Deck 6: The British Empire and the Colonial Crisis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/77
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: The British Empire and the Colonial Crisis
1
According to the inscription in "Silver Medal to Present to Indians," who were "HAPPY WHILE UNITED"?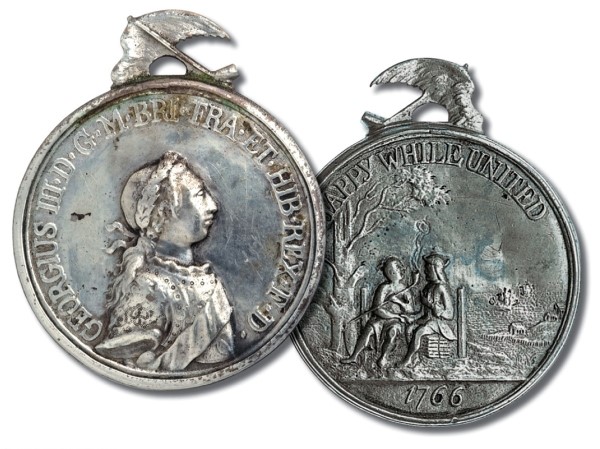 
A) All the European nations
B) The British and the Indians
C) The British among themselves
D) All colonists in the New World

A) All the European nations
B) The British and the Indians
C) The British among themselves
D) All colonists in the New World
The British and the Indians
2
The first street demonstrations against the Stamp Act occurred in which colony?
A) Massachusetts
B) Rhode Island
C) Pennsylvania
D) Virginia
A) Massachusetts
B) Rhode Island
C) Pennsylvania
D) Virginia
Massachusetts
3
Which territory did England receive in the Treaty of Paris?
A) Cuba
B) Canada
C) Martinique
D) New Orleans
A) Cuba
B) Canada
C) Martinique
D) New Orleans
Canada
4
What was the reaction to the Virginia Resolves?
A) Virginia's political leaders viewed them as moderate and necessary measures.
B) Few people discussed the Virginia Resolves outside of Virginia.
C) The crown adopted some of the resolves after protest from the colonists.
D) Colonists saw them as radical because newspapers printed all seven resolutions.
A) Virginia's political leaders viewed them as moderate and necessary measures.
B) Few people discussed the Virginia Resolves outside of Virginia.
C) The crown adopted some of the resolves after protest from the colonists.
D) Colonists saw them as radical because newspapers printed all seven resolutions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
How did the Stamp Act differ from the Sugar Act?
A) The Stamp Act was merely a revision of a previously existing tax.
B) The Stamp Act was a tax to be paid mainly by merchants and shippers.
C) The Stamp Act was enforced by British instead of American officials.
D) The Stamp Act was an internal tax that affected a great number of colonists.
A) The Stamp Act was merely a revision of a previously existing tax.
B) The Stamp Act was a tax to be paid mainly by merchants and shippers.
C) The Stamp Act was enforced by British instead of American officials.
D) The Stamp Act was an internal tax that affected a great number of colonists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Why did King George III seek to extract more money from the colonists?
A) He was displeased with the profits from colonial exports.
B) His policies were an extension of his aggressive personality.
C) He thought the colonists should help pay England's war debt.
D) He wanted to punish colonists who called for independence.
A) He was displeased with the profits from colonial exports.
B) His policies were an extension of his aggressive personality.
C) He thought the colonists should help pay England's war debt.
D) He wanted to punish colonists who called for independence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Who initiated a series of resolves in Virginia in protest of the Stamp Act?
A) Samuel Adams
B) Patrick Henry
C) John Hancock
D) Ebenezer MacIntosh
A) Samuel Adams
B) Patrick Henry
C) John Hancock
D) Ebenezer MacIntosh

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What did the colonists learn from the Seven Years' War?
A) British soldiers expertly engaged in frontier warfare.
B) Britain's leaders welcomed their participation in political affairs.
C) British military discipline was harsh.
D) Great Britain saw little value in maintaining the American colonies.
A) British soldiers expertly engaged in frontier warfare.
B) Britain's leaders welcomed their participation in political affairs.
C) British military discipline was harsh.
D) Great Britain saw little value in maintaining the American colonies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In an effort to generate income for England, in 1764 George Grenville initiated the
A) Currency Act.
B) Sugar Act.
C) Molasses Act.
D) Proclamation Act.
A) Currency Act.
B) Sugar Act.
C) Molasses Act.
D) Proclamation Act.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
George Grenville claimed that Americans had "virtual representation" because
A) the colonists were allowed to send delegates to the House of Commons.
B) each American colony had its own colonial assembly for governance.
C) the House of Commons represented all British subjects, wherever they were.
D) the colonists were represented in the Continental Congress.
A) the colonists were allowed to send delegates to the House of Commons.
B) each American colony had its own colonial assembly for governance.
C) the House of Commons represented all British subjects, wherever they were.
D) the colonists were represented in the Continental Congress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What did the protests of the Sons of Liberty prove to colonists?
A) British authority would quell such riots in the future.
B) Stamp distributors were more popular than they had realized.
C) The British police force would ignore demonstrations.
D) Demonstrations could have a decisive impact on politics.
A) British authority would quell such riots in the future.
B) Stamp distributors were more popular than they had realized.
C) The British police force would ignore demonstrations.
D) Demonstrations could have a decisive impact on politics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What did the attack at Fort Necessity reveal about the French commitment to the Ohio territory?
A) The French lacked the manpower to hold the territory.
B) The French had no intention of departing the disputed territory.
C) The French could not defeat General George Washington.
D) The French could not win without the help of the Mingo Indians.
A) The French lacked the manpower to hold the territory.
B) The French had no intention of departing the disputed territory.
C) The French could not defeat General George Washington.
D) The French could not win without the help of the Mingo Indians.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What role did the Indians play in the Treaty of Paris?
A) They negotiated protection for their land in the Ohio Valley.
B) They were invited to the negotiations but won no concessions.
C) The chief Minavavana negotiated on behalf of the Indians.
D) The major European powers did not consult the Indians at all.
A) They negotiated protection for their land in the Ohio Valley.
B) They were invited to the negotiations but won no concessions.
C) The chief Minavavana negotiated on behalf of the Indians.
D) The major European powers did not consult the Indians at all.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What did Benjamin Franklin and Thomas Hutchinson hope to accomplish with the Albany Plan of Union?
A) Peace with New France
B) Separation from Parliament
C) The formation of a strong federal government
D) The creation of an Indian policy
A) Peace with New France
B) Separation from Parliament
C) The formation of a strong federal government
D) The creation of an Indian policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What did the Virginia Resolves argue?
A) Colonists could not afford to pay more taxes.
B) Virginia alone had the right to tax Virginians.
C) Britain did not need more tax revenue.
D) The monarchy alone could tax Virginians.
A) Colonists could not afford to pay more taxes.
B) Virginia alone had the right to tax Virginians.
C) Britain did not need more tax revenue.
D) The monarchy alone could tax Virginians.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
According to Map 6.2: Europe Redraws the Map of North America, 1763, which of the following European powers had the smallest colonial presence by 1763? 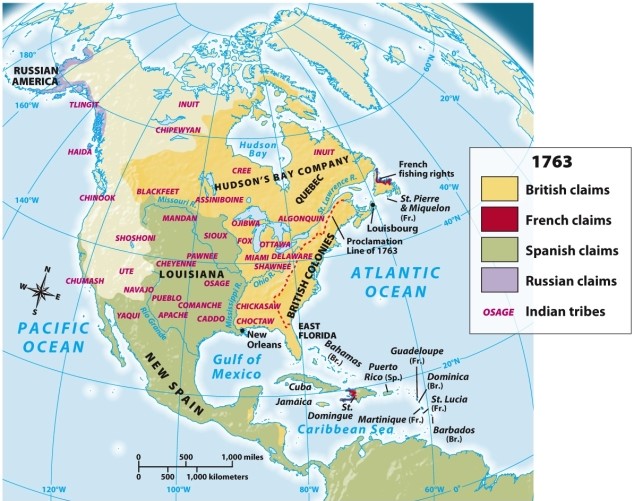
A) Britain
B) France
C) The Netherlands
D) Spain

A) Britain
B) France
C) The Netherlands
D) Spain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What was the purpose of the Proclamation of 1763?
A) To establish a permanent boundary line between Indians and colonists
B) To protect the French fur trade from assaults by colonists or Indians
C) To identify western lands as formally belonging to the Indians
D) To prevent colonists from settling west of the Appalachian Mountains
A) To establish a permanent boundary line between Indians and colonists
B) To protect the French fur trade from assaults by colonists or Indians
C) To identify western lands as formally belonging to the Indians
D) To prevent colonists from settling west of the Appalachian Mountains

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Who was credited with leading a violent rebellion against the British in 1763?
A) Minavavana
B) Jeffrey Amherst
C) Pontiac
D) The Paxton Boys
A) Minavavana
B) Jeffrey Amherst
C) Pontiac
D) The Paxton Boys

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
How did William Pitt turn the Seven Years' War in favor of the British?
A) He held successful negotiations with the Iroquois.
B) He captured of the French fortress city of Quebec.
C) He committed massive resources to the war.
D) He adopted the tactics of guerrilla warfare.
A) He held successful negotiations with the Iroquois.
B) He captured of the French fortress city of Quebec.
C) He committed massive resources to the war.
D) He adopted the tactics of guerrilla warfare.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What caused the Seven Years' War?
A) Conflicts over territory in the Ohio Valley
B) A dispute between Indians and the French
C) French fur trapping along the Hudson River
D) Conflicts between New England and New France
A) Conflicts over territory in the Ohio Valley
B) A dispute between Indians and the French
C) French fur trapping along the Hudson River
D) Conflicts between New England and New France

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
How did the British government respond to the colonial reaction to the Stamp Act?
A) It affirmed the governing power of the colonists.
B) It prepared for a long military conflict.
C) It repealed the Stamp Act in March 1766.
D) It initiated imperial restructuring.
A) It affirmed the governing power of the colonists.
B) It prepared for a long military conflict.
C) It repealed the Stamp Act in March 1766.
D) It initiated imperial restructuring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The Coercive Acts, passed by Parliament to punish Massachusetts for the Destruction of the Tea, included
A) a law closing Boston harbor until the tea was paid for.
B) a new set of high internal and external tax laws.
C) a law stipulating criminals would be tried in Canada.
D) the end of spring elections of town selectmen.
A) a law closing Boston harbor until the tea was paid for.
B) a new set of high internal and external tax laws.
C) a law stipulating criminals would be tried in Canada.
D) the end of spring elections of town selectmen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following statements characterizes the effects of the nonimportation agreements of 1768-69?
A) Nonimportation failed due to tensions between southern farmers and northern organizers.
B) Merchants and consumers needed little persuasion to join the nonimportation movement.
C) Nonimportation efforts collapsed because southern merchants refused to abandon British goods.
D) By 1769, merchants from New England to Charleston were supporting nonimportation.
A) Nonimportation failed due to tensions between southern farmers and northern organizers.
B) Merchants and consumers needed little persuasion to join the nonimportation movement.
C) Nonimportation efforts collapsed because southern merchants refused to abandon British goods.
D) By 1769, merchants from New England to Charleston were supporting nonimportation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What was the result of the anti-British boycotts of the late 1760s?
A) British merchants made more money.
B) Imports fell by 40 percent.
C) Anti-British sentiment decreased.
D) The Sons of Liberty ceased to exist.
A) British merchants made more money.
B) Imports fell by 40 percent.
C) Anti-British sentiment decreased.
D) The Sons of Liberty ceased to exist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Dissenting colonists believed the real goal of the Tea Act of 1773 was to
A) start a war with the colonies.
B) put Dutch tea companies out of business.
C) demonstrate cooperation on trade.
D) pay the salaries of royal officials.
A) start a war with the colonies.
B) put Dutch tea companies out of business.
C) demonstrate cooperation on trade.
D) pay the salaries of royal officials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
How did the colonists respond to the Townshend duties?
A) They argued they could not afford to pay the burdensome tax rate.
B) They resented that part of the revenue would pay royal governors' salaries.
C) They did not mind paying the external duties on trade goods.
D) They cheered the fact that it strengthened legislative government in America.
A) They argued they could not afford to pay the burdensome tax rate.
B) They resented that part of the revenue would pay royal governors' salaries.
C) They did not mind paying the external duties on trade goods.
D) They cheered the fact that it strengthened legislative government in America.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
How did the Declaratory Act show Britain's refusal to compromise on Parliament's power to tax?
A) It asserted Parliament's right to legislate for the colonies.
B) It gave more power to the colonial governors.
C) It initiated a new series of taxes on rarely used colonial goods.
D) It gave colonists authority to legislate for themselves.
A) It asserted Parliament's right to legislate for the colonies.
B) It gave more power to the colonial governors.
C) It initiated a new series of taxes on rarely used colonial goods.
D) It gave colonists authority to legislate for themselves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Lord North removed all the Townsend duties except for the tax on
A) tea.
B) glass.
C) lead.
D) paper.
A) tea.
B) glass.
C) lead.
D) paper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
"I observed with great concern a paragraph with the signature of 'Consideration,' calculated to deter you from paying for the tea, a measure at this alarming juncture highly necessary and what every REAL friend to the cause of America must think your indispensible duty. While we contend for liberty, let us not destroy the idea of justice. A trespass has been committed on private property in consequence of the Resolves of your town. Restore to the sufferers the most ample compensation for the injury they have received-convince your enemies that their property is secure in every Port on the British Continent-Convince them that you do not regard the value of the article destroyed-that you only deny the right of taxation. Let not the annals of your history be sullied by a refusal-pay for the tea-it will rejoice your friends-it will convince your adversaries that the cause you are attach'd to is a righteous and just cause. Convince them that you regard honesty as much as liberty, and that you detest libertinism and licentiousness. . . ." Why did this anonymous author think that the patriots should pay for the tea lost during the Boston Tea Party?
A) So that observers do not become distracted by the destruction of property and lose sight of the real goal of liberty
B) Because the author disagrees with the goal of independence
C) So that the patriots could show the British that they were rich
D) Because they were wrong to destroy the tea under any circumstances
A) So that observers do not become distracted by the destruction of property and lose sight of the real goal of liberty
B) Because the author disagrees with the goal of independence
C) So that the patriots could show the British that they were rich
D) Because they were wrong to destroy the tea under any circumstances

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
John Adams represented British captain Thomas Preston and his soldiers who were involved in the Boston Massacre in order to
A) please loyalist members of his family who had grown tired of his constant protests.
B) prove that the colonists had the upper hand.
C) sabotage the trial by offering a poor defense for the soldiers and guaranteeing their conviction.
D) show that local leaders believed even unpopular defendants deserved a fair trial.
A) please loyalist members of his family who had grown tired of his constant protests.
B) prove that the colonists had the upper hand.
C) sabotage the trial by offering a poor defense for the soldiers and guaranteeing their conviction.
D) show that local leaders believed even unpopular defendants deserved a fair trial.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
"[I]n short the Ministry may rely on it that Americans will never be tax'd without their own consent that the cause of Boston the despotick Measures in respect to it I mean now is and ever will be considerd as the cause of America (not that we approve their cond[uc]t in destroyg the Tea) & that we shall not suffer ourselves to be sacrificed by piecemeal though god only knows what is to become of us, threatned as we are with so many hoverg evils as hang over us at present; having a cruel & blood thirsty Enemy upon our Backs, the Indians, between whom & our Frontier Inhabitants many Skirmishes have happend, & with who(m) a general War is inevitable whilst those from whom we have a right to Seek protection are endeavouring by every piece of Art & despotism to fix the Shackles of Slavry upon us." In his letter to George William Fairfax, why did George Washington bring up Indians?
A) To propose them as potential allies in the struggle for independence
B) To compare the plight of the American colonists to those of the Indians
C) To bemoan that Americans must fight Indians while also being unprotected and oppressed by Britain
D) To suggest that the Indians are in cahoots with the British
A) To propose them as potential allies in the struggle for independence
B) To compare the plight of the American colonists to those of the Indians
C) To bemoan that Americans must fight Indians while also being unprotected and oppressed by Britain
D) To suggest that the Indians are in cahoots with the British

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What was the Boston Massacre?
A) A riot that killed two hundred people
B) A confrontation which left a customs official dead
C) A skirmish in which five people were killed
D) A mutiny aboard British ships carrying tea
A) A riot that killed two hundred people
B) A confrontation which left a customs official dead
C) A skirmish in which five people were killed
D) A mutiny aboard British ships carrying tea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The Daughters of Liberty suggested that women participate in public affairs and protest the Townshend duties by
A) participating in nonconsumption.
B) growing their own tea plants.
C) joining men in street protests.
D) marching on the governor's mansion.
A) participating in nonconsumption.
B) growing their own tea plants.
C) joining men in street protests.
D) marching on the governor's mansion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following was a consequence of the tea boycott, according to the illustration "Edenton Tea Ladies"? 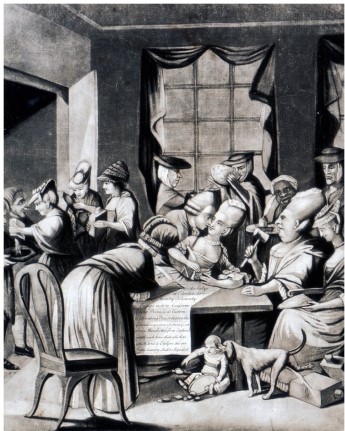
A) Women acting too masculine
B) Women neglecting their educations
C) Women ignoring their duties as wives
D) Widespread acceptance of interracial marriage

A) Women acting too masculine
B) Women neglecting their educations
C) Women ignoring their duties as wives
D) Widespread acceptance of interracial marriage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
According to the British, the major purpose of the Tea Act of 1773 was to
A) break the American boycott of tea imported from England.
B) raise more revenue to cover military costs in North America.
C) boost sales for Britain's East India Company.
D) punish the Americans for importing tea from Holland.
A) break the American boycott of tea imported from England.
B) raise more revenue to cover military costs in North America.
C) boost sales for Britain's East India Company.
D) punish the Americans for importing tea from Holland.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What was the result of the Boston Massacre trial?
A) All but two of the soldiers were acquitted.
B) All of the soldiers were convicted of manslaughter.
C) All of the soldiers were branded on the thumbs.
D) All but three of the soldiers served jail time.
A) All but two of the soldiers were acquitted.
B) All of the soldiers were convicted of manslaughter.
C) All of the soldiers were branded on the thumbs.
D) All but three of the soldiers served jail time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What was the significance of the Stamp Act Congress, held in New York in 1765?
A) Representatives could not agree on a unified policy.
B) It protested the enslavement of blacks in the South.
C) Delegates threatened rebellion against Britain.
D) It advanced the idea of intercolonial political action.
A) Representatives could not agree on a unified policy.
B) It protested the enslavement of blacks in the South.
C) Delegates threatened rebellion against Britain.
D) It advanced the idea of intercolonial political action.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In 1767, Charles Townshend enacted the Revenue Act, which
A) levied an internal tax against the colonists.
B) placed new duties on imported items.
C) was an innovative form of income tax.
D) taxed building materials, such as brick and wood.
A) levied an internal tax against the colonists.
B) placed new duties on imported items.
C) was an innovative form of income tax.
D) taxed building materials, such as brick and wood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
How did Massachusetts protestors target Lieutenant Governor Thomas Hutchinson?
A) Protestors ransacked his house until only the exterior walls stood.
B) Colonists attempted to assassinate him after he supported the Stamp Act.
C) Gangs of seamen in Boston tarred and feathered him.
D) A congressional meeting in Philadelphia called for his resignation.
A) Protestors ransacked his house until only the exterior walls stood.
B) Colonists attempted to assassinate him after he supported the Stamp Act.
C) Gangs of seamen in Boston tarred and feathered him.
D) A congressional meeting in Philadelphia called for his resignation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The Quebec Act offended many Americans because
A) it denied many political rights to Roman Catholics.
B) it permitted criminal cases to be adjudicated without the use of juries.
C) it gave French Canadians unrestricted entry into New England.
D) it gave Roman Catholic Quebec control of the Ohio Valley.
A) it denied many political rights to Roman Catholics.
B) it permitted criminal cases to be adjudicated without the use of juries.
C) it gave French Canadians unrestricted entry into New England.
D) it gave Roman Catholic Quebec control of the Ohio Valley.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Following the battles of Lexington and Concord, Lord Dunmore, the royal governor of Virginia, issued a proclamation
A) promising freedom to defecting, able-bodied slaves who would fight for the British.
B) stating that he would free any slave who volunteered to fight for the British.
C) calling for Virginians to join him in freeing their slaves to fight.
D) stating that any slave caught fighting for the British would be hanged immediately.
A) promising freedom to defecting, able-bodied slaves who would fight for the British.
B) stating that he would free any slave who volunteered to fight for the British.
C) calling for Virginians to join him in freeing their slaves to fight.
D) stating that any slave caught fighting for the British would be hanged immediately.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Why did General Gage plan a surprise attack on an ammunition storage site in Concord?
A) He believed that a small group in Concord was causing all colonial dissent.
B) He knew that the storage site contained all firepower in the area.
C) His intelligence revealed that the storage site would be unguarded.
D) British leaders ordered him to arrest the American troublemakers.
A) He believed that a small group in Concord was causing all colonial dissent.
B) He knew that the storage site contained all firepower in the area.
C) His intelligence revealed that the storage site would be unguarded.
D) British leaders ordered him to arrest the American troublemakers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which colony failed to send a delegate to the First Continental Congress in Philadelphia?
A) Rhode Island
B) New Jersey
C) Georgia
D) Pennsylvania
A) Rhode Island
B) New Jersey
C) Georgia
D) Pennsylvania

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Why did the northern slave Phillis Wheatley gain national attention?
A) She led Bostonian women in promoting spinning bees.
B) She wrote popular poetry about freedom for slaves.
C) She incited slaves to rebel against the British in Boston.
D) She started the Underground Railroad to free slaves.
A) She led Bostonian women in promoting spinning bees.
B) She wrote popular poetry about freedom for slaves.
C) She incited slaves to rebel against the British in Boston.
D) She started the Underground Railroad to free slaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Explain why Americans opposed to the Stamp Act adopted the rallying cry of "Liberty and property!"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Who fired the first shot at Lexington?
A) A British soldier
B) An American militiaman
C) A member of the Continental army
D) An unknown person
A) A British soldier
B) An American militiaman
C) A member of the Continental army
D) An unknown person

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The "powder alarm" of September 1774 convinced Thomas Gage that
A) colonial rebellions were led by a small cadre of radicals.
B) colonists were not prepared to fight for their demands.
C) Britain had complete control over the colonies.
D) ordinary colonists would unite for armed conflict.
A) colonial rebellions were led by a small cadre of radicals.
B) colonists were not prepared to fight for their demands.
C) Britain had complete control over the colonies.
D) ordinary colonists would unite for armed conflict.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What circumstances caused the British government to issue the Proclamation of 1763, and how did the terms of the act consider the Indians?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What did the members of the First Continental Congress discuss when they met in September 1774?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Why did many Americans who supported the patriot cause accept the legitimacy of the committees of public safety, the regrouped colonial assemblies, and the Continental Congress?
A) American colonists were ready to demand independence from Britain.
B) Britain formally recognized the new governing bodies and ordered American colonists to abide by their decisions.
C) The new governing bodies were composed of many of the same men who had held elective office before.
D) They hoped that recognizing these new government bodies would allow them to avoid further protest against the crown.
A) American colonists were ready to demand independence from Britain.
B) Britain formally recognized the new governing bodies and ordered American colonists to abide by their decisions.
C) The new governing bodies were composed of many of the same men who had held elective office before.
D) They hoped that recognizing these new government bodies would allow them to avoid further protest against the crown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Why did Bostonians throw tea overboard into Boston harbor in December 1773?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What was the purpose of the Continental Association created at the First Continental Congress?
A) To abolish individual colonial governments
B) To enforce a staggered and limited boycott of trade
C) To share plans for resisting British oppression
D) To prepare for the possibility of war with England
A) To abolish individual colonial governments
B) To enforce a staggered and limited boycott of trade
C) To share plans for resisting British oppression
D) To prepare for the possibility of war with England

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Explain how the imposition of the Townshend duties led to the Boston Massacre.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
After the conclusion of the Revolutionary War, slaves who had gained their freedom by joining the British army settled in Nova Scotia or
A) Sierra Leone.
B) Philadelphia.
C) Boston.
D) the West Indies.
A) Sierra Leone.
B) Philadelphia.
C) Boston.
D) the West Indies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What was "virtual representation," and why were the colonists opposed to it?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Why was Thomas Gage, military commander and the royal governor of Massachusetts, ordered to attack a suspected ammunition storage site at Concord in April 1775? Did he agree this was the best course of action?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What were the conflicting interests in the Ohio Valley before the Seven Years' War, and what was the outcome of the war for each participant?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
How did General Gage react to the increased violence and collapsing royal authority in Massachusetts early in 1775?
A) He endorsed William Pitt's plan for reconciliation with the colonies.
B) He arrested the leaders of the resistance and made a show of force.
C) He requested twenty thousand additional troops from England.
D) He attempted to negotiate with the leaders of the resistance.
A) He endorsed William Pitt's plan for reconciliation with the colonies.
B) He arrested the leaders of the resistance and made a show of force.
C) He requested twenty thousand additional troops from England.
D) He attempted to negotiate with the leaders of the resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What was the purpose of the committees of correspondence, and how did their role develop in the early 1770s?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Briefly describe the Sugar Act and the Stamp Act, two of George Grenville's attempts to generate income for Britain in 1764 and 1765. Why did the colonists object to these measures?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Use the following to answer questions :
The 1754-62 conflict between Britain and France that ended with British domination of North America. Its high expense laid the foundation for conflict that would lead to the American Revolution.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation
The 1754-62 conflict between Britain and France that ended with British domination of North America. Its high expense laid the foundation for conflict that would lead to the American Revolution.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Use the following to answer questions :
1766 law issued by Parliament to assert Parliament's unassailable right to legislate for its British colonies "in all cases whatsoever," putting Americans on notice that the simultaneous repeal of the Stamp Act changed nothing in the imperial powers of Britain.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation
1766 law issued by Parliament to assert Parliament's unassailable right to legislate for its British colonies "in all cases whatsoever," putting Americans on notice that the simultaneous repeal of the Stamp Act changed nothing in the imperial powers of Britain.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Use the following to answer questions :
A communications network established among towns in Massachusetts and also among colonial capital towns in 1772-73 to provide for rapid dissemination of news about important political developments. These bodies politicized ordinary townspeople, sparking a revolutionary language of rights and duties.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation
A communications network established among towns in Massachusetts and also among colonial capital towns in 1772-73 to provide for rapid dissemination of news about important political developments. These bodies politicized ordinary townspeople, sparking a revolutionary language of rights and duties.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Use the following to answer questions :
The 1765 British law imposing a tax on all paper used for official documents, for the purpose of raising revenue. Widespread resistance to the law led to its repeal in 1766.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation
The 1765 British law imposing a tax on all paper used for official documents, for the purpose of raising revenue. Widespread resistance to the law led to its repeal in 1766.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the following to answer questions :
Four British acts of 1774 meant to punish Massachusetts for the destruction of three shiploads of tea. These acts led to open rebellion in the northern colonies.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation
Four British acts of 1774 meant to punish Massachusetts for the destruction of three shiploads of tea. These acts led to open rebellion in the northern colonies.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Use the following to answer questions :
British act that lowered the existing tax on tea to entice boycotting Americans to buy it. Resistance to the act led to the passage of the Coercive Acts and imposition of military rule in Massachusetts.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation
British act that lowered the existing tax on tea to entice boycotting Americans to buy it. Resistance to the act led to the passage of the Coercive Acts and imposition of military rule in Massachusetts.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The First Continental Congress made it possible for colonists in different regions to respond to the British government with a strong and unified voice for the first time. Which factors helped or hindered colonial leaders in their attempts to bring together colonial British Americans?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use the following to answer questions :
British law that established new duties on tea, glass, lead, paper, and painters' colors imported into the colonies. The law led to boycotts and heightened tensions between Britain and the American colonies.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation
British law that established new duties on tea, glass, lead, paper, and painters' colors imported into the colonies. The law led to boycotts and heightened tensions between Britain and the American colonies.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Discuss the emergence of the Sons of Liberty and Daughters of Liberty. Include their goals and accomplishments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
By the 1770s, many white Americans saw the British government as a source of efforts to enslave them, while many African American slaves saw the British government as a potential source of freedom from slavery. Explain why these two groups held such fundamentally different views. Which group's view of the British was more legitimate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Use the following to answer questions :
A coordinated 1763 uprising of Native American tribes in the Northwest after the end of the Seven Year's War. It heightened Britain's determination to create a boundary between Americans and Indians, embodied in the Proclamation of 1763.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation
A coordinated 1763 uprising of Native American tribes in the Northwest after the end of the Seven Year's War. It heightened Britain's determination to create a boundary between Americans and Indians, embodied in the Proclamation of 1763.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Use the following to answer questions :
The 1764 British law that decreased the duty on French molasses, making it more attractive for shippers to obey the law, and at the same time raised penalties for smuggling. The law regulated trade but was also intended to raise revenue.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation
The 1764 British law that decreased the duty on French molasses, making it more attractive for shippers to obey the law, and at the same time raised penalties for smuggling. The law regulated trade but was also intended to raise revenue.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Use the following to answer questions :
September 1774 gathering of colonial delegates in Philadelphia to discuss the crisis precipitated by the Coercive Acts. The result was a declaration of rights and an agreement to impose a limited boycott of trade with Britain.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation
September 1774 gathering of colonial delegates in Philadelphia to discuss the crisis precipitated by the Coercive Acts. The result was a declaration of rights and an agreement to impose a limited boycott of trade with Britain.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In 1770, Lord North became the new British prime minister. North persuaded Parliament to remove all duties except the tax on tea, and peace seemed feasible for nearly two years. Discuss the events and renewed struggles that made this stable period short-lived.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Use the following to answer questions :
The theory that all British subjects were represented in Parliament, whether they had elected representatives in that body or not. American colonists rejected the theory, arguing that only direct representatives had the right to tax the colonists.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation
The theory that all British subjects were represented in Parliament, whether they had elected representatives in that body or not. American colonists rejected the theory, arguing that only direct representatives had the right to tax the colonists.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Following the Seven Years' War, England began taxing the colonies and placing restrictions on settlement beyond the Appalachian Mountains. Using specific examples, explain the actions English leaders took between 1763 and 1765 and why they did so. Did England achieve its goals? Why or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Use the following to answer questions :
March 1770 incident in Boston in which British soldiers fired on an American crowd, killing five. The incident became a rallying point for colonists who increasingly saw the British government as tyrannical and illegitimate.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation
March 1770 incident in Boston in which British soldiers fired on an American crowd, killing five. The incident became a rallying point for colonists who increasingly saw the British government as tyrannical and illegitimate.
A)Boston Massacre
B)Coercive (Intolerable) Acts
C)committees of correspondence
D)Declaratory Act
E)First Continental Congress
F)Pontiac's Rebellion
G)Seven Years' War
H)Stamp Act
I)Sugar (Revenue) Act
J)Tea Act of 1773
K)Townshend duties
L)virtual representation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



