tax rate is 10 percent for the first $30,000 of income, 15 percent for income between $30,000 and $70,000, and 20 percent for any income over $70,000. If Emily has taxable income equal to $80,000 for the year, what is her tax bill?
A) $16,000.
B) $11,000.
C) $8,000.
D) $12,000.
A) $16,000.
B) $11,000.
C) $8,000.
D) $12,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The many loopholes present in the federal income tax system prior to the 1986 tax reform caused all of the following except
A) Greater vertical inequity by making the income tax more regressive.
B) Greater horizontal inequity since the loopholes were more accessible to some taxpayers than others.
C) The system to be more progressive since loopholes favored those at lower income levels.
D) The Lorenz curve for after-tax income to shift away from absolute equality.
A) Greater vertical inequity by making the income tax more regressive.
B) Greater horizontal inequity since the loopholes were more accessible to some taxpayers than others.
C) The system to be more progressive since loopholes favored those at lower income levels.
D) The Lorenz curve for after-tax income to shift away from absolute equality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If the tax elasticity of supply is 0.6 and tax rates increase by 10 percent, the quantity of labor supplied will
A) Increase by 1.67 percent.
B) Decrease by 1.67 percent.
C) Increase by 6 percent.
D) Decrease by 6 percent.
A) Increase by 1.67 percent.
B) Decrease by 1.67 percent.
C) Increase by 6 percent.
D) Decrease by 6 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A tax that is designed to be progressive will improve
A) Efficiency.
B) Vertical equity.
C) Horizontal equity.
D) Equality.
A) Efficiency.
B) Vertical equity.
C) Horizontal equity.
D) Equality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
As exemptions are raised and allowable deductions are increased, there is
A) A smaller gap between effective and nominal tax rates.
B) Greater vertical inequity.
C) A smaller gap between gross income and taxable income.
D) Greater horizontal equity.
A) A smaller gap between effective and nominal tax rates.
B) Greater vertical inequity.
C) A smaller gap between gross income and taxable income.
D) Greater horizontal equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A tax elasticity of supply equal to zero indicates that
A) Employers will not hire any workers if tax rates increase.
B) Employers will hire more workers if tax rates increase.
C) Workers will not cut back on the number of hours worked if tax rates increase.
D) Workers will not work at all if tax rates increase.
A) Employers will not hire any workers if tax rates increase.
B) Employers will hire more workers if tax rates increase.
C) Workers will not cut back on the number of hours worked if tax rates increase.
D) Workers will not work at all if tax rates increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Increasing tax rates on businesses can be justified based on equity considerations when
A) Perfectly competitive conditions exist.
B) The tax is a flat tax.
C) Externalities exist.
D) Long-run economic profits exist.
A) Perfectly competitive conditions exist.
B) The tax is a flat tax.
C) Externalities exist.
D) Long-run economic profits exist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Additional loopholes in the personal income tax law tend to
A) Make the system less progressive.
B) Increase horizontal equity.
C) Increase the tax base.
D) Increase vertical equity.
A) Make the system less progressive.
B) Increase horizontal equity.
C) Increase the tax base.
D) Increase vertical equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Vertical equity can be determined by comparing the
A) Effective tax rate of the taxpayer with the highest nominal income to the effective tax rates of taxpayers with lower nominal incomes.
B) Marginal tax rate of the taxpayer with the highest nominal income to the marginal tax rates of taxpayers with lower nominal incomes.
C) Marginal tax rates for two taxpayers with the same nominal incomes.
D) Effective tax rates for two taxpayers with the same nominal incomes.
A) Effective tax rate of the taxpayer with the highest nominal income to the effective tax rates of taxpayers with lower nominal incomes.
B) Marginal tax rate of the taxpayer with the highest nominal income to the marginal tax rates of taxpayers with lower nominal incomes.
C) Marginal tax rates for two taxpayers with the same nominal incomes.
D) Effective tax rates for two taxpayers with the same nominal incomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The taxation principle that says people with higher incomes should pay more in taxes than those with lower incomes is called
A) A flat tax system.
B) A regressive tax system.
C) Vertical equity.
D) Horizontal equity.
A) A flat tax system.
B) A regressive tax system.
C) Vertical equity.
D) Horizontal equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If an accountant makes $80,000 and after deductions pays $8,000 in taxes while a secretary makes $35,000 and after deductions pays $4,000 in taxes, this is an example of
A) Marginal inequity.
B) Horizontal equity.
C) Vertical equity.
D) Effective inequity.
A) Marginal inequity.
B) Horizontal equity.
C) Vertical equity.
D) Effective inequity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If a tax system has no deductions, exemptions, or other loopholes, then the effective tax rate will be
A) Greater than the nominal tax rate.
B) Equal to the nominal tax rate.
C) Less than the nominal tax rate.
D) Equal to the vertical tax rate.
A) Greater than the nominal tax rate.
B) Equal to the nominal tax rate.
C) Less than the nominal tax rate.
D) Equal to the vertical tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The taxation principle that says people with equal incomes should pay equal taxes is called
A) Horizontal equity.
B) A progressive tax system.
C) A regressive tax system.
D) Vertical equity.
A) Horizontal equity.
B) A progressive tax system.
C) A regressive tax system.
D) Vertical equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The effective tax rate is
A) Equal to the taxes paid divided by taxable income.
B) The percentage of tax payable on the last dollar of income received.
C) Never higher than the nominal tax rate.
D) Always equal to the marginal tax rate.
A) Equal to the taxes paid divided by taxable income.
B) The percentage of tax payable on the last dollar of income received.
C) Never higher than the nominal tax rate.
D) Always equal to the marginal tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The changes contained in the Tax Reform Act (TRA) of 1986 included
A) Narrowing the tax base.
B) Lowering marginal tax rates.
C) A partial shift from corporate to personal taxes.
D) More tax brackets to increase vertical equity.
A) Narrowing the tax base.
B) Lowering marginal tax rates.
C) A partial shift from corporate to personal taxes.
D) More tax brackets to increase vertical equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following was a basic feature of the Tax Reform Act of 1986?
A) A shift from corporate to personal taxes.
B) Tax relief for the rich.
C) Loophole closing.
D) More tax brackets.
A) A shift from corporate to personal taxes.
B) Tax relief for the rich.
C) Loophole closing.
D) More tax brackets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Suppose a taxpayer has an income of $100,000 and a taxable income of $80,000, and pays taxes of $10,000. If the taxpayer talks of being taxed at a 10 percent rate, she is referring to the
A) Average tax rate.
B) Marginal tax rate.
C) Nominal tax rate.
D) Effective tax rate.
A) Average tax rate.
B) Marginal tax rate.
C) Nominal tax rate.
D) Effective tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Taxes paid divided by total income is the
A) Nominal tax rate.
B) Horizontal tax rate.
C) Marginal tax rate.
D) Effective tax rate.
A) Nominal tax rate.
B) Horizontal tax rate.
C) Marginal tax rate.
D) Effective tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If Luis makes $50,000 per year as a computer programmer and pays $6,000 in taxes while Hector makes $50,000 per year as a roofing contractor and pays $7,000 in taxes, this is an example of
A) A regressive tax system.
B) Horizontal inequity.
C) A flat tax.
D) Vertical inequity.
A) A regressive tax system.
B) Horizontal inequity.
C) A flat tax.
D) Vertical inequity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
An increase in deductions, exemptions, and credits in the tax code will
A) Reduce the tax base.
B) Allow lower rates to raise the same tax revenues.
C) Induce economic activity to go underground.
D) Increase the marginal tax rate.
A) Reduce the tax base.
B) Allow lower rates to raise the same tax revenues.
C) Induce economic activity to go underground.
D) Increase the marginal tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The nominal tax rate is
A) Lower than the effective tax rate.
B) Taxes paid divided by total economic income.
C) Taxes paid divided by taxable income.
D) Equal to the marginal tax rate.
A) Lower than the effective tax rate.
B) Taxes paid divided by total economic income.
C) Taxes paid divided by taxable income.
D) Equal to the marginal tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Horizontal equity can be determined by comparing the
A) Effective tax rate of the taxpayer with the highest nominal income to the effective tax rates of taxpayers with lower nominal incomes.
B) Marginal tax rate of the taxpayer with the highest nominal income to the marginal tax rates of taxpayers with lower nominal incomes.
C) Marginal tax rates for two taxpayers with the same nominal incomes.
D) Effective tax rates for two taxpayers with the same nominal incomes.
A) Effective tax rate of the taxpayer with the highest nominal income to the effective tax rates of taxpayers with lower nominal incomes.
B) Marginal tax rate of the taxpayer with the highest nominal income to the marginal tax rates of taxpayers with lower nominal incomes.
C) Marginal tax rates for two taxpayers with the same nominal incomes.
D) Effective tax rates for two taxpayers with the same nominal incomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Suppose a taxpayer has an income of $70,000 and a taxable income of $60,000, and pays $9,000 in taxes. If the taxpayer says she is taxed at a 15 percent tax rate, she is referring to the
A) Marginal tax rate.
B) Nominal tax rate.
C) Effective tax rate.
D) Average tax rate.
A) Marginal tax rate.
B) Nominal tax rate.
C) Effective tax rate.
D) Average tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The changes contained in the 1990 and 1993 tax increases
A) Increased the variation in the effective tax rates.
B) Left a lot of variation in the effective tax rates.
C) Reduced the variation in the nominal tax rates.
D) Resulted in a top marginal tax bracket of 85 percent.
A) Increased the variation in the effective tax rates.
B) Left a lot of variation in the effective tax rates.
C) Reduced the variation in the nominal tax rates.
D) Resulted in a top marginal tax bracket of 85 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If Alejandra makes $46,000 per year as a nurse and pays $7,000 in taxes while Emily makes $46,000 per year as a high school teacher and pays $6,500 in taxes, this is an example of
A) Horizontal inequity.
B) Marginal inequity.
C) A flat tax.
D) Vertical inequity.
A) Horizontal inequity.
B) Marginal inequity.
C) A flat tax.
D) Vertical inequity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
To determine horizontal equity, two taxpayers with
A) The same taxable incomes should be compared for their effective tax rates.
B) The same gross incomes should be compared for their effective tax rates.
C) Different gross incomes should be compared for their effective tax rates.
D) Different taxable incomes should be compared for their nominal tax rates.
A) The same taxable incomes should be compared for their effective tax rates.
B) The same gross incomes should be compared for their effective tax rates.
C) Different gross incomes should be compared for their effective tax rates.
D) Different taxable incomes should be compared for their nominal tax rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
An economy with nominal tax rates significantly higher than effective tax rates has
A) Loopholes in the tax code.
B) A regressive tax system.
C) A progressive tax system.
D) Large in-kind benefits.
A) Loopholes in the tax code.
B) A regressive tax system.
C) A progressive tax system.
D) Large in-kind benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Suppose a taxpayer has an income of $90,000 and a taxable income of $75,000, and pays $7,500 in taxes. If the taxpayer says he is taxed at a 10 percent tax rate, he is referring to the
A) Vertical tax rate.
B) Marginal tax rate.
C) Effective tax rate.
D) Nominal tax rate.
A) Vertical tax rate.
B) Marginal tax rate.
C) Effective tax rate.
D) Nominal tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Suppose a taxpayer has an income of $120,000 and a taxable income of $80,000, and pays $20,000 in taxes. If the taxpayer says she is taxed at a 25 percent tax rate, she is referring to the
A) Nominal tax rate.
B) Marginal tax rate.
C) Effective tax rate.
D) Average tax rate.
A) Nominal tax rate.
B) Marginal tax rate.
C) Effective tax rate.
D) Average tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Suppose a taxpayer has an income of $50,000 and a taxable income of $45,000, and pays $5,000 in taxes. If the taxpayer talks of being taxed at a 10 percent tax rate, she is referring to the
A) Effective tax rate.
B) Marginal tax rate.
C) Nominal tax rate.
D) Average tax rate.
A) Effective tax rate.
B) Marginal tax rate.
C) Nominal tax rate.
D) Average tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



