Deck 5: Languages
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/123
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Languages
1
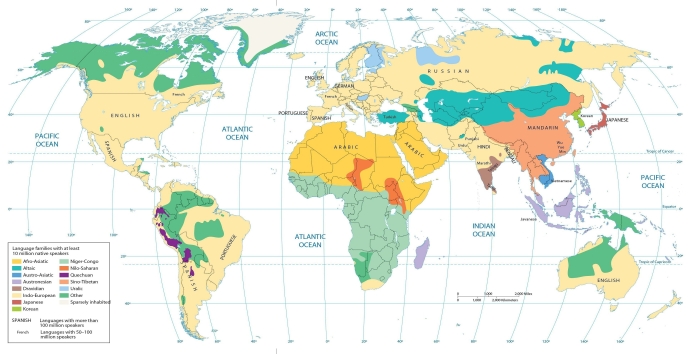
The maps in this chapter show that the second most widely spoken language family in Europe is
A) Balto-Slavic.
B) Indo-European.
C) Romance.
D) Uralic.
E) Celtic.
D
2
The first speakers of the language that evolved into English were tribes that lived in present-day
A) France.
B) Denmark.
C) United States.
D) Italy.
E) Switzerland.
A) France.
B) Denmark.
C) United States.
D) Italy.
E) Switzerland.
B
3
The main difference between languages in the same family, branch, or group is how
A) recently in time the languages were once the same.
B) closely the speakers of each language live to one other.
C) they correspond to the diffusion of free markets across much of the world.
D) similar the cultures of the speakers of each language are.
E) they all emerged at the same point in history, according to the Bible.
A) recently in time the languages were once the same.
B) closely the speakers of each language live to one other.
C) they correspond to the diffusion of free markets across much of the world.
D) similar the cultures of the speakers of each language are.
E) they all emerged at the same point in history, according to the Bible.
A
4
A group of languages that share a common origin but have since evolved into individual languages is a
A) dialect.
B) language branch.
C) language family.
D) language group.
E) language root.
A) dialect.
B) language branch.
C) language family.
D) language group.
E) language root.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A lingua franca is
A) an English word that has entered the French language.
B) a language understood by people who have different native languages.
C) an extinct language that has been revived.
D) an official language in a region of the world different from where the language originated.
E) a language used by French colonial administrations.
A) an English word that has entered the French language.
B) a language understood by people who have different native languages.
C) an extinct language that has been revived.
D) an official language in a region of the world different from where the language originated.
E) a language used by French colonial administrations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The charts or diagrams in this chapter indicate that the percentage of Austronesian language speakers in the world is greater than the percentage speaking ________ languages.
A) Sino-Tibetan
B) Dravidian
C) Indo-European
D) Niger-Congo
E) Afro-Asiatic
A) Sino-Tibetan
B) Dravidian
C) Indo-European
D) Niger-Congo
E) Afro-Asiatic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A group of languages that share a common ancestor before recorded history is a
A) dialect.
B) language branch.
C) language family.
D) language group.
E) language root.
A) dialect.
B) language branch.
C) language family.
D) language group.
E) language root.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The language spoken by soldiers stationed throughout the Roman Empire was known as
A) Official Latin.
B) Romance language.
C) standard language.
D) Vulgar Latin.
E) Catalan Latin.
A) Official Latin.
B) Romance language.
C) standard language.
D) Vulgar Latin.
E) Catalan Latin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is not a Romance language?
A) Bulgarian
B) Italian
C) Portuguese
D) Romanian
E) French
A) Bulgarian
B) Italian
C) Portuguese
D) Romanian
E) French

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The diagrams in this chapter show that the percentage of Sino-Tibetan speakers in the world is less than the percentage speaking ________ languages.
A) Austronesian
B) Indo-European
C) Dravidian
D) Altaic
E) Niger-Congo
A) Austronesian
B) Indo-European
C) Dravidian
D) Altaic
E) Niger-Congo

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The language family encompassing the languages of the People's Republic of China is
A) Indo-European.
B) Indo-Iranian.
C) Mandarin.
D) Sino-Tibetan.
E) Austro-Asiatic.
A) Indo-European.
B) Indo-Iranian.
C) Mandarin.
D) Sino-Tibetan.
E) Austro-Asiatic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Franglais is
A) the lingua franca of France.
B) a dialect of French.
C) the standard language of French.
D) the use of English in the French language.
E) a language used by French colonial administrations.
A) the lingua franca of France.
B) a dialect of French.
C) the standard language of French.
D) the use of English in the French language.
E) a language used by French colonial administrations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The two largest language families in the world are
A) Indo-Iranian and Balto-Slavic.
B) Sino-Tibetan and Indo-European.
C) Afro-Asiatic and Sino-Tibetan.
D) Balto-Slavic and Sino-Tibetan.
E) Altaic and Nilo-Saharan.
A) Indo-Iranian and Balto-Slavic.
B) Sino-Tibetan and Indo-European.
C) Afro-Asiatic and Sino-Tibetan.
D) Balto-Slavic and Sino-Tibetan.
E) Altaic and Nilo-Saharan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The most widely spoken language in Brazil is
A) Creole.
B) French.
C) Portuguese.
D) Spanish.
E) Catalan.
A) Creole.
B) French.
C) Portuguese.
D) Spanish.
E) Catalan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The charts or diagrams in this chapter indicate that the percentage of Altaic language speakers in the world is greater than the percentage speaking ________ languages.
A) Sino-Tibetan
B) Austro-Asiatic
C) Indo-European
D) Niger Congo
E) Austronesian
A) Sino-Tibetan
B) Austro-Asiatic
C) Indo-European
D) Niger Congo
E) Austronesian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Both the Angles and the Normans contributed to the development of the English language, because they
A) spoke ancient English languages.
B) invaded England.
C) spoke languages derived from Latin.
D) diffused English around the world.
E) agreed to divide Ireland from England.
A) spoke ancient English languages.
B) invaded England.
C) spoke languages derived from Latin.
D) diffused English around the world.
E) agreed to divide Ireland from England.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Dialects developed within England primarily because
A) different Germanic invaders settled in different regions.
B) the Normans invaded from the south.
C) the Viking invaders did not remain long in England.
D) British Received Pronunciation became the standard dialect.
E) commerce developed more slowly in England than on the European continent.
A) different Germanic invaders settled in different regions.
B) the Normans invaded from the south.
C) the Viking invaders did not remain long in England.
D) British Received Pronunciation became the standard dialect.
E) commerce developed more slowly in England than on the European continent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Basque is a good example of a(n)
A) language family.
B) globalizing language.
C) language group.
D) lingua franca.
E) isolated language.
A) language family.
B) globalizing language.
C) language group.
D) lingua franca.
E) isolated language.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When languages are depicted as leaves on trees, the trunks of the trees represent
A) dialects.
B) language groups.
C) language families.
D) possible prehistoric superfamilies.
E) language sects.
A) dialects.
B) language groups.
C) language families.
D) possible prehistoric superfamilies.
E) language sects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The geographic study of the distribution of languages provides a good example of
A) the interplay between globalization and local diversity.
B) the diffusion of folk culture in different areas of the world.
C) the role and spread of religion across much of the world.
D) the diffusion of free markets across much of the world.
E) political conflicts that arise due to ethnic tensions.
A) the interplay between globalization and local diversity.
B) the diffusion of folk culture in different areas of the world.
C) the role and spread of religion across much of the world.
D) the diffusion of free markets across much of the world.
E) political conflicts that arise due to ethnic tensions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The Kurgans
A) conquered much of East Asia several thousand years ago.
B) were a Germanic tribe that invaded England.
C) were herders from the steppes of Central Asia.
D) preserved Basque in present-day Spain.
E) were the earliest speakers of Sino-Caucasian, which they diffused through conquest.
A) conquered much of East Asia several thousand years ago.
B) were a Germanic tribe that invaded England.
C) were herders from the steppes of Central Asia.
D) preserved Basque in present-day Spain.
E) were the earliest speakers of Sino-Caucasian, which they diffused through conquest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which group of the Germanic family is extinct?
A) West Germanic
B) North Germanic
C) East Germanic
D) South Germanic
E) Uber Germanic
A) West Germanic
B) North Germanic
C) East Germanic
D) South Germanic
E) Uber Germanic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The two most important languages in South America are
A) Dutch and English.
B) English and Spanish.
C) French and Spanish.
D) Portuguese and Spanish.
E) Creole and Portuguese.
A) Dutch and English.
B) English and Spanish.
C) French and Spanish.
D) Portuguese and Spanish.
E) Creole and Portuguese.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
According to the maps and diagrams in this chapter, England was invaded by tribes from
A) English-speaking areas
B) Uric-speaking areas
C) Native American-speaking areas
D) Italian-speaking areas
E) Germanic-speaking areas
A) English-speaking areas
B) Uric-speaking areas
C) Native American-speaking areas
D) Italian-speaking areas
E) Germanic-speaking areas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Analyzing the maps and diagrams in this chapter, we can see that the branch of Indo-European that includes Ukrainian is
A) European.
B) Balto-Slavic.
C) Indo-Iranian.
D) Romance.
E) Germanic.
A) European.
B) Balto-Slavic.
C) Indo-Iranian.
D) Romance.
E) Germanic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
According to the maps and diagrams in this chapter, the branch of Indo-European that includes Rangpuri is
A) European.
B) Indo-Iranian.
C) Romance.
D) Balto-Slavic.
E) Germanic.
A) European.
B) Indo-Iranian.
C) Romance.
D) Balto-Slavic.
E) Germanic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
English is part of which language branch?
A) Germanic
B) Northern
C) Western
D) Indo-European
E) Austronesian
A) Germanic
B) Northern
C) Western
D) Indo-European
E) Austronesian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
According to the diagrams in this chapter, Turkmen is part of what language branch?
A) Altaic
B) Germanic
C) Indo-Iranian
D) Romance
E) Balto-Slavic
A) Altaic
B) Germanic
C) Indo-Iranian
D) Romance
E) Balto-Slavic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
According to the maps and diagrams in this chapter, the branch of Indo-European that includes Romanian is
A) European.
B) Romance.
C) Indo-Iranian.
D) Balto-Slavic.
E) Germanic.
A) European.
B) Romance.
C) Indo-Iranian.
D) Balto-Slavic.
E) Germanic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
According to the maps and diagrams in this chapter, the Germanic invaders of England included which groups or tribes?
A) Germans, Normans, and Danes
B) Brittans, Normans, and Welsh
C) Irish, Welsh, and English
D) Scots, Irish, and Welsh
E) Angles, Jutes, and Saxons
A) Germans, Normans, and Danes
B) Brittans, Normans, and Welsh
C) Irish, Welsh, and English
D) Scots, Irish, and Welsh
E) Angles, Jutes, and Saxons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Analysis of the maps and diagrams in this chapter shows that the Dutch language is from the branch of Indo-European known as
A) European.
B) Germanic.
C) Romance.
D) Balto-Slavic.
E) Indo-Iranian.
A) European.
B) Germanic.
C) Romance.
D) Balto-Slavic.
E) Indo-Iranian.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Colin Renfrew's research constitutes much of the ________ Hypothesis.
A) Nomadic Herder
B) Kurgan Farmer
C) Nomadic Warrior
D) Sedentary Farmer
E) Silk Road Trader
A) Nomadic Herder
B) Kurgan Farmer
C) Nomadic Warrior
D) Sedentary Farmer
E) Silk Road Trader

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The four most frequently spoken branches of Indo-European include all but
A) Balto-Slavic.
B) Celtic.
C) Indo-Iranian.
D) Romance.
E) Germanic.
A) Balto-Slavic.
B) Celtic.
C) Indo-Iranian.
D) Romance.
E) Germanic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The most widely spoken language in Argentina is
A) Creole.
B) French.
C) Spanish.
D) Portuguese.
E) Catalan.
A) Creole.
B) French.
C) Spanish.
D) Portuguese.
E) Catalan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Analysis of the maps and diagrams in this chapter shows that the branch of Indo-European that includes Kurdish is
A) European.
B) Indo-Iranian.
C) Romance.
D) Balto-Slavic.
E) Germanic.
A) European.
B) Indo-Iranian.
C) Romance.
D) Balto-Slavic.
E) Germanic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
According to the maps and diagrams in this chapter, the branch of Indo-European that includes Haitian Creole is
A) European.
B) Romance.
C) Indo-Iranian.
D) Balto-Slavic.
E) Germanic.
A) European.
B) Romance.
C) Indo-Iranian.
D) Balto-Slavic.
E) Germanic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
English is part of which language family?
A) Germanic
B) North Germanic
C) West Germanic
D) Indo-European
E) Romance
A) Germanic
B) North Germanic
C) West Germanic
D) Indo-European
E) Romance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
According to Colin Renfrew's research, Indo-European languages diffused across Europe
A) entirely by sea.
B) by way of the Kurgan homeland.
C) with the conquests of warriors on horseback.
D) with the diffusion of agriculture.
E) following the traders on the silk road.
A) entirely by sea.
B) by way of the Kurgan homeland.
C) with the conquests of warriors on horseback.
D) with the diffusion of agriculture.
E) following the traders on the silk road.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Russian is part of what language branch?
A) Balto-Slavic
B) Germanic
C) Indo-Iranian
D) Romance
E) Altaic
A) Balto-Slavic
B) Germanic
C) Indo-Iranian
D) Romance
E) Altaic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
According to the maps and diagrams in this chapter, the branch of Indo-European that includes Slovak is
A) European.
B) Balto-Slavic.
C) Indo-Iranian.
D) Romance.
E) Germanic.
A) European.
B) Balto-Slavic.
C) Indo-Iranian.
D) Romance.
E) Germanic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
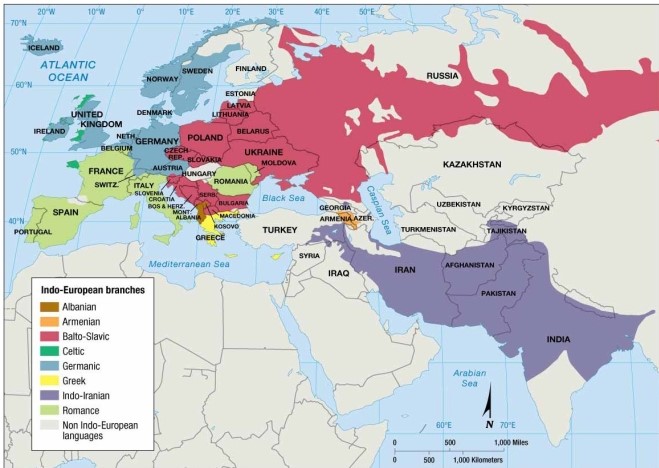
An analysis of the maps and diagrams in this chapter shows that every European country is dominated by Indo-European speakers except
A) Spain, Italy, and Portugal.
B) Romania, Serbia, and Slovenia.
C) Germany, Austria, and Switzerland.
D) Denmark, Sweden, and Norway.
E) Finland, Hungary, and Estonia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
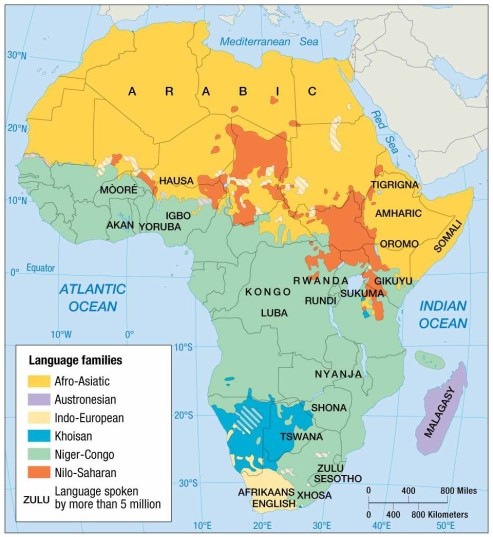
The most important language family in Sub-Saharan Africa is
A) Khoisan.
B) Niger-Congo.
C) Nilo-Saharan.
D) Afro-Asiatic.
E) Altaic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A form of a language spoken in a local area is a
A) dialect.
B) branch.
C) family.
D) group.
E) root.
A) dialect.
B) branch.
C) family.
D) group.
E) root.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Marija Gimbutas' theory points to the first speakers of the Indo-European language as the ancient
A) Celts.
B) Germans.
C) Kurgans.
D) Russians.
E) Dravidians.
A) Celts.
B) Germans.
C) Kurgans.
D) Russians.
E) Dravidians.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Marija Gimbutas has contributed to the ________ Hypothesis.
A) Sedentary Archer
B) Nomadic Fisher
C) Nomadic Warrior
D) Sedentary Farmer
E) Sedentary Farmer-Warrior
A) Sedentary Archer
B) Nomadic Fisher
C) Nomadic Warrior
D) Sedentary Farmer
E) Sedentary Farmer-Warrior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
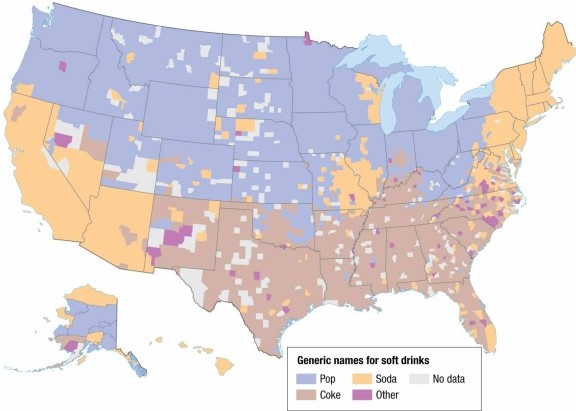
An analysis of the map of U.S. soft drink terminology shows that the word "Coke" is more common in
A) Illinois.
B) Mississippi.
C) New York.
D) Oregon.
E) California.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
English is part of which language group?
A) East Germanic
B) North Germanic
C) West Germanic
D) Indo-European
E) Semitic
A) East Germanic
B) North Germanic
C) West Germanic
D) Indo-European
E) Semitic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The second-largest language family is
A) Indo-European.
B) Sino-Tibetan.
C) Afro-Asiatic.
D) Austronesian.
E) Dravidian.
A) Indo-European.
B) Sino-Tibetan.
C) Afro-Asiatic.
D) Austronesian.
E) Dravidian.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Immigrants to which American colonies had the most diverse backgrounds in the 1700s and 1800s?
A) Middle Atlantic
B) New England
C) Northern
D) Southeast
E) French Canadian
A) Middle Atlantic
B) New England
C) Northern
D) Southeast
E) French Canadian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The Flemings and Walloons speak languages belonging to different
A) dialects.
B) language branches.
C) language families.
D) language groups.
E) language sects.
A) dialects.
B) language branches.
C) language families.
D) language groups.
E) language sects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The maps and diagrams in this chapter show that an Indo-European language is chiefly spoken in which of these countries?
A) Bulgaria
B) Finland
C) Hungary
D) Estonia
E) China
A) Bulgaria
B) Finland
C) Hungary
D) Estonia
E) China

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
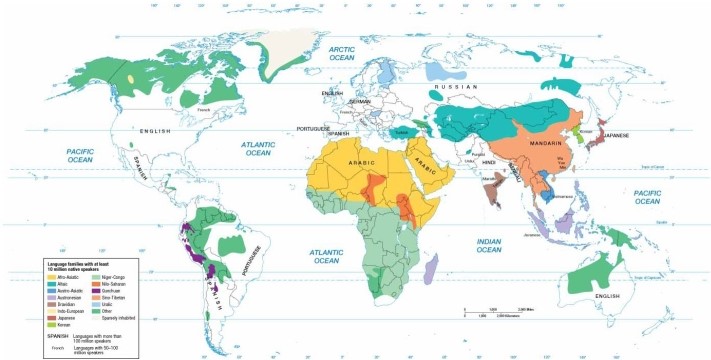
An analysis of the maps and diagrams in this chapter shows that Indo-European speakers dominate
A) Estonia
B) Madagascar
C) Malaysia
D) Finland
E) Sweden

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When languages are depicted as leaves on trees, the roots of the trees below the surface represent
A) dialects.
B) language groups.
C) language sects.
D) language families.
E) possible prehistoric superfamilies.
A) dialects.
B) language groups.
C) language sects.
D) language families.
E) possible prehistoric superfamilies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
British and American English differ in all but which of the following?
A) alphabet
B) pronunciation
C) spelling
D) vocabulary
E) prevalent dialects
A) alphabet
B) pronunciation
C) spelling
D) vocabulary
E) prevalent dialects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The survival of any language relies on
A) rapid migration into other areas.
B) the efficient "corrections" of the global free market.
C) the political and military strength of its speakers.
D) the spread of its speakers' material culture.
E) the homogenization of its dialects.
A) rapid migration into other areas.
B) the efficient "corrections" of the global free market.
C) the political and military strength of its speakers.
D) the spread of its speakers' material culture.
E) the homogenization of its dialects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
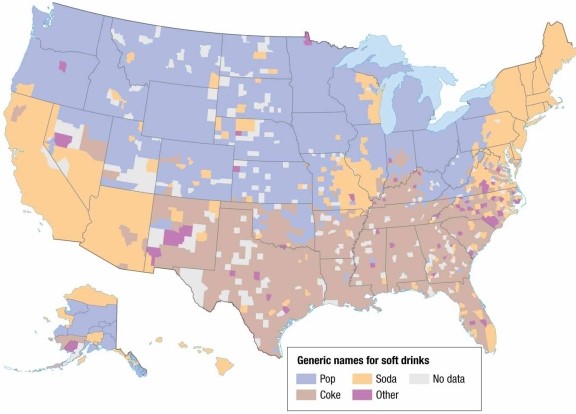
An analysis of the map of U.S. soft drink terminology shows that the word "pop" is more common in
A) California.
B) Oregon.
C) Mississippi.
D) Florida.
E) New Mexico.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A literary tradition is
A) a form of a language intended to be printed in official government documents.
B) a language spoken in an area.
C) a collection of languages related to one other.
D) the written form of a language.
E) the variety of dialects in a language used in obscure examples of poetry.
A) a form of a language intended to be printed in official government documents.
B) a language spoken in an area.
C) a collection of languages related to one other.
D) the written form of a language.
E) the variety of dialects in a language used in obscure examples of poetry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
An isogloss is
A) a form of a language spoken in a local area.
B) a collection of unique words.
C) a boundary between language regions.
D) a blending of two language families.
E) a line that separates literary traditions.
A) a form of a language spoken in a local area.
B) a collection of unique words.
C) a boundary between language regions.
D) a blending of two language families.
E) a line that separates literary traditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Gumbo and jazz are terms that originated in the English dialects of
A) New Englanders.
B) African Americans.
C) Jewish immigrants to the United States.
D) Irish Americans.
E) French Americans.
A) New Englanders.
B) African Americans.
C) Jewish immigrants to the United States.
D) Irish Americans.
E) French Americans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In the following answer choices, the best example of a literary tradition is
A) the diffusion of television and radio broadcasts.
B) the religious rituals and traditions of ancient European civilizations.
C) the oral traditions of Australia's Aborigines that were passed down from generation to generation without the aid of writing.
D) the historical documents and religious texts of the ancient Maya that were partly destroyed by Spanish conquerors.
E) the variety of dialects in a language used in obscure examples of spoken poetry.
A) the diffusion of television and radio broadcasts.
B) the religious rituals and traditions of ancient European civilizations.
C) the oral traditions of Australia's Aborigines that were passed down from generation to generation without the aid of writing.
D) the historical documents and religious texts of the ancient Maya that were partly destroyed by Spanish conquerors.
E) the variety of dialects in a language used in obscure examples of spoken poetry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Basque is spoken primarily in
A) Brittany.
B) the Swiss Alps.
C) the Pyrenees Mountains.
D) Barcelona, Spain.
E) Liechtenstein.
A) Brittany.
B) the Swiss Alps.
C) the Pyrenees Mountains.
D) Barcelona, Spain.
E) Liechtenstein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
All of the following describe the English language except
A) It is a lingua franca.
B) Its recent growth is due to expansion diffusion.
C) It is an Indo-European language.
D) It has diffused along with economic globalization.
E) It is an isogloss.
A) It is a lingua franca.
B) Its recent growth is due to expansion diffusion.
C) It is an Indo-European language.
D) It has diffused along with economic globalization.
E) It is an isogloss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A creolized language is
A) extinct.
B) a mix of indigenous and colonial languages.
C) an isolated language family.
D) a possible prehistoric superfamily.
E) a revived formerly extinct language.
A) extinct.
B) a mix of indigenous and colonial languages.
C) an isolated language family.
D) a possible prehistoric superfamily.
E) a revived formerly extinct language.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Spanish is an important language in the United States primarily because of
A) the diffusion of Spanish colonies and subsequent migration patterns.
B) the Mexican conquest of the U.S. Southwest in the 1800s.
C) the global dominance of the United States.
D) the diffusion of Mexican colonies into the northern territories.
E) official U.S. policies proclaiming Spanish a national language, along with English.
A) the diffusion of Spanish colonies and subsequent migration patterns.
B) the Mexican conquest of the U.S. Southwest in the 1800s.
C) the global dominance of the United States.
D) the diffusion of Mexican colonies into the northern territories.
E) official U.S. policies proclaiming Spanish a national language, along with English.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Chinese is traditionally written in the form of
A) a literary tradition.
B) a Latin alphabet.
C) ideograms.
D) Cantonese.
E) phonemes.
A) a literary tradition.
B) a Latin alphabet.
C) ideograms.
D) Cantonese.
E) phonemes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Celtic languages
A) were threatened by extinction in England.
B) are still spoken by people in France.
C) have been revived in some parts of the British Isles.
D) have an extensive body of literature.
E) all of the above
A) were threatened by extinction in England.
B) are still spoken by people in France.
C) have been revived in some parts of the British Isles.
D) have an extensive body of literature.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The English language is a "second" or "third" language in many regions where it is used as a(n)
A) colonial dialect.
B) expansion diffusion.
C) Indo-European import.
D) global lingua.
E) lingua franca.
A) colonial dialect.
B) expansion diffusion.
C) Indo-European import.
D) global lingua.
E) lingua franca.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The language maps in this chapter show that Urdu is one of the most important languages of
A) Bangladesh.
B) Iran.
C) Pakistan.
D) Sri Lanka.
A) Bangladesh.
B) Iran.
C) Pakistan.
D) Sri Lanka.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Hebrew is an example of
A) an isolated language.
B) an extinct language.
C) a revived language.
D) a language family.
E) an Altaic language.
A) an isolated language.
B) an extinct language.
C) a revived language.
D) a language family.
E) an Altaic language.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The Flemings and Walloons live in
A) Belgium.
B) France.
C) South Africa.
D) Switzerland.
E) Liechtenstein.
A) Belgium.
B) France.
C) South Africa.
D) Switzerland.
E) Liechtenstein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The Icelandic language has changed less than any other Germanic language because of
A) Iceland's close contact with other people and activities.
B) migration by German tribes.
C) Iceland's relative isolation from other places.
D) the extinction of the East Germanic group.
E) continuous exchange with Norway and Sweden.
A) Iceland's close contact with other people and activities.
B) migration by German tribes.
C) Iceland's relative isolation from other places.
D) the extinction of the East Germanic group.
E) continuous exchange with Norway and Sweden.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A language that was nearly extinct in British-controlled areas but which is now being revived is
A) Slavic.
B) Celtic.
C) Iranian.
D) English.
E) Pictish.
A) Slavic.
B) Celtic.
C) Iranian.
D) English.
E) Pictish.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The language spoken by the greatest number of native speakers in the world is
A) Cantonese.
B) English.
C) Hindi.
D) Mandarin.
E) Spanish.
A) Cantonese.
B) English.
C) Hindi.
D) Mandarin.
E) Spanish.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
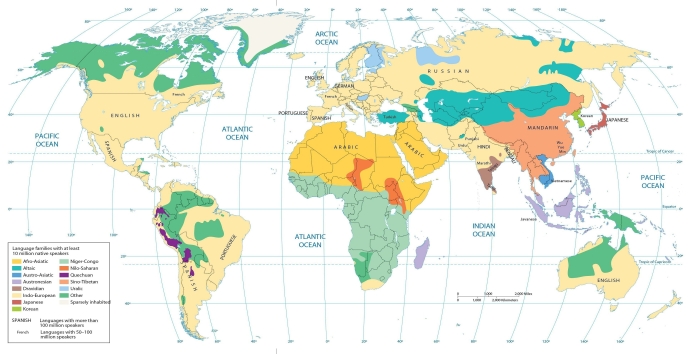
The language maps in this chapter show that Tamil is an important language in
A) Bangladesh and India.
B) Pakistan and India.
C) Iran and Pakistan.
D) India and Sri Lanka.
E) Pakistan and Sri Lanka.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
________ is to Canada as ________ is to the United States.
A) French; Spanish
B) English; French
C) French; English
D) Conflict over ethnicity; conflict over language
E) Alaska; Greenland
A) French; Spanish
B) English; French
C) French; English
D) Conflict over ethnicity; conflict over language
E) Alaska; Greenland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The large number of individual languages documented in Africa has resulted primarily from
A) thousands of years of isolation between cultural groups.
B) repeated invasions by outsiders.
C) introduction of many different languages by the colonial powers.
D) frequent migration by the different tribal groups.
E) colonial administration of native lands.
A) thousands of years of isolation between cultural groups.
B) repeated invasions by outsiders.
C) introduction of many different languages by the colonial powers.
D) frequent migration by the different tribal groups.
E) colonial administration of native lands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Official languages in Switzerland include all but which of the following?
A) Italian
B) Flemish
C) Romansh
D) French
E) German
A) Italian
B) Flemish
C) Romansh
D) French
E) German

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A pidgin language
A) has no native speakers.
B) is spread by folk culture.
C) stems from invasion.
D) cannot exist for more than a generation.
E) cannot exist without globalization.
A) has no native speakers.
B) is spread by folk culture.
C) stems from invasion.
D) cannot exist for more than a generation.
E) cannot exist without globalization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
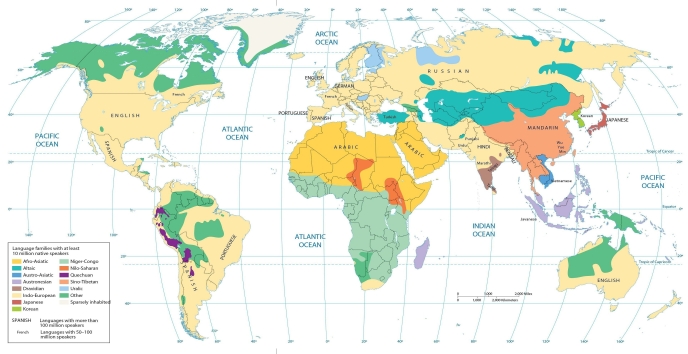
The language maps in this chapter show that Quechuan is widely spoken in at least ________ South American countries.
A) two
B) eight
C) ten
D) four
E) twelve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
When people who speak a given language migrate to a different location and become isolated from other members of their group
A) their language usually shows very little change even over a long period of time, despite the appearance of a small number of changes typical of different dialects.
B) they immediately develop a literary tradition.
C) isolation usually results in the differentiation of one language into dialects, followed eventually by two distinct languages.
D) they lose their linguistic abilities.
E) groups form multiple dialects.
A) their language usually shows very little change even over a long period of time, despite the appearance of a small number of changes typical of different dialects.
B) they immediately develop a literary tradition.
C) isolation usually results in the differentiation of one language into dialects, followed eventually by two distinct languages.
D) they lose their linguistic abilities.
E) groups form multiple dialects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



