Deck 18: Income Inequality and Poverty
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Income Inequality and Poverty
1
If permanent income were utilized to measure the income distribution instead of current annual income, the income distribution would appear to be wider.
False
2
Figure 1 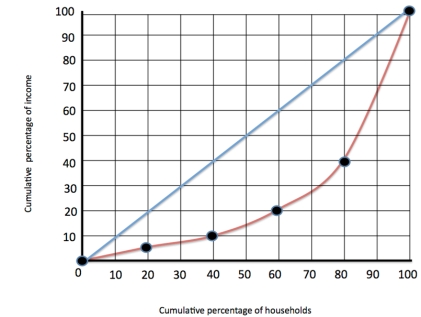 Refer to figure 1. The top 20% of the population have what % of the income
Refer to figure 1. The top 20% of the population have what % of the income
A) 5%
B) 40%
C) 60%
D) 50%
 Refer to figure 1. The top 20% of the population have what % of the income
Refer to figure 1. The top 20% of the population have what % of the incomeA) 5%
B) 40%
C) 60%
D) 50%
C
3
The distribution of income in the UK became more equal between 1979 and 2000.
False
4
Figure 2 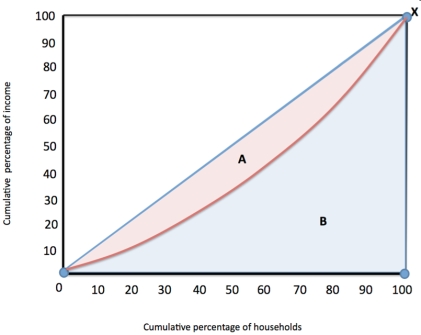 Refer to figure 2. The Gini coefficient is calculated by
Refer to figure 2. The Gini coefficient is calculated by
A) Taking area B from area A
B) Dividing area B by area A
C) Dividing area A + B by area A
D) Dividing A by B
 Refer to figure 2. The Gini coefficient is calculated by
Refer to figure 2. The Gini coefficient is calculated byA) Taking area B from area A
B) Dividing area B by area A
C) Dividing area A + B by area A
D) Dividing A by B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
There is an easy and perfectly acceptable solution to the problem of poverty traps: recipients' benefit income should be reduced more gradually as they increase their earnings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
It is more efficient for the government to provide in-kind transfers instead of cash payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Figure 1 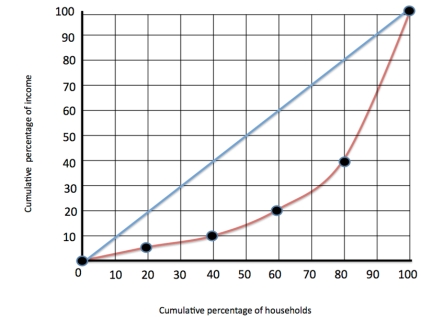 Refer to figure 1. The red line refers to
Refer to figure 1. The red line refers to
A) The Gini coefficient
B) The Lorenz curve
C) The line of perfect inequality
D) The line of perfect equality
 Refer to figure 1. The red line refers to
Refer to figure 1. The red line refers toA) The Gini coefficient
B) The Lorenz curve
C) The line of perfect inequality
D) The line of perfect equality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A Gini coefficient of .7 suggests a country has a very unequal distribution of income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When households are divided into deciles, each group covers what percentage of the population?
A) 5%
B) 10%
C) 15%
D) 20%
A) 5%
B) 10%
C) 15%
D) 20%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Utilitarianism is based on the assumption of diminishing marginal product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The political philosophies of utilitarianism and liberalism both suggest that income should be equalized across the population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Libertarians are more concerned with equal opportunity than with equal outcome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Figure 1 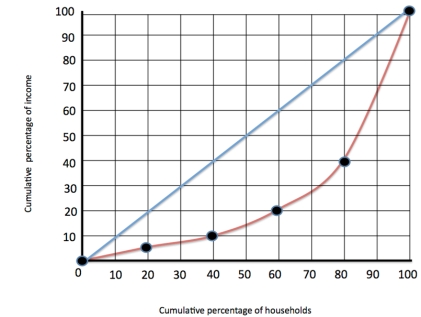 Refer to figure 1. The middle quintile group earn
Refer to figure 1. The middle quintile group earn
A) 10%
B) 20%
C) 30%
D) 7%
 Refer to figure 1. The middle quintile group earn
Refer to figure 1. The middle quintile group earnA) 10%
B) 20%
C) 30%
D) 7%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The UK Gini coefficient suggests that
A) the UK's inequality levels have change in the last 30 years
B) the UK's income distribution has become more equable.
C) the UK's income distribution has become more unequal.
D) the UK has a very equal distribution of income.
A) the UK's inequality levels have change in the last 30 years
B) the UK's income distribution has become more equable.
C) the UK's income distribution has become more unequal.
D) the UK has a very equal distribution of income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Figure 2 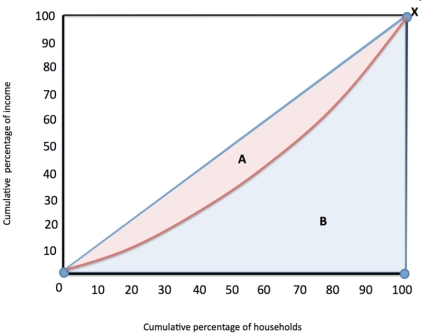 Refer to figure 2. The Gini coefficient is
Refer to figure 2. The Gini coefficient is
A) zero
B) one
C) Less than 0.3 but higher than 0
D) Over 0.7 but less than 1
 Refer to figure 2. The Gini coefficient is
Refer to figure 2. The Gini coefficient isA) zero
B) one
C) Less than 0.3 but higher than 0
D) Over 0.7 but less than 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Because of in-kind transfers to the poor and because people's incomes vary from year to year and across their lifetimes, standard measures of income distribution exaggerate the degree of inequality in standards of living.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Permanent income is
A) Social Security income of the elderly and disabled.
B) the maximum earned during a worker's lifetime.
C) wages fixed by a union or other labour contract.
D) equal to the minimum wage.
E) a person's normal, or average, income.
A) Social Security income of the elderly and disabled.
B) the maximum earned during a worker's lifetime.
C) wages fixed by a union or other labour contract.
D) equal to the minimum wage.
E) a person's normal, or average, income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Figure 1 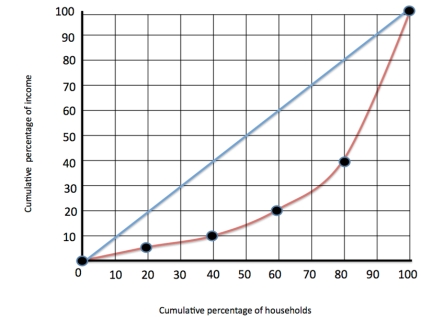 Refer to figure 1. The blue 45 degree line refers to
Refer to figure 1. The blue 45 degree line refers to
A) The Gini coefficient
B) The Lorenz curve
C) The line of perfect inequality
D) The line of perfect equality
 Refer to figure 1. The blue 45 degree line refers to
Refer to figure 1. The blue 45 degree line refers toA) The Gini coefficient
B) The Lorenz curve
C) The line of perfect inequality
D) The line of perfect equality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
John Rawls argues that economic justice would result if society chose a set of rules for the redistribution of income from behind a "veil of ignorance" and he argues that the set of rules would be the maximin criterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Because in-kind transfers are not accounted for in standard measures of income distribution, the standard measures of income distribution
A) accurately represent the true inequality of living standards.
B) understate the inequality of living standards.
C) exaggerate the inequality of living standards.
D) could exaggerate or understate the inequality of living standards depending on whether the transfers are goods or services.
A) accurately represent the true inequality of living standards.
B) understate the inequality of living standards.
C) exaggerate the inequality of living standards.
D) could exaggerate or understate the inequality of living standards depending on whether the transfers are goods or services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If people can borrow and lend to perfectly smooth out their lifetime living standards, then
A) transitory income is a good measure of the distribution of living standards.
B) none of these answers.
C) permanent income is a good measure of the distribution of living standards.
D) life-cycle income is a good measure of the distribution of living standards.
E) current annual income is a good measure of the distribution of living standards.
A) transitory income is a good measure of the distribution of living standards.
B) none of these answers.
C) permanent income is a good measure of the distribution of living standards.
D) life-cycle income is a good measure of the distribution of living standards.
E) current annual income is a good measure of the distribution of living standards.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Current anti-poverty programs discourage work because
A) benefits are reduced at such a high rate when recipients earn more income that there is little or no incentive to work once one is receiving benefits.
B) in order to be eligible for benefits, a recipient cannot have a job.
C) they make recipients more comfortable than most middle-class citizens.
D) anti-poverty programs attract naturally lazy people to begin with.
A) benefits are reduced at such a high rate when recipients earn more income that there is little or no incentive to work once one is receiving benefits.
B) in order to be eligible for benefits, a recipient cannot have a job.
C) they make recipients more comfortable than most middle-class citizens.
D) anti-poverty programs attract naturally lazy people to begin with.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Someone said to live in relative poverty is
A) poor and single, with no relatives.
B) poor relative to their neighbours.
C) unable to access the standard of living considered to be the minimum acceptable standard in their society.
D) unable to access the necessities of life: food, shelter and clothing.
A) poor and single, with no relatives.
B) poor relative to their neighbours.
C) unable to access the standard of living considered to be the minimum acceptable standard in their society.
D) unable to access the necessities of life: food, shelter and clothing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
John Rawls's suggestion that policy should be directed at maximizing the welfare of the least well off person in society is derived from
A) the idea that people should consider policy as if behind a veil of ignorance as to what their circumstances might be in society, and the idea that as long as there is no theft then there is no need for governments to intervene and redistribute income.
B) the idea that people should consider policy as if behind a veil of ignorance as to what their circumstances might be in society, and the idea that people will then be particularly concerned about the possibility that they might find themselves at the bottom of the income distribution.
C) the idea that people should consider policy as if behind a veil of ignorance as to what their circumstances might be in society, and the ignorant people should be looked after.
D) the idea that everyone in society should have an equal income.
A) the idea that people should consider policy as if behind a veil of ignorance as to what their circumstances might be in society, and the idea that as long as there is no theft then there is no need for governments to intervene and redistribute income.
B) the idea that people should consider policy as if behind a veil of ignorance as to what their circumstances might be in society, and the idea that people will then be particularly concerned about the possibility that they might find themselves at the bottom of the income distribution.
C) the idea that people should consider policy as if behind a veil of ignorance as to what their circumstances might be in society, and the ignorant people should be looked after.
D) the idea that everyone in society should have an equal income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In-kind transfers are:
A) cash payments made to poor people so that they can buy medical treatment.
B) cash payments made to poor people in excess of what they need.
C) transfers to the poor given in the form of goods and services rather than cash.
D) transfers to the poor given by charities rather than the government.
A) cash payments made to poor people so that they can buy medical treatment.
B) cash payments made to poor people in excess of what they need.
C) transfers to the poor given in the form of goods and services rather than cash.
D) transfers to the poor given by charities rather than the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The philosopher John Rawls argued that
A) people would choose income equality if they had to determine an economic distribution system before knowing their place in it.
B) people would choose income inequality to allow the maximum use of their individual talents.
C) government has a role to ensure income equality to prevent social unrest.
D) people would choose income equality because it is morally right.
A) people would choose income equality if they had to determine an economic distribution system before knowing their place in it.
B) people would choose income inequality to allow the maximum use of their individual talents.
C) government has a role to ensure income equality to prevent social unrest.
D) people would choose income equality because it is morally right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The distribution of income in a country is:
According to the table, what percentage of households have income levels above €60,000?
A) 80 per cent
B) 60 per cent
C) 50 per cent
D) 40 per cent
According to the table, what percentage of households have income levels above €60,000?
A) 80 per cent
B) 60 per cent
C) 50 per cent
D) 40 per cent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A libertarian would be likely to argue that
A) equality of outcomes in a society does not matter; it's the fairness of the processes that lead to those outcomes that matters.
B) equality of opportunities is more important than equality of incomes.
C) the government should not redistribute resources from some individuals to others.
D) all of the above.
A) equality of outcomes in a society does not matter; it's the fairness of the processes that lead to those outcomes that matters.
B) equality of opportunities is more important than equality of incomes.
C) the government should not redistribute resources from some individuals to others.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Because people's incomes vary over the life cycle and because there are transitory shocks to people's incomes, the standard measures of income distribution
A) exaggerate the inequality of living standards.
B) could exaggerate or understate the inequality of living standards depending on whether the transitory shocks are positive or negative.
C) understate the inequality of living standards.
D) accurately represent the true inequality of living standards.
A) exaggerate the inequality of living standards.
B) could exaggerate or understate the inequality of living standards depending on whether the transitory shocks are positive or negative.
C) understate the inequality of living standards.
D) accurately represent the true inequality of living standards.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An increase in the minimum wage will cause a relatively large increase in unemployment among
A) unskilled workers if the demand for labour is relatively inelastic.
B) unskilled workers if the demand for labour is relatively elastic.
C) skilled workers if the demand for labour is relatively elastic.
D) skilled workers if the demand for labour is relatively inelastic.
A) unskilled workers if the demand for labour is relatively inelastic.
B) unskilled workers if the demand for labour is relatively elastic.
C) skilled workers if the demand for labour is relatively elastic.
D) skilled workers if the demand for labour is relatively inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The maximin criterion suggested by John Rawls's theory of justice means that the government should aim to
A) maximize the total utility of society.
B) maximize the well-being of the worst-off person in society.
C) minimize the difference between the rich and poor.
D) maximize the economic freedom of individuals by minimizing government interference in private decision making.
E) minimize the well-being of the best-off person in society.
A) maximize the total utility of society.
B) maximize the well-being of the worst-off person in society.
C) minimize the difference between the rich and poor.
D) maximize the economic freedom of individuals by minimizing government interference in private decision making.
E) minimize the well-being of the best-off person in society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Raising the welfare of the worst-off person in society is an important goal of which political philosophy?
A) utilitarianism
B) liberalism
C) libertarianism
D) secularism
A) utilitarianism
B) liberalism
C) libertarianism
D) secularism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Marie earns more than Seamus and she came by her income fairly and honestly. Which of the following political philosophies would argue against the redistribution of income from Marie to Seamus?
A) all of these answers
B) libertarianism
C) liberalism
D) utilitarianism
E) communism
A) all of these answers
B) libertarianism
C) liberalism
D) utilitarianism
E) communism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
John Rawls's maximin criterion does not mean that there should be redistribution so as to equalize everyone's incomes in society because
A) such redistribution would mean that those who worked hard were no better off than those who were lazy and this would be unfair.
B) such redistribution would not maximize the total income of all members of society.
C) such redistribution would remove the incentive to work hard, so society's total income would fall, and so the least well off person would be worse off than they could be under a system in which there was some inequality in income.
D) such redistribution would amount to confiscation of honestly earned income from higher earners and so would be unjust.
A) such redistribution would mean that those who worked hard were no better off than those who were lazy and this would be unfair.
B) such redistribution would not maximize the total income of all members of society.
C) such redistribution would remove the incentive to work hard, so society's total income would fall, and so the least well off person would be worse off than they could be under a system in which there was some inequality in income.
D) such redistribution would amount to confiscation of honestly earned income from higher earners and so would be unjust.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Rank utilitarianism, liberalism, and libertarianism in sequence from the political philosophy that would redistribute income the greatest to the one that would redistribute income the least.
A) utilitarianism, liberalism, libertarianism
B) liberalism, libertarianism, utilitarianism
C) libertarianism, liberalism, utilitarianism
D) liberalism, utilitarianism, libertarianism
A) utilitarianism, liberalism, libertarianism
B) liberalism, libertarianism, utilitarianism
C) libertarianism, liberalism, utilitarianism
D) liberalism, utilitarianism, libertarianism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Susan had a big win at the casino on her birthday. The money she won is considered to be
A) permanent income.
B) life-cycle income.
C) transitory income.
D) an in-kind transfer.
A) permanent income.
B) life-cycle income.
C) transitory income.
D) an in-kind transfer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which political philosophy believes that the government should equalize the incomes of all members of society?
A) Utilitarianism.
B) Liberalism.
C) Libertarianism.
D) None of the above is correct.
A) Utilitarianism.
B) Liberalism.
C) Libertarianism.
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A period of unemployment due to recession will:
A) increase a worker's current income and permanent income.
B) reduce a worker's current income but not necessarily their permanent income
C) affect neither the current nor the permanent income of a worker.
D) reduce a worker's permanent income but not their current income.
A) increase a worker's current income and permanent income.
B) reduce a worker's current income but not necessarily their permanent income
C) affect neither the current nor the permanent income of a worker.
D) reduce a worker's permanent income but not their current income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Permanent income is more equally distributed than is current income because:
A) permanent income includes income from social security benefits.
B) permanent income includes winnings from gambling.
C) current income is usually lower than permanent income.
D) current income is subject to transitory changes which sometimes raise a person's income and sometimes reduce it.
A) permanent income includes income from social security benefits.
B) permanent income includes winnings from gambling.
C) current income is usually lower than permanent income.
D) current income is subject to transitory changes which sometimes raise a person's income and sometimes reduce it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Utilitarianism suggests that the government should choose policies that maximize the total utility of everyone in society by
A) redistributing income from rich to poor because this is what the members of society would choose to do if they were behind a "veil of ignorance."
B) redistributing income from rich to poor because, due to the diminishing marginal utility of income, taking a pound from the rich reduces their utility by less than the gain in utility generated by giving a pound to the poor.
C) allowing individuals to maximize their own utility without interference from the government.
D) redistributing income from rich to poor because this would maximize the well-being of the worst-off person in society.
A) redistributing income from rich to poor because this is what the members of society would choose to do if they were behind a "veil of ignorance."
B) redistributing income from rich to poor because, due to the diminishing marginal utility of income, taking a pound from the rich reduces their utility by less than the gain in utility generated by giving a pound to the poor.
C) allowing individuals to maximize their own utility without interference from the government.
D) redistributing income from rich to poor because this would maximize the well-being of the worst-off person in society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Assume that the government proposes a negative income tax that calculates taxes owed by the formula, Taxes Owed = (a Income) -
a. What is the value for "a"?
b. A family with an income of €40,000 pays €5,000 in taxes, and a family with an income of €12,000 receives an income subsidy of €2,000.
b. What is the value for "b"?
c. What is the tax liability of a family with an income of €50,000?
d. At what level of income will a family neither pay taxes, nor receive an income subsidy?
a. What is the value for "a"?
b. A family with an income of €40,000 pays €5,000 in taxes, and a family with an income of €12,000 receives an income subsidy of €2,000.
b. What is the value for "b"?
c. What is the tax liability of a family with an income of €50,000?
d. At what level of income will a family neither pay taxes, nor receive an income subsidy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A key economic argument against complete equalization of incomes is that
A) it would be unfair.
B) it would remove incentives for people to work harder and to invest in human capital.
C) we don't really know what choices people would make if they were behind a veil of ignorance.
D) people would never vote for such a measure.
A) it would be unfair.
B) it would remove incentives for people to work harder and to invest in human capital.
C) we don't really know what choices people would make if they were behind a veil of ignorance.
D) people would never vote for such a measure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Explain what is meant by "in-kind transfer" programs. Briefly outline the advantages and disadvantages of an in-kind transfer program.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Assume that the government proposes a negative income tax that calculates taxes owed by the following formula,
Taxes Owed = (1/3 x Income) - €10,000.
Compute the tax that would be owed given each level of income.
a. €120,000
b. €90,000
c. €60,000
d. €30,000
e. €0
Taxes Owed = (1/3 x Income) - €10,000.
Compute the tax that would be owed given each level of income.
a. €120,000
b. €90,000
c. €60,000
d. €30,000
e. €0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Using the same assumption as above about a negative income tax system, if a person who was earning no income takes a job paying an annual salary of €15,000, how much better off will that person be after taking income tax into account?
A) No better off.
B) €3,750 better off.
C) €11,250 better off.
D) €15,000 better off.
A) No better off.
B) €3,750 better off.
C) €11,250 better off.
D) €15,000 better off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Using the same assumption as above about a negative income tax system complete this sentence:
A person who is earning an annual salary of €20,000 will receive __________ of income from work and __________ of income from the government.
A) €20,000; €15,000
B) €20,000; €10,000
C) €20,000; €5,000
D) €20,000; €0
A person who is earning an annual salary of €20,000 will receive __________ of income from work and __________ of income from the government.
A) €20,000; €15,000
B) €20,000; €10,000
C) €20,000; €5,000
D) €20,000; €0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A problem with a negative income tax system is that it
A) guarantees every household a minimum level of income.
B) causes excessive government meddling in people's lives.
C) is too complex to administer fairly.
D) supports people who are simply lazy.
A) guarantees every household a minimum level of income.
B) causes excessive government meddling in people's lives.
C) is too complex to administer fairly.
D) supports people who are simply lazy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Given the table shown, which country has a more equal income distribution? Explain your answer.
Country
Bottom Fifth
Second Fifth
Middle Fifth
Fourth Fifth
Top Fifth
Country A
9.0%
13.5%
17.5%
22.9%
37.1%
Country B
4.8%
10.5%
16.0%
23.5%
45.2%
Country
Bottom Fifth
Second Fifth
Middle Fifth
Fourth Fifth
Top Fifth
Country A
9.0%
13.5%
17.5%
22.9%
37.1%
Country B
4.8%
10.5%
16.0%
23.5%
45.2%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Social security benefits are examples of
A) transfer payments.
B) negative income payments.
C) property income.
D) compensating differentials.
A) transfer payments.
B) negative income payments.
C) property income.
D) compensating differentials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is meant by a perfectly equal distribution of income? Use a graph to depict such a situation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Explain how a "leaky bucket" can be used to illustrate the utilitarian argument that governments should not attempt to completely equalize individual incomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The greatest advantage of a negative income tax is that it
A) generates a smaller disincentive to work than most alternative anti-poverty policies.
B) reduces the cost to the government of fighting poverty.
C) would not provide benefits to lazy people.
D) ensures that the poor actually receive what the government thinks they need.
E) means no-one is taxed unfairly
A) generates a smaller disincentive to work than most alternative anti-poverty policies.
B) reduces the cost to the government of fighting poverty.
C) would not provide benefits to lazy people.
D) ensures that the poor actually receive what the government thinks they need.
E) means no-one is taxed unfairly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Suppose a negative income tax system is established and the formula to compute a person's annual tax liability is: tax due = (25% of income) - €15,000.
If a person earns no income then he would receive a negative income tax payment of
A) €3,750.
B) €15,000.
C) €18,750.
D) €60,000.
If a person earns no income then he would receive a negative income tax payment of
A) €3,750.
B) €15,000.
C) €18,750.
D) €60,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Explain the relationship between labour earnings and the distribution of income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Briefly describe the three prominent schools of thought in political philosophy. Identify one of the most well-known philosophers in each school.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Social security benefit payments may increase poverty in the long run because they tend to
A) decrease the incentive to work among the poor.
B) increase the level of saving among the rich.
C) increase productivity of labour among the rich and poor.
D) promote investment activity by the rich.
A) decrease the incentive to work among the poor.
B) increase the level of saving among the rich.
C) increase productivity of labour among the rich and poor.
D) promote investment activity by the rich.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Explain the concept of diminishing marginal utility, and describe the role that it plays in the utilitarian argument for the redistribution of income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Compare and contrast the "life cycle" hypothesis and the "permanent income" hypothesis. What are their respective implications for inequality in the income distribution?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is most likely to occur when the government enacts policies to make the distribution of income more equal?
A) a more efficient allocation of resources
B) a distortion of incentives
C) unchanged behavior
D) All of the above are correct.
A) a more efficient allocation of resources
B) a distortion of incentives
C) unchanged behavior
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The poverty trap refers to
A) a situation in which those receiving state benefits may be almost no better off if they choose to work more to earn more income for themselves and their families because doing so will mean they have to pay back the benefits they have previously received.
B) a situation in which workers are unable to find jobs.
C) a situation in which those receiving state benefits may be almost no better off if they choose to work more to earn more income for themselves and their families because doing so will reduce the amount of benefit income to which they are entitled and increase the amount of tax they must pay.
D) a situation in which those receiving state benefits are discriminated against by employers and so find it more difficult to find jobs.
A) a situation in which those receiving state benefits may be almost no better off if they choose to work more to earn more income for themselves and their families because doing so will mean they have to pay back the benefits they have previously received.
B) a situation in which workers are unable to find jobs.
C) a situation in which those receiving state benefits may be almost no better off if they choose to work more to earn more income for themselves and their families because doing so will reduce the amount of benefit income to which they are entitled and increase the amount of tax they must pay.
D) a situation in which those receiving state benefits are discriminated against by employers and so find it more difficult to find jobs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



