Deck 26: Monopolistic Competition
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/132
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 26: Monopolistic Competition
1
Monopolistically competitive firms have a "monopoly" element to them because
A)There is only one seller.
B)There are high barriers to entry.
C)Brand loyalty gives them a captive audience.
A)There is only one seller.
B)There are high barriers to entry.
C)Brand loyalty gives them a captive audience.
Brand loyalty gives them a captive audience.
2
If there are many firms in an industry producing goods that are similar but slightly different,this is an example of
A)Perfect competition.
B)Monopolistic competition.
C)Oligopoly.
A)Perfect competition.
B)Monopolistic competition.
C)Oligopoly.
Monopolistic competition.
3
One of the main differences between an oligopoly and a monopolistically competitive firm is that a monopolistically competitive firm
A)Faces a horizontal demand curve;an oligopoly does not.
B)Is relatively independent;an oligopoly is interdependent.
C)Has no market power;an oligopoly has some market power.
A)Faces a horizontal demand curve;an oligopoly does not.
B)Is relatively independent;an oligopoly is interdependent.
C)Has no market power;an oligopoly has some market power.
Is relatively independent;an oligopoly is interdependent.
4
A major difference between oligopoly and monopolistic competition is that monopolistically competitive firms and oligopolies do not
A)Have high concentration ratios.
B)Have many competitors.
C)Have high barriers to entry.
A)Have high concentration ratios.
B)Have many competitors.
C)Have high barriers to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is similar for oligopoly and monopolistic competition?
A)Both have many firms.
B)Both have low concentration ratios.
C)Both have market power.
A)Both have many firms.
B)Both have low concentration ratios.
C)Both have market power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The kinked oligopoly demand curve does not describe the demand curve for monopolistic competition because in monopolistically competitive markets,
A)Firms are not as interdependent as oligopolistic firms.
B)Firms have no market power.
C)There is not as much product differentiation as in oligopoly.
A)Firms are not as interdependent as oligopolistic firms.
B)Firms have no market power.
C)There is not as much product differentiation as in oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Each producer in monopolistic competition has
A)Complete market power.
B)Substantial market power.
C)Some market power.
A)Complete market power.
B)Substantial market power.
C)Some market power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following characterizes monopolistic competition?
A)Many interdependent firms sell a homogeneous product.
B)A few firms produce a particular type of product.
C)Many firms produce a particular type of product,but each maintains some independent control over its own price.
A)Many interdependent firms sell a homogeneous product.
B)A few firms produce a particular type of product.
C)Many firms produce a particular type of product,but each maintains some independent control over its own price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Entry into a market characterized by monopolistic competition is generally
A)Entirely blocked by existing firms.
B)Very easy because few barriers exist.
C)As difficult as in oligopoly.
A)Entirely blocked by existing firms.
B)Very easy because few barriers exist.
C)As difficult as in oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Product differentiation refers to
A)Features that make one product appear different from competing products in the same market.
B)Different prices for the same product in a certain market.
C)The selling of identical products in different markets.
A)Features that make one product appear different from competing products in the same market.
B)Different prices for the same product in a certain market.
C)The selling of identical products in different markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In monopolistic competition,a firm
A)Has no market power.
B)Captures significant economies of scale.
C)Has a downward-sloping demand curve.
A)Has no market power.
B)Captures significant economies of scale.
C)Has a downward-sloping demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The combined market share of the top four firms in a monopolistically competitive industry will typically be in the range of
A)Zero to 2 percent.
B)Zero to 5 percent.
C)20 to 40 percent.
A)Zero to 2 percent.
B)Zero to 5 percent.
C)20 to 40 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A concentration ratio measures the
A)Proportion of industry output produced by all firms.
B)Proportion of industry output produced by the largest firms.
C)Dollar value of total industry output produced by all firms.
A)Proportion of industry output produced by all firms.
B)Proportion of industry output produced by the largest firms.
C)Dollar value of total industry output produced by all firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following most characterizes monopolistic competition?
A)Price leadership.
B)Product differentiation.
C)Price discrimination.
A)Price leadership.
B)Product differentiation.
C)Price discrimination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Product differentiation occurs when
A)A completely new process is used to produce a familiar product.
B)One firm produces many varieties of a product.
C)Buyers perceive differences in the products of several companies.
A)A completely new process is used to produce a familiar product.
B)One firm produces many varieties of a product.
C)Buyers perceive differences in the products of several companies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The demand curve faced by a monopolistically competitive firm is
A)Downward-sloping.
B)Flat.
C)Kinked.
A)Downward-sloping.
B)Flat.
C)Kinked.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A major difference between monopoly and monopolistic competition is
A)One maximizes profits by setting MR equal to MC,and the other does not.
B)The number of firms in the market.
C)One type of firm has market power,and the other does not.
A)One maximizes profits by setting MR equal to MC,and the other does not.
B)The number of firms in the market.
C)One type of firm has market power,and the other does not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If a monopolistically competitive firm raises its price,it will
A)Not lose any of its customers.
B)Lose most of its customers.
C)Lose some of its customers,but nowhere close to all its customers.
A)Not lose any of its customers.
B)Lose most of its customers.
C)Lose some of its customers,but nowhere close to all its customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Monopolistically competitive industries are characterized by all of the following except
A)Homogenous products.
B)Low entry barriers.
C)Low concentration ratios.
A)Homogenous products.
B)Low entry barriers.
C)Low concentration ratios.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The competitive dimension of monopolistic competition is that
A)High barriers to entry tend to push economic profits toward zero.
B)Consumers view each firm's products as interchangeable.
C)Low barriers to entry tend to push economic profits toward zero.
A)High barriers to entry tend to push economic profits toward zero.
B)Consumers view each firm's products as interchangeable.
C)Low barriers to entry tend to push economic profits toward zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Entry into a market characterized by monopolistic competition
A)Is rare because firms have market power.
B)Is frequent because barriers to entry are low.
C)Occurs when a firm's demand is everywhere below its long-run average cost curve.
A)Is rare because firms have market power.
B)Is frequent because barriers to entry are low.
C)Occurs when a firm's demand is everywhere below its long-run average cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The main difference between perfect competition and monopolistic competition is
A)The degree of product differentiation.
B)The long-run economic profits that are expected.
C)The number of firms in the market.
A)The degree of product differentiation.
B)The long-run economic profits that are expected.
C)The number of firms in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In monopolistic competition,a firm's demand curve is tangent to the ATC curve in the long run because
A)Barriers to entry are high.
B)Entry eliminates economic profit,and exit eliminates losses.
C)Advertising is ineffective in differentiating the product.
A)Barriers to entry are high.
B)Entry eliminates economic profit,and exit eliminates losses.
C)Advertising is ineffective in differentiating the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If a monopolistic competitor is maximizing profit,it is producing at a point where marginal cost
A)Is less than price.
B)Equals price.
C)Is greater than price.
A)Is less than price.
B)Equals price.
C)Is greater than price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A monopolistically competitive firm can raise its price somewhat without fear of great change in unit sales because
A)The demand for its product is typically very price-elastic.
B)Its demand curve is horizontal.
C)Of product differentiation and brand loyalty.
A)The demand for its product is typically very price-elastic.
B)Its demand curve is horizontal.
C)Of product differentiation and brand loyalty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Brand loyalty usually makes the demand curve for a product
A)More price-elastic.
B)Less price-elastic.
C)Unitary elastic.
A)More price-elastic.
B)Less price-elastic.
C)Unitary elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Firms in a monopolistically competitive market will
A)Produce efficiently.
B)Make economic profits in the long run.
C)Use the profit-maximizing rule MC = MR.
A)Produce efficiently.
B)Make economic profits in the long run.
C)Use the profit-maximizing rule MC = MR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
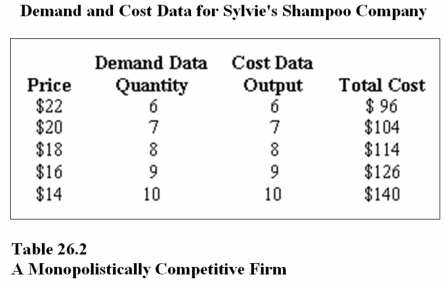
Refer to Table 26.2.To maximize profit,Sylvie's Shampoo Company.should produce _______ bottles of shampoo and charge a price of _______ each.
A)6;$22
B)7;$20
C)8;$18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
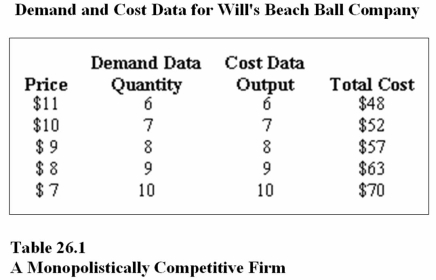
Refer to Table 26.1.At the profit-maximizing output and price,Will's Beach Ball Company will earn a profit equal to
A)$18.
B)$70.
C)$72.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When a monopolistically competitive firm advertises,it is attempting to increase
A)The demand and decrease the price elasticity of demand for its product.
B)The demand and increase the price elasticity of demand for its product.
C)Long-run profits.
A)The demand and decrease the price elasticity of demand for its product.
B)The demand and increase the price elasticity of demand for its product.
C)Long-run profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Large cities typically have many drugstores that offer different levels of service and product selection.The drugstore market in big cities can best be classified as
A)A competitive market.
B)Monopolistic competition.
C)Oligopoly.
A)A competitive market.
B)Monopolistic competition.
C)Oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The cross-price elasticity of demand for the products of monopolistically competitive firms is
A)Very high.
B)Low.
C)An indication that most of the products are complementary goods.
A)Very high.
B)Low.
C)An indication that most of the products are complementary goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A monopolistically competitive firm maximizes profits or minimizes losses in the short run by
A)Setting price equal to marginal cost.
B)Producing at the output level where ATC is minimized.
C)Producing at the output level where MR equals MC.
A)Setting price equal to marginal cost.
B)Producing at the output level where ATC is minimized.
C)Producing at the output level where MR equals MC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is an example of product differentiation?
A)Two shampoos differ only in their labels,but consumers pay $0.20 more for the label they recognize.
B)Sugar can be made from sugar beets or sugar cane,and consumers cannot tell the difference.
C)Consumers substitute SUVs for cars because SUVs accommodate more passengers.
A)Two shampoos differ only in their labels,but consumers pay $0.20 more for the label they recognize.
B)Sugar can be made from sugar beets or sugar cane,and consumers cannot tell the difference.
C)Consumers substitute SUVs for cars because SUVs accommodate more passengers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Brand loyalty
A)Makes the demand curve facing the firm more price-elastic.
B)Leads to one price for all brands.
C)Exists even when products are virtually identical.
A)Makes the demand curve facing the firm more price-elastic.
B)Leads to one price for all brands.
C)Exists even when products are virtually identical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
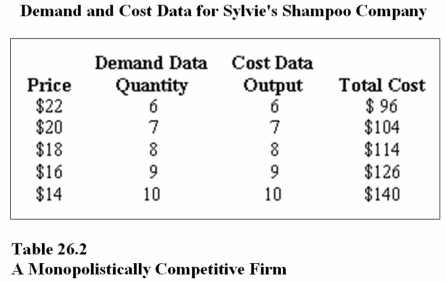
Refer to Table 26.2.At the profit-maximizing output and price,Sylvie's Shampoo Company.will earn a profit equal to
A)$36.
B)$30.
C)$140.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Cross price elasticity measures
A)The change in quantity demanded for one good due to a change in the price of another good.
B)How sensitive quantity demanded is to a change in price.
C)The change in quantity demanded when income changes.
A)The change in quantity demanded for one good due to a change in the price of another good.
B)How sensitive quantity demanded is to a change in price.
C)The change in quantity demanded when income changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
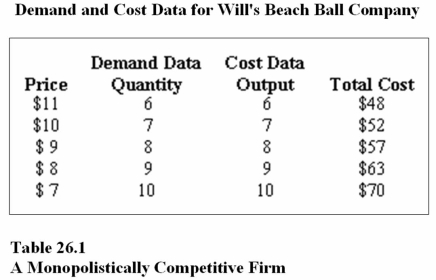
Refer to Table 26.1.In order to maximize profit,Will's Beach Ball Company should produce _______ and charge a price of _______ each.
A)6 beach balls;$11
B)7 beach balls;$10
C)8 beach balls;$9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A monopolistically competitive firm can raise its price somewhat without fear of great change in unit sales because of
A)Brand loyalty.
B)Economies of scale.
C)Inelastic demand.
A)Brand loyalty.
B)Economies of scale.
C)Inelastic demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
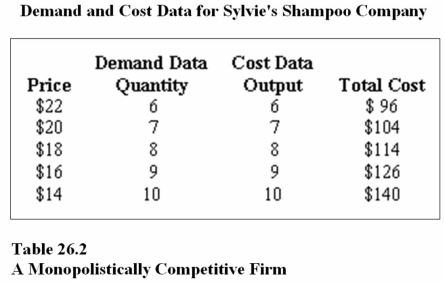
Refer to Table 26.2.At the profit-maximizing output and price,Sylvie's Shampoo Company.will earn a ________ economic profit,and ________ the market will occur.
A)negative;entry into
B)negative;exit from
C)positive;entry into

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In a monopolistically competitive market with negative economic profits,
A)Firms will enter until accounting profits are zero.
B)Firms will enter until economic profits are zero.
C)Firms will exit until economic profits are zero.
A)Firms will enter until accounting profits are zero.
B)Firms will enter until economic profits are zero.
C)Firms will exit until economic profits are zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following market structures will have only normal profit in the long run?
A)Monopoly.
B)Duopoly.
C)Monopolistic competition.
A)Monopoly.
B)Duopoly.
C)Monopolistic competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When new firms enter a monopolistically competitive industry,ceteris paribus,the
A)Market price decreases.
B)Market price increases.
C)Market price remains unchanged.
A)Market price decreases.
B)Market price increases.
C)Market price remains unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
One of the reasons for low cross-price elasticity in monopolistic competition and high cross-price elasticity in perfect competition is that
A)Firms in perfect competition differentiate their products.
B)In monopolistic competition brand loyal consumers view other available products as poor substitutes.
C)Consumers do not have perfect substitutes in perfect competition.
A)Firms in perfect competition differentiate their products.
B)In monopolistic competition brand loyal consumers view other available products as poor substitutes.
C)Consumers do not have perfect substitutes in perfect competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Both perfect competitors and monopolistic competitors
A)Experience product differentiation.
B)Earn zero economic profit in the long run.
C)Find prices pushed to the minimum of long-run ATC by entry.
A)Experience product differentiation.
B)Earn zero economic profit in the long run.
C)Find prices pushed to the minimum of long-run ATC by entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following market structures will have lower prices in the long run than monopoly,ceteris paribus?
A)Perfect competition,oligopoly,and monopolistic competition.
B)Perfect competition,but not oligopoly or monopolistic competition.
C)Perfect competition and oligopoly,but not monopolistic competition.
A)Perfect competition,oligopoly,and monopolistic competition.
B)Perfect competition,but not oligopoly or monopolistic competition.
C)Perfect competition and oligopoly,but not monopolistic competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following characterizes the difference between oligopoly and monopolistic competition?
A)Oligopolists are independent of each other;monopolistically competitive firms are interdependent.
B)Monopolistically competitive firms experience zero long-run economic profit;oligopolists may experience positive long-run economic profit.
C)There are many oligopolists but only a few monopolistically competitive firms.
A)Oligopolists are independent of each other;monopolistically competitive firms are interdependent.
B)Monopolistically competitive firms experience zero long-run economic profit;oligopolists may experience positive long-run economic profit.
C)There are many oligopolists but only a few monopolistically competitive firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If economic profits are earned in a monopolistically competitive market,
A)More firms will enter the market.
B)The market supply curve will shift to the left.
C)Price will rise.
A)More firms will enter the market.
B)The market supply curve will shift to the left.
C)Price will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the short run,a monopolistically competitive firm
A)May make economic profits,but it fails to make economic profits in the long run because of the entry of new firms.
B)May make profits just as it does in the long run because firms can enter easily.
C)Produces at a rate at which long-run average cost equals price,but not at which long-run marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
A)May make economic profits,but it fails to make economic profits in the long run because of the entry of new firms.
B)May make profits just as it does in the long run because firms can enter easily.
C)Produces at a rate at which long-run average cost equals price,but not at which long-run marginal cost equals marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is true about a monopolistically competitive firm in the long run?
A)It is as efficient as a purely competitive firm.
B)It tends to realize only a normal profit.
C)It produces at the level where costs are minimized.
A)It is as efficient as a purely competitive firm.
B)It tends to realize only a normal profit.
C)It produces at the level where costs are minimized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If new firms enter a monopolistically competitive market,the demand curves for the existing firms will
A)Shift to the left.
B)Shift to the right.
C)Remain unchanged.
A)Shift to the left.
B)Shift to the right.
C)Remain unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is true about a monopolistically competitive industry?
A)Marginal cost pricing occurs.
B)There is excess capacity.
C)Resources are allocated efficiently.
A)Marginal cost pricing occurs.
B)There is excess capacity.
C)Resources are allocated efficiently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Monopolistic competition results in
A)Allocative efficiency.
B)Production efficiency.
C)The wrong mix of output.
A)Allocative efficiency.
B)Production efficiency.
C)The wrong mix of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When new firms enter a monopolistically competitive industry,the market
A)Supply curve shifts to the left.
B)Supply curve shifts to the right.
C)Demand curve shifts to the left.
A)Supply curve shifts to the left.
B)Supply curve shifts to the right.
C)Demand curve shifts to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In monopolistic competition,the entry of new firms will cause all of the following to happen except
A)Long-run economic profits will be zero.
B)The industry cost curves will shift to the left.
C)The firm's demand curve will shift to the left.
A)Long-run economic profits will be zero.
B)The industry cost curves will shift to the left.
C)The firm's demand curve will shift to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If new firms enter a monopolistically competitive market,the demand curves for the existing firms will shift to the
A)Left and become more price-inelastic.
B)Left,and there will be no change in price elasticity.
C)Left and become more price-elastic.
A)Left and become more price-inelastic.
B)Left,and there will be no change in price elasticity.
C)Left and become more price-elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following market structures will have lower output in the long run than perfect competition,ceteris paribus?
A)Monopolistic competition,but not oligopoly or monopoly.
B)Monopolistic competition,oligopoly,and monopoly.
C)Monopolistic competition and oligopoly,but not monopoly.
A)Monopolistic competition,but not oligopoly or monopoly.
B)Monopolistic competition,oligopoly,and monopoly.
C)Monopolistic competition and oligopoly,but not monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following market structures will have higher output in the long run than monopolistic competition,ceteris paribus?
A)Perfect competition.
B)Monopoly.
C)Duopoly.
A)Perfect competition.
B)Monopoly.
C)Duopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following characterizes monopolistic competition?
A)Price leadership.
B)Zero long-run profit.
C)Retaliation.
A)Price leadership.
B)Zero long-run profit.
C)Retaliation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
For which of the following market structures will the firm's demand curve be tangent to the ATC curve in the long run?
A)Duopoly.
B)Monopolistic competition.
C)Oligopoly.
A)Duopoly.
B)Monopolistic competition.
C)Oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
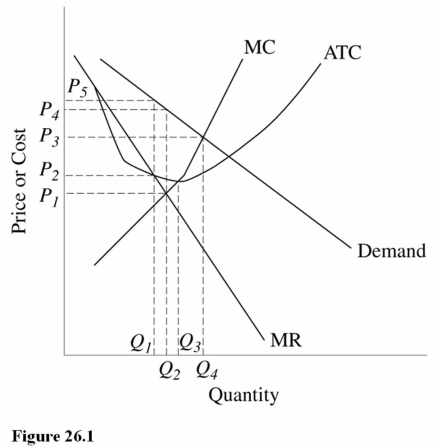
Refer to Figure 26.1.The output that maximizes production efficiency for this firm is
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Q3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
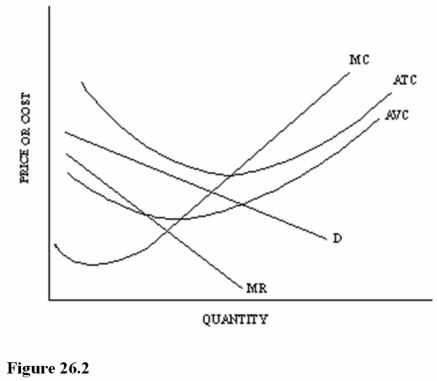
Refer to Figure 26.2 for a monopolistically competitive firm.At the profit-maximizing output and price,this firm is
A)Earning an economic profit.
B)Earning an economic loss.
C)Breaking even.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In monopolistic competition,a firm
A)Uses marginal cost pricing.
B)Uses nonprice competition.
C)Faces a horizontal demand curve.
A)Uses marginal cost pricing.
B)Uses nonprice competition.
C)Faces a horizontal demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Monopolistically competitive firms are productively inefficient because long-run equilibrium occurs at an output rate where
A)MC is greater than MR.
B)Price is greater than MC.
C)ATC is greater than minimum ATC.
A)MC is greater than MR.
B)Price is greater than MC.
C)ATC is greater than minimum ATC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
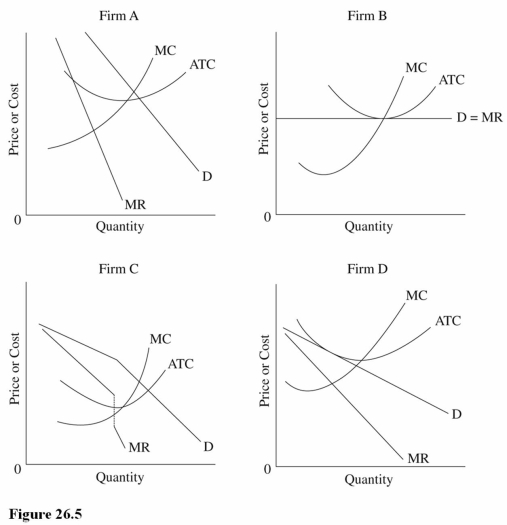
Refer to Figure 26.5.Which firm is producing the allocatively efficient level of output and is using the least amount of economic resources to produce each unit of output?
A)All of the firms.
B)Firms B and D only.
C)Firm B only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which type of firm engages in nonprice competition?
A)Monopolistically competitive firms.
B)Perfectly competitive firms.
C)Price takers.
A)Monopolistically competitive firms.
B)Perfectly competitive firms.
C)Price takers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
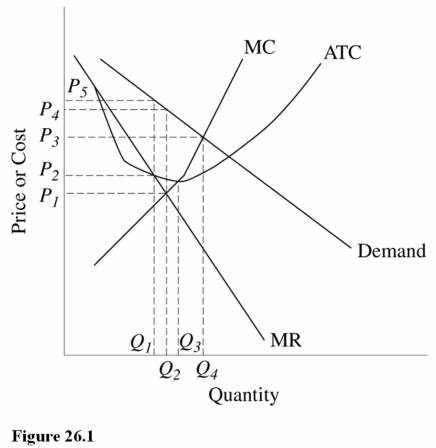
Refer to Figure 26.1.The output level that will be produced by this firm in the long run is
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Q3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
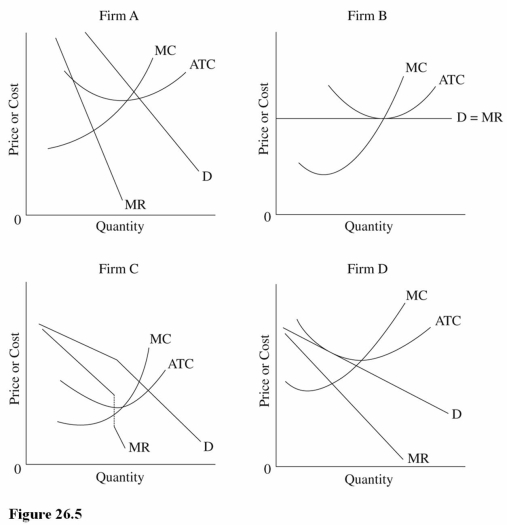
Which firm in Figure 26.5 is producing at the output level that maximizes production efficiency?
A)Firms A and C only.
B)Firm A only.
C)Firm B only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
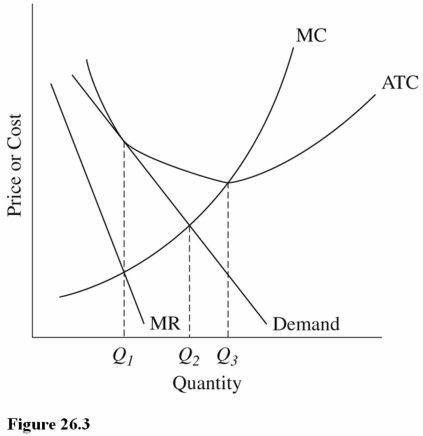
Refer to Figure 26.3 for a monopolistically competitive firm in the long run.Which of the following observations results in the problem of excess capacity?
A)The firm is producing less than the minimum-ATC output rate.
B)The firm is producing at Q3 instead of where MR = MC.
C)The firm is earning only zero economic profits in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
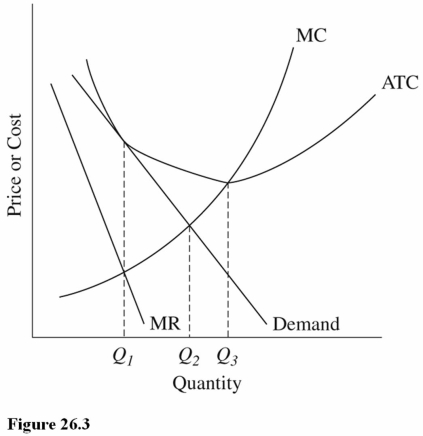
Refer to Figure 26.3 for a monopolistically competitive firm.The allocatively efficient output for this firm is
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Q3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Monopolistic competition results in allocative
A)Inefficiency and productive efficiency.
B)Inefficiency and productive inefficiency.
C)Efficiency and productive efficiency.
A)Inefficiency and productive efficiency.
B)Inefficiency and productive inefficiency.
C)Efficiency and productive efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
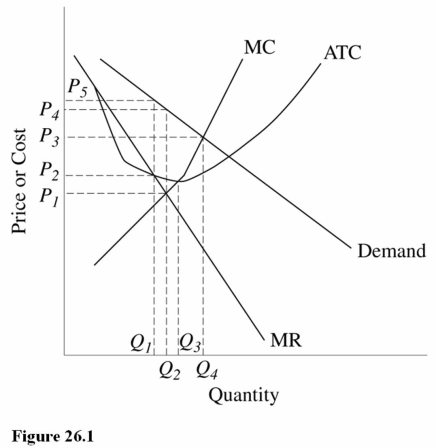
Refer to Figure 26.1 for a monopolistically competitive firm.The profit-maximizing output and price combination for this firm in the short run is
A)Q1,P1.
B)Q2,P4.
C)Q2,P1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Suppose that an economy wants to eliminate the resource waste associated with excess capacity in monopolistically competitive markets.Which of the following would achieve this goal?
A)Firms are allowed to establish significant barriers to entry.
B)Firms are encouraged to produce less output.
C)Firms are required to set price equal to marginal cost.
A)Firms are allowed to establish significant barriers to entry.
B)Firms are encouraged to produce less output.
C)Firms are required to set price equal to marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
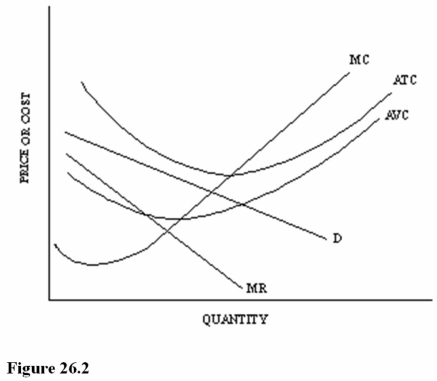
Refer to Figure 26.2 for a monopolistically competitive firm.At the profit-maximizing output and price,this firm is experiencing economic
A)Profits and should stay in this market in the long run.
B)Profits but could make even higher economic profits producing the next best alternative good.
C)Losses but should keep producing in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
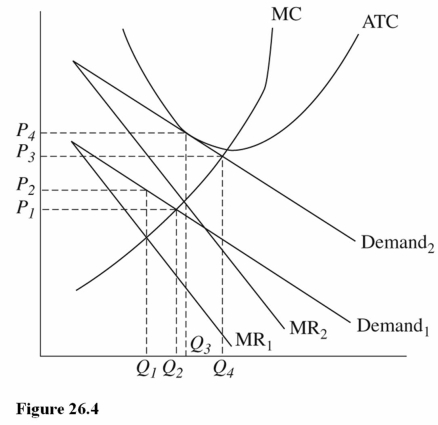
Refer to Figure 26.4 for a monopolistically competitive firm.If the firm currently faces Demand1 and MR1,then it will earn
A)A positive economic profit,and firms will enter the industry.
B)A negative economic profit,and firms will enter the industry.
C)A negative economic profit,and firms will exit the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following real-world situations is the result of excess capacity in a monopolistically competitive market?
A)A factory producing women's clothing produces more than it can sell during a season.
B)Gas stations with infrequently used pumps are located at all four corners of an intersection.
C)A retail auto tire store orders too much inventory.
A)A factory producing women's clothing produces more than it can sell during a season.
B)Gas stations with infrequently used pumps are located at all four corners of an intersection.
C)A retail auto tire store orders too much inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Compared to the outcome under a marginal cost pricing strategy,a monopolistically competitive firm will produce a
A)Lower output and charge a higher price.
B)Greater output and charge a higher price.
C)Lower output and charge a lower price.
A)Lower output and charge a higher price.
B)Greater output and charge a higher price.
C)Lower output and charge a lower price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
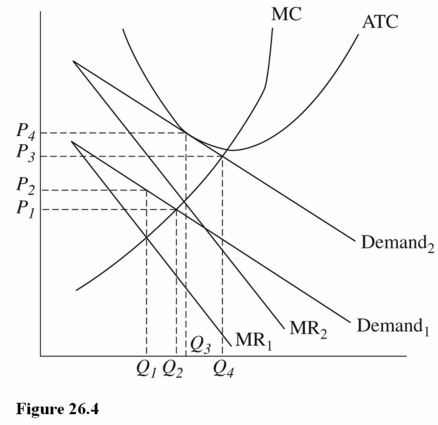
Refer to Figure 26.4 for a monopolistically competitive firm.In the long run this firm is most likely to face
A)Demand1 and MR1.
B)Demand1 and MR2.
C)Demand2 and MR2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79

Which firm in Figure 26.5 is using marginal cost pricing?
A)Firms B and D only.
B)Firm B only.
C)Firm C only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
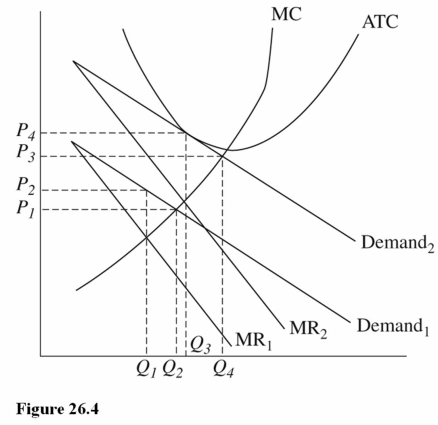
Refer to Figure 26.4 for a monopolistically competitive firm.In the long run this firm will charge a price of ________ and produce an output of _______.
A)P2;Q1
B)P4; Q3
C)P1; Q2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



