Deck 32: Secondary Hemostasis and Fibrinolysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/35
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 32: Secondary Hemostasis and Fibrinolysis
1
Which domain of the blood coagulation protein is responsible for its distinctive identity?
A) Signal peptide domain
B) Catalytic domain
C) Epidermal growth factor domain
D) Noncatalytic domain
A) Signal peptide domain
B) Catalytic domain
C) Epidermal growth factor domain
D) Noncatalytic domain
Noncatalytic domain
2
Hemostasis depends on which of the following?
A) The interaction between coagulation and fibrinolysis inhibitors
B) The interaction between platelets, coagulation proteins, and blood vessels
C) The rate of platelet destruction
D) The rate of endothelial cell turnover
A) The interaction between coagulation and fibrinolysis inhibitors
B) The interaction between platelets, coagulation proteins, and blood vessels
C) The rate of platelet destruction
D) The rate of endothelial cell turnover
The interaction between platelets, coagulation proteins, and blood vessels
3
Which of the following degrades factors V and VIII?
A) TFPI
B) SERPINs
C) Proteins C and S
D) APS
A) TFPI
B) SERPINs
C) Proteins C and S
D) APS
Proteins C and S
4
Which of the following is primarily responsible for neutralizing the extrinsic tenase (Xase) complex?
A) TFPI
B) SERPINs
C) Proteins C and S
D) APS
A) TFPI
B) SERPINs
C) Proteins C and S
D) APS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The role of vitamin K in hemostasis is to:
A) Promote contact factor activation
B) Facilitate calcium binding to essential factors
C) Initiate extrinsic pathway activation
D) Cross-link the fibrin monomers
A) Promote contact factor activation
B) Facilitate calcium binding to essential factors
C) Initiate extrinsic pathway activation
D) Cross-link the fibrin monomers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The substance directly responsible for the physical breakdown of the thrombus is:
A) Plasmin
B) Plasminogen
C) Tissue plasminogen activator
D) Fibrin
A) Plasmin
B) Plasminogen
C) Tissue plasminogen activator
D) Fibrin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is not formed on a phospholipid surface?
A) Extrinsic Xase
B) Intrinsic Xase
C) Prothrombinase
D) Factor VIIa
A) Extrinsic Xase
B) Intrinsic Xase
C) Prothrombinase
D) Factor VIIa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Platelet activation and subsequent formation of the platelet plug are involved in:
A) Primary hemostasis
B) Secondary hemostasis
C) Fibrinolysis
D) Inhibitory system
A) Primary hemostasis
B) Secondary hemostasis
C) Fibrinolysis
D) Inhibitory system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following coagulation factors is(are) found in the extrinsic pathway?
A) HK and FXII
B) FXI and FIX
C) FVII and TF
D) FX
A) HK and FXII
B) FXI and FIX
C) FVII and TF
D) FX

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Why is vitamin K necessary for some coagulation proteins to become functional?
A) Vitamin K activates coagulation zymogens.
B) Vitamin K binds coagulation factors to a phospholipid surface.
C) Vitamin K combines with VWF in the circulation.
D) Vitamin K is required for gamma-carboxylation of glutamic acid residues.
A) Vitamin K activates coagulation zymogens.
B) Vitamin K binds coagulation factors to a phospholipid surface.
C) Vitamin K combines with VWF in the circulation.
D) Vitamin K is required for gamma-carboxylation of glutamic acid residues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is responsible for urokinase-catalyzed plasminogen (PLG) activation?
A) ADAMTS-13
B) LRP
C) UPAR
D) EPCR
A) ADAMTS-13
B) LRP
C) UPAR
D) EPCR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Activation of circulating zymogens is achieved through:
A) Sympathetic nervous system stimulation
B) Endomitosis
C) Splenic sequestration
D) Proteolytic cleavage
A) Sympathetic nervous system stimulation
B) Endomitosis
C) Splenic sequestration
D) Proteolytic cleavage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is not involved in "contact activation"?
A) Factor XII
B) Factor XI
C) PK
D) Factor X
A) Factor XII
B) Factor XI
C) PK
D) Factor X

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which plasminogen activator (PA) is distinctive among the serine proteases because it does not circulate as a zymogen but is fully active toward its substrate plasminogen in a single-chain form?
A) uPA
B) uPAR
C) PLG
D) tPA
A) uPA
B) uPAR
C) PLG
D) tPA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The prothrombin group includes of which of the following?
A) Factor V
B) Factor VII
C) Factor XII
D) Factor VIII
A) Factor V
B) Factor VII
C) Factor XII
D) Factor VIII

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
All of the following are necessary for a clot to form except:
A) Platelets
B) Coagulation protein
C) Plasmin
D) Endothelial cells
A) Platelets
B) Coagulation protein
C) Plasmin
D) Endothelial cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is the smallest degradation product of fibrin?
A) Fragment X
B) Fragment Y
C) D-dimer
D) E fragment
A) Fragment X
B) Fragment Y
C) D-dimer
D) E fragment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Triggering the contact activation factors of the intrinsic pathway does not require which of the following components?
A) Vitamin K
B) Calcium
C) Serine protease
D) Kinins
A) Vitamin K
B) Calcium
C) Serine protease
D) Kinins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the key component in secondary hemostasis that binds the platelets into a solid plug?
A) Fibrin
B) Tissue factor
C) Plasminogen
D) Thrombin
A) Fibrin
B) Tissue factor
C) Plasminogen
D) Thrombin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is responsible for cleaving ultra-large VWF multimers into functional units?
A) LRP
B) ADAMTS-13
C) EPCR
D) UPAR
A) LRP
B) ADAMTS-13
C) EPCR
D) UPAR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Compare and contrast systemic and physiologic fibrinolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What reflex test should be done on a patient with an abnormal APTT who is suspected of having hemophilia?
A) Platelet function assay
B) Factor assay
C) Quantitative fibrinogen assay
D) Assay for D-dimer
A) Platelet function assay
B) Factor assay
C) Quantitative fibrinogen assay
D) Assay for D-dimer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What are the roles of thrombin in coagulation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is a role of thrombin?
A) Activates anticoagulant (protein C)
B) Increases fibrinolysis
C) Inhibits endothelial cell release of tissue plasminogen activator
D) Inhibits the formation of fibrin monomers
A) Activates anticoagulant (protein C)
B) Increases fibrinolysis
C) Inhibits endothelial cell release of tissue plasminogen activator
D) Inhibits the formation of fibrin monomers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What factor does the extrinsic pathway require that the intrinsic and common pathways do not?
A) Vitamin K
B) Zymogens
C) Tissue factor
D) tPA
A) Vitamin K
B) Zymogens
C) Tissue factor
D) tPA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
How does systemic fibrinolysis differ from physiologic fibrinolysis?
A) Systemic produces rapid fibrinolysis, whereas physiologic produces adequate fibrinolysis.
B) Systemic results from improper plasminogen activation, whereas physiologic results from proper plasminogen activation.
C) Physiologic is naturally occurring, whereas systemic results from an external trigger.
D) Physiologic is localized to the fibrin clot, whereas systemic results in circulating plasmin.
A) Systemic produces rapid fibrinolysis, whereas physiologic produces adequate fibrinolysis.
B) Systemic results from improper plasminogen activation, whereas physiologic results from proper plasminogen activation.
C) Physiologic is naturally occurring, whereas systemic results from an external trigger.
D) Physiologic is localized to the fibrin clot, whereas systemic results in circulating plasmin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
How do the following systems contribute to coagulation?
a. Complement
b. Fibrinolysis
c. Kinin
a. Complement
b. Fibrinolysis
c. Kinin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Interpret the following results: • Patient: 12-year-old boy with unexplained bruising, swollen knee joints, and prolonged bleeding from injuries
• Screening tests:
O PT = 12.2 sec (control: 11.5-13.3 sec)/INR: 1.09
O APTT = 57 sec (control: 23-32 sec)
O Bleeding time = 5 min (control: 2-10 min)
Pending results from confirmation tests, this patient could be suffering from:
A) An intrinsic pathway problem
B) An extrinsic pathway problem
C) A primary hemostasis problem
D) A common pathway problem
• Screening tests:
O PT = 12.2 sec (control: 11.5-13.3 sec)/INR: 1.09
O APTT = 57 sec (control: 23-32 sec)
O Bleeding time = 5 min (control: 2-10 min)
Pending results from confirmation tests, this patient could be suffering from:
A) An intrinsic pathway problem
B) An extrinsic pathway problem
C) A primary hemostasis problem
D) A common pathway problem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
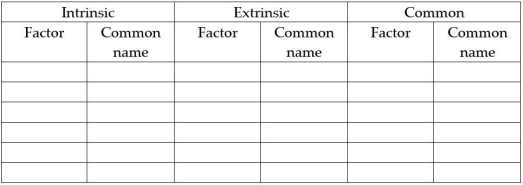
Complete the following table by listing the coag factors in the Intrinsic, Extrinsic and Common Pathways using both the Factor designation and common name.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is not a role of high molecular weight kininogen?
A) Accelerate the rate of surface-dependent activation of F-XII
B) Serves as a non-enzymatic cofactor in contact factor activation
C) Provide bradykinin
D) Accelerates the formation of Factor VIIa
A) Accelerate the rate of surface-dependent activation of F-XII
B) Serves as a non-enzymatic cofactor in contact factor activation
C) Provide bradykinin
D) Accelerates the formation of Factor VIIa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
During activation of coagulation, all of the following bind to the phospholipid membrane surface forming a complex except:
A) Procoagulant zymogen (substrate)
B) Coagulation inhibitors
C) Procoagulant cofactors
D) Activated serine protease
A) Procoagulant zymogen (substrate)
B) Coagulation inhibitors
C) Procoagulant cofactors
D) Activated serine protease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
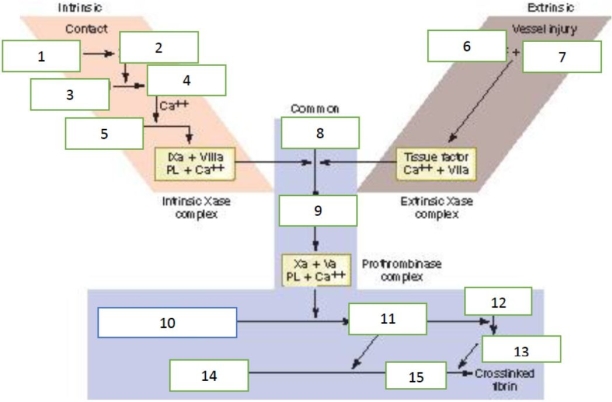
Fill in the missing factors in the traditional coagulation cascade:


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI) is defined as a:
A) Procoagulant
B) Anticoagulant
C) Profibrinolytic
D) Antifibrinolytic
A) Procoagulant
B) Anticoagulant
C) Profibrinolytic
D) Antifibrinolytic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
On which chromosome does the factor VIII locus reside?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 11
D) X
A) 3
B) 4
C) 11
D) X

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Thrombin activity impacts coagulation by which of the following mechanism(s)?
A) Altering blood flow
B) Positive feedback only
C) Negative feedback only
D) Positive and negative feedback
A) Altering blood flow
B) Positive feedback only
C) Negative feedback only
D) Positive and negative feedback

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



