Deck 31: Labor Unions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/123
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 31: Labor Unions
1
Public sector unions now
A)Represent a smaller percentage of workers than private sector unions.
B)Are growing at a smaller rate than private sector unions.
C)Represent over five times the percentage of workers in private sector unions.
A)Represent a smaller percentage of workers than private sector unions.
B)Are growing at a smaller rate than private sector unions.
C)Represent over five times the percentage of workers in private sector unions.
Represent over five times the percentage of workers in private sector unions.
2
Because firms are willing to hire additional workers at lower wages,the market labor demand curve is
A)Vertical.
B)Perfectly elastic.
C)Downward-sloping.
A)Vertical.
B)Perfectly elastic.
C)Downward-sloping.
Downward-sloping.
3
Labor supply can be defined as the
A)Total number of people who are employable.
B)Total number of people in paid employment.
C)Willingness and ability of people to work at alternative wage rates in a given period of time,ceteris paribus.
A)Total number of people who are employable.
B)Total number of people in paid employment.
C)Willingness and ability of people to work at alternative wage rates in a given period of time,ceteris paribus.
Willingness and ability of people to work at alternative wage rates in a given period of time,ceteris paribus.
4
The largest employer in the United States is
A)The federal government.
B)General Motors.
C)Walmart.
A)The federal government.
B)General Motors.
C)Walmart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Because a union is a form of monopoly,it must be concerned about the ________ slope of the demand curve for labor.
A)vertical
B)horizontal
C)downward
A)vertical
B)horizontal
C)downward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The largest labor union in the United States is the
A)International Brotherhood of Teamsters (Teamsters).
B)International Union,United Automobile,Aerospace and Agricultural Implement Workers of America (UAW).
C)Service Employees International Union.
A)International Brotherhood of Teamsters (Teamsters).
B)International Union,United Automobile,Aerospace and Agricultural Implement Workers of America (UAW).
C)Service Employees International Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The equilibrium wage rate is determined by
A)Individuals but not firms.
B)Market labor supply and market labor demand.
C)Labor unions.
A)Individuals but not firms.
B)Market labor supply and market labor demand.
C)Labor unions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Workers who demand a wage that is higher than the equilibrium wage
A)Will find it difficult to secure a job.
B)Will easily secure a job.
C)Must belong to a union in order to secure a job.
A)Will find it difficult to secure a job.
B)Will easily secure a job.
C)Must belong to a union in order to secure a job.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Workers with a particular skill are represented by
A)Craft unions.
B)Skill unions.
C)Market unions.
A)Craft unions.
B)Skill unions.
C)Market unions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Typical goals of a labor union in the United States include
A)Higher wages,better working conditions,and more job security.
B)Higher profit,lower output,and greater productivity.
C)Less work,more workers,and more overtime.
A)Higher wages,better working conditions,and more job security.
B)Higher profit,lower output,and greater productivity.
C)Less work,more workers,and more overtime.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If the total wages paid change from $200,000 to $250,000 when the quantity of labor employed increases from five to seven workers,the marginal wage is
A)$35,714.
B)$25,000.
C)$250,000.
A)$35,714.
B)$25,000.
C)$250,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The demand for labor determines the
A)Total number of people who want to work.
B)Number of available jobs.
C)Willingness and ability of people to work at alternative wage rates.
A)Total number of people who want to work.
B)Number of available jobs.
C)Willingness and ability of people to work at alternative wage rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A union evaluates job offers based on the
A)Individual interests of its members.
B)Collective interests of its members.
C)Location of the work,either in the private or public sector.
A)Individual interests of its members.
B)Collective interests of its members.
C)Location of the work,either in the private or public sector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The difference between craft unions and industrial unions is that industrial unions usually
A)Are organized along democratic lines,while craft unions are undemocratic.
B)Include workers in an industry,while craft unions represent workers with a particular skill.
C)Include workers with a particular skill,while craft unions represent workers in an industry.
A)Are organized along democratic lines,while craft unions are undemocratic.
B)Include workers in an industry,while craft unions represent workers with a particular skill.
C)Include workers with a particular skill,while craft unions represent workers in an industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is an example of an industrial union?
A)The International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers.
B)The Carpenters Union.
C)The United Auto Workers.
A)The International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers.
B)The Carpenters Union.
C)The United Auto Workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Unions must worry about the marginal wage because it indicates the
A)Wage at which demand and supply intersect.
B)Opportunity wage available to workers.
C)Effect on the total wage bill of hiring additional workers.
A)Wage at which demand and supply intersect.
B)Opportunity wage available to workers.
C)Effect on the total wage bill of hiring additional workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The marginal wage is measured by
A)The percentage change in wages divided by the percentage change in the quantity of labor employed.
B)Total wages paid divided by the quantity of labor employed.
C)The change in total wages paid divided by the change in the quantity of labor employed.
A)The percentage change in wages divided by the percentage change in the quantity of labor employed.
B)Total wages paid divided by the quantity of labor employed.
C)The change in total wages paid divided by the change in the quantity of labor employed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Workers who organize themselves along industry lines are represented by
A)Skill unions.
B)Industrial unions.
C)Manufacturing unions.
A)Skill unions.
B)Industrial unions.
C)Manufacturing unions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Walmart,the largest employer in the United States,employs
A)Approximately 2 percent of the labor force.
B)Less than 1 percent of the labor force.
C)More than 15 percent of the labor force.
A)Approximately 2 percent of the labor force.
B)Less than 1 percent of the labor force.
C)More than 15 percent of the labor force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Typical goals of a labor union in the United States include
A)Higher profit,higher output,and greater productivity.
B)Higher wages,better working conditions,and more nonwage compensation.
C)More vacation time,higher profit,and more flexible workplace rules.
A)Higher profit,higher output,and greater productivity.
B)Higher wages,better working conditions,and more nonwage compensation.
C)More vacation time,higher profit,and more flexible workplace rules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The United Farm Workers have been unsuccessful for decades in their attempts to organize California's strawberry pickers because the workers
A)Know that replacement workers are readily available.
B)Don't care about earning higher wages.
C)Don't understand English.
A)Know that replacement workers are readily available.
B)Don't care about earning higher wages.
C)Don't understand English.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Union shops are subject to potential competition
A)Because some union shop workers refuse to join the union.
B)From replacement or substitute workers.
C)Since most union members do not take strikes seriously.
A)Because some union shop workers refuse to join the union.
B)From replacement or substitute workers.
C)Since most union members do not take strikes seriously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
To be successful in changing wage rates and employment conditions,labor unions need to have control over only
A)Their own members.
B)The labor supply decisions of individual workers.
C)The MRP of employers.
A)Their own members.
B)The labor supply decisions of individual workers.
C)The MRP of employers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The old industrial unions are being supplanted by
A)Public service unions.
B)Craft unions.
C)Union shops.
A)Public service unions.
B)Craft unions.
C)Union shops.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If 10 workers will be hired by a firm at a wage rate of $15 per hour,but the 11th worker will be hired only if the wage rate falls to $14 per hour,then the marginal wage of the 11th worker is
A)$4 per hour.
B)$14 per hour.
C)$154 per hour.
A)$4 per hour.
B)$14 per hour.
C)$154 per hour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The current unionization rate for the U.S.labor force
A)Has been rising since the mid-1950s.
B)Reflects the relative decline in U.S.manufacturing.
C)Is above 20 percent.
A)Has been rising since the mid-1950s.
B)Reflects the relative decline in U.S.manufacturing.
C)Is above 20 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The unionization ratio grew most rapidly in the United States between
A)1950 and 1953.
B)1980 and 1988.
C)1935 and 1945.
A)1950 and 1953.
B)1980 and 1988.
C)1935 and 1945.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the last 10 years,private union membership has
A)Decreased,while public union membership has increased.
B)Increased along with public union membership.
C)Decreased along with public union membership.
A)Decreased,while public union membership has increased.
B)Increased along with public union membership.
C)Decreased along with public union membership.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If the sellers of labor in a competitive market decided to unionize,ceteris paribus,then wages would
A)Rise and employment would fall.
B)Fall and employment would fall.
C)Rise and employment would rise.
A)Rise and employment would fall.
B)Fall and employment would fall.
C)Rise and employment would rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A monopsony
A)Is a market in which there is a single buyer.
B)Is a market in which there is a single seller.
C)Occurs when sellers have declining long-run average costs.
A)Is a market in which there is a single buyer.
B)Is a market in which there is a single seller.
C)Occurs when sellers have declining long-run average costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The unionization ratio represents the
A)Percentage of the total labor force belonging to unions.
B)Market power of unions relative to the market power of nonunion labor.
C)Proportion of industries that are dominated by unions.
A)Percentage of the total labor force belonging to unions.
B)Market power of unions relative to the market power of nonunion labor.
C)Proportion of industries that are dominated by unions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
With a union,the total number of workers hired is where
A)Employment is lower than at the competitive equilibrium.
B)The marginal wage is negative.
C)Employment and wages are both at the maximum possible levels.
A)Employment is lower than at the competitive equilibrium.
B)The marginal wage is negative.
C)Employment and wages are both at the maximum possible levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The percentage of the labor force that belongs to a union is known as the
A)Union share ratio.
B)Unionization ratio.
C)Union participation ratio.
A)Union share ratio.
B)Unionization ratio.
C)Union participation ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Over the last 10 years in the United States,the private sector unionization rate has ______ and the public sector unionization rate has _______.
A)fallen;fallen
B)fallen;risen
C)risen;fallen
A)fallen;fallen
B)fallen;risen
C)risen;fallen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A workplace that requires workers to become union members within 30 days of being hired by a firm is
A)A craft union.
B)An industrial union.
C)A union shop.
A)A craft union.
B)An industrial union.
C)A union shop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If a firm hires 12 workers at $9 per hour each and the 13th worker will be hired only if the wage rate falls to $8 per hour,the marginal wage rate must be
A)-$8.
B)$8.
C)-$4.
A)-$8.
B)$8.
C)-$4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If a firm hires 10 workers at $6 per hour each and the 11th worker will be hired only if the wage rate falls to $5 per hour,the marginal wage rate must be
A)-$5.
B)$5.
C)-$5.50.
A)-$5.
B)$5.
C)-$5.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Public sector unionization in the United States is currently closest to ________ percent.
A)36
B)23
C)8.2
A)36
B)23
C)8.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
From a union's perspective,the optimal level of employment is determined by the intersection of the
A)Labor demand curve and the labor supply curve.
B)Marginal wage curve and the labor supply curve.
C)Labor demand curve and the marginal wage curve.
A)Labor demand curve and the labor supply curve.
B)Marginal wage curve and the labor supply curve.
C)Labor demand curve and the marginal wage curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Suppose a union collects dues at 1 percent of the total wage bill.Maximum dues (and maximum total labor cost)would be achieved by hiring the amount of labor where
A)The supply curve intersects the marginal wage curve.
B)The marginal wage is zero.
C)The factor demand curve intersects the factor supply curve.
A)The supply curve intersects the marginal wage curve.
B)The marginal wage is zero.
C)The factor demand curve intersects the factor supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Collective bargaining
A)Involves direct negotiations between labor unions and employers.
B)Takes place when unions compete to see who should represent workers in a given industry.
C)Occurs when employers determine which union should represent their workers.
A)Involves direct negotiations between labor unions and employers.
B)Takes place when unions compete to see who should represent workers in a given industry.
C)Occurs when employers determine which union should represent their workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The marginal factor cost for labor is
A)The net cost to a monopsonist of hiring an additional unit of labor.
B)The net gain to a monopolist seller of labor if an additional unit of labor is hired.
C)The demand for labor.
A)The net cost to a monopsonist of hiring an additional unit of labor.
B)The net gain to a monopolist seller of labor if an additional unit of labor is hired.
C)The demand for labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
An oligopsony exists if
A)Only a few firms produce most of the industry's output.
B)Only a few firms account for most of the industry's employment.
C)Only one firm accounts for most of the industry's employment.
A)Only a few firms produce most of the industry's output.
B)Only a few firms account for most of the industry's employment.
C)Only one firm accounts for most of the industry's employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If there are many employers in a market and each has limited market power,the demand for labor is likely to be characterized as
A)Competitive.
B)Monopsonistic.
C)Oligopolistic.
A)Competitive.
B)Monopsonistic.
C)Oligopolistic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The wage rate that a monopsonist would find most profitable is the wage
A)At the intersection of the marginal wage curve and the marginal cost curve.
B)On the labor supply curve corresponding to the level of employment at which the marginal factor cost curve (for labor)intersects the labor demand curve.
C)On the labor demand curve corresponding to the level of employment at which the marginal factor cost equals market supply.
A)At the intersection of the marginal wage curve and the marginal cost curve.
B)On the labor supply curve corresponding to the level of employment at which the marginal factor cost curve (for labor)intersects the labor demand curve.
C)On the labor demand curve corresponding to the level of employment at which the marginal factor cost equals market supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
From an economic perspective,the efforts of professional football,baseball,and basketball players in the United States to win the right to become free agents was really an effort to
A)Raise wages to the level of the players' MRP.
B)Raise wages to competitive levels.
C)Reduce the supply of professional players and thus increase wages.
A)Raise wages to the level of the players' MRP.
B)Raise wages to competitive levels.
C)Reduce the supply of professional players and thus increase wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The marginal factor cost for a buyer with market power is
A)Above the marginal revenue product curve.
B)Above the wage rate paid by a monopsonist.
C)Below the labor supply curve.
A)Above the marginal revenue product curve.
B)Above the wage rate paid by a monopsonist.
C)Below the labor supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If the marginal factor cost is less than labor demand,a monopsonist should
A)Reduce the wage rate.
B)Hire additional workers.
C)Increase the wage rate.
A)Reduce the wage rate.
B)Hire additional workers.
C)Increase the wage rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Suppose a monopsonist must pay $10 per hour to attract 10 workers.If the same monopsonist must raise its wage to $11 per hour to attract the 11th worker,what is its marginal factor cost for labor?
A)$121 per hour.
B)$21 per hour.
C)$11 per hour.
A)$121 per hour.
B)$21 per hour.
C)$11 per hour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In a bilateral monopoly,wages and employment are determined by
A)Negotiation.
B)The intersection of market supply and demand.
C)The intersection of marginal cost and marginal revenue product.
A)Negotiation.
B)The intersection of market supply and demand.
C)The intersection of marginal cost and marginal revenue product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
When management shuts down a plant and does not allow workers to perform their jobs,there is a
A)Walkout.
B)Lockout.
C)Strike.
A)Walkout.
B)Lockout.
C)Strike.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A monopsonist must pay a higher net wage rate to hire additional workers because as a single
A)Seller,it has market power.
B)Seller,it does not have to compete with other firms for customers.
C)Buyer in the market,it faces an upward-sloping supply curve for labor.
A)Seller,it has market power.
B)Seller,it does not have to compete with other firms for customers.
C)Buyer in the market,it faces an upward-sloping supply curve for labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The distinguishing characteristic of labor market monopsonies is the fact that
A)They can hire any number of workers they want without affecting the market wage.
B)Their hiring decisions directly affect the market wage rate.
C)They can pay any wage they want for the number of workers they need.
A)They can hire any number of workers they want without affecting the market wage.
B)Their hiring decisions directly affect the market wage rate.
C)They can pay any wage they want for the number of workers they need.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In equilibrium,the monopsonist's labor demand will
A)Exceed labor supply.
B)Be greater than the marginal factor cost.
C)Equal labor supply.
A)Exceed labor supply.
B)Be greater than the marginal factor cost.
C)Equal labor supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A market that experiences both strikes and lockouts at different times is most likely characterized by
A)Monopoly.
B)Monopsony.
C)Bilateral monopoly.
A)Monopoly.
B)Monopsony.
C)Bilateral monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A market with one buyer and one seller is a
A)Bilateral monopsony.
B)Multiopoly.
C)Bilateral monopoly.
A)Bilateral monopsony.
B)Multiopoly.
C)Bilateral monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A profit-maximizing monopsonist will hire the quantity of labor where
A)MRP equals the wage rate.
B)MRP equals zero.
C)MRP equals MFC.
A)MRP equals the wage rate.
B)MRP equals zero.
C)MRP equals MFC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Suppose a firm finds that it must raise wages for all of its workers every time it tries to expand its workforce.This means
A)It will produce more than it would in a competitive labor market.
B)The marginal factor cost curve is below the average cost of labor curve.
C)The firm has market power.
A)It will produce more than it would in a competitive labor market.
B)The marginal factor cost curve is below the average cost of labor curve.
C)The firm has market power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When only one buyer has access to a particular labor market,
A)A monopoly exists.
B)There is no seller concentration.
C)A monopsony exists.
A)A monopoly exists.
B)There is no seller concentration.
C)A monopsony exists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Compared with a competitive market,a monopsonist will pay a ________ wage and hire ________ workers.
A)higher;fewer
B)higher;more
C)lower;fewer
A)higher;fewer
B)higher;more
C)lower;fewer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The labor share of total income is the proportion of total income earned by
A)The unionized workforce.
B)The nonunionized workforce.
C)All workers.
A)The unionized workforce.
B)The nonunionized workforce.
C)All workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The decline in unionization can be explained by all of the following except
A)Increased worldwide investment barriers.
B)Increased global competition.
C)Downsizing of major corporations.
A)Increased worldwide investment barriers.
B)Increased global competition.
C)Downsizing of major corporations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
When a strike or a lockout occurs,
A)Only labor suffers.
B)Both labor and management suffer.
C)Only management suffers.
A)Only labor suffers.
B)Both labor and management suffer.
C)Only management suffers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
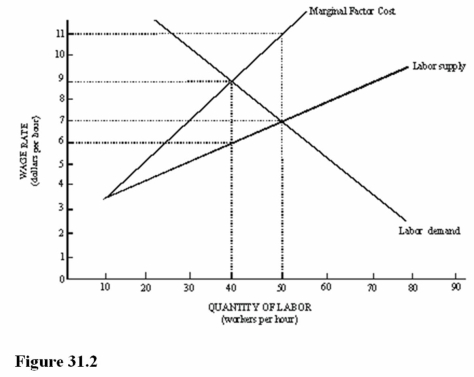
In Figure 31.2,what is the difference between the marginal revenue product of the last worker hired by the monopsonist and the wages the monopsonist pays the last worker?
A)$3 per hour.
B)$5 per hour.
C)$4 per hour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
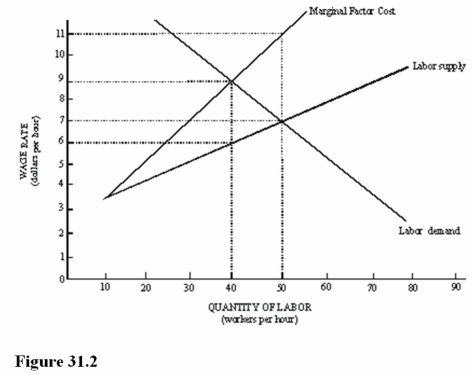
Refer to Figure 31.2.What is the competitive level of wages and employment?
A)$11 per hour and 50 workers.
B)$9 per hour and 40 workers.
C)$7 per hour and 50 workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The effect of union exclusion of nonunion workers is to
A)Increase the shortages of nonunion workers.
B)Reduce the wages of nonunion workers.
C)Increase the number of jobs for nonunion workers.
A)Increase the shortages of nonunion workers.
B)Reduce the wages of nonunion workers.
C)Increase the number of jobs for nonunion workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Refer to Figure 31.3 for a competitive labor market. 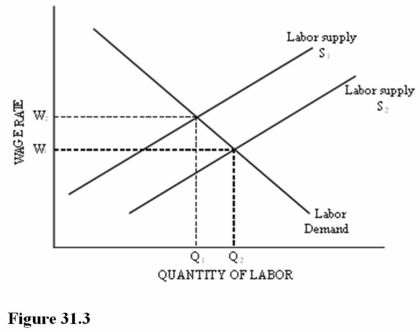 A shift in labor supply from S1 to S2 could be caused by:.
A shift in labor supply from S1 to S2 could be caused by:.
A)An increase in the wage rate.
B)The unionization of another labor market.
C)An increase in the price of the product being produced.
 A shift in labor supply from S1 to S2 could be caused by:.
A shift in labor supply from S1 to S2 could be caused by:.A)An increase in the wage rate.
B)The unionization of another labor market.
C)An increase in the price of the product being produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Productivity is
A)The inverse of cost efficiency.
B)Output per unit of input.
C)The increment of output produced when one more unit of an input is employed in the production process.
A)The inverse of cost efficiency.
B)Output per unit of input.
C)The increment of output produced when one more unit of an input is employed in the production process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
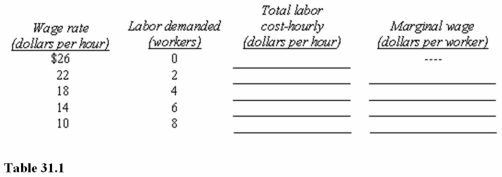
Table 31.1 shows the number of workers a firm is willing to hire per hour at different wage rates.Complete the table by computing the total wage bill (total labor cost)and the marginal wage.Assume the union collects dues of 1 percent of the total wage bill.At what wage in Table 31.1 would the union maximize the amount of dues it collects?
A)$10 per hour.
B)$14 per hour.
C)$18 per hour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Union work rules may restrict productivity in all of the following ways except
A)Limiting the pace of production.
B)Restricting the types of jobs a particular individual can do.
C)Requiring a maximum number of workers for a certain task.
A)Limiting the pace of production.
B)Restricting the types of jobs a particular individual can do.
C)Requiring a maximum number of workers for a certain task.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Unions may lower real wages in the nonunion sector because
A)Nonunion firms have difficulty attracting skilled workers away from the unions.
B)Nonunion firms adjust wages to avoid the threat of unionization.
C)Workers who are displaced by higher wages in the unionized sector increase the labor supply in the nonunion sector.
A)Nonunion firms have difficulty attracting skilled workers away from the unions.
B)Nonunion firms adjust wages to avoid the threat of unionization.
C)Workers who are displaced by higher wages in the unionized sector increase the labor supply in the nonunion sector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
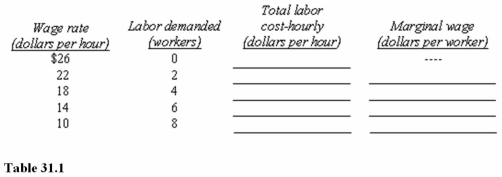
Table 31.1 shows the number of workers a firm is willing to hire per hour at different wage rates.Complete the table by computing the total wage bill (total labor cost)and the marginal wage.Which of the following wages,in Table 31.1,would allow the most workers to be hired?
A)$10 per hour.
B)$14 per hour.
C)$18 per hour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
One World View table titled "Union Membership" shows the unionization rates for several countries including the United States.The decline in the U.S.unionization rate is the result of
A)A relative decline in manufacturing.
B)A relative decline in service industries.
C)The growth of large firms relative to small firms.
A)A relative decline in manufacturing.
B)A relative decline in service industries.
C)The growth of large firms relative to small firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A firm that attempts to pass along the cost of higher union wages to consumers in the form of higher prices will be more successful if the price elasticity of demand for its product is
A)Inelastic.
B)Elastic.
C)Unitary.
A)Inelastic.
B)Elastic.
C)Unitary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The trend in the United States toward the merger of unions is driven by the labor movement's desire to accomplish all of the following except
A)Increase representation.
B)Avoid low-wage workers in service industries.
C)Gain financial strength.
A)Increase representation.
B)Avoid low-wage workers in service industries.
C)Gain financial strength.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Management's power in collective bargaining sessions rests on
A)The company's stock valuation.
B)The ability to lock out workers by closing stores or factories.
C)The ability to fire nonunionized workers.
A)The company's stock valuation.
B)The ability to lock out workers by closing stores or factories.
C)The ability to fire nonunionized workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77

What is the difference between the competitive level of employment and the union optimum level of employment in Figure 31.1?
A)22 workers.
B)6 workers.
C)3 workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The exercise of union power will tend to
A)Reduce the supply of labor available to nonunion industries.
B)Cause profits to be higher in unionized industries.
C)Increase the supply of labor available to nonunion industries.
A)Reduce the supply of labor available to nonunion industries.
B)Cause profits to be higher in unionized industries.
C)Increase the supply of labor available to nonunion industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Relative to nonunion wages,one reason union wages are
A)Higher is because unions are more likely in capital-intensive industries where wages tend to be higher.
B)Lower is because unions exclude workers from the market,which hurts their ability to raise wages.
C)Higher is because unions have workers that contribute more to society.
A)Higher is because unions are more likely in capital-intensive industries where wages tend to be higher.
B)Lower is because unions exclude workers from the market,which hurts their ability to raise wages.
C)Higher is because unions have workers that contribute more to society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
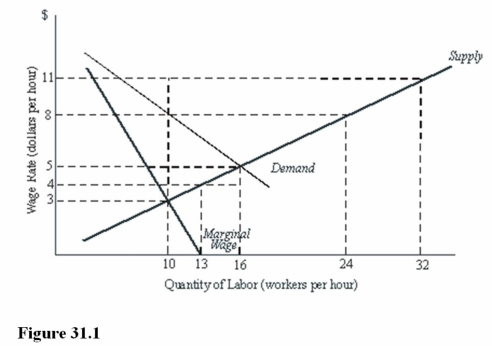
What are the competitive equilibrium wage and employment level in Figure 31.1?
A)$8;10 workers.
B)$5;16 workers.
C)$4;13 workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



