Deck 8: The Business Cycle
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/112
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: The Business Cycle
1
A decline in total real output for two or more consecutive quarters is referred to as
A)Laissez faire.
B)A recession.
C)A growth recession.
D)Say's Law.
A)Laissez faire.
B)A recession.
C)A growth recession.
D)Say's Law.
A recession.
2
Real GDP is better than nominal GDP for measuring growth because real GDP has been adjusted for changes in
A)The price level.
B)Unemployment.
C)The business cycle.
D)Productivity.
A)The price level.
B)Unemployment.
C)The business cycle.
D)Productivity.
The price level.
3
According to classical theory,
A)Keynes had "neglected to take account of the drag on prosperity which can be exercised by an insufficiency of effective demand."
B)Macro equilibrium might start out badly and get worse in the absence of government intervention.
C)Flexible wages and prices allow a laissez faire economy to adjust wages and prices to shifts in aggregate demand.
D)Business cycles are not relevant and do not occur.
A)Keynes had "neglected to take account of the drag on prosperity which can be exercised by an insufficiency of effective demand."
B)Macro equilibrium might start out badly and get worse in the absence of government intervention.
C)Flexible wages and prices allow a laissez faire economy to adjust wages and prices to shifts in aggregate demand.
D)Business cycles are not relevant and do not occur.
Flexible wages and prices allow a laissez faire economy to adjust wages and prices to shifts in aggregate demand.
4
Based on the classical view,
A)Unemployment never occurs.
B)Cyclical unemployment might occur temporarily.
C)All goods produced are always purchased at an unchanging price.
D)Persistent unemployment might be a problem.
A)Unemployment never occurs.
B)Cyclical unemployment might occur temporarily.
C)All goods produced are always purchased at an unchanging price.
D)Persistent unemployment might be a problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Before the year 2000,the most prolonged departure from the long-term growth path for the United States occurred during
A)The 1980s.
B)The Great Depression.
C)World War II.
D)The years following World War II.
A)The 1980s.
B)The Great Depression.
C)World War II.
D)The years following World War II.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If wages and prices are flexible,then a recession is best eliminated when prices
A)And wages both rise.
B)And wages both fall.
C)Rise and wages drop.
D)Drop and wages rise.
A)And wages both rise.
B)And wages both fall.
C)Rise and wages drop.
D)Drop and wages rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Unlike the classical economists,Keynes asserted that
A)The economy was inherently unstable.
B)Laissez faire policies would lead to macro equilibrium.
C)Prices and wages were flexible.
D)Markets would naturally self-adjust.
A)The economy was inherently unstable.
B)Laissez faire policies would lead to macro equilibrium.
C)Prices and wages were flexible.
D)Markets would naturally self-adjust.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
According to Keynes,which of the following should the government do when the economy overheats?
A)Employ more people.
B)Increase spending.
C)Raise taxes.
D)Practice laissez faire policies.
A)Employ more people.
B)Increase spending.
C)Raise taxes.
D)Practice laissez faire policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Alternating periods of economic growth and contraction in real GDP define
A)Capitalism.
B)The business cycle.
C)Macro equilibrium.
D)Say's Law.
A)Capitalism.
B)The business cycle.
C)Macro equilibrium.
D)Say's Law.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
According to classical economists,market-driven economies
A)Are typically self-adjusting.
B)Are inherently unstable.
C)Require government intervention.
D)Are always in long-run equilibrium.
A)Are typically self-adjusting.
B)Are inherently unstable.
C)Require government intervention.
D)Are always in long-run equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A recession can be represented by a point
A)Inside the production possibilities curve.
B)Outside the production possibilities curve.
C)On the production possibilities curve.
D)At either end of the production possibilities curve.
A)Inside the production possibilities curve.
B)Outside the production possibilities curve.
C)On the production possibilities curve.
D)At either end of the production possibilities curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Changes in real GDP are used to measure
A)Inflation.
B)Price level changes.
C)Business cycles.
D)Population growth.
A)Inflation.
B)Price level changes.
C)Business cycles.
D)Population growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
According to Keynes,which of the following can be used to slow down an overheated economy?
A)Decrease government purchases.
B)Decrease taxes.
C)Make more money available.
D)Employ more people.
A)Decrease government purchases.
B)Decrease taxes.
C)Make more money available.
D)Employ more people.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is true about business cycles in the United States?
A)They are remarkably similar in length but vary greatly in intensity.
B)They vary greatly in length,frequency,and intensity.
C)They are similar in frequency and intensity but not in length.
D)They are similar in length, frequency, and intensity.
A)They are remarkably similar in length but vary greatly in intensity.
B)They vary greatly in length,frequency,and intensity.
C)They are similar in frequency and intensity but not in length.
D)They are similar in length, frequency, and intensity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Say's Law states that
A)Supply creates its own demand.
B)Shifts of either supply or demand can achieve a given market equilibrium.
C)Wages and prices are inflexible,which prevents the achievement of market equilibrium.
D)Increased prices lead to increased supply.
A)Supply creates its own demand.
B)Shifts of either supply or demand can achieve a given market equilibrium.
C)Wages and prices are inflexible,which prevents the achievement of market equilibrium.
D)Increased prices lead to increased supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is characteristic of a downturn in the business cycle?
A)Lower unemployment rates.
B)Lower real output.
C)Higher interest rates.
D)None of the choices are correct.
A)Lower unemployment rates.
B)Lower real output.
C)Higher interest rates.
D)None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
According to Keynes,when the economy falters,the government should do any of the following except
A)Practice a laissez faire policy approach.
B)Provide more dollars for unemployment benefits.
C)Make more money available.
D)Buy more output.
A)Practice a laissez faire policy approach.
B)Provide more dollars for unemployment benefits.
C)Make more money available.
D)Buy more output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
According to the classical view,if consumer demand slowed down,
A)Prices would decrease,and the economy would return to its long-term growth trend.
B)Prices would increase,and the economy would return to its long-term growth trend.
C)Wages would increase,and the economy would return to its long-term growth trend.
D)Investment and government demand would increase, and the economy would return to its long-term growth trend.
A)Prices would decrease,and the economy would return to its long-term growth trend.
B)Prices would increase,and the economy would return to its long-term growth trend.
C)Wages would increase,and the economy would return to its long-term growth trend.
D)Investment and government demand would increase, and the economy would return to its long-term growth trend.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The study of aggregate economic activity for the economy as a whole is
A)Opportunity cost.
B)Scarcity.
C)Macroeconomics.
D)Microeconomics
A)Opportunity cost.
B)Scarcity.
C)Macroeconomics.
D)Microeconomics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Who believed that small disturbances in output,prices,or unemployment were likely to be magnified by the invisible hand of the marketplace?
A)President Herbert Hoover.
B)Adam Smith.
C)John Maynard Keynes.
D)Jean-Baptiste Say.
A)President Herbert Hoover.
B)Adam Smith.
C)John Maynard Keynes.
D)Jean-Baptiste Say.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Determinants of macro performance work on macro outcomes through
A)Aggregate supply and demand.
B)International balances.
C)External shocks.
D)Internal market forces.
A)Aggregate supply and demand.
B)International balances.
C)External shocks.
D)Internal market forces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Ceteris paribus,if average prices in the U.S.economy fall,then the
A)Real balances effect will lead to a lower quantity of U.S.output demanded.
B)Foreign trade effect will lead to a lower quantity of U.S.output demanded.
C)Interest rate effect will lead to a higher quantity of U.S.output demanded.
D)Cost effect will lead to a higher quantity of U.S. output demanded.
A)Real balances effect will lead to a lower quantity of U.S.output demanded.
B)Foreign trade effect will lead to a lower quantity of U.S.output demanded.
C)Interest rate effect will lead to a higher quantity of U.S.output demanded.
D)Cost effect will lead to a higher quantity of U.S. output demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A growth recession is said to occur when the economy grows at a
A)Rate less than that of population.
B)Rate less than the long-term average.
C)Slower rate in the current year than the preceding year.
D)Negative rate.
A)Rate less than that of population.
B)Rate less than the long-term average.
C)Slower rate in the current year than the preceding year.
D)Negative rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is not associated with the aggregate supply curve?
A)Factors of production.
B)The interest rate effect.
C)The profit effect.
D)The cost effect.
A)Factors of production.
B)The interest rate effect.
C)The profit effect.
D)The cost effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is generally considered a desirable outcome of government intervention?
A)More jobs.
B)A higher price level.
C)Higher unemployment rates.
D)Greater deficits.
A)More jobs.
B)A higher price level.
C)Higher unemployment rates.
D)Greater deficits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is used to explain why the AD curve slopes downward?
A)The interest rate effect.
B)The cost effect.
C)The profit effect.
D)The laissez faire effect.
A)The interest rate effect.
B)The cost effect.
C)The profit effect.
D)The laissez faire effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Assume you have $2,000 in a savings account at the beginning of the year and the price level is equal to 100.If the price level is equal to 120 at the end of the year,the real value of your savings is closest to
A)$1,667.
B)$1,880.
C)$2,120.
D)$2,400.
A)$1,667.
B)$1,880.
C)$2,120.
D)$2,400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following caused a recession in the years immediately following World War II?
A)A surge in investment spending.
B)Pent-up demand for consumer goods.
C)Cutbacks in defense production.
D)Technological advances.
A)A surge in investment spending.
B)Pent-up demand for consumer goods.
C)Cutbacks in defense production.
D)Technological advances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Assume you have $1,000 in a savings account at the beginning of the year and the price level is equal to 100.If the price level is equal to 92 at the end of the year,the real value of your savings is closest to
A)$908.
B)$920.
C)$1,087.
D)$1,092.
A)$908.
B)$920.
C)$1,087.
D)$1,092.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Assume you have $5,000 in a savings account at the beginning of the year and the price level is equal to 100.If the price level is equal to 125 at the end of the year,the real value of your savings is closest to
A)$4,000.
B)$4,875.
C)$5,125.
D)$6,250.
A)$4,000.
B)$4,875.
C)$5,125.
D)$6,250.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Internal market forces include
A)Wars,natural disasters,and trade disruptions.
B)Tax policy,government spending,and availability of money.
C)Population growth,spending behavior,and invention.
D)External shocks and policy levers.
A)Wars,natural disasters,and trade disruptions.
B)Tax policy,government spending,and availability of money.
C)Population growth,spending behavior,and invention.
D)External shocks and policy levers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
According to the profit effect,
A)Some costs do not rise when average prices rise.
B)The aggregate supply curve is vertical in the short run.
C)The aggregate supply curve has a negative slope.
D)All costs rise when average prices rise.
A)Some costs do not rise when average prices rise.
B)The aggregate supply curve is vertical in the short run.
C)The aggregate supply curve has a negative slope.
D)All costs rise when average prices rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
External shocks include all of the following except
A)Population growth.
B)Natural disasters.
C)Terrorist attacks.
D)Wars.
A)Population growth.
B)Natural disasters.
C)Terrorist attacks.
D)Wars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is not considered a macro outcome?
A)The level of unemployment.
B)External shocks such as weather.
C)The average price of goods and services.
D)The year-to-year expansion in overall productive capacity.
A)The level of unemployment.
B)External shocks such as weather.
C)The average price of goods and services.
D)The year-to-year expansion in overall productive capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The aggregate demand curve is downward-sloping because,other things being equal,
A)People buy fewer goods and services at lower average incomes.
B)People buy more goods and services at lower average prices.
C)A higher average price level will induce producers to offer more output than otherwise.
D)People buy more goods and services at higher average prices.
A)People buy fewer goods and services at lower average incomes.
B)People buy more goods and services at lower average prices.
C)A higher average price level will induce producers to offer more output than otherwise.
D)People buy more goods and services at higher average prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Ceteris paribus,if average prices in the U.S.economy fall,then the
A)Real balances effect will lead to a lower quantity of U.S.output demanded.
B)Foreign trade effect will lead to a higher quantity of U.S.output demanded.
C)Interest rate effect will lead to a lower quantity of U.S.output demanded.
D)Profit effect will lead to a higher quantity of U.S. output demanded.
A)Real balances effect will lead to a lower quantity of U.S.output demanded.
B)Foreign trade effect will lead to a higher quantity of U.S.output demanded.
C)Interest rate effect will lead to a lower quantity of U.S.output demanded.
D)Profit effect will lead to a higher quantity of U.S. output demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A positively sloped aggregate supply curve reflects
A)The idea that greater production lowers profit margins,which raises quantity demanded.
B)The decrease in the real value of money as the price level rises.
C)The rising costs associated with increased capacity utilization.
D)None or the other choices.
A)The idea that greater production lowers profit margins,which raises quantity demanded.
B)The decrease in the real value of money as the price level rises.
C)The rising costs associated with increased capacity utilization.
D)None or the other choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In the absence of external shocks or government policy,an economy would
A)Still experience business cycle fluctuations because of internal market forces.
B)Not experience business cycle fluctuations.
C)Not be able to expand production and output.
D)None of the choices are correct.
A)Still experience business cycle fluctuations because of internal market forces.
B)Not experience business cycle fluctuations.
C)Not be able to expand production and output.
D)None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Assume you have $1,000 in a savings account at the beginning of the year and the price level is equal to 100.If the price level is equal to 115 at the end of the year,the real value of your savings is closest to
A)$870.
B)$885.
C)$1,115.
D)$1,150.
A)$870.
B)$885.
C)$1,115.
D)$1,150.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is illustrated by the aggregate demand curve?
A)How real personal income varies with the inflation rate.
B)How total quantity of output demanded varies with the average price level.
C)How real output varies with the inflation rate.
D)How real personal income varies with the price level.
A)How real personal income varies with the inflation rate.
B)How total quantity of output demanded varies with the average price level.
C)How real output varies with the inflation rate.
D)How real personal income varies with the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Keynesian levers include
A)Deregulation.
B)Fiscal policy.
C)Monetary policy.
D)Aggregate supply.
A)Deregulation.
B)Fiscal policy.
C)Monetary policy.
D)Aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is a potential problem at macro equilibrium?
A)It is inconsistent with the macroeconomic goals.
B)A surplus of goods exists.
C)A shortage of goods exists.
D)The economy is permanently stuck there.
A)It is inconsistent with the macroeconomic goals.
B)A surplus of goods exists.
C)A shortage of goods exists.
D)The economy is permanently stuck there.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is the best example of supply-side policy?
A)The government response to the Great Depression.
B)Inflation during the 1970s.
C)The Reagan tax cuts in 1981.
D)Government policy before 1930.
A)The government response to the Great Depression.
B)Inflation during the 1970s.
C)The Reagan tax cuts in 1981.
D)Government policy before 1930.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When the AS curve is vertical,increases in AD will
A)Increase the average price level but have no impact on unemployment.
B)Increase the average price level and decrease unemployment.
C)Increase both the average price level and unemployment.
D)Have no impact on either the average price level or unemployment.
A)Increase the average price level but have no impact on unemployment.
B)Increase the average price level and decrease unemployment.
C)Increase both the average price level and unemployment.
D)Have no impact on either the average price level or unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
According to Keynesian theory,the correct fiscal policy to stimulate the economy would be to
A)Raise taxes to increase aggregate demand.
B)Increase the money supply to increase aggregate supply.
C)Increase government expenditures to increase aggregate demand.
D)Lower taxes to increase aggregate supply.
A)Raise taxes to increase aggregate demand.
B)Increase the money supply to increase aggregate supply.
C)Increase government expenditures to increase aggregate demand.
D)Lower taxes to increase aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following economic perspectives focuses on the need for government to use spending and taxes to shift aggregate demand and thus correct problems of unemployment and inflation?
A)Supply-side.
B)Keynesian.
C)Classical.
D)Monetarists.
A)Supply-side.
B)Keynesian.
C)Classical.
D)Monetarists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Macro equilibrium always occurs when
A)Aggregate supply is greater than aggregate demand.
B)The labor force is fully employed.
C)Aggregate demand equals aggregate supply at a given average price level.
D)The level of output is expanding.
A)Aggregate supply is greater than aggregate demand.
B)The labor force is fully employed.
C)Aggregate demand equals aggregate supply at a given average price level.
D)The level of output is expanding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Alternating periods of economic growth and contraction are
A)The result of government intervention according to Keynes.
B)The result of recurrent shifts of aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
C)Indicative of an unstable economy and require government intervention according to classical economists.
D)Not typical of the U.S. economy.
A)The result of government intervention according to Keynes.
B)The result of recurrent shifts of aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
C)Indicative of an unstable economy and require government intervention according to classical economists.
D)Not typical of the U.S. economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following would result if the price level were below the equilibrium level?
A)Aggregate demand would increase.
B)Aggregate supply would decrease.
C)Consumers would bid prices up by competing for goods currently in shortage.
D)Shortages would force sellers to lower prices in order to increase aggregate quantity demanded.
A)Aggregate demand would increase.
B)Aggregate supply would decrease.
C)Consumers would bid prices up by competing for goods currently in shortage.
D)Shortages would force sellers to lower prices in order to increase aggregate quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A vertical aggregate supply curve
A)Implies that supply-side policies will have no effect on the macro equilibrium.
B)Implies that aggregate demand shifts have no impact on output.
C)Is likely in the short run.
D)Reflects the inflexibility of prices and wages.
A)Implies that supply-side policies will have no effect on the macro equilibrium.
B)Implies that aggregate demand shifts have no impact on output.
C)Is likely in the short run.
D)Reflects the inflexibility of prices and wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The cost effect implies that
A)Higher costs are reflected in higher average prices.
B)The aggregate supply curve is linear.
C)Lower average prices result in greater quantity supplied.
D)The aggregate demand curve is downward-sloping.
A)Higher costs are reflected in higher average prices.
B)The aggregate supply curve is linear.
C)Lower average prices result in greater quantity supplied.
D)The aggregate demand curve is downward-sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The unique situation in which the behavior of buyers and sellers is compatible is referred to as
A)Full-employment GDP.
B)Macro equilibrium.
C)Micro equilibrium.
D)Labor market balance.
A)Full-employment GDP.
B)Macro equilibrium.
C)Micro equilibrium.
D)Labor market balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
According to Keynes,unemployment results from
A)Increased business investment that reduces consumer spending.
B)Flexible wages and price.
C)Insufficient spending on the part of consumers,business,and government.
D)Increased government spending that reduces consumer spending.
A)Increased business investment that reduces consumer spending.
B)Flexible wages and price.
C)Insufficient spending on the part of consumers,business,and government.
D)Increased government spending that reduces consumer spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Ceteris paribus,the price level will decrease if the aggregate
A)Supply curve shifts to the left.
B)Demand curve shifts to the left.
C)Demand curve shifts to the right.
D)Supply and demand curves both shift to the right.
A)Supply curve shifts to the left.
B)Demand curve shifts to the left.
C)Demand curve shifts to the right.
D)Supply and demand curves both shift to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Controversies between Keynesian,monetarist,and supply-side theories focus on the
A)Shape and sensitivity of aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves.
B)Existence or nonexistence of the aggregate supply curve.
C)Importance of international balances to the economy.
D)Usefulness of aggregate demand and supply to analyze adjustment of the macro equilibrium.
A)Shape and sensitivity of aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves.
B)Existence or nonexistence of the aggregate supply curve.
C)Importance of international balances to the economy.
D)Usefulness of aggregate demand and supply to analyze adjustment of the macro equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The emphasis by some economists on long-term outcomes is reminiscent of
A)Keynesian theory.
B)Classical theory.
C)Supply-side theory.
D)None of the choices are correct.
A)Keynesian theory.
B)Classical theory.
C)Supply-side theory.
D)None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which combination of shifts of aggregate demand and supply would definitely cause an increase in real GDP?
A)Demand shifts to the left and supply shifts to the right.
B)Demand shifts to the left and supply shifts to the left.
C)Demand shifts to the right and supply shifts to the right.
D)Demand shifts to the right and supply shifts to the left.
A)Demand shifts to the left and supply shifts to the right.
B)Demand shifts to the left and supply shifts to the left.
C)Demand shifts to the right and supply shifts to the right.
D)Demand shifts to the right and supply shifts to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In the long run,an increase in aggregate demand will lead to
A)A higher price level and an increase in real GDP.
B)A higher price level only.
C)An increase in real GDP only.
D)A decrease in real GDP.
A)A higher price level and an increase in real GDP.
B)A higher price level only.
C)An increase in real GDP only.
D)A decrease in real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which group of economists believes that there is a natural rate of output that is relatively immune to short-run fluctuations in aggregate demand?
A)Supply-siders.
B)Keynesians.
C)Monetarists.
D)Fiscal economists.
A)Supply-siders.
B)Keynesians.
C)Monetarists.
D)Fiscal economists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following economic perspectives focuses on the need for government to shift aggregate supply to correct problems of unemployment and inflation?
A)Supply-side.
B)Keynesian.
C)Classical.
D)Monetary.
A)Supply-side.
B)Keynesian.
C)Classical.
D)Monetary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
International trade and money flows can increase aggregate supply and aggregate demand if
A)Trade barriers are increased.
B)Trade barriers are reduced.
C)Tariffs are increased.
D)Quotas are increased.
A)Trade barriers are increased.
B)Trade barriers are reduced.
C)Tariffs are increased.
D)Quotas are increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Use the following figure to answer the questions : Figure 8.3: 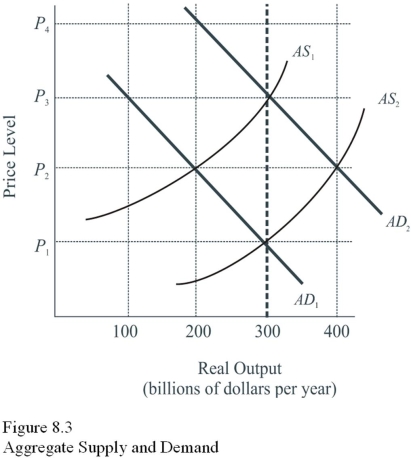
Given AD2 and AS1,the equilibrium price level in Figure 8.3 is
A)P1.
B)P2.
C)P3.
D)P4.

Given AD2 and AS1,the equilibrium price level in Figure 8.3 is
A)P1.
B)P2.
C)P3.
D)P4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
When the AS curve is vertical,fiscal policy will be
A)Ineffective against both inflation and unemployment.
B)Effective against inflation but not unemployment.
C)Effective against unemployment but not inflation.
D)Effective against both inflation and unemployment.
A)Ineffective against both inflation and unemployment.
B)Effective against inflation but not unemployment.
C)Effective against unemployment but not inflation.
D)Effective against both inflation and unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Use the following figure to answer the questions : Figure 8.3: 
Macro equilibrium is established at which level of real output,given AD1 and AS2 in Figure 8.3?
A)$100 billion.
B)$200 billion.
C)$300 billion.
D)$400 billion.

Macro equilibrium is established at which level of real output,given AD1 and AS2 in Figure 8.3?
A)$100 billion.
B)$200 billion.
C)$300 billion.
D)$400 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the following figure to answer the questions : Figure 8.5: 
In Figure 8.5,if this economy's inflation goal is a price level of P2 but the equilibrium price level is P3,one way to accomplish this using fiscal policy would be to
A)Decrease AD by decreasing income taxes.
B)Decrease AS by decreasing the money supply.
C)Decrease AD by reducing transfer payments.
D)Increase AS by reducing government regulations.

In Figure 8.5,if this economy's inflation goal is a price level of P2 but the equilibrium price level is P3,one way to accomplish this using fiscal policy would be to
A)Decrease AD by decreasing income taxes.
B)Decrease AS by decreasing the money supply.
C)Decrease AD by reducing transfer payments.
D)Increase AS by reducing government regulations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Use the following figure to answer the questions : Figure 8.4: 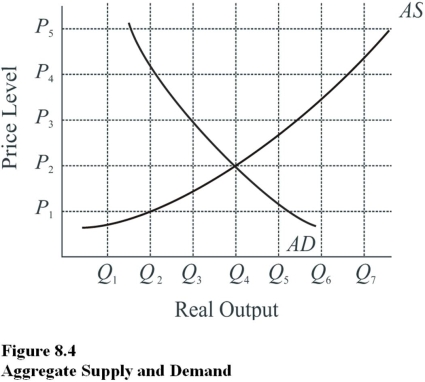
At what price level does equilibrium occur in Figure 8.4?
A)P1.
B)P2.
C)P3.
D)P4.

At what price level does equilibrium occur in Figure 8.4?
A)P1.
B)P2.
C)P3.
D)P4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Use the following figure to answer the questions : Figure 8.3: 
Given AD1 and AS1,if the average price level in Figure 8.3 were at P3,
A)A surplus would exist initially.
B)The aggregate quantity demanded would exceed the aggregate quantity supplied.
C)The average price level would rise.
D)The equilibrium price level would be P3.

Given AD1 and AS1,if the average price level in Figure 8.3 were at P3,
A)A surplus would exist initially.
B)The aggregate quantity demanded would exceed the aggregate quantity supplied.
C)The average price level would rise.
D)The equilibrium price level would be P3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use the following figure to answer the questions : Figure 8.4: 
At which of the following price levels would a shortage occur in Figure 8.4?
A)P1.
B)P2.
C)P3.
D)P4.

At which of the following price levels would a shortage occur in Figure 8.4?
A)P1.
B)P2.
C)P3.
D)P4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Use the following figure to answer the questions : Figure 8.5: 
In Figure 8.5,if equilibrium real output is Q1 and full-employment real output is Q2,an appropriate monetarist policy lever would be to increase
A)AD by decreasing income taxes.
B)AS by increasing the money supply.
C)AD by reducing interest rates.
D)AD by reducing government regulations.

In Figure 8.5,if equilibrium real output is Q1 and full-employment real output is Q2,an appropriate monetarist policy lever would be to increase
A)AD by decreasing income taxes.
B)AS by increasing the money supply.
C)AD by reducing interest rates.
D)AD by reducing government regulations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A laissez faire policy approach during a recession would advocate
A)Noninterference by the government.
B)Increasing AS by funding programs that improve worker skills.
C)Increasing AD by increasing government spending.
D)Increasing both AD and AS.
A)Noninterference by the government.
B)Increasing AS by funding programs that improve worker skills.
C)Increasing AD by increasing government spending.
D)Increasing both AD and AS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Fiscal policy is the use of
A)Government spending and taxes to alter macroeconomic outcomes.
B)Money and credit controls to alter macroeconomic outcomes.
C)Tax incentives,deregulation,and other mechanisms to increase the ability and willingness to produce goods and services.
D)Trade policy to alter macroeconomic outcomes.
A)Government spending and taxes to alter macroeconomic outcomes.
B)Money and credit controls to alter macroeconomic outcomes.
C)Tax incentives,deregulation,and other mechanisms to increase the ability and willingness to produce goods and services.
D)Trade policy to alter macroeconomic outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Use the following figure to answer the questions : Figure 8.4: 
Using Figure 8.5,if the equilibrium real output is Q2 then
A)Aggregate demand must be AD1.
B)Aggregate demand could be either AD1 or AD2 depending on the level of aggregate supply.
C)The equilibrium price level is P2.
D)Aggregate supply must be AS1 and the equilibrium price level must be P1.

Using Figure 8.5,if the equilibrium real output is Q2 then
A)Aggregate demand must be AD1.
B)Aggregate demand could be either AD1 or AD2 depending on the level of aggregate supply.
C)The equilibrium price level is P2.
D)Aggregate supply must be AS1 and the equilibrium price level must be P1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In the long run,which of the following is true?
A)Profit effects are equal to cost effects.
B)Profit effects are larger than cost effects.
C)Cost effects are larger than profit effects.
D)None of the choices are correct.
A)Profit effects are equal to cost effects.
B)Profit effects are larger than cost effects.
C)Cost effects are larger than profit effects.
D)None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Use the following figure to answer the questions : Figure 8.3: 
A supply-side policy approach in Figure 8.3,given AD1 and AS1,to achieve both lower prices and more output would be to
A)Increase the growth of the money supply.
B)Reduce marginal tax rates and government regulation in an effort to move AS1 to AS2.
C)Wait until natural market forces establish full employment.
D)Increase aggregate spending.

A supply-side policy approach in Figure 8.3,given AD1 and AS1,to achieve both lower prices and more output would be to
A)Increase the growth of the money supply.
B)Reduce marginal tax rates and government regulation in an effort to move AS1 to AS2.
C)Wait until natural market forces establish full employment.
D)Increase aggregate spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Use the following figure to answer the questions : Figure 8.5: 
In Figure 8.5,if this economy's inflation goal is a price level of P2 but the equilibrium price level is P3,an appropriate monetary policy lever would be to
A)Decrease AS by increasing the money supply.
B)Decrease AD by increasing interest rates.
C)Decrease AD by increasing income taxes.
D)Increase AS by increasing the money supply.

In Figure 8.5,if this economy's inflation goal is a price level of P2 but the equilibrium price level is P3,an appropriate monetary policy lever would be to
A)Decrease AS by increasing the money supply.
B)Decrease AD by increasing interest rates.
C)Decrease AD by increasing income taxes.
D)Increase AS by increasing the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Use the following figure to answer the questions : Figure 8.3: 
Given AD1 and AS1 in Figure 8.3,the classical approach to achieving full employment at an output of $300 billion would be to
A)Increase taxes and increase government spending to shift AD1 to AD2.
B)Increase the growth of the money supply to shift AD1 to AD2.
C)Do nothing and wait for "natural" market forces to achieve full employment.
D)Use all available supply-side options.

Given AD1 and AS1 in Figure 8.3,the classical approach to achieving full employment at an output of $300 billion would be to
A)Increase taxes and increase government spending to shift AD1 to AD2.
B)Increase the growth of the money supply to shift AD1 to AD2.
C)Do nothing and wait for "natural" market forces to achieve full employment.
D)Use all available supply-side options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Use the following figure to answer the questions : Figure 8.3: 
Assume the economy is initially in equilibrium on AD2 and AS2.Which curve would have shifted,and in what direction would it have shifted,if a new equilibrium were to occur at an output level of $300 billion and a price level of P3 in Figure 8.3?
A)Aggregate supply would have shifted to the left.
B)Aggregate supply would have shifted to the right.
C)Aggregate demand would have shifted to the left.
D)Aggregate demand would have shifted to the right.

Assume the economy is initially in equilibrium on AD2 and AS2.Which curve would have shifted,and in what direction would it have shifted,if a new equilibrium were to occur at an output level of $300 billion and a price level of P3 in Figure 8.3?
A)Aggregate supply would have shifted to the left.
B)Aggregate supply would have shifted to the right.
C)Aggregate demand would have shifted to the left.
D)Aggregate demand would have shifted to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Use the following figure to answer the questions : Figure 8.3: 
Macro equilibrium is established at which price level,given AD1 and AS1 in Figure 8.3?
A)P1.
B)P2.
C)P3.
D)P4.

Macro equilibrium is established at which price level,given AD1 and AS1 in Figure 8.3?
A)P1.
B)P2.
C)P3.
D)P4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The only policy lever that is effective against unemployment when the AS curve is vertical is
A)Fiscal policy.
B)Monetary policy.
C)Supply-side policy.
D)Laissez faire policy.
A)Fiscal policy.
B)Monetary policy.
C)Supply-side policy.
D)Laissez faire policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Use the following figure to answer the questions : Figure 8.5: 
In Figure 8.5,according to Keynesians,if equilibrium real output is Q1 and full-employment real output is Q2,an appropriate fiscal policy lever would be to
A)Increase AD by increasing income taxes.
B)Increase AD by increasing government spending.
C)Increase AS by reducing government regulations.
D)Reduce AS by tightening air pollution standards to improve air quality.

In Figure 8.5,according to Keynesians,if equilibrium real output is Q1 and full-employment real output is Q2,an appropriate fiscal policy lever would be to
A)Increase AD by increasing income taxes.
B)Increase AD by increasing government spending.
C)Increase AS by reducing government regulations.
D)Reduce AS by tightening air pollution standards to improve air quality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



