Deck 18: Decision-Making Tools
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/107
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Decision-Making Tools
1
Decision trees and decision tables can both solve problems requiring a single decision, but decision tables are the preferred method when a sequence of decisions is involved.
False
2
If a decision maker has to make a certain decision only once, expected monetary value is a good indication of the payoff associated with the decision.
False
3
Which of the following is not considered a step in the decision-making process?
A) Clearly identify the problem.
B) Select the best alternative.
C) Develop objectives.
D) Evaluate alternatives.
E) Minimize costs whenever possible.
A) Clearly identify the problem.
B) Select the best alternative.
C) Develop objectives.
D) Evaluate alternatives.
E) Minimize costs whenever possible.
E
4
The expected value of perfect information is the same as the expected value with perfect information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An example of expected monetary value would be the payoff from selecting a particular alternative when a particular state of nature occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In a decision tree, a square symbol represents a state of nature node.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A state of nature is an occurrence of a situation over which the decision maker has little or no control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The maximax criterion of decision making requires that all decision alternatives have an equal probability of occurrence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If a decision maker knows for sure which state of nature will occur, he/she is making a decision under certainty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An example of a conditional value would be the payoff from selecting a particular alternative when a particular state of nature occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If a decision maker can assign probabilities of occurrences to the states of nature, then the decision-making environment is Decision Making under Uncertainty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A square node on a decision tree infers that
A) the node splits into various states of nature, of which only one will occur.
B) there are several alternatives available.
C) the manager must choose an alternative.
D) there are several alternatives available and the manager must choose an alternative.
E) the node splits into various states of nature, of which only one will occur, there are several alternatives available and the manager must choose an alternative.
A) the node splits into various states of nature, of which only one will occur.
B) there are several alternatives available.
C) the manager must choose an alternative.
D) there are several alternatives available and the manager must choose an alternative.
E) the node splits into various states of nature, of which only one will occur, there are several alternatives available and the manager must choose an alternative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The last step in the analytic decision process clearly defines the problem and the factors that influence it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The first step, and a key element, in the decision-making process is to
A) consult a specialist.
B) clearly define the problem.
C) develop objectives.
D) monitor the results.
E) select the best alternative.
A) consult a specialist.
B) clearly define the problem.
C) develop objectives.
D) monitor the results.
E) select the best alternative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The last step of the decision-making process is to
A) develop a model.
B) evaluate each alternative.
C) pick the best alternative.
D) implement the decision.
E) check the decision with senior management.
A) develop a model.
B) evaluate each alternative.
C) pick the best alternative.
D) implement the decision.
E) check the decision with senior management.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In a decision tree, the expected monetary values are computed by working from right to left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The expected value with perfect information assumes that all states of nature are equally likely.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The expected monetary value of a decision alternative is the sum of all possible payoffs from the alternative, each weighted by the probability of that payoff occurring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Analytic decision making is based on logic and considers all available data and possible alternatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The maximin criterion is pessimistic, while the maximax criterion is optimistic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A plant manager wants to know how much he should be willing to pay for perfect market research. Currently there are two states of nature facing his decision to expand or do nothing. Under favorable market conditions the manager would make $100,000 for the large plant and $5,000 for the small plant. Under unfavorable market conditions the large plant would lose $50,000 and the small plant would make $0. If the two states of nature are equally likely, how much should he pay for perfect information?
A) $0
B) $25,000
C) $50,000
D) $100,000
E) unable to determine
A) $0
B) $25,000
C) $50,000
D) $100,000
E) unable to determine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Doing nothing would yield how much profit if favorable market conditions prevail according to the following decision table
A) $5,000
B) $20,000
C) -$10,000
D) $0
E) unable to determine
A) $5,000
B) $20,000
C) -$10,000
D) $0
E) unable to determine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A tabular presentation that shows the outcome for each decision alternative under the various possible states of nature is called a(n)
A) isoquant table.
B) payback period matrix.
C) payoff table.
D) feasible region.
E) decision tree.
A) isoquant table.
B) payback period matrix.
C) payoff table.
D) feasible region.
E) decision tree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A decision-maker using the maximin criterion on the problem below would choose Alternative ________ because the maximum of the row minimums is ________. States of Nature
A) A; 55
B) B; 30
C) C; 70
D) D; 140
E) D; 10
A) A; 55
B) B; 30
C) C; 70
D) D; 140
E) D; 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The expected value of perfect information (EVPI) is the
A) payoff for a decision made under perfect information.
B) payoff under minimum risk.
C) average expected payoff.
D) difference between the payoff under perfect information and the payoff under risk.
E) payoff for a decision made under maximum risk.
A) payoff for a decision made under perfect information.
B) payoff under minimum risk.
C) average expected payoff.
D) difference between the payoff under perfect information and the payoff under risk.
E) payoff for a decision made under maximum risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When solving decision trees, what phrase represents the act of dropping an alternative from consideration because it is less favorable than another available option?
A) cut the leaf
B) open the hatch
C) shake the tree
D) punt the ball
E) prune the branch
A) cut the leaf
B) open the hatch
C) shake the tree
D) punt the ball
E) prune the branch

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The difference between the expected payoff under perfect information and the maximum expected payoff under risk is
A) expected monetary value.
B) economic order quantity.
C) expected value of perfect information.
D) PERT.
E) expected monetary payoff.
A) expected monetary value.
B) economic order quantity.
C) expected value of perfect information.
D) PERT.
E) expected monetary payoff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The following decision tree has how many state of nature nodes? 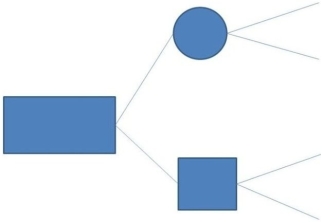
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the EMV for Option 1 in the following decision table? States of Nature
A) 15,000
B) 17,000
C) 17,500
D) 18,500
E) 20,000
A) 15,000
B) 17,000
C) 17,500
D) 18,500
E) 20,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In terms of decision theory, an occurrence or situation over which the decision maker has no control is called a(n)
A) decision under uncertainty.
B) decision tree.
C) state of nature.
D) alternative.
E) probable state.
A) decision under uncertainty.
B) decision tree.
C) state of nature.
D) alternative.
E) probable state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The expected value with perfect information
A) equals EVPI - EMV.
B) requires that each decision alternative have a known probability of occurrence.
C) is an input into the calculation of the expected value of perfect information.
D) is the average of the maximax and the maximin.
E) none of the above.
A) equals EVPI - EMV.
B) requires that each decision alternative have a known probability of occurrence.
C) is an input into the calculation of the expected value of perfect information.
D) is the average of the maximax and the maximin.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A decision-maker using the maximax criterion on the problem below would choose Alternative ________ because the maximum of the row maximums is ________. States of Nature
A) A; 60
B) B; 80
C) C; 70
D) D; -100
E) D; 140
A) A; 60
B) B; 80
C) C; 70
D) D; -100
E) D; 140

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The highest value for the equally likely criterion is ________; this occurs with alternative ________. States of Nature
A) $20,000; Option 1
B) $25,000; Option 2
C) $28,000; Option 3
D) $32,000; Option 3
E) $60,000; Option 3
A) $20,000; Option 1
B) $25,000; Option 2
C) $28,000; Option 3
D) $32,000; Option 3
E) $60,000; Option 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The expected value with perfect information is
A) the maximum EMV for a set of alternatives.
B) the same as the expected value of perfect information.
C) valuable in situations involving risk.
D) the average return obtained when the decision maker knows which state of nature is going to occur before the decision is made.
E) obtained using conditional probabilities.
A) the maximum EMV for a set of alternatives.
B) the same as the expected value of perfect information.
C) valuable in situations involving risk.
D) the average return obtained when the decision maker knows which state of nature is going to occur before the decision is made.
E) obtained using conditional probabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The decision criterion that would be used by an optimistic decision maker solving a problem under conditions of uncertainty would be the
A) expected monetary value criterion.
B) equally likely criterion.
C) maximax criterion.
D) maximin criterion.
E) minimin criterion.
A) expected monetary value criterion.
B) equally likely criterion.
C) maximax criterion.
D) maximin criterion.
E) minimin criterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The outcome of an alternative/state of nature combination is a(n)
A) price.
B) conditional value.
C) expected value.
D) conditional probability.
E) maximum value.
A) price.
B) conditional value.
C) expected value.
D) conditional probability.
E) maximum value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Expected monetary value is most appropriate for problem solving that takes place
A) when conditions are average.
B) when all states of nature are equally likely.
C) when all alternatives are equally likely.
D) under conditions of uncertainty.
E) under conditions of risk.
A) when conditions are average.
B) when all states of nature are equally likely.
C) when all alternatives are equally likely.
D) under conditions of uncertainty.
E) under conditions of risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The likelihood that a decision maker will ever receive a payoff precisely equal to the EMV when making any one decision is
A) low (near 0%).
B) high (near 100%).
C) dependent upon the number of alternatives.
D) dependent upon the number of states of nature.
E) 50%.
A) low (near 0%).
B) high (near 100%).
C) dependent upon the number of alternatives.
D) dependent upon the number of states of nature.
E) 50%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
There are three equally likely states of nature (High, Medium, and Low demand). If the large factory will post profits of $50,000, $25,000, and - $10,000 under these states of nature, respectively, what is the EMV of the factory?
A) $50,000
B) $25,000
C) $28,333.33
D) $21,666.67
E) $2,166.67
A) $50,000
B) $25,000
C) $28,333.33
D) $21,666.67
E) $2,166.67

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A decision maker who uses the maximin criterion when solving a problem under conditions of uncertainty is
A) an optimist.
B) a pessimist.
C) an economist.
D) an optometrist.
E) making a serious mistake; maximin is not appropriate for conditions of uncertainty.
A) an optimist.
B) a pessimist.
C) an economist.
D) an optometrist.
E) making a serious mistake; maximin is not appropriate for conditions of uncertainty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A primary advantage of decision trees compared to decision tables is that decision trees
A) are more accurate.
B) provide a graphic.
C) are smaller.
D) are cheaper.
E) can be used for sequential problems.
A) are more accurate.
B) provide a graphic.
C) are smaller.
D) are cheaper.
E) can be used for sequential problems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the expected value of perfect information of the following decision table? States of Nature
A) 0
B) 20
C) 50
D) 150
E) 200
A) 0
B) 20
C) 50
D) 150
E) 200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
________ is the expected payout or value of a variable that has different possible states of nature, each with an associated probability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Decision trees
A) give more accurate solutions than decision tables.
B) give less accurate solutions than decision tables.
C) are especially powerful when a sequence of decisions must be made.
D) are rarely used because one needs specialized software to graph them.
E) are too complex to be used by decision makers.
A) give more accurate solutions than decision tables.
B) give less accurate solutions than decision tables.
C) are especially powerful when a sequence of decisions must be made.
D) are rarely used because one needs specialized software to graph them.
E) are too complex to be used by decision makers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is the EMV for Option 2 in the following decision table? States of Nature
A) 5,000
B) 21,000
C) 25,000
D) 29,000
E) 45,000
A) 5,000
B) 21,000
C) 25,000
D) 29,000
E) 45,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A decision tree is a(n)
A) algebraic representation of alternatives and states of nature.
B) behavioral representation of alternatives and states of nature.
C) matrix representation of alternatives and states of nature.
D) graphic representation of alternatives and states of nature.
E) tabular representation of alternatives and states of nature.
A) algebraic representation of alternatives and states of nature.
B) behavioral representation of alternatives and states of nature.
C) matrix representation of alternatives and states of nature.
D) graphic representation of alternatives and states of nature.
E) tabular representation of alternatives and states of nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
________ is the criterion for decision making under certainty that assigns equal probability to each state of nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the EMV for Option 2 in the following decision table? States of Nature
A) 10,000
B) 16,000
C) 20,000
D) 24,000
E) 30,000
A) 10,000
B) 16,000
C) 20,000
D) 24,000
E) 30,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What is the expected value with perfect information of the following decision table? States of Nature
A) 5,000
B) 10,000
C) 40,000
D) 60,000
E) 70,000
A) 5,000
B) 10,000
C) 40,000
D) 60,000
E) 70,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A retailer is deciding how many of a certain product to stock. The historical probability distribution of sales for this product is 0 units, 0.2; 1 unit, 0.3; 2 units, 0.4, and 3 units, 0.1. The product costs $8 per unit and sells for $25 per unit. The conditional value for the decision alternative "Stock 3" and state of nature "Sell 1" is
A) 1.4 units.
B) $1 profit.
C) $25 profit.
D) $-8 profit.
E) 25 units.
A) 1.4 units.
B) $1 profit.
C) $25 profit.
D) $-8 profit.
E) 25 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
All of the following steps are taken to analyse problems with decision trees except
A) define the problem.
B) structure or draw a decision tree.
C) assign probabilities to the alternatives.
D) estimate payoffs for each possible alternative/state of nature combination.
E) solve the problem by computing expected monetary values for each state of nature node.
A) define the problem.
B) structure or draw a decision tree.
C) assign probabilities to the alternatives.
D) estimate payoffs for each possible alternative/state of nature combination.
E) solve the problem by computing expected monetary values for each state of nature node.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What is the EMV for Option 2 in the following decision table? States of Nature
A) 50
B) 100
C) 170
D) 200
E) 350
A) 50
B) 100
C) 170
D) 200
E) 350

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A problem that involves a sequence of decisions
A) cannot be analyzed with expected monetary value.
B) can be better analyzed with a decision tree than by a decision table.
C) must be analyzed in the same order that the decisions are made.
D) cannot be analyzed with decision tree software.
E) can only be analyzed using decision making under certainty.
A) cannot be analyzed with expected monetary value.
B) can be better analyzed with a decision tree than by a decision table.
C) must be analyzed in the same order that the decisions are made.
D) cannot be analyzed with decision tree software.
E) can only be analyzed using decision making under certainty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the EMV for Option 1 in the following decision table? States of Nature
A) 200
B) 240
C) 250
D) 260
E) 300
A) 200
B) 240
C) 250
D) 260
E) 300

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
________ is the criterion for decision making under uncertainty that finds an alternative that maximizes the minimum outcome or consequences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What is the EMV for Option 1 in the following decision table? States of Nature
A) 10,000
B) 18,000
C) 20,000
D) 22,000
E) 30,000
A) 10,000
B) 18,000
C) 20,000
D) 22,000
E) 30,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
________ is the difference between the payoff under perfect information and the payoff under risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A(n) ________ is a tabular means of analyzing decision alternatives and states of nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What is the expected value with perfect information in the following decision table? States of Nature
A) 50
B) 200
C) 260
D) 300
E) 350
A) 50
B) 200
C) 260
D) 300
E) 350

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A retailer is deciding how many of a certain product to stock. The historical probability distribution of sales for this product is 0 units, 0.2; 1 unit, 0.3; 2 units, 0.4, and 3 units, 0.1. The product costs $8 per unit and sells for $25 per unit. The largest conditional value (profit) in the entire payoff table for this scenario is
A) $-24 profit.
B) $-8 profit.
C) $17 profit.
D) $51 profit.
E) $75 profit.
A) $-24 profit.
B) $-8 profit.
C) $17 profit.
D) $51 profit.
E) $75 profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How is the expected value of perfect information (EVPI) found?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
An operations manager's staff has compiled the information below for four manufacturing alternatives (E, F, G, and H) that vary by production technology and the capacity of the machinery. All choices enable the same level of total production and have the same lifetime. The four states of nature represent four levels of consumer acceptance of the firm's products. Values in the table are net present value of future profits in millions of dollars. Forecasts indicate that there is a 0.1 probability of acceptance level 1, 0.2 chance of acceptance level 2, 0.4 chance of acceptance level 3, and 0.3 change of acceptance level 4.
States of Nature
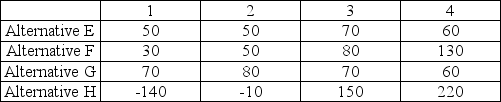 Using the criterion of expected monetary value, which production alternative should be chosen?
Using the criterion of expected monetary value, which production alternative should be chosen?
States of Nature
 Using the criterion of expected monetary value, which production alternative should be chosen?
Using the criterion of expected monetary value, which production alternative should be chosen?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Describe the meaning of EVPI. Provide an example in which EVPI can help a manager.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
An operations manager's staff has compiled the information below for four manufacturing alternatives (A, B, C, and
D) that vary by production technology and the capacity of the machinery. All choices enable the same level of total production and have the same lifetime. The four states of nature represent four levels of consumer acceptance of the firm's products. Values in the table are net present value of future profits in millions of dollars.
States of Nature
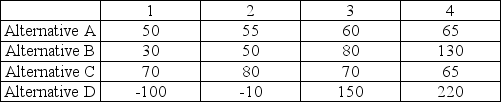
a. Assuming a maximax strategy, which alternative would be chosen?
b. If maximin were used, which would be chosen?
c. If the states of nature were equally likely, which alternative should be chosen?
D) that vary by production technology and the capacity of the machinery. All choices enable the same level of total production and have the same lifetime. The four states of nature represent four levels of consumer acceptance of the firm's products. Values in the table are net present value of future profits in millions of dollars.
States of Nature

a. Assuming a maximax strategy, which alternative would be chosen?
b. If maximin were used, which would be chosen?
c. If the states of nature were equally likely, which alternative should be chosen?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What are decision tables?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A branch of a decision tree that is less favorable than other available options may be ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In the context of decision-making, define state of nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The construction manager for Acme Construction, Inc. must decide whether to build single family homes, apartments, or condominiums. This is not a product-mix problem, but an all-or nothing decision. He will hire workers and rent equipment appropriate for one action only. He estimates annual profits (in thousands of dollars) will vary with population trends as follows:
 a. If he uses the maximin criterion, which type of dwellings will he choose to build? Show your supporting calculations.
a. If he uses the maximin criterion, which type of dwellings will he choose to build? Show your supporting calculations.
b. If he uses the equally likely criterion, which kind of dwellings will he choose to build? Show your supporting calculations.
c. If the construction manager were an optimist, what criterion would he choose? What would be the choice of dwelling for that criterion? Show your supporting calculations.
 a. If he uses the maximin criterion, which type of dwellings will he choose to build? Show your supporting calculations.
a. If he uses the maximin criterion, which type of dwellings will he choose to build? Show your supporting calculations.b. If he uses the equally likely criterion, which kind of dwellings will he choose to build? Show your supporting calculations.
c. If the construction manager were an optimist, what criterion would he choose? What would be the choice of dwelling for that criterion? Show your supporting calculations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A(n) ________ is an occurrence or situation over which the decision maker has little or no control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The square symbol used in drawing a decision trees represents a ________ node.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In the context of decision-making, define alternative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Identify and describe three methods used for decision making under conditions of uncertainty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Explain the graphical shapes used in decision tree analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A(n) ________ is a graphical means of analyzing decision alternatives and states of nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What limitation(s) do decision trees overcome compared to decision tables?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What is a conditional value?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which technique results in an optimistic decision? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Identify, in order, the six steps of analytical decision making.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Define expected monetary value (EMV).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If a decision maker is a pessimist, what decision-making criterion is appropriate? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



