Deck 24: Monopoly
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/128
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 24: Monopoly
1
Which of the following is true for a monopolist?
A)It faces a perfectly elastic demand curve.
B)It must lower its price on all of its units in order to sell any additional units.
C)Its marginal revenue curve is equal to its demand curve.
A)It faces a perfectly elastic demand curve.
B)It must lower its price on all of its units in order to sell any additional units.
C)Its marginal revenue curve is equal to its demand curve.
It must lower its price on all of its units in order to sell any additional units.
2
If a monopolist is producing a level of output where MR exceeds MC,then it should
A)Raise its price.
B)Increase its output.
C)Lower its output.
A)Raise its price.
B)Increase its output.
C)Lower its output.
Increase its output.
3
Monopolists are price
A)Takers,as are competitive firms.
B)Takers,but competitive firms are price makers.
C)Makers,but competitive firms are price takers.
A)Takers,as are competitive firms.
B)Takers,but competitive firms are price makers.
C)Makers,but competitive firms are price takers.
Makers,but competitive firms are price takers.
4
If a monopolist is producing a level of output where MR is less than MC,then it should
A)Shift its marginal cost curve upward.
B)Increase its output.
C)Lower its output.
A)Shift its marginal cost curve upward.
B)Increase its output.
C)Lower its output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The marginal revenue curve is below the demand curve
A)If a firm must lower its price to sell additional output.
B)For a competitive firm.
C)When a market is characterized by economies of scale.
A)If a firm must lower its price to sell additional output.
B)For a competitive firm.
C)When a market is characterized by economies of scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A monopolist has market power because it
A)Faces a downward-sloping demand curve for its own output.
B)Can raise price as much as it wishes and not lose any customers.
C)Is a price taker.
A)Faces a downward-sloping demand curve for its own output.
B)Can raise price as much as it wishes and not lose any customers.
C)Is a price taker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The marginal revenue of a monopolist falls below price because the firm
A)Is not limited by market demand.
B)Faces a market demand curve that is inelastic.
C)Confronts a downward-sloping demand curve.
A)Is not limited by market demand.
B)Faces a market demand curve that is inelastic.
C)Confronts a downward-sloping demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Both a competitive industry and a monopoly
A)Use marginal cost pricing.
B)Maximize profit per unit where P = MC.
C)Face downward-sloping market demand curves.
A)Use marginal cost pricing.
B)Maximize profit per unit where P = MC.
C)Face downward-sloping market demand curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If a firm can change market prices by altering its output,then it
A)Has market power.
B)Faces a flat demand curve.
C)Is a price taker.
A)Has market power.
B)Faces a flat demand curve.
C)Is a price taker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A monopolist will find that its marginal revenue curve
A)Is the same as its demand curve.
B)Lies above its demand curve and is flatter than its demand curve.
C)Lies below its demand curve and is steeper than its demand curve.
A)Is the same as its demand curve.
B)Lies above its demand curve and is flatter than its demand curve.
C)Lies below its demand curve and is steeper than its demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose a monopoly firm produces bicycles and can sell 10 bicycles per month at a price of $700 per bicycle.In order to increase sales by one bicycle per month,the monopolist must lower the price of its bicycles by $50 to $650 per bicycle.The marginal revenue of the 11th bicycle is
A)$150.
B)-$50.
C)$50.
A)$150.
B)-$50.
C)$50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If a firm can raise market price by reducing its output,then
A)It has no market power.
B)It faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
C)It is a price taker.
A)It has no market power.
B)It faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
C)It is a price taker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Suppose a monopoly concrete contractor builds 20 driveways per month for $10,000 each.In order to increase sales to 21 driveways,the contractor must lower the price of driveways to $9,500.The marginal revenue of the 21st driveway is
A)$500.
B)$199,500.
C)-$500.
A)$500.
B)$199,500.
C)-$500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Monopolists set prices
A)On the marginal revenue curve.
B)Without constraints since there is no competition.
C)At the output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
A)On the marginal revenue curve.
B)Without constraints since there is no competition.
C)At the output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If the entire output of a market is produced by a single seller,the firm
A)Is a monopoly.
B)Faces perfectly inelastic demand.
C)Can charge any price it wants and not lose customers.
A)Is a monopoly.
B)Faces perfectly inelastic demand.
C)Can charge any price it wants and not lose customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is likely to be a monopolist?
A)A drug firm that has a patent granting it the exclusive right to produce a drug.
B)A large firm like GM,which has a substantial portion of the car market.
C)The Boeing Company,which is one of the largest producers of airplanes.
A)A drug firm that has a patent granting it the exclusive right to produce a drug.
B)A large firm like GM,which has a substantial portion of the car market.
C)The Boeing Company,which is one of the largest producers of airplanes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In monopoly and perfect competition,a firm should expand production when
A)Marginal revenue is below marginal cost.
B)Price is below marginal cost.
C)Marginal revenue is above marginal cost.
A)Marginal revenue is below marginal cost.
B)Price is below marginal cost.
C)Marginal revenue is above marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The marginal revenue of a monopolist
A)Is equal to price at all output levels.
B)Is above a downward-sloping demand curve.
C)Is positive up to the rate of output that maximizes total revenue.
A)Is equal to price at all output levels.
B)Is above a downward-sloping demand curve.
C)Is positive up to the rate of output that maximizes total revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following rules is satisfied when a monopoly maximizes profits?
A)Price = AVC.
B)Price < MC.
C)MR = MC.
A)Price = AVC.
B)Price < MC.
C)MR = MC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Market power is
A)A characteristic of all market structures.
B)The ability to alter the market price of a product.
C)Most common for competitive firms.
A)A characteristic of all market structures.
B)The ability to alter the market price of a product.
C)Most common for competitive firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following statements is not correct?
A)A monopolist's ability to act as a price setter guarantees economic profits in the short run.
B)The monopolist's marginal revenue is less than the price for any output greater than one.
C)A monopolist's demand curve is the same as the market demand curve for the product.
A)A monopolist's ability to act as a price setter guarantees economic profits in the short run.
B)The monopolist's marginal revenue is less than the price for any output greater than one.
C)A monopolist's demand curve is the same as the market demand curve for the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
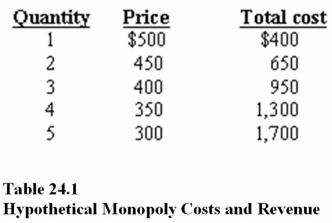
In Table 24.1,using the profit maximization rule,a monopolist will produce
A)1 unit.
B)3 units.
C)4 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
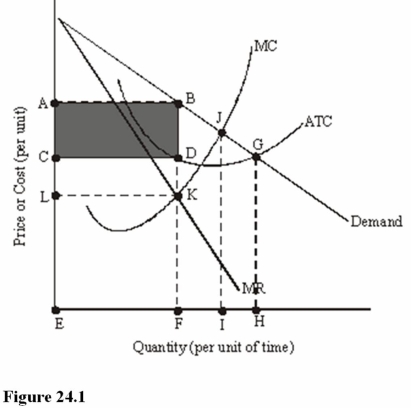
In Figure 24.1 total cost is represented by the area
A)ABFE.
B)CDFE.
C)ABGHE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
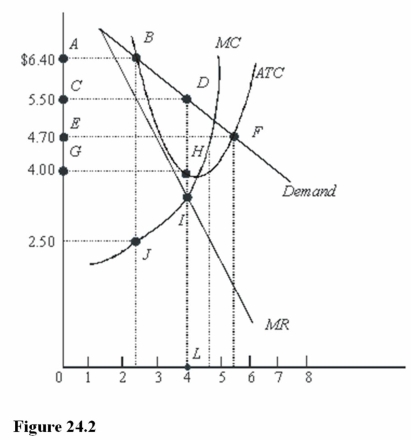
In Figure 24.2,the profit-maximizing monopolist will earn a profit per unit of
A)$1.50.
B)$4.00.
C)$4.70.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
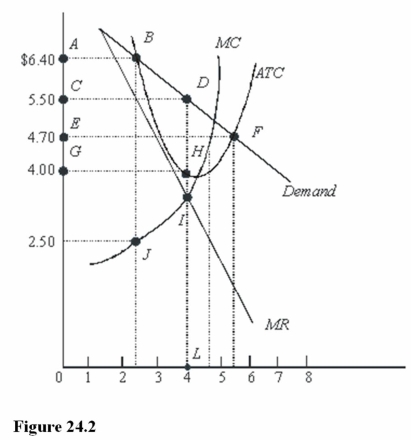
In Figure 24.2,total revenue at the profit-maximizing rate of output is
A)$22.00.
B)$6.40.
C)$4.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
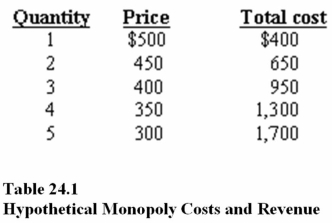
In Table 24.1,according to the profit maximization rule,at the profit-maximizing level of output,marginal revenue is
A)$300.
B)$200.
C)$100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following would definitely not be used by any unregulated monopolist?
A)Marginal cost pricing.
B)The profit-maximizing rule.
C)Price discrimination.
A)Marginal cost pricing.
B)The profit-maximizing rule.
C)Price discrimination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
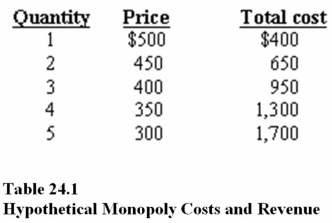
In Table 24.1,according to the profit maximization rule,at the profit-maximizing level of output marginal,cost is
A)$200.
B)$250.
C)$300.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
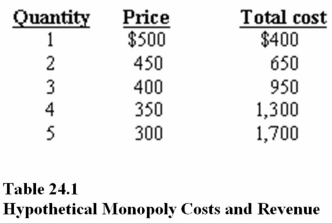
In Table 24.1,according to the profit maximization rule,at the profit-maximizing level of output,total revenue is
A)$900.
B)$1,200.
C)$650.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
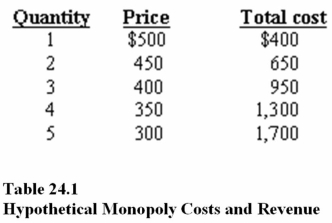
In Table 24.1,using the profit maximization rule,a monopolist will charge a price of
A)$450.
B)$400.
C)$350.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A profit-maximizing monopolist produces the rate of output where
A)MR = MC and determines price based on the demand curve.
B)Price = MC.
C)MR = MC and can set price at any amount it chooses.
A)MR = MC and determines price based on the demand curve.
B)Price = MC.
C)MR = MC and can set price at any amount it chooses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
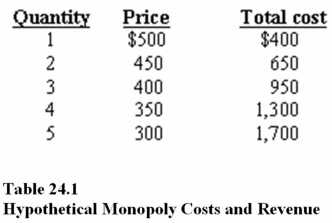
In Table 24.1,according to the profit maximization rule,at the profit-maximizing level of output,the average total cost is
A)$316.67.
B)$325.
C)$400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is the same for monopoly and competition under the same cost and demand conditions?
A)The amount of output that is produced.
B)Economic profits.
C)The goal of maximizing profits.
A)The amount of output that is produced.
B)Economic profits.
C)The goal of maximizing profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
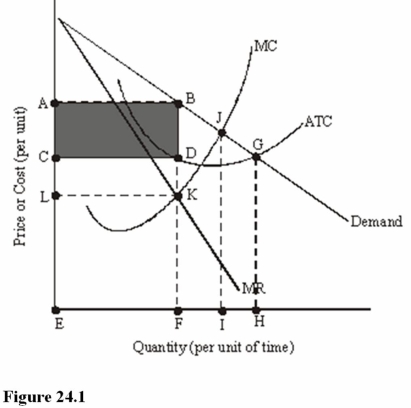
The shaded area in Figure 24.1 represents
A)Total revenue.
B)Total cost.
C)Total profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
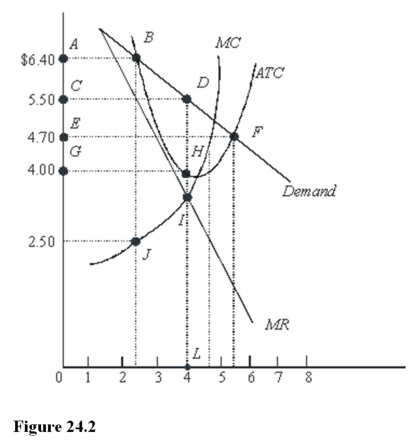
In Figure 24.2,total profit at the profit-maximizing rate of output is
A)$16.00.
B)$5.50.
C)$6.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
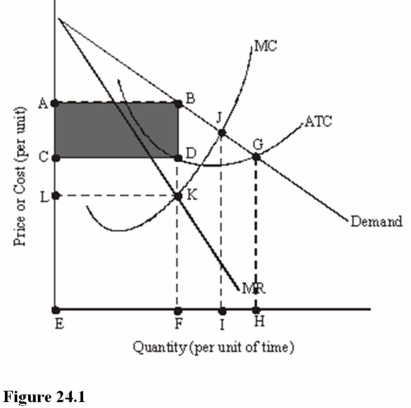
In Figure 24.1,total revenue is represented by the area
A)ABFE.
B)CDFE.
C)ABGHE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
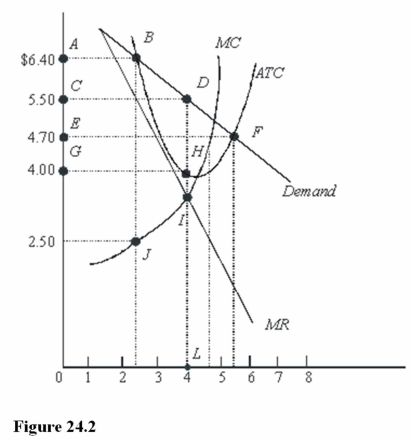
In Figure 24.2,the profit-maximizing level of output is
A)Between 2 and 3 units.
B)Between 4 and 5 units.
C)4 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
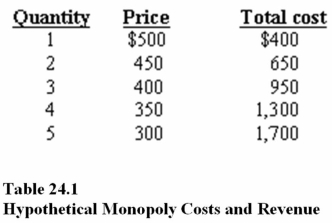
In Table 24.1,the maximum profit that can be achieved is
A)-$200.
B)$100.
C)$250.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is true about the output level where marginal revenue equals marginal cost?
A)Economic profits are equal to zero.
B)The firm should increase its output.
C)The firm is maximizing profit.
A)Economic profits are equal to zero.
B)The firm should increase its output.
C)The firm is maximizing profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
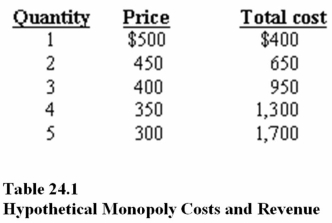
In Table 24.1,marginal revenue at the profit-maximizing level of output is
A)$150.00
B)$250.00
C)$300.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
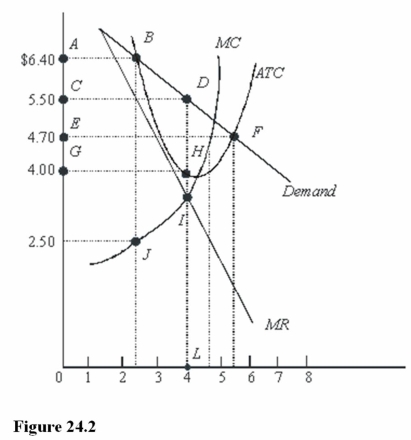
In Figure 24.2,total cost at the profit-maximizing rate of output is
A)$16.00.
B)$18.80.
C)$22.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Any firm that has economies of scale will
A)Try to spread production over many plants.
B)Be able to produce at a lower unit cost as it increases production.
C)Face an upward-sloping long-run average total cost curve.
A)Try to spread production over many plants.
B)Be able to produce at a lower unit cost as it increases production.
C)Face an upward-sloping long-run average total cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Reductions in minimum average costs that come about through increases in the size of plants and equipment are called
A)Barriers to entry.
B)Economies to monopoly power.
C)Economies of scale.
A)Barriers to entry.
B)Economies to monopoly power.
C)Economies of scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Compared with a competitive market with the same cost and market demand circumstances,a monopolist has
A)Less pressure to reduce costs and less reason to improve quality.
B)Less pressure to reduce costs and more reason to improve quality.
C)More pressure to reduce costs and less reason to improve quality.
A)Less pressure to reduce costs and less reason to improve quality.
B)Less pressure to reduce costs and more reason to improve quality.
C)More pressure to reduce costs and less reason to improve quality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
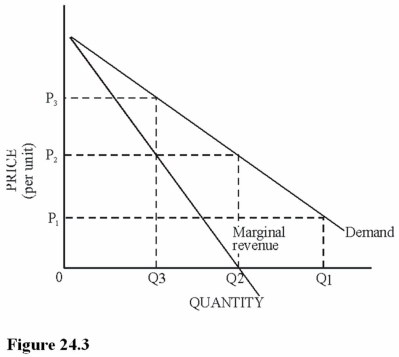
Refer to Figure 24.3.Suppose this good could somehow be produced at no cost (that is,the total cost at any level of output was zero).This single-price monopoly firm would maximize profit by
A)Raising the price as high as possible until the quantity demanded began to decrease.
B)Producing an infinite amount and selling at the highest price possible.
C)Producing Q2 and charging P2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The price charged by a profit-maximizing monopolist occurs
A)At the minimum of the long-run average total cost curve.
B)Where P = MR = MC.
C)At a price on the demand curve above the intersection where MR = MC.
A)At the minimum of the long-run average total cost curve.
B)Where P = MR = MC.
C)At a price on the demand curve above the intersection where MR = MC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A monopolist will not use marginal cost pricing because at that output
A)MR is greater than MC.
B)MR is below the ATC curve.
C)MC is greater than MR.
A)MR is greater than MC.
B)MR is below the ATC curve.
C)MC is greater than MR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is an argument in favor of a competitive market structure rather than monopoly?
A)Monopolies have greater ability to pursue research and design.
B)The lure of monopoly power provides a greater incentive for invention and innovation.
C)Monopolies produce less at a higher price than competitive markets,ceteris paribus.
A)Monopolies have greater ability to pursue research and design.
B)The lure of monopoly power provides a greater incentive for invention and innovation.
C)Monopolies produce less at a higher price than competitive markets,ceteris paribus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
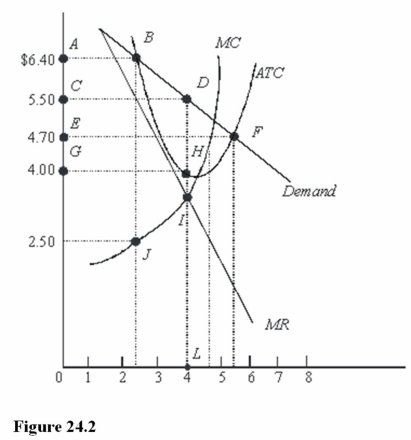
In Figure 24.2,total profit at the profit-maximizing rate of output is
A)CDLK.
B)CDHG.
C)ABDLK.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A firm can take advantage of economies of scale through
A)Investment decisions to increase capacity.
B)A production decision to increase capacity.
C)Investment decisions to reduce capacity.
A)Investment decisions to increase capacity.
B)A production decision to increase capacity.
C)Investment decisions to reduce capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
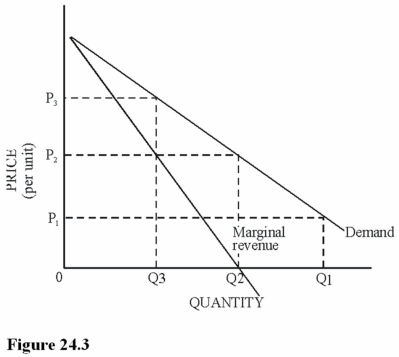
Refer to Figure 24.3.Which of the following statements is true about the price elasticity of demand at price P3?
A)The price elasticity is elastic.
B)The price elasticity is unitary.
C)The price elasticity is inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is likely to occur if a monopoly suddenly loses its ability to deny potential competitors entry into the market?
A)The market price of the product will fall.
B)The total market quantity of output produced will fall.
C)Profits for the market will increase.
A)The market price of the product will fall.
B)The total market quantity of output produced will fall.
C)Profits for the market will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
At equilibrium in a monopoly,economic profits will most likely be
A)Greater than zero.
B)Zero.
C)Normal.
A)Greater than zero.
B)Zero.
C)Normal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Like a competitive industry,a monopoly must
A)Practice marginal cost pricing.
B)Deal with the law of demand.
C)Confront a demand curve equal to its marginal revenue curve.
A)Practice marginal cost pricing.
B)Deal with the law of demand.
C)Confront a demand curve equal to its marginal revenue curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A monopoly
A)Maximizes profits at the output level where MR > MC.
B)Produces less output than a competitive industry,ceteris paribus.
C)Charges the same price as a competitive industry,ceteris paribus.
A)Maximizes profits at the output level where MR > MC.
B)Produces less output than a competitive industry,ceteris paribus.
C)Charges the same price as a competitive industry,ceteris paribus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A monopoly
A)Maximizes profits at the output level where P = MC.
B)Is one of many sellers in a given market.
C)Charges higher prices than competitive firms,ceteris paribus.
A)Maximizes profits at the output level where P = MC.
B)Is one of many sellers in a given market.
C)Charges higher prices than competitive firms,ceteris paribus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
There is an inherent tendency of a monopoly industry to
A)Lower prices and increase output.
B)Inhibit productivity advances.
C)Increase innovation.
A)Lower prices and increase output.
B)Inhibit productivity advances.
C)Increase innovation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is a barrier to entry in a monopoly market?
A)Economic profits greater than zero for the monopolist.
B)A rising long-run average total cost curve.
C)A patent on a new product.
A)Economic profits greater than zero for the monopolist.
B)A rising long-run average total cost curve.
C)A patent on a new product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The ultimate market constraint on the exercise of market power
A)Is the demand curve facing the monopolist.
B)Is marginal cost pricing.
C)Is the ATC curve facing the monopolist.
A)Is the demand curve facing the monopolist.
B)Is marginal cost pricing.
C)Is the ATC curve facing the monopolist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
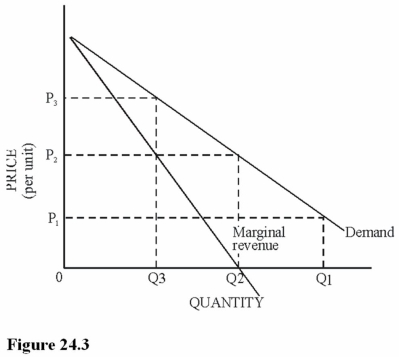
Refer to Figure 24.3.Which of the following statements is true about the price elasticity of demand at price P2?
A)The price elasticity is elastic.
B)The price elasticity is unitary.
C)The price elasticity is inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Price-discriminating firms charge higher prices to those who
A)Have greater incomes.
B)Have lower price elasticities of demand.
C)Have many substitutes available to them.
A)Have greater incomes.
B)Have lower price elasticities of demand.
C)Have many substitutes available to them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In a contestable market,
A)Product differentiation results in nonprice competition as well as price competition.
B)There are economies of scale that heighten competition.
C)Barriers to entry and long-run economic profits are low.
A)Product differentiation results in nonprice competition as well as price competition.
B)There are economies of scale that heighten competition.
C)Barriers to entry and long-run economic profits are low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
All of the following are limitations on the market power of a monopoly except
A)The elasticity of demand.
B)The ability of a firm to control demand.
C)The ability of a company to control the quantity supplied.
A)The elasticity of demand.
B)The ability of a firm to control demand.
C)The ability of a company to control the quantity supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following contributes to a firm maintaining a monopoly?
A)Exclusive franchises.
B)The existence of substitute goods.
C)A large number of firms in the industry.
A)Exclusive franchises.
B)The existence of substitute goods.
C)A large number of firms in the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Even if a market is not competitive,the firms in the market may behave competitively if
A)Potential competition exists.
B)There are economies of scale.
C)A natural monopoly exists.
A)Potential competition exists.
B)There are economies of scale.
C)A natural monopoly exists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
According to the text,a convincing argument against concentration of market power is that
A)Market power increases incentives for innovation and invention.
B)Market power results in lower barriers to entry.
C)The exercise of market power results in a higher price.
A)Market power increases incentives for innovation and invention.
B)Market power results in lower barriers to entry.
C)The exercise of market power results in a higher price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If tourists are charged a much higher price than the natives of a country for exactly the same item,what kind of pricing is involved?
A)Monopoly pricing.
B)Price discrimination.
C)Competitive pricing.
A)Monopoly pricing.
B)Price discrimination.
C)Competitive pricing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Price discrimination allows a producer to
A)Reap the highest possible average price for the quantity supplied.
B)Increase the elasticity of consumer demand.
C)Minimize marginal costs.
A)Reap the highest possible average price for the quantity supplied.
B)Increase the elasticity of consumer demand.
C)Minimize marginal costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
All of the following can be used to increase monopoly power except
A)Acquisitions.
B)Lawsuits.
C)Antitrust laws.
A)Acquisitions.
B)Lawsuits.
C)Antitrust laws.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Price discrimination is best defined as
A)Charging an excessive price for a product.
B)The charging of different prices by different companies for the same product.
C)The selling of an identical good at different prices to different consumers by a single seller.
A)Charging an excessive price for a product.
B)The charging of different prices by different companies for the same product.
C)The selling of an identical good at different prices to different consumers by a single seller.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A monopolist that does not practice price discrimination should never produce in the
A)Elastic portion of its demand curve because it can increase total revenue and reduce total costs by lowering the price.
B)Inelastic portion of its demand curve because it can increase total revenue and reduce total costs by increasing the price.
C)Inelastic portion of its demand curve because it can increase total revenue by more than it increases total cost by reducing the price.
A)Elastic portion of its demand curve because it can increase total revenue and reduce total costs by lowering the price.
B)Inelastic portion of its demand curve because it can increase total revenue and reduce total costs by increasing the price.
C)Inelastic portion of its demand curve because it can increase total revenue by more than it increases total cost by reducing the price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Sky-High Skywriters charges competitive prices for its skywriting services even though it has no competition.This is most likely because
A)There are no economies of scale in this industry.
B)It operates in a contestable market.
C)It is a natural monopoly.
A)There are no economies of scale in this industry.
B)It operates in a contestable market.
C)It is a natural monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Markets that exhibit economies of scale over the entire range of market output
A)Are natural monopolies.
B)Are perfectly competitive.
C)Have downward-sloping short-run average total cost curves.
A)Are natural monopolies.
B)Are perfectly competitive.
C)Have downward-sloping short-run average total cost curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following markets best illustrates the practice of price discrimination?
A)The airline market.
B)The fast-food market.
C)Wheat farming.
A)The airline market.
B)The fast-food market.
C)Wheat farming.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The argument that concentration of market power enhances research and development efforts may be weak because
A)Monopolies cannot afford basic research.
B)A monopoly may have no clear incentive to pursue new research and development.
C)No one has attempted to gather any empirical evidence.
A)Monopolies cannot afford basic research.
B)A monopoly may have no clear incentive to pursue new research and development.
C)No one has attempted to gather any empirical evidence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following is a barrier to entry into a monopoly market?
A)Economic profits for the monopolist.
B)Economies of scale.
C)A large number of firms in the industry.
A)Economic profits for the monopolist.
B)Economies of scale.
C)A large number of firms in the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Price-discriminating firms that sell in two markets will charge higher prices in the market,ceteris paribus,
A)With a higher positive cross-price elasticity of demand with respect to substitutes.
B)With the more price-inelastic demand.
C)With the more income-elastic demand.
A)With a higher positive cross-price elasticity of demand with respect to substitutes.
B)With the more price-inelastic demand.
C)With the more income-elastic demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A patent gives a firm the exclusive right to produce a product for
A)6 months.
B)2 years.
C)20 years.
A)6 months.
B)2 years.
C)20 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Dynamic pricing allows a seller to
A)Always charge the highest price.
B)Move prices up when demand is high,and lower prices for a similar product when the demand is low.
C)Keep the same price no matter what happens with demand.
A)Always charge the highest price.
B)Move prices up when demand is high,and lower prices for a similar product when the demand is low.
C)Keep the same price no matter what happens with demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In a contestable market,
A)Entry occurs when prices rise above average total costs.
B)Many firms compete,which drives prices down to minimum long-run average total cost.
C)A few firms use predatory prices to achieve market share.
A)Entry occurs when prices rise above average total costs.
B)Many firms compete,which drives prices down to minimum long-run average total cost.
C)A few firms use predatory prices to achieve market share.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



