Deck 29: Controlling Manufacturing Costs: Standard Costs
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/118
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 29: Controlling Manufacturing Costs: Standard Costs
1
A key purpose of a manufacturing cost budget is to provide a basis for measuring performance.
True
2
The cost per unit of direct materials changes as output changes.
False
3
A fixed budget is one that shows only one level of activity.
True
4
Material budgets are computed by multiplying units to be produced by the unit cost of direct materials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A price variance for an item is the difference between its actual price and its standard price multiplied by the standard quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If a price variance for materials is unfavorable,the quantity variance for materials also must be unfavorable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If the predetermined overhead application rate is a percentage of labor cost,then a favorable labor time variance will be accompanied by a favorable manufacturing overhead variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If the standard cost for an item exceeds the actual cost,the variance is favorable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A fixed budget includes only fixed manufacturing costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In order to analyze the differences between actual costs and standard costs,it is necessary to identify the fixed and variable components of semi-variable costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Semi-variable costs are sometimes called mixed costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Direct materials and direct labor are examples of costs that tend to vary directly with the volume of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The manufacturing cost budget will include both variable and fixed manufacturing costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Weaver Corporation has a three-year contract with a security firm that sets hourly wage rates for the firm at $10 per hour.At 7,000 units of output,factory security costs were $14,000.With an expected increase in production next year to a level of 10,000 units,the anticipated security costs are expected to remain the same.The security costs are an example of fixed factory costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A flexible budget shows budgeted costs at several different levels of activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Semi-variable costs vary in direct proportion to the volume of activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
To measure manufacturing efficiency,it is necessary to first identify cost behavior and separate cost into their components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A budget performance report compares actual costs for a period with the budgeted costs for that period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
As the volume of output decreases,the fixed cost per unit of output increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Budgeting for manufacturing overhead is the simplest of total product costs to compute as its cost behavior is fixed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Costs that do not vary in total during a period even though the volume of manufacturing activity changes are called ____________________ costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Regression analysis is a more sophisticated technique than the high-low method,and often leads to higher confidence in the projected costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The controllable overhead variance compares the actual overhead costs incurred with what the costs should have been for the units produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Management expresses its operating plan in monetary units when it completes a(n)____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If the actual cost of an item is lower than the standard cost,a(n)____________________ price variance will be recognized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Standard costs reflect what costs should be for the units of product manufactured during the period under the normal efficient operating conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Usually,a well-run manufacturing company prepares only annual manufacturing cost budgets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The production manager is accountable for all material quantity variances as defective product and scrap is a result of inexperienced workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Two variances associated with analyzing manufacturing overhead costs are the production volume variance and the flexible budget variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Costs are expected to behave in a similar manner within a relevant range of activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The price variance for an item is the difference between its actual price and its standard price,multiplied by the ____________________ quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Variance analysis is a tool used by management to pinpoint inefficiencies in the manufacturing process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A flexible budget that is prepared based on the actual activity level achieved in a period provides a more precise measure of efficiency and control when evaluating actual costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The purchasing department can determine the standard quantity per unit of each type of raw material required to manufacture a product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The ____________________ cost per unit does not change as output changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The quantity variance for an item is the difference between its actual quantity and its standard quantity,multiplied by the ____________________ cost of the item.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The high-low point method results can be misleading if the activity is not reflective of the normal activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The setting of standard wage rates is usually a function of the personnel department.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The difference between the actual cost of an item and its standard cost is called a(n)___________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Costs that tend to change in total directly with the volume of manufacturing activity are called ____________________ costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The labor time (efficiency)variance and the labor ____________________ variance together make up the total labor variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A decrease in activity level will result in:
A) a decrease in fixed unit cost.
B) total fixed cost remaining constant.
C) a decrease in total fixed cost.
D) a decrease in unit variable cost.
A) a decrease in fixed unit cost.
B) total fixed cost remaining constant.
C) a decrease in total fixed cost.
D) a decrease in unit variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Costs that vary in some degree with the volume of activity,but not in direct proportion to it are called ____________________ costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An increase in activity level will result in:
A) an increase in fixed unit cost.
B) an increase in unit variable cost.
C) decrease in fixed unit cost.
D) a decrease in unit variable cost.
A) an increase in fixed unit cost.
B) an increase in unit variable cost.
C) decrease in fixed unit cost.
D) a decrease in unit variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
To separate the semi-variable costs into their fixed and variable components,one can use which of the following methods?
A) labor variance method
B) material variance method
C) relevant range of activity method
D) high-low point method
A) labor variance method
B) material variance method
C) relevant range of activity method
D) high-low point method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Costs in excess of established standards are ___________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
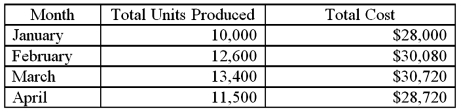 Use the high-low point method to determine variable cost per unit:
Use the high-low point method to determine variable cost per unit:A) $0.60 per unit.
B) $0.80 per unit.
C) $1.00 per unit.
D) $1.20 per unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
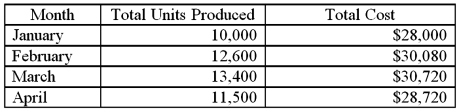 Use the high-low point method to determine total costs if 16,000 units are produced.
Use the high-low point method to determine total costs if 16,000 units are produced.A) $20,000
B) $22,800
C) $30,000
D) $32,800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The range of activity at which the factory is likely to operate is referred to as the ____________________ range of activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following costs are generally semi-variable?
A) clerical salaries
B) depreciation
C) repairs and maintenance
D) property taxes
A) clerical salaries
B) depreciation
C) repairs and maintenance
D) property taxes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Deducting the total variable cost from the total cost results in the
A) overhead.
B) fixed cost.
C) manufacturing cost.
D) semivariable cost.
A) overhead.
B) fixed cost.
C) manufacturing cost.
D) semivariable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
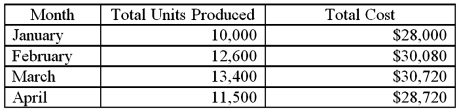 Use the high-low point method to determine total fixed cost:
Use the high-low point method to determine total fixed cost:A) $20,000.
B) $28,000.
C) $16,000.
D) $24,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Petersen Company produces a single product with the following production and average cost data: 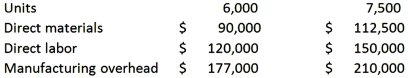 The best estimate of the variable cost per unit is:
The best estimate of the variable cost per unit is:
A) $36.00 per unit
B) $57.00 per unit
C) $15.00 per unit
D) $42.00 per unit
 The best estimate of the variable cost per unit is:
The best estimate of the variable cost per unit is:A) $36.00 per unit
B) $57.00 per unit
C) $15.00 per unit
D) $42.00 per unit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Costs that reflect what costs should be for the units of product manufactured during the period under normal efficient operating conditions are called ____________________ costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A budget that shows expected costs at only one level of production activity is called a(n)____________________ budget.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A budget that shows expected costs at more than one level of activity is called a(n)____________________ budget.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The difference between the total standard cost and the total actual cost is the ___________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
As the volume of output increases,the ____________________ cost per unit of output decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A simple method used to analyze the fixed and variable components in semi-variable costs is called the ____________________ point method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Petersen Company produces a single product with the following production and average cost data: 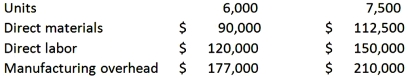 The best estimate of the monthly fixed cost is:
The best estimate of the monthly fixed cost is:
A) $45,000
B) $120,000
C) $177,000
D) $135,000
 The best estimate of the monthly fixed cost is:
The best estimate of the monthly fixed cost is:A) $45,000
B) $120,000
C) $177,000
D) $135,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The salary of the factory supervisor is a good example of
A) a variable cost.
B) a fixed cost.
C) a semi-variable cost.
D) a standard cost.
A) a variable cost.
B) a fixed cost.
C) a semi-variable cost.
D) a standard cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The general model for computing a price variance is:
A) difference in unit price × actual quantity of inputs.
B) difference in unit price × standard quantity of inputs.
C) standard price × (actual quantity of inputs - standard quantity allowed for units of output).
D) actual price × difference in quantity of inputs.
A) difference in unit price × actual quantity of inputs.
B) difference in unit price × standard quantity of inputs.
C) standard price × (actual quantity of inputs - standard quantity allowed for units of output).
D) actual price × difference in quantity of inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The quantity variance for an item is the difference between its actual quantity and its standard quantity multiplied by
A) the standard cost of the item.
B) the actual cost of the item.
C) the price variance.
D) the budgeted amount for the item.
A) the standard cost of the item.
B) the actual cost of the item.
C) the price variance.
D) the budgeted amount for the item.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
SweetBerry Ice-creams uses a standard cost system.The following data is available for June:  The actual material cost for June was:
The actual material cost for June was:
A) $48,000.
B) $50,400.
C) $49,770.
D) $51,030.
 The actual material cost for June was:
The actual material cost for June was:A) $48,000.
B) $50,400.
C) $49,770.
D) $51,030.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The labor standard for a product was five hours at a wage rate of $8 per hour.The firm produced 900 units of the item.Labor costs totaled $35,250 and 4,700 hours of labor were used.An analysis of labor costs would indicate
A) a $750 favorable labor time variance.
B) a $1,600 unfavorable labor time variance.
C) a $750 unfavorable labor rate variance.
D) a $1,600 favorable labor rate variance.
A) a $750 favorable labor time variance.
B) a $1,600 unfavorable labor time variance.
C) a $750 unfavorable labor rate variance.
D) a $1,600 favorable labor rate variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The materials price variance for an item is the difference between its actual price and its standard cost
A) multiplied by the actual quantity purchased.
B) multiplied by the standard quantity allowed.
C) multiplied by the difference between the actual quantity and the standard quantity.
D) divided by the actual quantity.
A) multiplied by the actual quantity purchased.
B) multiplied by the standard quantity allowed.
C) multiplied by the difference between the actual quantity and the standard quantity.
D) divided by the actual quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Examples of fixed manufacturing costs include all of the following except:
A) depreciation.
B) utilities.
C) insurance.
D) taxes.
A) depreciation.
B) utilities.
C) insurance.
D) taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The labor standard for a product was five hours at a wage rate of $8 per hour.The firm produced 900 units of the item.Labor costs totaled $35,250 and 4,700 hours of labor were used.An analysis of labor costs would indicate
A) a $750 favorable labor time variance.
B) a $1,600 favorable labor time variance.
C) a $2,350 unfavorable labor rate variance.
D) a $2,350 favorable labor rate variance.
A) a $750 favorable labor time variance.
B) a $1,600 favorable labor time variance.
C) a $2,350 unfavorable labor rate variance.
D) a $2,350 favorable labor rate variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which variance is controllable by the purchasing manager?
A) standard overhead variance.
B) labor rate variance.
C) material usage variance.
D) material price variance.
A) standard overhead variance.
B) labor rate variance.
C) material usage variance.
D) material price variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Petersen Company produces a single product with the following production and average cost data: 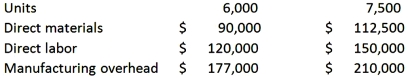 The best estimate of total cost at an activity level of 7,250 units is:
The best estimate of total cost at an activity level of 7,250 units is:
A) $424,500
B) $433,250
C) $439,500
D) $458,250
 The best estimate of total cost at an activity level of 7,250 units is:
The best estimate of total cost at an activity level of 7,250 units is:A) $424,500
B) $433,250
C) $439,500
D) $458,250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
An unfavorable price variance for materials means that
A) the actual cost of the materials was more than the budgeted amount.
B) more materials were used in production than anticipated.
C) more labor hours were required to work with the materials than expected.
D) the actual cost of the materials was more than the standard cost.
A) the actual cost of the materials was more than the budgeted amount.
B) more materials were used in production than anticipated.
C) more labor hours were required to work with the materials than expected.
D) the actual cost of the materials was more than the standard cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A material usage variance is calculated as:
A) the difference in unit price × actual quantity of inputs.
B) the difference in unit price × standard quantity of inputs.
C) standard price × (actual quantity of inputs - standard quantity allowed for units of output).
D) actual price × difference in quantity of inputs.
A) the difference in unit price × actual quantity of inputs.
B) the difference in unit price × standard quantity of inputs.
C) standard price × (actual quantity of inputs - standard quantity allowed for units of output).
D) actual price × difference in quantity of inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Direct factory labor is usually considered to be
A) a variable cost.
B) a fixed cost.
C) a semi-variable cost.
D) a mixed cost.
A) a variable cost.
B) a fixed cost.
C) a semi-variable cost.
D) a mixed cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
WinterRec uses a standard cost system.The following data is available for November:  The actual direct labor rate for November is:
The actual direct labor rate for November is:
A) $8 per hour.
B) $7.60 per hour.
C) $8.40 per hour.
D) $8.20 per hour.
 The actual direct labor rate for November is:
The actual direct labor rate for November is:A) $8 per hour.
B) $7.60 per hour.
C) $8.40 per hour.
D) $8.20 per hour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Reelmates manufactures fishing poles.In a recent month,the company budgeted production of 2,000 poles.Actual production was 2,200.According to the standard cost card,each pole requires 3 feet of fiberglass rod at a cost of $9 per foot.Reelmates used 6,500 feet of rod at a net cost of $65,000 for the period. The material usage variance was:
A) $900 unfavorable.
B) $900 favorable.
C) $6,500 favorable.
D) $5,600 unfavorable.
A) $900 unfavorable.
B) $900 favorable.
C) $6,500 favorable.
D) $5,600 unfavorable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Reelmates manufactures fishing poles.In a recent month,the company budgeted production of 2,000 poles.Actual production was 2,200.According to the standard cost card,each pole requires 3 feet of fiberglass rod at a cost of $9 per foot.Reelmates used 6,500 feet of rod at a net cost of $65,000 for the period. The total material variance was:
A) $900 unfavorable.
B) $900 favorable.
C) $6,500 favorable.
D) $5,600 unfavorable.
A) $900 unfavorable.
B) $900 favorable.
C) $6,500 favorable.
D) $5,600 unfavorable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A fixed budget is a meaningful way to evaluate manufacturing performance if the activity level used for the budget is
A) similar to actual.
B) less than actual.
C) more than actual.
D) a reasonable/logical activity measure.
A) similar to actual.
B) less than actual.
C) more than actual.
D) a reasonable/logical activity measure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The cost of utilities consumed in the factory is a good example of
A) a variable cost.
B) a fixed cost.
C) a semi-variable cost.
D) a standard cost.
A) a variable cost.
B) a fixed cost.
C) a semi-variable cost.
D) a standard cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A budget prepared using several differing levels of activity is a
A) fixed budget.
B) flexible budget.
C) manufacturing cost budget.
D) budget performance report.
A) fixed budget.
B) flexible budget.
C) manufacturing cost budget.
D) budget performance report.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which variance is controllable by the production manager?
A) standard overhead variance.
B) labor rate variance.
C) labor usage variance.
D) material price variance.
A) standard overhead variance.
B) labor rate variance.
C) labor usage variance.
D) material price variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



