Deck 7: Rome’s Three Heirs: 500–950
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Rome’s Three Heirs: 500–950
1
The Byzantine economy in the early Middle Ages was:
A) highly regulated, including wage and price controls.
B) subject to wild fluctuations due to currency debasement.
C) industrially underdeveloped.
D) renowned for its use of paper money.
E) depressed due to being cut off from trade with northern Europe.
A) highly regulated, including wage and price controls.
B) subject to wild fluctuations due to currency debasement.
C) industrially underdeveloped.
D) renowned for its use of paper money.
E) depressed due to being cut off from trade with northern Europe.
highly regulated, including wage and price controls.
2
The early Byzantine religion was known for its:
A) intense interest in matters of doctrine and orthodoxy.
B) beautifully decorated churches.
C) rejection of the emperor as the leader of the Church.
D) ability to enforce religious doctrine throughout the eastern empire.
E) doctrinal merging of elements from Christianity and Islam.
A) intense interest in matters of doctrine and orthodoxy.
B) beautifully decorated churches.
C) rejection of the emperor as the leader of the Church.
D) ability to enforce religious doctrine throughout the eastern empire.
E) doctrinal merging of elements from Christianity and Islam.
intense interest in matters of doctrine and orthodoxy.
3
The Byzantine church of Santa Sophia was influential in the history of architecture because it:
A) was constructed in a way that made light appear to come from directly above.
B) placed a massive dome on a building with a square shape.
C) was highly innovative in its external appearance and marble embellishment.
D) was the first Christian church converted into a mosque.
E) was the first building constructed completely from concrete.
A) was constructed in a way that made light appear to come from directly above.
B) placed a massive dome on a building with a square shape.
C) was highly innovative in its external appearance and marble embellishment.
D) was the first Christian church converted into a mosque.
E) was the first building constructed completely from concrete.
placed a massive dome on a building with a square shape.
4
In Byzantine schools,classical Greek literature was:
A) considered pagan and suspect, and so was read only with great reluctance.
B) the basis of the curriculum, with much study of the epics of Homer.
C) out of fashion, because people preferred to read the easier Greek of the Bible.
D) regarded as useless and impractical, but not offensive to Christian sensibilities.
E) not studied: Byzantium thought of itself as the heir of Rome and so read Latin classics.
A) considered pagan and suspect, and so was read only with great reluctance.
B) the basis of the curriculum, with much study of the epics of Homer.
C) out of fashion, because people preferred to read the easier Greek of the Bible.
D) regarded as useless and impractical, but not offensive to Christian sensibilities.
E) not studied: Byzantium thought of itself as the heir of Rome and so read Latin classics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Between 610 and 1071,the major security threats to the Byzantine empire came from:
A) Persia, then Egypt.
B) Persia, then the Umayyad and the Abbasids.
C) Persia, then the Turks.
D) Persia, then the Slavs.
E) the western Roman Empire.
A) Persia, then Egypt.
B) Persia, then the Umayyad and the Abbasids.
C) Persia, then the Turks.
D) Persia, then the Slavs.
E) the western Roman Empire.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the late sixth century C.E.,the economy of Arabia:
A) was in a state of crisis brought on by the wars between Byzantium and Persia.
B) became much more commercially sophisticated as a result of changing trade routes.
C) was still almost entirely made up of nomadic Bedouins.
D) was based on the production of figs, wool, and goats at desert oases.
E) was practically nonexistent due to Arabia's domination by the Byzantine empire.
A) was in a state of crisis brought on by the wars between Byzantium and Persia.
B) became much more commercially sophisticated as a result of changing trade routes.
C) was still almost entirely made up of nomadic Bedouins.
D) was based on the production of figs, wool, and goats at desert oases.
E) was practically nonexistent due to Arabia's domination by the Byzantine empire.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The Hijrah (Hegira)refers to the Prophet Muhammad's move from:
A) Medina to Mecca.
B) Mecca to Quadratic.
C) Medina to Quadratic.
D) Quadratic to Mecca.
E) Mecca to Medina.
A) Medina to Mecca.
B) Mecca to Quadratic.
C) Medina to Quadratic.
D) Quadratic to Mecca.
E) Mecca to Medina.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In their worship of Allah,Muslims worship:
A) the Prophet Muhammad.
B) the angel Gabriel.
C) the same deity worshiped by Christians and Jews.
D) a pantheon of gods.
E) the same deities worshiped by Hindus.
A) the Prophet Muhammad.
B) the angel Gabriel.
C) the same deity worshiped by Christians and Jews.
D) a pantheon of gods.
E) the same deities worshiped by Hindus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The seventh century C.E.was a turning point in the history of Western civilization because:
A) the entire Mediterranean world converted to Christianity.
B) the Greco-Roman world of antiquity divided into Byzantine, Islamic, and Latin Christian realms.
C) trade connections between North Africa and the Near East were ruptured by the Islamic conquests.
D) the entire Mediterranean world converted to Islam.
E) all of these
A) the entire Mediterranean world converted to Christianity.
B) the Greco-Roman world of antiquity divided into Byzantine, Islamic, and Latin Christian realms.
C) trade connections between North Africa and the Near East were ruptured by the Islamic conquests.
D) the entire Mediterranean world converted to Islam.
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The stability of Byzantine government was the product of:
A) a highly centralized palace government.
B) a predictable system of succession to the imperial throne.
C) an efficient bureaucracy.
D) regulated wages and prices.
E) all of these
A) a highly centralized palace government.
B) a predictable system of succession to the imperial throne.
C) an efficient bureaucracy.
D) regulated wages and prices.
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Although the Iconoclastic Controversy was eventually resolved,its lasting effects included:
A) the sale or handing over of Byzantine portraits to the Muslims.
B) the destruction of nearly all pre-eighth-century religious art in the Byzantine empire.
C) the adoption of conservative clothing styles by nobles and common people.
D) the gradual acceptance of religious diversity in the East.
E) the banning of all monastic orders within the Byzantine empire.
A) the sale or handing over of Byzantine portraits to the Muslims.
B) the destruction of nearly all pre-eighth-century religious art in the Byzantine empire.
C) the adoption of conservative clothing styles by nobles and common people.
D) the gradual acceptance of religious diversity in the East.
E) the banning of all monastic orders within the Byzantine empire.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The Qu' 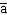 rn contains:
rn contains:
A) the revelations sent by God to Muhammad.
B) Christian teaching about Christ's divinity.
C) excerpts from the Hebrew Torah.
D) a detailed plan for the expansion of Islam after Muhammad's death.
E) the sole guide for behavior for converts to Islam.
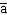 rn contains:
rn contains:A) the revelations sent by God to Muhammad.
B) Christian teaching about Christ's divinity.
C) excerpts from the Hebrew Torah.
D) a detailed plan for the expansion of Islam after Muhammad's death.
E) the sole guide for behavior for converts to Islam.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
It is difficult to date the beginning of Byzantine history with precision because:
A) Constantine never administered the Roman Empire from Constantinople.
B) Greek was the only language ever used by Roman emperors in Constantinople.
C) the Byzantine empire was the uninterrupted successor of the Roman Empire.
D) Justinian resisted new forms of thought and art throughout his life.
E) it began during the so-called Dark Ages during which very few records were kept.
A) Constantine never administered the Roman Empire from Constantinople.
B) Greek was the only language ever used by Roman emperors in Constantinople.
C) the Byzantine empire was the uninterrupted successor of the Roman Empire.
D) Justinian resisted new forms of thought and art throughout his life.
E) it began during the so-called Dark Ages during which very few records were kept.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The word Islam meAnswer:
A) pilgrimage.
B) migration.
C) submission.
D) recitation.
E) prayer.
A) pilgrimage.
B) migration.
C) submission.
D) recitation.
E) prayer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Why did Justinian's reconquest of the western Roman Empire fail?
A) Justinian codified Roman law, which made a permanent merger impossible.
B) Western Christians no longer felt kinship with eastern Christians, and they fought against Justinian from within.
C) The costs associated with conquering and defending the vast western empire were too great.
D) Constantinople fell to Persian invaders and brought an end to the eastern Roman Empire.
E) Justinian was forced to withdraw his army to meet the greater Islamic threat from the south.
A) Justinian codified Roman law, which made a permanent merger impossible.
B) Western Christians no longer felt kinship with eastern Christians, and they fought against Justinian from within.
C) The costs associated with conquering and defending the vast western empire were too great.
D) Constantinople fell to Persian invaders and brought an end to the eastern Roman Empire.
E) Justinian was forced to withdraw his army to meet the greater Islamic threat from the south.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Within Byzantium,social mobility was generally dependent on:
A) the tolerance of the general society.
B) geographical mobility.
C) the wealth of the individual.
D) one's status.
E) one's religion.
A) the tolerance of the general society.
B) geographical mobility.
C) the wealth of the individual.
D) one's status.
E) one's religion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Why did Justinian try to reconquer the western Roman Empire?
A) because the Persians had been defeated in the East, so he could safely launch military expeditions to the West
B) because his empire required continuing conquests in order to prosper
C) because he sought to revive and reconstruct wholly the old empire
D) because he needed to keep his army as far away from his capital as possible
E) because he believed that he should be the head of a unified Christian Church
A) because the Persians had been defeated in the East, so he could safely launch military expeditions to the West
B) because his empire required continuing conquests in order to prosper
C) because he sought to revive and reconstruct wholly the old empire
D) because he needed to keep his army as far away from his capital as possible
E) because he believed that he should be the head of a unified Christian Church

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Women from wealthy Byzantine families:
A) did not receive classical educations, since they were destined for domestic life.
B) could read but were not allowed to write history, novels, or poetry.
C) were generally educated at home by tutors, and some became literary figures of note.
D) were encouraged by parents to become actresses and singers like the Empress Theodora.
E) were educated in the public schools alongside the men.
A) did not receive classical educations, since they were destined for domestic life.
B) could read but were not allowed to write history, novels, or poetry.
C) were generally educated at home by tutors, and some became literary figures of note.
D) were encouraged by parents to become actresses and singers like the Empress Theodora.
E) were educated in the public schools alongside the men.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Chapter 7 dates the beginning of Byzantine history with the accession of:
A) Diocletian in 284.
B) Constantine in 312.
C) Julian in 360.
D) Justinian in 527.
E) Heraclius in 610.
A) Diocletian in 284.
B) Constantine in 312.
C) Julian in 360.
D) Justinian in 527.
E) Heraclius in 610.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The Iconoclastic Controversy of the eighth century C.E.was about:
A) the biblical laws forbidding "the work of Satan" on Sundays.
B) Emperor Leo's decision to stop wearing the toga, the symbol of imperial manhood.
C) the impossibility of smashing all the pagan idols, so some were allowed to remain.
D) the use or prohibition of images in church, where people might worship the objects.
E) prohibition of the display of the crucifix in Byzantine churches.
A) the biblical laws forbidding "the work of Satan" on Sundays.
B) Emperor Leo's decision to stop wearing the toga, the symbol of imperial manhood.
C) the impossibility of smashing all the pagan idols, so some were allowed to remain.
D) the use or prohibition of images in church, where people might worship the objects.
E) prohibition of the display of the crucifix in Byzantine churches.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Opportunity for advancement in Islamic cultures depended on:
A) the social class into which one was born.
B) the sect of Islam that one professed.
C) one's ability and one's talent.
D) the level of bribes one was able to offer.
E) whom one knew within the bureaucracy.
A) the social class into which one was born.
B) the sect of Islam that one professed.
C) one's ability and one's talent.
D) the level of bribes one was able to offer.
E) whom one knew within the bureaucracy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The Merovingian dynasty in France traced its origin back to Clovis's legendary grandfather,Merovech,who was:
A) the last commander of the Roman legions in the West.
B) a sea monster.
C) also believed to be the grandfather of England's King Arthur.
D) a Benedictine monk who converted the Franks.
E) a Viking who had settled in northern France and conquered the Lombards.
A) the last commander of the Roman legions in the West.
B) a sea monster.
C) also believed to be the grandfather of England's King Arthur.
D) a Benedictine monk who converted the Franks.
E) a Viking who had settled in northern France and conquered the Lombards.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The key figure in creating an alliance between the Carolingian family,the papacy,and Benedictine monasticism was:
A) Clovis.
B) Saint Martin of Tours.
C) Charlemagne.
D) Charles Martel.
E) Saint Boniface.
A) Clovis.
B) Saint Martin of Tours.
C) Charlemagne.
D) Charles Martel.
E) Saint Boniface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The Arabian Nights describes the extravagant behavior of the Abbasid caliph:
A) Ali.
B) Utahan.
C) Al-Hakems II.
D) Harun al-Rashid.
E) Abu-Bakr.
A) Ali.
B) Utahan.
C) Al-Hakems II.
D) Harun al-Rashid.
E) Abu-Bakr.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Within Islam,social mobility was encouraged because of:
A) a decree by the Umayyad dynasty outlawing discrimination of all kinds.
B) the teachings of the twelfth imam that everyone should be tolerant of everyone else.
C) the origins of the faith where no one could take advantage of anyone else.
D) the teachings of Muhammad, which stressed the equality of all Muslim men.
E) a decree of the Abbasid dynasty outlawing discrimination of all kinds.
A) a decree by the Umayyad dynasty outlawing discrimination of all kinds.
B) the teachings of the twelfth imam that everyone should be tolerant of everyone else.
C) the origins of the faith where no one could take advantage of anyone else.
D) the teachings of Muhammad, which stressed the equality of all Muslim men.
E) a decree of the Abbasid dynasty outlawing discrimination of all kinds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In general,the Christian monasticism of the fourth,fifth,and sixth centuries was a response to:
A) unprecedented cooperation among the first popes and Roman emperors.
B) the high level of religious devotion found in the cities of the late Roman Empire.
C) the increasing worldliness of the church and a hunger to transform lives in accordance with the will of God.
D) religious teachings that encouraged extraordinary feats of self-denial and self-abasement.
E) the devastation caused by the collapse of the Roman Empire and the desire to escape from the prevailing turmoil.
A) unprecedented cooperation among the first popes and Roman emperors.
B) the high level of religious devotion found in the cities of the late Roman Empire.
C) the increasing worldliness of the church and a hunger to transform lives in accordance with the will of God.
D) religious teachings that encouraged extraordinary feats of self-denial and self-abasement.
E) the devastation caused by the collapse of the Roman Empire and the desire to escape from the prevailing turmoil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The instability faced in the West by the mid-seventh century may be attributed to:
A) Justinian's failed efforts to reconquer the western empire.
B) excessive taxes on agricultural lands.
C) Muslim raiders who disrupted trade routes.
D) the increasing inability of aristocrats to give lavish gifts.
E) all of these
A) Justinian's failed efforts to reconquer the western empire.
B) excessive taxes on agricultural lands.
C) Muslim raiders who disrupted trade routes.
D) the increasing inability of aristocrats to give lavish gifts.
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In comparison to the Umayyad,the Abbasid caliphate:
A) was more like a Byzantine successor state.
B) adopted more of the style of Persian royal absolutism.
C) moved its capital from Baghdad to Damascus.
D) modeled itself on the imperial court of Rome.
E) all of these
A) was more like a Byzantine successor state.
B) adopted more of the style of Persian royal absolutism.
C) moved its capital from Baghdad to Damascus.
D) modeled itself on the imperial court of Rome.
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The Shiite claim to legitimacy rests on the direct connection to Muhammad through his daughter:
A) Aisha.
B) Yasmina.
C) Fatimah.
D) Khadijah.
E) Sawda.
A) Aisha.
B) Yasmina.
C) Fatimah.
D) Khadijah.
E) Sawda.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
As a Christian king responsible for ruling a Christian society,Charlemagne:
A) was careful to observe the distinctions between religious and political authority established by Saint Augustine of Hippo.
B) placed the Frankish church under the control of the pope, while he ruled the kingdom politically.
C) took responsibility for reforming the religious life of his kingdom just as he reformed its government.
D) became a monk at the end of his life, thus ensuring his own salvation.
E) established his empire as a theocratic state ruled by the laws set forth in the Bible.
A) was careful to observe the distinctions between religious and political authority established by Saint Augustine of Hippo.
B) placed the Frankish church under the control of the pope, while he ruled the kingdom politically.
C) took responsibility for reforming the religious life of his kingdom just as he reformed its government.
D) became a monk at the end of his life, thus ensuring his own salvation.
E) established his empire as a theocratic state ruled by the laws set forth in the Bible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The Shiite party arose among Muslims because:
A) nineteenth-century disputes between Muslims in Iran created a schism.
B) of a dispute about the proper succession of caliphs in seventh-century Arabia.
C) the Umayyad dynasty wanted to expand westward.
D) the Abbasid dynasty wanted to expand eastward.
E) of a dispute in the eighth century regarding the proper interpretation of the Qu'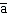 rn.
rn.
A) nineteenth-century disputes between Muslims in Iran created a schism.
B) of a dispute about the proper succession of caliphs in seventh-century Arabia.
C) the Umayyad dynasty wanted to expand westward.
D) the Abbasid dynasty wanted to expand eastward.
E) of a dispute in the eighth century regarding the proper interpretation of the Qu'
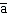 rn.
rn.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Islam spread so quickly in the seventh and eighth centuries because:
A) Muslims insisted that all conquered peoples convert to Islam.
B) there were no Christians in the first lands that Muslims conquered.
C) the Pact of Unmark allowed for the total destruction of subject cities.
D) the Byzantines and Persians had become exhausted by their long wars against each other.
E) the subject peoples in conquered land welcomed the Muslims as liberators.
A) Muslims insisted that all conquered peoples convert to Islam.
B) there were no Christians in the first lands that Muslims conquered.
C) the Pact of Unmark allowed for the total destruction of subject cities.
D) the Byzantines and Persians had become exhausted by their long wars against each other.
E) the subject peoples in conquered land welcomed the Muslims as liberators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The gradual conversion of the early medieval European countryside to Christianity was carried out primarily by:
A) kings, whose armies ordered non-Christians to convert or leave Europe.
B) lay missionaries commissioned by the pope.
C) Frankish bishops seeking to enlarge their dioceses.
D) monks who founded new monasteries in frontier areas.
E) nuns working with the peasantry.
A) kings, whose armies ordered non-Christians to convert or leave Europe.
B) lay missionaries commissioned by the pope.
C) Frankish bishops seeking to enlarge their dioceses.
D) monks who founded new monasteries in frontier areas.
E) nuns working with the peasantry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Why were so many convents (monastic houses for women)founded during the seventh century C.E.?
A) Convents met a variety of social and spiritual needs for aristocratic families.
B) Lower-class women flocked to convents as an improvement on the drudgery of their lives.
C) Nuns were the only women allowed to become priests.
D) Convents were a way for the families that founded them to make money.
E) all of these
A) Convents met a variety of social and spiritual needs for aristocratic families.
B) Lower-class women flocked to convents as an improvement on the drudgery of their lives.
C) Nuns were the only women allowed to become priests.
D) Convents were a way for the families that founded them to make money.
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Sexual relations within upper-class Muslim society around the year 1000 differed from classical Greek and Roman patterns because:
A) Muslims abhorred homosexuality, whereas Greeks and Romans did not.
B) Muslim men had sexual access to slaves and concubines, whereas Greeks and Romans did not.
C) women were highly valued in Muslim society, whereas they were not in Greece or Rome.
D) Muslim men were permitted to have more than one wife, whereas Greek and Roman men were not.
E) all of these
A) Muslims abhorred homosexuality, whereas Greeks and Romans did not.
B) Muslim men had sexual access to slaves and concubines, whereas Greeks and Romans did not.
C) women were highly valued in Muslim society, whereas they were not in Greece or Rome.
D) Muslim men were permitted to have more than one wife, whereas Greek and Roman men were not.
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
As a theologian,Pope Gregory I is regarded as the successor to:
A) Francis of Assisi.
B) John Chrysostom.
C) Arius of Alexandria.
D) Athanasius.
E) Augustine.
A) Francis of Assisi.
B) John Chrysostom.
C) Arius of Alexandria.
D) Athanasius.
E) Augustine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Compared to medieval Europe in the eleventh and twelfth centuries,the Islamic world was:
A) less diverse ethnically.
B) largely united politically.
C) less advanced in technological sophistication, science, and philosophy.
D) more advanced in technological sophistication, science, and philosophy.
E) comparable in terms of economics, politics, and technology.
A) less diverse ethnically.
B) largely united politically.
C) less advanced in technological sophistication, science, and philosophy.
D) more advanced in technological sophistication, science, and philosophy.
E) comparable in terms of economics, politics, and technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In Arabic,caliph meAnswer:
A) king.
B) deputy.
C) prince.
D) general.
E) imam.
A) king.
B) deputy.
C) prince.
D) general.
E) imam.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Historians looking for a rupture in western European attitudes toward ancient Roman culture and traditions will likely find it between the lives of:
A) Charlemagne and the Burgundian kings of Germany.
B) Gregory of Tours and Charlemagne.
C) Constantine and Justinian.
D) Cicero and Diocletian.
E) Gregory of Tours and Justinian.
A) Charlemagne and the Burgundian kings of Germany.
B) Gregory of Tours and Charlemagne.
C) Constantine and Justinian.
D) Cicero and Diocletian.
E) Gregory of Tours and Justinian.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Charlemagne and Harun al-Rashid formed an alliance partially because of their shared enemy,the:
A) Umayyad.
B) Persians.
C) Byzantines.
D) Sunnis.
E) Abbasid.
A) Umayyad.
B) Persians.
C) Byzantines.
D) Sunnis.
E) Abbasid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which was the most significant event in creating Byzantine hostility toward the Latin Christian world?
A) the coronation of Charlemagne as Roman emperor on Christmas Day, 800
B) the First Crusade
C) the Iconoclastic Controversy
D) the Fourth Crusade in 1204
E) the execution of the Byzantine ambassador to Rome in 816
A) the coronation of Charlemagne as Roman emperor on Christmas Day, 800
B) the First Crusade
C) the Iconoclastic Controversy
D) the Fourth Crusade in 1204
E) the execution of the Byzantine ambassador to Rome in 816

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The Abbasid empire effectively came to an end in:
A) 1258, when the invading Mongol armies captured the Abbasid capital of Baghdad.
B) 733, when the Abbasid army was defeated by Charles Martel at Tours.
C) 1066, when the dominant Shiites defeated the Sunnis at Damascus.
D) 930, when a Shiite army attacked and captured Mecca.
E) 1186, when Philip of France and Richard of England captured Jerusalem.
A) 1258, when the invading Mongol armies captured the Abbasid capital of Baghdad.
B) 733, when the Abbasid army was defeated by Charles Martel at Tours.
C) 1066, when the dominant Shiites defeated the Sunnis at Damascus.
D) 930, when a Shiite army attacked and captured Mecca.
E) 1186, when Philip of France and Richard of England captured Jerusalem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Byzantine culture was the means by which the heritage of Western civilization was preserved for the Europe where Greek had become very rare.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
After 750,the Umayyad dynasty abandoned Spain and focused its rule in Damascus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Most Arabs were city dwellers and mainly merchants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Why did the Carolingian empire collapse during the ninth century?
A) because the structural limits of its expansion had been reached
B) because of the division of the empire among all the legitimate heirs of Louis
C) because of Viking raids
D) because the loyalty of vassals toward Charlemagne collapsed after his death
E) all of these
A) because the structural limits of its expansion had been reached
B) because of the division of the empire among all the legitimate heirs of Louis
C) because of Viking raids
D) because the loyalty of vassals toward Charlemagne collapsed after his death
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Islam created its own culture and actively destroyed the artifacts of those civilizations that came before them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Spain was largely abandoned by Islam as a cultural backwater.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The Vikings are generally regarded as being a destructive force in European history:
A) but such a view may not be correct in light of the principalities they established across northern Europe from Ireland to Russia.
B) as evidenced by the raids they staged on virtually every population center in Europe from London to Paris to Rome itself.
C) because of the destruction caused to a great many monasteries throughout Europe and the accompanying loss of the libraries in those monasteries.
D) but this has been exaggerated since they stayed mostly in Scandinavia with only a few raids into England and northern France, destructive though those were.
E) which is true, but they have an undeservedly bad reputation when compared with the Magyars who conducted raids into western and southern Europe.
A) but such a view may not be correct in light of the principalities they established across northern Europe from Ireland to Russia.
B) as evidenced by the raids they staged on virtually every population center in Europe from London to Paris to Rome itself.
C) because of the destruction caused to a great many monasteries throughout Europe and the accompanying loss of the libraries in those monasteries.
D) but this has been exaggerated since they stayed mostly in Scandinavia with only a few raids into England and northern France, destructive though those were.
E) which is true, but they have an undeservedly bad reputation when compared with the Magyars who conducted raids into western and southern Europe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The literary and cultural value of Homer was as great to the Byzantines as the Bible was to the West.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The economic base of the Abbasid caliphate lay in:
A) the Tigris-Euphrates basin of Mesopotamia.
B) the Nile Delta.
C) Syria and Lebanon.
D) Anatolia, in modern-day Turkey.
E) its capital, Constantinople.
A) the Tigris-Euphrates basin of Mesopotamia.
B) the Nile Delta.
C) Syria and Lebanon.
D) Anatolia, in modern-day Turkey.
E) its capital, Constantinople.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Underlying the Carolingian Renaissance was the basic conviction that:
A) classical learning was the foundation on which Christian wisdom rested.
B) the Bible could be best appreciated if it were translated into robust French and German idioms.
C) original Latin poetry and epic literature were the highest form of art.
D) proper Christian doctrine should be widely disseminated and heretical beliefs should be strictly punished.
E) to be better Christians, everyone should pray and devote their lives to the Church.
A) classical learning was the foundation on which Christian wisdom rested.
B) the Bible could be best appreciated if it were translated into robust French and German idioms.
C) original Latin poetry and epic literature were the highest form of art.
D) proper Christian doctrine should be widely disseminated and heretical beliefs should be strictly punished.
E) to be better Christians, everyone should pray and devote their lives to the Church.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
One factor in the success of cities in Arabia was the protracted wars between the Byzantine empire and Persia,which made the Arabian trade routes safer than the northern ones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The overall unity of the Muslim world disintegrated during the tenth and eleventh centuries because of:
A) a special tax levied on Jews and Christians.
B) failures among the Umayyad rulers of Spain.
C) repeated attacks by the Mughal empire of India.
D) economic problems and a stagnating intellectual life.
E) ethnic tensions among Arabs, Turks, Berbers, and Persians.
A) a special tax levied on Jews and Christians.
B) failures among the Umayyad rulers of Spain.
C) repeated attacks by the Mughal empire of India.
D) economic problems and a stagnating intellectual life.
E) ethnic tensions among Arabs, Turks, Berbers, and Persians.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The division between Islam and Christianity was not an impenetrable barrier as communication and gifts between the Abbasid and Carolingian empires illustrates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Islam is a religion without sacraments or priests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The Carolingian empire depended in large measure on ___ for its maintenance.
A) the sworn loyalty of Charlemagne's counts
B) a continuous supply of silver from the Abbasids
C) the development of a new educational system
D) the support of the monasteries within the kingdom
E) the regular use of written records
A) the sworn loyalty of Charlemagne's counts
B) a continuous supply of silver from the Abbasids
C) the development of a new educational system
D) the support of the monasteries within the kingdom
E) the regular use of written records

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
One of the few rulers to successfully defend their lands against the Vikings was:
A) Alfred.
B) Arthur.
C) Bede.
D) Charles.
E) Thomas.
A) Alfred.
B) Arthur.
C) Bede.
D) Charles.
E) Thomas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The Vikings settled the area in Europe known today as:
A) the Netherlands.
B) Normandy.
C) East Anglia.
D) Brittany.
E) Burgundy.
A) the Netherlands.
B) Normandy.
C) East Anglia.
D) Brittany.
E) Burgundy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Sufism is a mystical sect of Judaism whose members stressed contemplation and ecstasy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Gregory VII was the first pope to assert his autonomy from the Byzantine emperors and the Orthodox Church.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
How can Muhammad be described as both a prophet and a statesman?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What was the legacy of the Carolingians?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
By the seventh century,western Europe had become a more fluid economy in which luxury goods and coinage circulated,albeit to differing degrees,among all levels of society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What was the impact of Justinian's law code on the Middle Ages?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What factors allowed the Byzantine empire to survive into the Middle Ages?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What innovations characterize the Carolingian Renaissance?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What accounts for the rapid growth of Islam?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
How did monasticism aid the growth and prosperity of secular empires?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
To what extent did the Carolingians owe their success to the Merovingians?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In the eyes of early medieval Europe,law and Latin Christianity were the pinnacles of Roman cultural achievement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Charles Martel is regarded as one of the founders of the Frankish Kingdom due to his defeat of a Muslim force near Paris.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Pope Gregory was not only a reformer of the church and theologian,but was the first pope to break free of Byzantine control and establish an autonomous,Western-oriented Latin church.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What were the causes of the decline of the Abbasid dynasty?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Explain how Justinian's conquest of the Mediterranean was both a success and a failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



