Deck 27: Natural Monopolies: Deregulation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/122
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 27: Natural Monopolies: Deregulation
1
Market failure can result from all of the following except
A)Market power.
B)Regulation.
C)Restricted output.
A)Market power.
B)Regulation.
C)Restricted output.
Regulation.
2
A natural monopoly occurs because of
A)Legal restrictions preventing entry into the industry.
B)Low fixed costs.
C)The existence of economies of scale.
A)Legal restrictions preventing entry into the industry.
B)Low fixed costs.
C)The existence of economies of scale.
The existence of economies of scale.
3
An industry in which one firm can achieve economies of scale over the entire range of market supply is a
A)Contestable market.
B)Kinked demand curve oligopoly.
C)Natural monopoly.
A)Contestable market.
B)Kinked demand curve oligopoly.
C)Natural monopoly.
Natural monopoly.
4
To maximize profit,a natural monopolist produces the level of output at which
A)Price equals marginal cost.
B)Price equals average total cost.
C)Marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
A)Price equals marginal cost.
B)Price equals average total cost.
C)Marginal revenue equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The major aim of government regulation is to
A)Control the structure of an industry.
B)Alter industry behavior.
C)Prevent monopolies from forming.
A)Control the structure of an industry.
B)Alter industry behavior.
C)Prevent monopolies from forming.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Economies of scale refer to the
A)Reduction in minimum average costs due to an increase in the number of workers hired.
B)Reduction in minimum average costs due to an increase in plant size.
C)Downward-sloping portion of the marginal cost curve.
A)Reduction in minimum average costs due to an increase in the number of workers hired.
B)Reduction in minimum average costs due to an increase in plant size.
C)Downward-sloping portion of the marginal cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following can the government use to alter both firm behavior and industry structure?
A)Deregulation.
B)Regulation.
C)Antitrust laws.
A)Deregulation.
B)Regulation.
C)Antitrust laws.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is a form of government intervention?
A)Natural monopoly.
B)Public goods.
C)Regulation.
A)Natural monopoly.
B)Public goods.
C)Regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is a form of government intervention that is designed to correct market failures?
A)Antitrust laws.
B)Laissez faire.
C)Public goods.
A)Antitrust laws.
B)Laissez faire.
C)Public goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The long-run average total cost curve of a natural monopolist
A)Is U-shaped.
B)Reflects declining average fixed costs.
C)Falls continuously as more output is produced.
A)Is U-shaped.
B)Reflects declining average fixed costs.
C)Falls continuously as more output is produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An unregulated natural monopoly can lead to
A)Higher prices for consumers.
B)An optimal mix of output.
C)Loss of economies of scale.
A)Higher prices for consumers.
B)An optimal mix of output.
C)Loss of economies of scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Market failure
A)Occurs whenever the government intervenes in the market mechanism.
B)Occurs whenever the government pursues laissez-faire policies.
C)Occurs whenever an imperfection in the market mechanism prevents optimal outcomes.
A)Occurs whenever the government intervenes in the market mechanism.
B)Occurs whenever the government pursues laissez-faire policies.
C)Occurs whenever an imperfection in the market mechanism prevents optimal outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
All of the following are examples of natural monopolies except
A)Local telephone companies.
B)Electricity companies.
C)College bookstores.
A)Local telephone companies.
B)Electricity companies.
C)College bookstores.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If a natural monopoly was broken into several smaller competing firms,
A)Consumers would lose because of less competition.
B)Producers would be better off because they would have greater market share.
C)Society would be worse off because the economies of scale would be destroyed.
A)Consumers would lose because of less competition.
B)Producers would be better off because they would have greater market share.
C)Society would be worse off because the economies of scale would be destroyed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The long-run average total cost curve of a natural monopolist
A)Is downward-sloping in the relevant range of production.
B)Is U-shaped.
C)Reflects diseconomies of scale.
A)Is downward-sloping in the relevant range of production.
B)Is U-shaped.
C)Reflects diseconomies of scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A natural monopoly is a desirable market structure because
A)It allows the producer to earn greater profit than is possible under competition.
B)It allows the producer to deliver a higher-quality product to the market.
C)It allows the producer to deliver products to the market at the lowest possible cost.
A)It allows the producer to earn greater profit than is possible under competition.
B)It allows the producer to deliver a higher-quality product to the market.
C)It allows the producer to deliver products to the market at the lowest possible cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When firms have the ability to restrict output,raise prices,stifle competition,and inhibit innovation,the market failure involved is
A)Public goods.
B)Externalities.
C)Market power.
A)Public goods.
B)Externalities.
C)Market power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Antitrust enforcement focuses on market structure,while government regulation deals with all of the following except
A)Prices.
B)Output.
C)Perfect competition.
A)Prices.
B)Output.
C)Perfect competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If a natural monopoly was forced to break up into several small competitive firms,the
A)Cost of production should fall as the smaller firms become more efficient.
B)Price charged by the competitive firms should decrease as the firms become more efficient.
C)Price charged by the competitive firms should increase because they no longer have economies of scale.
A)Cost of production should fall as the smaller firms become more efficient.
B)Price charged by the competitive firms should decrease as the firms become more efficient.
C)Price charged by the competitive firms should increase because they no longer have economies of scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When the market does not lead to an optimal allocation of resources,there must be
A)Too much regulation.
B)A market failure.
C)Proper antitrust laws in place.
A)Too much regulation.
B)A market failure.
C)Proper antitrust laws in place.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Profit regulation occurs when regulation requires the natural monopolist to set
A)Price equal to average total cost.
B)Price equal to marginal cost.
C)Marginal revenue equal to average total cost.
A)Price equal to average total cost.
B)Price equal to marginal cost.
C)Marginal revenue equal to average total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If a natural monopoly is forced to use marginal cost pricing,which of the following is not true?
A)Average total costs increase.
B)Output increases.
C)Allocative efficiency is achieved.
A)Average total costs increase.
B)Output increases.
C)Allocative efficiency is achieved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If the government regulated a natural monopolist to achieve price efficiency without subsidies or price discrimination,the monopolist would
A)Lose money and go out of business.
B)Earn only normal profits.
C)Earn economic profits.
A)Lose money and go out of business.
B)Earn only normal profits.
C)Earn economic profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Output regulation is likely to result in
A)A surplus of the product.
B)A decline in the quality of the product.
C)An increase in the cost of subsidies.
A)A surplus of the product.
B)A decline in the quality of the product.
C)An increase in the cost of subsidies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If profit regulation is used to control a natural monopolist,the monopolist is likely to
A)Attempt to reduce the costs of production.
B)Inflate or pad the costs of production.
C)Increase the quality of its product in an effort to increase sales.
A)Attempt to reduce the costs of production.
B)Inflate or pad the costs of production.
C)Increase the quality of its product in an effort to increase sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A major drawback of providing subsidies to private companies that are natural monopolies is that
A)Taxpayers dislike this use of their tax dollars.
B)Private companies are less efficient than public companies.
C)The companies have no incentive to limit costs.
A)Taxpayers dislike this use of their tax dollars.
B)Private companies are less efficient than public companies.
C)The companies have no incentive to limit costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If the government forces a natural monopoly to produce the output level at which P = MC,the firm will
A)Fail to produce efficiently.
B)Produce less than the profit-maximizing level of output.
C)Incur losses.
A)Fail to produce efficiently.
B)Produce less than the profit-maximizing level of output.
C)Incur losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A natural monopoly can purposely increase its cost of production by
A)Using its own unregulated subsidiary to inflate its cost.
B)Substituting cheaper inputs.
C)Keeping marginal costs low.
A)Using its own unregulated subsidiary to inflate its cost.
B)Substituting cheaper inputs.
C)Keeping marginal costs low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Profit regulation of a natural monopoly is achieved when
A)P = ATC.
B)P = MC.
C)MR = MC.
A)P = ATC.
B)P = MC.
C)MR = MC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An unregulated natural monopoly is most likely to
A)Earn an economic profit.
B)Produce where marginal cost equals price.
C)Charge a lower price than if the same product were produced in a competitive market because of the monopolist's greater technical efficiency.
A)Earn an economic profit.
B)Produce where marginal cost equals price.
C)Charge a lower price than if the same product were produced in a competitive market because of the monopolist's greater technical efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A natural monopoly has an incentive to pad its cost of production under which type of regulation?
A)Price regulation.
B)Profit regulation.
C)Output regulation.
A)Price regulation.
B)Profit regulation.
C)Output regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Market failure occurs in natural monopolies because
A)The monopolist fails to maximize profits.
B)The monopolist charges a price lower than marginal cost.
C)Consumers get inaccurate information about the opportunity cost of the product.
A)The monopolist fails to maximize profits.
B)The monopolist charges a price lower than marginal cost.
C)Consumers get inaccurate information about the opportunity cost of the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Suppose the quality of service provided by a newly regulated firm begins to deteriorate soon after regulation is enforced.Which of the following types of regulation is most likely being used?
A)Price regulation.
B)Profit regulation.
C)Output regulation.
A)Price regulation.
B)Profit regulation.
C)Output regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Output regulation forces the natural monopolist to produce at an output
A)That perfectly competitive firms would choose.
B)Where MR = MC.
C)Greater than its profit-maximizing choice.
A)That perfectly competitive firms would choose.
B)Where MR = MC.
C)Greater than its profit-maximizing choice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is meant by price efficiency?
A)Price is greater than marginal cost.
B)Price is equal to marginal cost.
C)Price is equal to average total cost.
A)Price is greater than marginal cost.
B)Price is equal to marginal cost.
C)Price is equal to average total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If the government wants a natural monopolist to achieve allocative efficiency,the government should
A)Subsidize the firm and require marginal cost pricing.
B)Ensure that the firm produces at full capacity.
C)Regulate the firm so that it produces the output level at which economic profit is zero.
A)Subsidize the firm and require marginal cost pricing.
B)Ensure that the firm produces at full capacity.
C)Regulate the firm so that it produces the output level at which economic profit is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Marginal cost pricing means that a firm charges
A)A price that is marginally lower than the average total cost of production.
B)A price that is marginally higher than the average total cost of production.
C)A price that is equal to the marginal cost of production.
A)A price that is marginally lower than the average total cost of production.
B)A price that is marginally higher than the average total cost of production.
C)A price that is equal to the marginal cost of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is not a regulatory option when the government is trying to prevent market failure in the case of a natural monopoly?
A)Cost regulation.
B)Profit regulation.
C)Output regulation.
A)Cost regulation.
B)Profit regulation.
C)Output regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
For a natural monopolist,if costs start to climb once it is subject to government regulation,then it is most likely facing
A)Cost regulation.
B)Profit regulation.
C)Output regulation.
A)Cost regulation.
B)Profit regulation.
C)Output regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Compared with the profit-maximizing choice of a natural monopolist,output regulation will result in a
A)Higher level of output and a higher price.
B)Lower level of output and a higher price.
C)Higher level of output and a lower price.
A)Higher level of output and a higher price.
B)Lower level of output and a higher price.
C)Higher level of output and a lower price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The over 260,000 people employed in regulatory agencies of the federal government represent
A)A compliance cost.
B)An efficiency cost.
C)An administrative cost.
A)A compliance cost.
B)An efficiency cost.
C)An administrative cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Before deregulation of the telephone industry,
A)Telephone service prices were lower than after deregulation.
B)Cutthroat competition eliminated profits.
C)The volume of communication was lower than after deregulation.
A)Telephone service prices were lower than after deregulation.
B)Cutthroat competition eliminated profits.
C)The volume of communication was lower than after deregulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The case for deregulation rests on the argument that
A)Government imperfections are worse than the market imperfections they were designed to cure.
B)Public goods are best provided by laissez faire.
C)Economies of scale are better achieved with the invisible hand.
A)Government imperfections are worse than the market imperfections they were designed to cure.
B)Public goods are best provided by laissez faire.
C)Economies of scale are better achieved with the invisible hand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Prior to the deregulation of the railroad industry,there was little incentive to invest in new technology or equipment.This is an example of
A)The failure of deregulation.
B)The inefficiencies of regulation
C)Market failure.
A)The failure of deregulation.
B)The inefficiencies of regulation
C)Market failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The first major regulatory target in the United States was
A)Airlines.
B)Railroads.
C)Trucking firms.
A)Airlines.
B)Railroads.
C)Trucking firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Regulation is appropriate if
A)Government failure exists.
B)Market failure exists and the benefits of regulation exceed the costs.
C)It improves market outcomes regardless of costs.
A)Government failure exists.
B)Market failure exists and the benefits of regulation exceed the costs.
C)It improves market outcomes regardless of costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Government failure occurs when
A)Dealing with a natural monopoly.
B)There is market power.
C)Government intervention fails to improve economic outcomes.
A)Dealing with a natural monopoly.
B)There is market power.
C)Government intervention fails to improve economic outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which regulatory cost is borne by the firms that are regulated?
A)Efficiency costs.
B)Subsidy costs.
C)Compliance costs.
A)Efficiency costs.
B)Subsidy costs.
C)Compliance costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Before the deregulation in telecommunications,AT&T charged higher rates on long-distance service in order to make local service rates lower.Such a practice is an example of
A)Price discrimination because different prices were charged for the same service.
B)The pricing of public goods.
C)Cross-subsidization of local phone service.
A)Price discrimination because different prices were charged for the same service.
B)The pricing of public goods.
C)Cross-subsidization of local phone service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When the FCC hires a new lawyer to help enforce government regulation,her salary is an example of
A)An administrative cost of regulation.
B)An efficiency cost of regulation.
C)A compliance cost of regulation.
A)An administrative cost of regulation.
B)An efficiency cost of regulation.
C)A compliance cost of regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The Braden brothers considered starting a new skydiving company.Once they read the government regulations they would have to comply with,they changed their minds.This is an example of
A)An administrative cost of regulation.
B)An efficiency cost of regulation.
C)A compliance cost of regulation.
A)An administrative cost of regulation.
B)An efficiency cost of regulation.
C)A compliance cost of regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If Synergy Energy Corp.hires attorneys to keep it informed about new regulations,their salaries represent
A)Administrative costs.
B)Compliance costs.
C)Capital costs.
A)Administrative costs.
B)Compliance costs.
C)Capital costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When market outcomes improve after government regulation is enforced,
A)Technical efficiency is achieved.
B)The net effect of government intervention on society is definitely beneficial.
C)Government intervention still may not be justified if the economic costs are too high.
A)Technical efficiency is achieved.
B)The net effect of government intervention on society is definitely beneficial.
C)Government intervention still may not be justified if the economic costs are too high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is an example of government failure?
A)Too much regulation resulting in wasted resources.
B)Public goods.
C)Externalities.
A)Too much regulation resulting in wasted resources.
B)Public goods.
C)Externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In cost-benefit analysis,regulatory intervention can be justified if the
A)Marginal benefit of regulation exceeds its marginal cost.
B)Economic cost of regulation exceeds the value of the improvements in government intervention.
C)Value of government failure exceeds the value of market failure.
A)Marginal benefit of regulation exceeds its marginal cost.
B)Economic cost of regulation exceeds the value of the improvements in government intervention.
C)Value of government failure exceeds the value of market failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Regulations that offer imperfect answers
A)Are options that should never be implemented.
B)Reflect the realistic choices that society must make between imperfect markets and imperfect government intervention.
C)Are not consistent with utility maximization in the real world.
A)Are options that should never be implemented.
B)Reflect the realistic choices that society must make between imperfect markets and imperfect government intervention.
C)Are not consistent with utility maximization in the real world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If government failure did not exist,
A)Laissez faire would apply to all markets.
B)Deregulation would be unnecessary.
C)The invisible hand would be the most efficient and equitable way to run the economy.
A)Laissez faire would apply to all markets.
B)Deregulation would be unnecessary.
C)The invisible hand would be the most efficient and equitable way to run the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Hiring over 260,000 U.S.federal workers to oversee and operate regulatory agencies involves
A)Zero costs since the market outcomes will be improved.
B)Government failure in every case.
C)Forgoing output that could be produced if the workers were employed elsewhere.
A)Zero costs since the market outcomes will be improved.
B)Government failure in every case.
C)Forgoing output that could be produced if the workers were employed elsewhere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When regulation results in an inferior mix of output,there are
A)Administrative costs.
B)Compliance costs.
C)Efficiency costs.
A)Administrative costs.
B)Compliance costs.
C)Efficiency costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following markets has not been subject to substantial deregulation?
A)Airlines.
B)Computers.
C)Telecommunications.
A)Airlines.
B)Computers.
C)Telecommunications.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The collapse of AT&T's natural monopoly in long-distance telephone service was caused by
A)Satellite technology that made it easier and less expensive for new companies to provide long-distance service.
B)The takeover of the telephone industry by the U.S.government.
C)Government regulation because of illegal collusion between AT&T and foreign competitors.
A)Satellite technology that made it easier and less expensive for new companies to provide long-distance service.
B)The takeover of the telephone industry by the U.S.government.
C)Government regulation because of illegal collusion between AT&T and foreign competitors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62

In Figure 27.2,regulation designed to achieve allocative efficient pricing for the natural monopoly will result in a price of
A)PA.
B)PB.
C)PC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
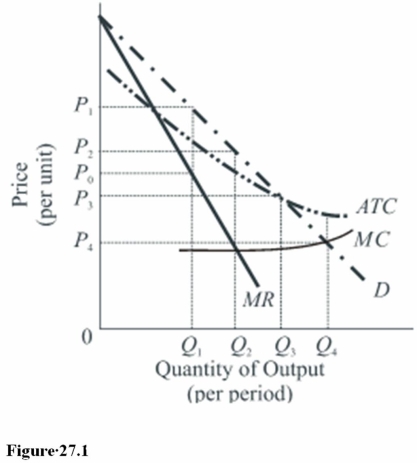
Adherence to marginal cost pricing in Figure 27.1 will necessitate
A)Taxing away the economic profits that will be realized.
B)Giving the firm a subsidy.
C)Regulation of the firm's profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In which of the following markets did deregulation contribute to increased industry concentration?
A)Airlines.
B)Cable TV.
C)Trucking.
A)Airlines.
B)Cable TV.
C)Trucking.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
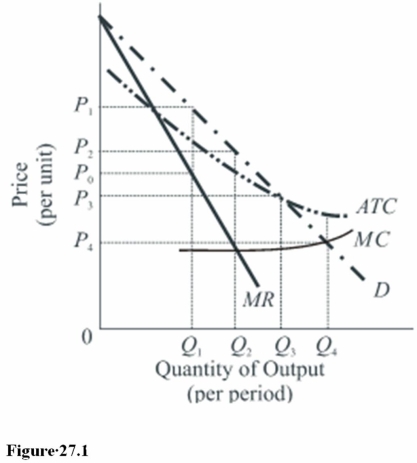
The socially optimal price and output combination in Figure 27.1 is
A)P4,Q4.
B)P0,Q1.
C)P3,Q3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The electric utility industry became a target for deregulation when
A)The cost of constructing nuclear power plants declined.
B)Technological advances destroyed the basis for natural monopolies in power production.
C)Local utility companies began behaving like monopolies.
A)The cost of constructing nuclear power plants declined.
B)Technological advances destroyed the basis for natural monopolies in power production.
C)Local utility companies began behaving like monopolies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Proponents of electric utility industry deregulation argue that
A)Profit regulation resulted in increased costs and higher prices.
B)Profit regulation resulted in too much investment in highly efficient energy production.
C)Profit regulation resulted in industry output that was too great.
A)Profit regulation resulted in increased costs and higher prices.
B)Profit regulation resulted in too much investment in highly efficient energy production.
C)Profit regulation resulted in industry output that was too great.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If entry barriers into a monopolized market are kept low,
A)Market power increases.
B)A market is contestable.
C)Government failure exists.
A)Market power increases.
B)A market is contestable.
C)Government failure exists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Deregulation of the cable TV market by the Telecommunications Turns Act of 1996 resulted in
A)Lower prices and better service.
B)Little change in either prices or service.
C)Significantly higher prices.
A)Lower prices and better service.
B)Little change in either prices or service.
C)Significantly higher prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
One In the News article is titled "Bell Monopolies Push to Disconnect Competition." If rivals are required to pay an access fee to the local phone monopoly in order to enter a market and the fee is high enough,the fee
A)Is a barrier to entry.
B)Causes cross-subsidization.
C)Creates an oligopoly.
A)Is a barrier to entry.
B)Causes cross-subsidization.
C)Creates an oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
When the CAB allowed airlines to charge high prices on longer,more efficient routes as long as they maintained service on shorter,unprofitable routes,it was allowing
A)Profit sharing.
B)Cross-subsidization.
C)Substitute pricing.
A)Profit sharing.
B)Cross-subsidization.
C)Substitute pricing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Cross-subsidization occurs when
A)Profits on one product are used to subsidize low prices on another product.
B)The government subsidizes production of a product.
C)Profitable firms in an industry are forced to share their profits with the unprofitable firms.
A)Profits on one product are used to subsidize low prices on another product.
B)The government subsidizes production of a product.
C)Profitable firms in an industry are forced to share their profits with the unprofitable firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following would be most likely to give the American public more air travel at a lower cost?
A)Reregulate the airline market by reestablishing the CAB.
B)Allow foreign airlines to enter the U.S.market.
C)Limit entry of new firms to allow the current firms to gain greater financial strength.
A)Reregulate the airline market by reestablishing the CAB.
B)Allow foreign airlines to enter the U.S.market.
C)Limit entry of new firms to allow the current firms to gain greater financial strength.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The industry that is the most recent target of deregulation is the
A)Trucking industry.
B)Electric utility industry.
C)Airline industry.
A)Trucking industry.
B)Electric utility industry.
C)Airline industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
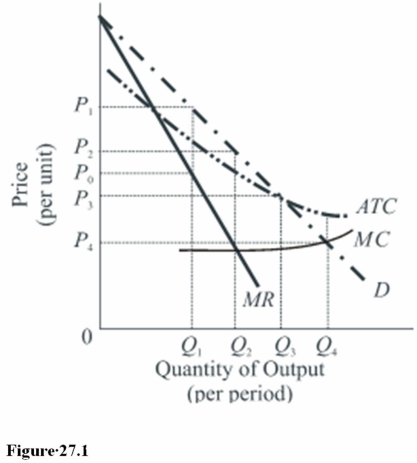
The use of marginal cost pricing in Figure 27.1 will result in
A)Economic profits.
B)Economic losses.
C)A fair rate of return on invested capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
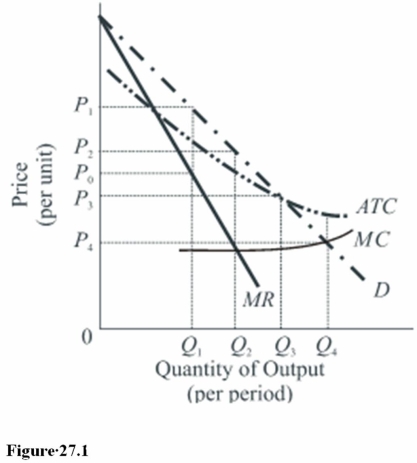
If regulation of the firm called for it to earn only a normal profit or rate of return in Figure 27.1,the regulatory agency should set the price at
A)P1.
B)P2.
C)P3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
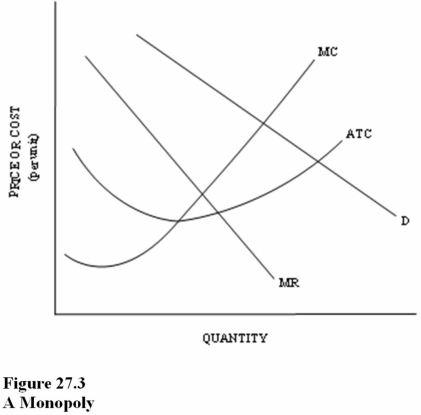 Which of the following is true about this firm?
Which of the following is true about this firm?A)It is a natural monopoly.
B)Society can benefit from government regulation using marginal cost pricing without a subsidy.
C)Marginal cost pricing will assure technical efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What development turned the cable TV market into a contestable one?
A)Economies of scale.
B)Satellite and broadband technology.
C)Cable TV firms raised prices.
A)Economies of scale.
B)Satellite and broadband technology.
C)Cable TV firms raised prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
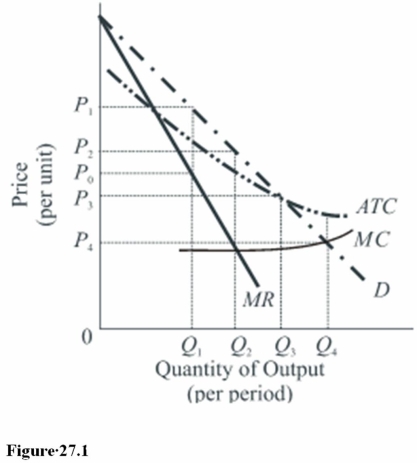
To maximize profits,an unregulated natural monopolist would choose which combination of price and output in Figure 27.1?
A)P4,Q4.
B)P2,Q2.
C)P3,Q3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
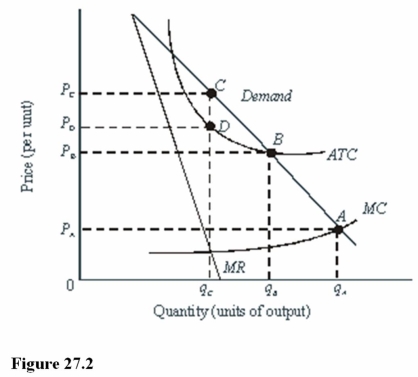
The unregulated monopoly in Figure 27.2 will experience
A)Profits equal to PCPDDC.
B)Losses equal to PA0qAA.
C)Profits equal to PD0qCD.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



