Deck 7: Inflation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/152
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Inflation
1
If the price of iPods rises 10 percent during a year when the level of average prices rises 3 percent,the relative price of iPods compared with other goods
A)Remains constant.
B)Increases.
C)Decreases.
D)More information is required to answer this question.
A)Remains constant.
B)Increases.
C)Decreases.
D)More information is required to answer this question.
B
2
When there is no deflation or inflation,
A)Prices of all goods change by the same percentage.
B)Relative prices remain unchanged.
C)Average prices do not change.
D)Full employment is achieved.
A)Prices of all goods change by the same percentage.
B)Relative prices remain unchanged.
C)Average prices do not change.
D)Full employment is achieved.
C
3
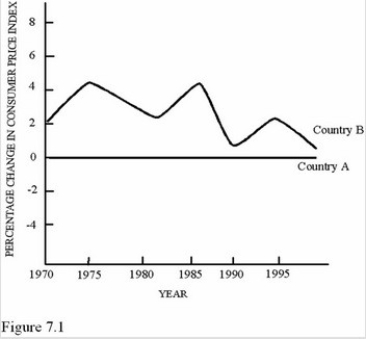 According to Figure 7.1,which of the following statements was definitely true about Country B?
According to Figure 7.1,which of the following statements was definitely true about Country B?A)Relative prices were changing.
B)The average price in general increased over the time period 1970 to 1995.
C)Real incomes were increasing.
D)The price level was about the same in 1970 and 1995.
B
4
Inflation is
A)A rise in the price of every good but not any service.
B)An increase in relative prices of all goods and services.
C)A situation in which purchasing power increases.
D)An increase in the average level of prices of goods and services.
A)A rise in the price of every good but not any service.
B)An increase in relative prices of all goods and services.
C)A situation in which purchasing power increases.
D)An increase in the average level of prices of goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Deflation is a/an ________ in the average level of prices of goods and services.
A)increase
B)decrease
C)stagnation
D)increase followed by a decrease
A)increase
B)decrease
C)stagnation
D)increase followed by a decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Changes in the relative prices of two goods indicate
A)Inflation.
B)Nominal price changes adjusted for the inflation in the price of the goods.
C)That average prices for the period must not be stable.
D)Changes in the desired mix of output.
A)Inflation.
B)Nominal price changes adjusted for the inflation in the price of the goods.
C)That average prices for the period must not be stable.
D)Changes in the desired mix of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Inflation means
A)Specific prices are rising,and relative prices are falling.
B)Both relative prices and average prices are rising.
C)Relative prices are rising,but it is not certain what is happening to average prices.
D)Average prices are rising,but it is not certain what is happening to relative prices.
A)Specific prices are rising,and relative prices are falling.
B)Both relative prices and average prices are rising.
C)Relative prices are rising,but it is not certain what is happening to average prices.
D)Average prices are rising,but it is not certain what is happening to relative prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Relative price is
A)The price of one good in comparison with the price of other goods.
B)A decrease in purchasing power because of rising prices.
C)The amount of income a particular good requires.
D)The current price paid for a good or service.
A)The price of one good in comparison with the price of other goods.
B)A decrease in purchasing power because of rising prices.
C)The amount of income a particular good requires.
D)The current price paid for a good or service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A decrease in the average level of prices of goods and services is
A)Deflation.
B)Recession.
C)Depression.
D)Inflation.
A)Deflation.
B)Recession.
C)Depression.
D)Inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
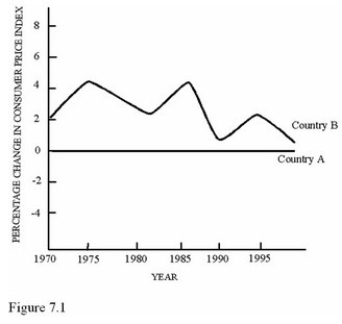 During the time period represented in Figure 7.1,Country A
During the time period represented in Figure 7.1,Country AA)Experienced periods of both inflation and deflation.
B)Never achieved the inflation goal set by the Full Employment and Balanced Growth Act of 1978.
C)Had no need for COLAs.
D)Experienced only inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Comparing changes in relative prices is more useful than examining average prices in
A)Determining the redistribution of income.
B)Determining the inflation rate.
C)Deflating nominal income.
D)Determining if there is deflation.
A)Determining the redistribution of income.
B)Determining the inflation rate.
C)Deflating nominal income.
D)Determining if there is deflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Changes in relative prices may occur in a period of
A)Stable prices only.
B)Inflation only.
C)Deflation only.
D)Stable prices,inflation,or deflation.
A)Stable prices only.
B)Inflation only.
C)Deflation only.
D)Stable prices,inflation,or deflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If the price of Bluetooth headsets rises 12 percent during a year when the level of average prices rises 13 percent,the relative price of Bluetooth headsets
A)Remains constant.
B)Increases.
C)Decreases.
D)More information is required to answer this question.
A)Remains constant.
B)Increases.
C)Decreases.
D)More information is required to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Inflation rates above 10 percent occur
A)In most countries today.
B)Rarely in the United States.
C)During wartime periods.
D)None of the other choices.
A)In most countries today.
B)Rarely in the United States.
C)During wartime periods.
D)None of the other choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
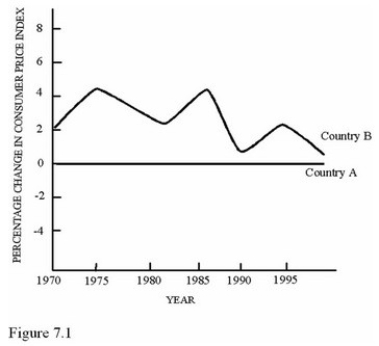 According to Figure 7.1 in Country A,
According to Figure 7.1 in Country A,A)Relative prices may have been changing,but average prices were constant.
B)Relative prices were definitely constant.
C)Average prices and relative prices were definitely changing.
D)Average prices were constant,and unemployment was increasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following explains why redistribution occurs during inflation?
A)Rising prices fail to signal desirable changes in the mix of output.
B)Because all prices do not change at the same rate,people buy different combinations of goods and services and own different combinations of wealth.
C)Relative prices remain unchanged.
D)All loans are indexed to inflation.
A)Rising prices fail to signal desirable changes in the mix of output.
B)Because all prices do not change at the same rate,people buy different combinations of goods and services and own different combinations of wealth.
C)Relative prices remain unchanged.
D)All loans are indexed to inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
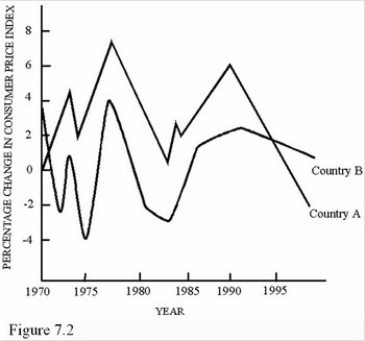 In the year 1995,which of the following statements is true about the two countries represented in Figure 7.2?
In the year 1995,which of the following statements is true about the two countries represented in Figure 7.2?A)The countries had approximately the same rate of inflation.
B)The CPI was virtually equal in the two countries.
C)The market basket cost approximately the same in both countries.
D)Real incomes were rising at the same rate in both countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When the price of a good decreases more slowly than an index of average prices decreases,the good's relative price
A)Has risen while its actual price has fallen.
B)And its actual price has risen.
C)And its actual price has fallen.
D)Has fallen while its actual price has risen.
A)Has risen while its actual price has fallen.
B)And its actual price has risen.
C)And its actual price has fallen.
D)Has fallen while its actual price has risen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following results from unexpected increases in the rate of inflation?
A)Decreased uncertainty.
B)Increased windfall profits to creditors who have lent large amounts of money.
C)Redistributions of income and wealth between different groups.
D)Creditors are made better off.
A)Decreased uncertainty.
B)Increased windfall profits to creditors who have lent large amounts of money.
C)Redistributions of income and wealth between different groups.
D)Creditors are made better off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following functions are performed by changes in relative prices but not by changes in average prices?
A)Computing real income from nominal income.
B)Indicating an overheating economy.
C)Signaling changes in the desired mix of output.
D)Measuring the rates of inflation.
A)Computing real income from nominal income.
B)Indicating an overheating economy.
C)Signaling changes in the desired mix of output.
D)Measuring the rates of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Real income is
A)Nominal income adjusted for inflation.
B)The amount of money income received in a given time period,measured in current dollars.
C)The use of nominal dollars to gauge changes in income.
D)None of the other choices.
A)Nominal income adjusted for inflation.
B)The amount of money income received in a given time period,measured in current dollars.
C)The use of nominal dollars to gauge changes in income.
D)None of the other choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If the price of your cell phone service increases from $70 to $105 over a period of one year and your income rises from $1,500 to $1,525,your nominal income has
A)Increased,and your real income has increased.
B)Increased,but your real income has decreased.
C)Decreased,and your real income has decreased.
D)Increased,but your real income has remained the same.
A)Increased,and your real income has increased.
B)Increased,but your real income has decreased.
C)Decreased,and your real income has decreased.
D)Increased,but your real income has remained the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Inflation ________ the purchasing power of money.
A)increases
B)decreases
C)does not affect
D)stabilizes
A)increases
B)decreases
C)does not affect
D)stabilizes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is a microeconomic consequence of inflation?
A)Greater unemployment.
B)Greater real income.
C)Wealth effects.
D)None of the other choices.
A)Greater unemployment.
B)Greater real income.
C)Wealth effects.
D)None of the other choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Income in constant dollars is
A)Nominal income.
B)Real income.
C)Bracket creep.
D)Income effect.
A)Nominal income.
B)Real income.
C)Bracket creep.
D)Income effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
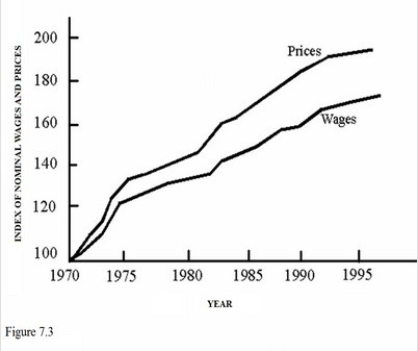 According to Figure 7.3,prices and wages were rising,so
According to Figure 7.3,prices and wages were rising,soA)Sellers of output were better off than wage earners.
B)Everyone must have been worse off since the price level rose faster than incomes.
C)There were no redistributive effects of inflation.
D)The economy was experiencing stagflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
All of the following are microeconomic consequences of inflation except
A)A price effect.
B)An income effect.
C)A wealth effect.
D)A profit effect.
A)A price effect.
B)An income effect.
C)A wealth effect.
D)A profit effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The redistributive mechanics of inflation include all of the following except
A)Price effects.
B)Income effects.
C)Wealth effects.
D)Output effects.
A)Price effects.
B)Income effects.
C)Wealth effects.
D)Output effects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The term "nominal income" refers to
A)Money income adjusted for any change in the price level.
B)Real purchasing power.
C)Real purchasing power deflated for rising prices.
D)Money income measured in current dollars.
A)Money income adjusted for any change in the price level.
B)Real purchasing power.
C)Real purchasing power deflated for rising prices.
D)Money income measured in current dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following groups is protected from a sudden increase in inflation?
A)Borrowers who have loans at fixed interest rates.
B)Fixed-income groups.
C)Workers who receive fixed wages under multiyear contracts.
D)People who rent their homes under short-term leases in comparison with those who own their homes.
A)Borrowers who have loans at fixed interest rates.
B)Fixed-income groups.
C)Workers who receive fixed wages under multiyear contracts.
D)People who rent their homes under short-term leases in comparison with those who own their homes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When the price of a product rises faster than the inflation rate,
A)Nominal incomes of the consumers of that product fall.
B)Users of that product have higher real incomes than people who do not consume the product.
C)Nominal incomes of the consumers of that product rise.
D)Real incomes of the consumers of that product fall.
A)Nominal incomes of the consumers of that product fall.
B)Users of that product have higher real incomes than people who do not consume the product.
C)Nominal incomes of the consumers of that product rise.
D)Real incomes of the consumers of that product fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Generally speaking,which of the following groups would tend to gain real income from the wealth effects of inflation?
A)People with fixed income.
B)People who have savings accounts at fixed rates of interest.
C)People who own assets that are appreciating faster than the inflation rate.
D)People who hold all of their assets in the form of cash.
A)People with fixed income.
B)People who have savings accounts at fixed rates of interest.
C)People who own assets that are appreciating faster than the inflation rate.
D)People who hold all of their assets in the form of cash.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The amount of income received in a given time period,measured in current dollars,is
A)Nominal income.
B)Real income.
C)Relative income.
D)The Consumer Price Index.
A)Nominal income.
B)Real income.
C)Relative income.
D)The Consumer Price Index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is not true about your nominal income?
A)It is the amount of money you receive during a given time period.
B)It is measured in current dollars.
C)It is not an accurate measure of purchasing power.
D)It is the same as your real income in times of high inflation.
A)It is the amount of money you receive during a given time period.
B)It is measured in current dollars.
C)It is not an accurate measure of purchasing power.
D)It is the same as your real income in times of high inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If deflation is 0.5 percent per year and you receive a 1 percent decrease in your salary,then your
A)Real income falls,but your nominal income remains unchanged.
B)Real and nominal income both fall.
C)Real income remains unchanged,but your nominal income rises.
D)Real and nominal income both rise.
A)Real income falls,but your nominal income remains unchanged.
B)Real and nominal income both fall.
C)Real income remains unchanged,but your nominal income rises.
D)Real and nominal income both rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Your real income is
A)The amount of money you receive during a given time period.
B)Measured in current dollars.
C)The purchasing power of the money you receive.
D)The same as your nominal income in times of high inflation.
A)The amount of money you receive during a given time period.
B)Measured in current dollars.
C)The purchasing power of the money you receive.
D)The same as your nominal income in times of high inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If a bank has already lent money at fixed interest rates,then during a period of higher-than-expected inflation,it experiences
A)Negative real income effects.
B)Hyperinflation.
C)Rising real interest rates.
D)Deflation.
A)Negative real income effects.
B)Hyperinflation.
C)Rising real interest rates.
D)Deflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
During a period of unanticipated inflation,
A)Debtors are better off and creditors are worse off.
B)Debtors and creditors are both better off because of lower real interest rates.
C)Individuals on fixed incomes are better off.
D)All individuals are worse off because of the level of uncertainty.
A)Debtors are better off and creditors are worse off.
B)Debtors and creditors are both better off because of lower real interest rates.
C)Individuals on fixed incomes are better off.
D)All individuals are worse off because of the level of uncertainty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the cost of your gasoline purchases decrease from $150 per month to $80 over a period of one year due to lower prices and your income decreases from $1,600 per month to $1,500 per month,your nominal income has
A)Increased,but your real income has decreased.
B)Decreased,but your real income has increased.
C)Increased,and your real income has increased.
D)Increased,but your real income has remained the same.
A)Increased,but your real income has decreased.
B)Decreased,but your real income has increased.
C)Increased,and your real income has increased.
D)Increased,but your real income has remained the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If your rent increases from $1,000 to $1,100 over a period of one year and your income rises from $6,000 to $7,000,your nominal income has
A)Increased,but your real income has decreased.
B)Increased,and your real income has increased.
C)Decreased,and your real income has decreased.
D)Increased,but your real income has remained the same.
A)Increased,but your real income has decreased.
B)Increased,and your real income has increased.
C)Decreased,and your real income has decreased.
D)Increased,but your real income has remained the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When people make decisions on the basis of the face value of currency rather than the real value,their decisions reflect
A)The price effect of inflation.
B)The income effect of inflation.
C)The wealth effect of inflation.
D)Money illusion.
A)The price effect of inflation.
B)The income effect of inflation.
C)The wealth effect of inflation.
D)Money illusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is a likely macroeconomic consequence of inflation?
A)Focus on long-term planning.
B)Speculation.
C)Antitrust issues.
D)None of the other choices.
A)Focus on long-term planning.
B)Speculation.
C)Antitrust issues.
D)None of the other choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The uncertainty that results from inflation causes changes in
A)Consumption,saving,and investment behavior.
B)Saving and investment behavior,but not consumption.
C)Consumption,but not saving and investment behavior.
D)Income,but not consumption.
A)Consumption,saving,and investment behavior.
B)Saving and investment behavior,but not consumption.
C)Consumption,but not saving and investment behavior.
D)Income,but not consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A friend tells you that his income has risen every year by 5 percent.At the same time,prices,on average,have risen by 5 percent.Your friend claims he is better off.Your friend
A)Is experiencing money illusion.
B)Really is better off as he suggests.
C)Has experienced an increase in nominal and real income.
D)Has experienced an increase in real income only.
A)Is experiencing money illusion.
B)Really is better off as he suggests.
C)Has experienced an increase in nominal and real income.
D)Has experienced an increase in real income only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Hyperinflation is
A)An inflation rate in excess of 200 percent,lasting at least one year.
B)An inflation rate in excess of 20 percent,lasting at least one year.
C)A common problem in the United States.
D)The movement of taxpayers to higher tax brackets because of rising prices.
A)An inflation rate in excess of 200 percent,lasting at least one year.
B)An inflation rate in excess of 20 percent,lasting at least one year.
C)A common problem in the United States.
D)The movement of taxpayers to higher tax brackets because of rising prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
During a period of deflation,
A)The price level rises.
B)People on fixed incomes are better off.
C)People who hold cash are worse off.
D)Lenders are worse off.
A)The price level rises.
B)People on fixed incomes are better off.
C)People who hold cash are worse off.
D)Lenders are worse off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Last year you earned $20,000 and paid taxes in the second tax bracket at 15 percent.This year you earned $25,000,the extra $5,000 just compensating you for inflation.However,this year you paid taxes in the third bracket at 20 percent.This illustrates the concept of
A)Stagflation.
B)Speculation.
C)Deflation.
D)Bracket creep.
A)Stagflation.
B)Speculation.
C)Deflation.
D)Bracket creep.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Money illusion is the
A)Use of nominal dollars rather than real dollars to gauge changes in one's income or wealth.
B)Movement of taxpayers into higher tax brackets as nominal income increases.
C)Focus on real dollars rather than nominal dollars to determine purchasing power over time.
D)Uncertainty that occurs because of inflation.
A)Use of nominal dollars rather than real dollars to gauge changes in one's income or wealth.
B)Movement of taxpayers into higher tax brackets as nominal income increases.
C)Focus on real dollars rather than nominal dollars to determine purchasing power over time.
D)Uncertainty that occurs because of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following is a macro consequence of a sudden increase in the average level of prices?
A)People on fixed incomes benefit.
B)Uncertainty is greater.
C)Nominal income falls by a smaller percentage than real income.
D)People lengthen their time horizons.
A)People on fixed incomes benefit.
B)Uncertainty is greater.
C)Nominal income falls by a smaller percentage than real income.
D)People lengthen their time horizons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
During a period of deflation,
A)Time horizons are longer.
B)Consumer confidence increases.
C)Lenders are better off.
D)Borrowers are better off.
A)Time horizons are longer.
B)Consumer confidence increases.
C)Lenders are better off.
D)Borrowers are better off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
All of the following are macroeconomic effects of inflation except
A)Uncertainty.
B)Speculation.
C)Bracket creep.
D)Lower taxes.
A)Uncertainty.
B)Speculation.
C)Bracket creep.
D)Lower taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
To construct the Consumer Price Index,the Bureau of Labor Statistics must
A)Find out what people buy with their incomes and how the prices of what they buy change.
B)Find out why people buy,what they buy,and how the prices of what they buy change.
C)Find out what is in the typical consumer market basket on the basis of what producers produce.
D)Conduct producer surveys to determine how much prices rise.
A)Find out what people buy with their incomes and how the prices of what they buy change.
B)Find out why people buy,what they buy,and how the prices of what they buy change.
C)Find out what is in the typical consumer market basket on the basis of what producers produce.
D)Conduct producer surveys to determine how much prices rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Inflation affects production decisions because it
A)Decreases input costs.
B)Reduces speculation.
C)Causes businesses to focus more on the future.
D)Causes businesses to be more cautious since the future appears more uncertain.
A)Decreases input costs.
B)Reduces speculation.
C)Causes businesses to focus more on the future.
D)Causes businesses to be more cautious since the future appears more uncertain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Speculation during periods of inflation can result in all of the following except
A)People buying resources for resale later,rather than using the resources for current production.
B)A movement inward from the production possibilities curve.
C)People buying gold,silver,jewelry,and the like instead of capital for production.
D)More resources going into the production process.
A)People buying resources for resale later,rather than using the resources for current production.
B)A movement inward from the production possibilities curve.
C)People buying gold,silver,jewelry,and the like instead of capital for production.
D)More resources going into the production process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If the price level is falling,all of the following are true except
A)Lenders are better off.
B)Businesses are reluctant to borrow money.
C)Purchasing power increases.
D)Borrowers are not affected.
A)Lenders are better off.
B)Businesses are reluctant to borrow money.
C)Purchasing power increases.
D)Borrowers are not affected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following measures changes in the average price of consumer goods and services?
A)Inflation rate.
B)CPI.
C)Deflation rate.
D)Market basket.
A)Inflation rate.
B)CPI.
C)Deflation rate.
D)Market basket.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The movement of taxpayers into higher tax brackets as nominal incomes grow is
A)Bracket leap.
B)Bracket hike.
C)Bracket creep.
D)Inflation hike.
A)Bracket leap.
B)Bracket hike.
C)Bracket creep.
D)Inflation hike.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
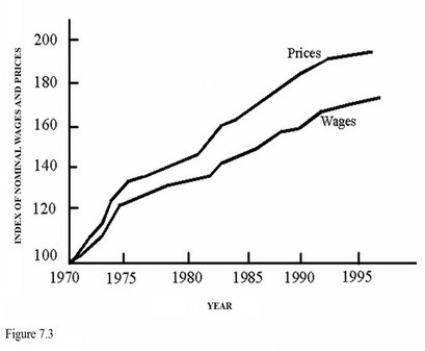 During the time period represented in Figure 7.3,the purchasing power of the average worker
During the time period represented in Figure 7.3,the purchasing power of the average workerA)Increased because nominal wages increased.
B)Decreased because real income decreased.
C)Stay the same because COLAs reduced purchasing power.
D)Decreased because nominal income decreased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The Consumer Price Index is
A)A measure of changes in the average price of all goods and services.
B)A measure of changes in the average price of consumer goods and services.
C)Used to measure the impact of business speculation on consumers.
D)The impact felt by consumers who move into a higher tax bracket because of inflation.
A)A measure of changes in the average price of all goods and services.
B)A measure of changes in the average price of consumer goods and services.
C)Used to measure the impact of business speculation on consumers.
D)The impact felt by consumers who move into a higher tax bracket because of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
All of the following push a country inside its production possibilities curve except
A)A sudden burst of inflation that has not been anticipated.
B)A sudden burst of deflation that has not been anticipated.
C)The withholding of resources from the production process because of speculation.
D)An increase in labor force participation.
A)A sudden burst of inflation that has not been anticipated.
B)A sudden burst of deflation that has not been anticipated.
C)The withholding of resources from the production process because of speculation.
D)An increase in labor force participation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
To compute the real income of a household,the index that should be used is the
A)Producer Price Index (PPI).
B)Consumer Price Index (CPI).
C)GDP deflator.
D)Cost of Living Adjustment (COLA).
A)Producer Price Index (PPI).
B)Consumer Price Index (CPI).
C)GDP deflator.
D)Cost of Living Adjustment (COLA).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If the Consumer Price Index rose from 180.9 in 2005 to 418.5 in 2015,what is the total percentage change in prices over this 10-year period?
A)131.34 percent.
B)18.5 percent.
C)80.9 percent.
D)127.21 percent.
A)131.34 percent.
B)18.5 percent.
C)80.9 percent.
D)127.21 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The percentage of total expenditure spent on a specific product is called
A)Core inflation.
B)A market basket.
C)A budget.
D)The item weight.
A)Core inflation.
B)A market basket.
C)A budget.
D)The item weight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If the CPI increases from 110 to 125 for one year,the rate of inflation for that year is
A)15 percent.
B)13.6 percent.
C)1.13 percent.
D)50 percent.
A)15 percent.
B)13.6 percent.
C)1.13 percent.
D)50 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Assume the CPI increases from 110 to 121,and Manny's nominal income increases from $100,000 to $120,000 over the same period.Manny's real income has
A)Increased by approximately 12 percent.
B)Increased by approximately 9 percent.
C)Decreased by approximately 8 percent.
D)Remained the same.
A)Increased by approximately 12 percent.
B)Increased by approximately 9 percent.
C)Decreased by approximately 8 percent.
D)Remained the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The price index that refers to all final goods and services produced in a country is the
A)GDP deflator.
B)PPI.
C)CPI.
D)GDP inflator.
A)GDP deflator.
B)PPI.
C)CPI.
D)GDP inflator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The GDP deflator
A)Is the price index based on a fixed basket of goods and services for the government.
B)Is the best measure of inflation for consumers.
C)Reflects the price changes felt by producers but not consumers.
D)Is the broadest price index,covering all output.
A)Is the price index based on a fixed basket of goods and services for the government.
B)Is the best measure of inflation for consumers.
C)Reflects the price changes felt by producers but not consumers.
D)Is the broadest price index,covering all output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
For the CPI,the market basket is expressed in terms of what the goods cost in
A)1929.
B)2000.
C)The base period.
D)The optimal period.
A)1929.
B)2000.
C)The base period.
D)The optimal period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If the CPI increases from 250 to 275 for one year,the rate of inflation for that year is
A)13 percent.
B)10 percent.
C)25 percent.
D)15 percent.
A)13 percent.
B)10 percent.
C)25 percent.
D)15 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
At the beginning of 2000,the CPI was 159.3.At the beginning of 2001,it was 177.6.What was the approximate rate of inflation in 2000?
A)7.6 percent.
B)18.3 percent.
C)10.0 percent.
D)11.5 percent.
A)7.6 percent.
B)18.3 percent.
C)10.0 percent.
D)11.5 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The Producer Price Index (PPI)is the best index to measure average price changes faced by
A)Consumers.
B)Producers.
C)Importers.
D)Labor unions negotiating COLAs.
A)Consumers.
B)Producers.
C)Importers.
D)Labor unions negotiating COLAs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The base period is the
A)Time period used for comparative analysis.
B)Absence of significant changes in the average price level.
C)Time period when full employment is reached.
D)First year in which inflation figures were calculated.
A)Time period used for comparative analysis.
B)Absence of significant changes in the average price level.
C)Time period when full employment is reached.
D)First year in which inflation figures were calculated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Item weight is the
A)Measure of how much consumers demand a particular item.
B)Percentage of total expenditure spent on a particular product.
C)Significance placed on a particular item by the wealthiest households.
D)Physical weight of a good or service.
A)Measure of how much consumers demand a particular item.
B)Percentage of total expenditure spent on a particular product.
C)Significance placed on a particular item by the wealthiest households.
D)Physical weight of a good or service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
At the beginning of 2006 the CPI was 216.2.At the beginning of 2007,it was 225.1.What was the rate of inflation in 2006?
A)4.9 percent.
B)4.1 percent.
C)3.6 percent.
D)8.9 percent.
A)4.9 percent.
B)4.1 percent.
C)3.6 percent.
D)8.9 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If you were interested in charting prices of resources used by producers of energy,which of the following would you use?
A)The Producer Price Index (PPI).
B)The Consumer Price Index (CPI).
C)The GDP deflator.
D)The Cost of Living Adjustment (COLA).
A)The Producer Price Index (PPI).
B)The Consumer Price Index (CPI).
C)The GDP deflator.
D)The Cost of Living Adjustment (COLA).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following is often watched closely as a clue to potential changes in consumer prices in the future?
A)The CPI.
B)The PPI.
C)The GDP deflator.
D)The COLAs.
A)The CPI.
B)The PPI.
C)The GDP deflator.
D)The COLAs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The inflation rate is the
A)Monthly percentage rate increase in the price of all goods and services.
B)Annual percentage rate increase in tax brackets.
C)Annual percentage rate increase in the average price level.
D)Monthly adjustment of wages to the cost of living.
A)Monthly percentage rate increase in the price of all goods and services.
B)Annual percentage rate increase in tax brackets.
C)Annual percentage rate increase in the average price level.
D)Monthly adjustment of wages to the cost of living.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If a price index changed from 150 in 2008 to 148.5 in 2009,while Jim Bob's nominal wage fell from $25 to $24,then Jim Bob is
A)Better off like everyone else in the economy since prices are lower for consumers.
B)Neither better nor worse off since his real wage remained constant.
C)Better off since his nominal wage fell slower than the price level did.
D)Worse off since his nominal wage fell faster than the price level did.
A)Better off like everyone else in the economy since prices are lower for consumers.
B)Neither better nor worse off since his real wage remained constant.
C)Better off since his nominal wage fell slower than the price level did.
D)Worse off since his nominal wage fell faster than the price level did.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A sudden increase in inflation,ceteris paribus,
A)Raises the real income of lenders relative to borrowers.
B)Raises the CPI and reduces real income.
C)Reduces the nominal income of those who have constant real incomes.
D)Makes everyone worse off.
A)Raises the real income of lenders relative to borrowers.
B)Raises the CPI and reduces real income.
C)Reduces the nominal income of those who have constant real incomes.
D)Makes everyone worse off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The base period used in computing a price index is
A)The year in which prices were at their lowest level.
B)The year in which prices were at their average level.
C)A fixed reference year from which meaningful comparisons can be made.
D)The earliest year for which data are available.
A)The year in which prices were at their lowest level.
B)The year in which prices were at their average level.
C)A fixed reference year from which meaningful comparisons can be made.
D)The earliest year for which data are available.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



