Deck 22: Fungi : the Diversity of Life 2
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/49
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Fungi : the Diversity of Life 2
1
Where are the food materials digested by fungi located?
A) within their cells
B) within food vacuoles
C) externally
D) within their mitochondria
A) within their cells
B) within food vacuoles
C) externally
D) within their mitochondria
C
2
What is the best explanation of why we have identified only a small fraction of fungi species?
A) Most fungi species are unicellular and microscopic.
B) Fungi species lack chlorophyll and are transparent.
C) Fungi species have extremely short life spans and are seldom found alive.
D) Most fungi species grow underground and in inaccessible places.
A) Most fungi species are unicellular and microscopic.
B) Fungi species lack chlorophyll and are transparent.
C) Fungi species have extremely short life spans and are seldom found alive.
D) Most fungi species grow underground and in inaccessible places.
D
3
A more or less circular ring of mushrooms appears in your yard, apparently overnight. The circle is several yards in diameter. The most likely explanation for this circle of mushrooms is that:
A) the mushrooms are all part of the same organism, with mycelia radiating out from the location of a germinated spore.
B) a circle is nature's most perfect shape for asexual reproduction structures.
C) one mushroom in the circle reproduced sexually to make all the other mushrooms in the circle.
D) the fungus produces a toxin in the center to prevent too many mushrooms from being produced.
A) the mushrooms are all part of the same organism, with mycelia radiating out from the location of a germinated spore.
B) a circle is nature's most perfect shape for asexual reproduction structures.
C) one mushroom in the circle reproduced sexually to make all the other mushrooms in the circle.
D) the fungus produces a toxin in the center to prevent too many mushrooms from being produced.
A
4
Yeast are an example of:
A) photosynthetic fungi.
B) unicellular fungi.
C) fungi-like bacteria.
D) fungi with no cell walls.
A) photosynthetic fungi.
B) unicellular fungi.
C) fungi-like bacteria.
D) fungi with no cell walls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The cell walls of fungi contain:
A) chitin.
B) cellulose.
C) phospholipids.
D) DNA.
A) chitin.
B) cellulose.
C) phospholipids.
D) DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which statement about fungi and plant disease is most accurate?
A) Far more plant diseases are caused by fungi than bacteria.
B) About equal numbers of plant diseases are caused by fungi and bacteria.
C) Viruses cause more plant diseases than fungi.
D) Fungi rarely cause diseases.
A) Far more plant diseases are caused by fungi than bacteria.
B) About equal numbers of plant diseases are caused by fungi and bacteria.
C) Viruses cause more plant diseases than fungi.
D) Fungi rarely cause diseases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Fungi that reproduce by "budding" are:
A) prokaryotic.
B) yeasts.
C) autotrophic.
D) made of hyphae to form a reproductive mycelium.
A) prokaryotic.
B) yeasts.
C) autotrophic.
D) made of hyphae to form a reproductive mycelium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
All fungi are:
A) unicellular.
B) multicellular.
C) autotrophic.
D) heterotrophic.
A) unicellular.
B) multicellular.
C) autotrophic.
D) heterotrophic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Conspicuous shelf-like or saddle-like structures on the surface of a tree that indicate a fungus is growing within the tree are for:
A) showy display to attract a mate.
B) defense from predators.
C) reproduction and spore dispersal.
D) pollination.
A) showy display to attract a mate.
B) defense from predators.
C) reproduction and spore dispersal.
D) pollination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A branching web of hyphae is a:
A) spore.
B) mycelium.
C) root.
D) leaf.
A) spore.
B) mycelium.
C) root.
D) leaf.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A major reason why fungi can grow and sprout mushrooms so quickly is that:
A) mushrooms are essentially fluid-filled bags and almost entirely water.
B) porous connections between cells allow rapid movement of materials toward the growing tips of hyphae.
C) fungi cells divide more like bacteria than eukaryotic cells.
D) fungal spores contain large food reserves.
A) mushrooms are essentially fluid-filled bags and almost entirely water.
B) porous connections between cells allow rapid movement of materials toward the growing tips of hyphae.
C) fungi cells divide more like bacteria than eukaryotic cells.
D) fungal spores contain large food reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Fungi are more closely related to:
A) plants.
B) photosynthetic protists.
C) animals.
D) archaea.
A) plants.
B) photosynthetic protists.
C) animals.
D) archaea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Bacteria and fungi are important decomposers. However, which decomposition function is almost entirely the work of fungi?
A) decomposition of bacterial mass
B) digestion of metallic materials in landfills
C) large-animal decomposition
D) final breakdown of woody material
A) decomposition of bacterial mass
B) digestion of metallic materials in landfills
C) large-animal decomposition
D) final breakdown of woody material

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Fungi obtain food by:
A) engulfing food through phagocytosis and then digesting it within fungal cells.
B) producing antibiotics that internally destroy bacteria.
C) photosynthesis.
D) absorbing predigested material.
A) engulfing food through phagocytosis and then digesting it within fungal cells.
B) producing antibiotics that internally destroy bacteria.
C) photosynthesis.
D) absorbing predigested material.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When club fungi reproduce sexually, which of the following occurs?
A) Two spores merge into a seed that produces hyphae.
B) Two mushroom caps from different fungi exchange genes.
C) Sperm and egg cells fuse.
D) Nuclei from two different fungi fuse.
A) Two spores merge into a seed that produces hyphae.
B) Two mushroom caps from different fungi exchange genes.
C) Sperm and egg cells fuse.
D) Nuclei from two different fungi fuse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
For fungi that produce mushrooms, the majority of the organism is located:
A) above ground.
B) in fruiting bodies.
C) in spores.
D) underground.
A) above ground.
B) in fruiting bodies.
C) in spores.
D) underground.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is a fungal skin disease?
A) dry rot
B) ringworm
C) Dutch elm disease
D) skin rust
A) dry rot
B) ringworm
C) Dutch elm disease
D) skin rust

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A feature unique to some fungi is:
A) a lack of chlorophyll.
B) cells with three haploid nuclei.
C) dikaryotic cells.
D) diploid cells.
A) a lack of chlorophyll.
B) cells with three haploid nuclei.
C) dikaryotic cells.
D) diploid cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A fungus is examined microscopically and found to have a "lollypop-shaped" sporangium. This fungus must belong to:
A) chytrids.
B) basidiomycetes.
C) zygomycetes.
D) ascomycetes.
A) chytrids.
B) basidiomycetes.
C) zygomycetes.
D) ascomycetes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An important role of fungi in human society is that fungi are the source of:
A) the anti-inflammatory drug ibuprofen.
B) immune-system-suppressing drugs important for organ transplants.
C) nutrition for farm animals.
D) bio-fuels.
A) the anti-inflammatory drug ibuprofen.
B) immune-system-suppressing drugs important for organ transplants.
C) nutrition for farm animals.
D) bio-fuels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Most fungi are ________, or fixed in one spot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Although some fungi are multicellular, most are unicellular.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Mycorrhizae are a:
A) parasitic association between algae and fungi.
B) parasitic association between animals and fungi.
C) mutualistic association between plant roots and a fungus.
D) mutualistic association between algae and plant roots.
A) parasitic association between algae and fungi.
B) parasitic association between animals and fungi.
C) mutualistic association between plant roots and a fungus.
D) mutualistic association between algae and plant roots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Fungi obtain food exclusively by decomposing dead organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Yeasts are all members of the chytrids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In which group are smuts and rusts found?
A) basidiomycetes
B) ascomycetes
C) zygomycetes
D) chytrids
A) basidiomycetes
B) ascomycetes
C) zygomycetes
D) chytrids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
As part of your independent study of pond water samples, you notice one of the flagellated organisms latch on to a pollen grain and eventually release spores. You initially thought you were looking at a group exclusively made of protists, but upon further observation, you realize the organism you have been observing is classified with the fungi. In which group would you place this organism?
A) basidiomycetes
B) ascomycetes
C) zygomycetes
D) chytrids
A) basidiomycetes
B) ascomycetes
C) zygomycetes
D) chytrids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Some antibiotics are important products of fungi.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Dikaryotic cells of a fungus contain diploid nuclei.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Spores are reproductive cells of a fungus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Some fungi are photosynthetic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An organism that obtains its nutrition from dead organic matter is a:
A) parasite.
B) saprophyte.
C) neophyte.
D) phytoplankton.
A) parasite.
B) saprophyte.
C) neophyte.
D) phytoplankton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Nearly all fungi reproduce using mushrooms as their reproductive structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Most of the "body" of a fungus consists of slender, tube-like filaments called ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The cell walls of fungi contain chitin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The fungal group with the largest number of known species is:
A) zygomycetes.
B) ascomycetes.
C) basidiomycetes.
D) chytrids.
A) zygomycetes.
B) ascomycetes.
C) basidiomycetes.
D) chytrids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A mycelium is characteristic of yeasts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The two most closely related groups of fungi are the:
A) zygomycetes and chytrids.
B) basidiomycetes and ascomycetes.
C) basidiomycetes and zygomycetes.
D) ascomycetes and zygomycetes.
A) zygomycetes and chytrids.
B) basidiomycetes and ascomycetes.
C) basidiomycetes and zygomycetes.
D) ascomycetes and zygomycetes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Ecologically speaking, most soil fungi are to plant roots as:
A) viruses are to animals.
B) smut fungi are to corn.
C) mosquitoes are to mammals.
D) intestinal bacteria are to humans.
A) viruses are to animals.
B) smut fungi are to corn.
C) mosquitoes are to mammals.
D) intestinal bacteria are to humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Lichens are:
A) a mutualistic association of algae or photosynthetic bacteria and fungi.
B) algae-like fungi.
C) fungi that grow on the roots of plants.
D) fungi adapted for life in rocky soil.
A) a mutualistic association of algae or photosynthetic bacteria and fungi.
B) algae-like fungi.
C) fungi that grow on the roots of plants.
D) fungi adapted for life in rocky soil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
You are a biologist traveling with a group of explorers who encounter an ancient tomb. You find an amazingly well-preserved mummy and notice a little fungus growing on some bandages. When you examine your samples of the fungus back at the lab, you notice the fungus has small sac-like, spore-releasing structures. Based on the information you have so far, you will start the process of classifying this organism by placing it in this category of fungus: ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The cells released from reproductive structures such as mushrooms that can develop into a new organism without fusing with another cell are called ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The spore-releasing structure found in the zygomycetes is called a ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Discuss the ways in which fungi are both helpful and harmful to human society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Refer to the figure below, and then answer the following question(s). 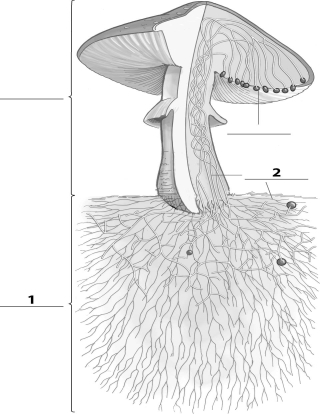
The missing label indicated by a "2" corresponds to:
A) a spore.
B) the fruiting body.
C) hyphae.
D) mycelium.

The missing label indicated by a "2" corresponds to:
A) a spore.
B) the fruiting body.
C) hyphae.
D) mycelium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Refer to the figure below, and then answer the following question(s). 
The missing label indicated by a "1" corresponds to:
A) a spore.
B) the fruiting body.
C) hyphae.
D) mycelium.

The missing label indicated by a "1" corresponds to:
A) a spore.
B) the fruiting body.
C) hyphae.
D) mycelium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Appraise and evaluate the following statement, and cite evidence from the chapter as appropriate: Despite having a closer "outward" appearance to plants in some ways, evidence support fungi as being far more closely related to animals than plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Each nucleus is haploid in dikaryotic cells in certain fungi. What does this mean regarding the chromosomes in each nucleus?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Fungi and plants have a long-term relationship in the history of life on Earth. Appraise the evidence in support of this concept.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



