Deck 13: The Slave South
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/77
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: The Slave South
1
How did larger planters have the time to concentrate on marketing and finance while still running a profitable plantation?
A) They left their wives in charge of plantation discipline.
B) They had so many slaves that they policed themselves.
C) They hired overseers to go to the fields with the slaves.
D) They hired white servants to work the fields with the slaves.
A) They left their wives in charge of plantation discipline.
B) They had so many slaves that they policed themselves.
C) They hired overseers to go to the fields with the slaves.
D) They hired white servants to work the fields with the slaves.
They hired overseers to go to the fields with the slaves.
2
In 1831, Alexis de Tocqueville observed that the major differences between the North and South revolved around
A) the vast amounts of free land available to southerners.
B) the fact that the northern states were overcrowded.
C) the southerners' preference for a weak centralized government.
D) the southern institution of slavery.
A) the vast amounts of free land available to southerners.
B) the fact that the northern states were overcrowded.
C) the southerners' preference for a weak centralized government.
D) the southern institution of slavery.
the southern institution of slavery.
3
According to Map 13.2: The Agricultural Economy of the South, 1860, which southern state grew both corn and cotton? 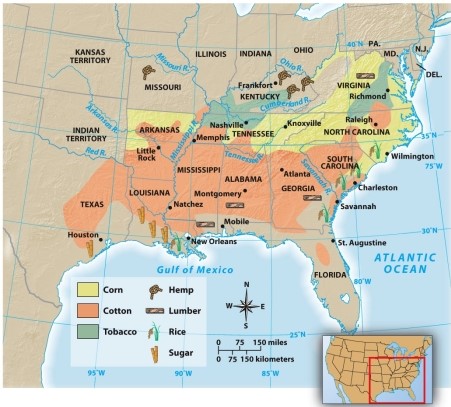
A) Texas
B) Arkansas
C) Mississippi
D) Kentucky

A) Texas
B) Arkansas
C) Mississippi
D) Kentucky
Arkansas
4
The lithograph "The Fruits of Amalgamation" portrays anxiety over what possible effect of emancipation? 
A) Free blacks taking white jobs
B) Interracial marriage
C) Revenge killing of white slave owners by free blacks
D) The economic collapse of the South

A) Free blacks taking white jobs
B) Interracial marriage
C) Revenge killing of white slave owners by free blacks
D) The economic collapse of the South

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Mid-nineteenth century planters began to treat their slaves marginally better because
A) it was in the master's best interest to treat his slaves well enough so they could have children.
B) legislatures passed laws mandating a certain minimum level of physical welfare for slaves.
C) masters became more fearful of slave uprisings with the passage of time.
D) slaves could block sales to plantation owners who had a bad reputation.
A) it was in the master's best interest to treat his slaves well enough so they could have children.
B) legislatures passed laws mandating a certain minimum level of physical welfare for slaves.
C) masters became more fearful of slave uprisings with the passage of time.
D) slaves could block sales to plantation owners who had a bad reputation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which statement characterizes white southerners in the antebellum South?
A) Most worked small farms with the help of only a few slaves.
B) The average white southerner owned about twenty slaves.
C) Most white southerners did not own slaves.
D) The majority of whites considered themselves planters.
A) Most worked small farms with the help of only a few slaves.
B) The average white southerner owned about twenty slaves.
C) Most white southerners did not own slaves.
D) The majority of whites considered themselves planters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
How did the institution of slavery affect social relations in the South?
A) Poor whites identified more with free blacks than with planters.
B) People who owned no slaves generally disapproved of the planters' practices.
C) Planters treated whites who owned no slaves as far inferior to themselves.
D) Whites were unified around race rather than divided by social class.
A) Poor whites identified more with free blacks than with planters.
B) People who owned no slaves generally disapproved of the planters' practices.
C) Planters treated whites who owned no slaves as far inferior to themselves.
D) Whites were unified around race rather than divided by social class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
According to South Carolina political leader John C. Calhoun, what happened in states where slavery was abolished?
A) The condition of blacks got worse.
B) Blacks began to dominate politics.
C) Former slaves lived happy lives.
D) Blacks continued to contribute to the economy.
A) The condition of blacks got worse.
B) Blacks began to dominate politics.
C) Former slaves lived happy lives.
D) Blacks continued to contribute to the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
How important was agriculture to the economy of the North in the mid-nineteenth century?
A) It played no role in the northern economy.
B) It dominated the northern economy as it did in the South.
C) It combined with commerce and manufacturing in a mixed economy.
D) It flourished in New England only.
A) It played no role in the northern economy.
B) It dominated the northern economy as it did in the South.
C) It combined with commerce and manufacturing in a mixed economy.
D) It flourished in New England only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Prior to the Civil War, why did the South remain agriculturally based instead of diversifying its economy?
A) Southerners shunned the idea of capitalism.
B) Planters made good profits and feared economic change.
C) There were too few cities in the South to support industry.
D) The South's earlier experiment with textile manufacture had failed.
A) Southerners shunned the idea of capitalism.
B) Planters made good profits and feared economic change.
C) There were too few cities in the South to support industry.
D) The South's earlier experiment with textile manufacture had failed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What was a consequence of the mid-nineteenth-century South's lack of economic diversity?
A) Newly arrived European immigrants tended to settle in the North.
B) The South was dependent on the North for food products.
C) Southern legislatures could not create banking systems.
D) Southern governments increased the income tax.
A) Newly arrived European immigrants tended to settle in the North.
B) The South was dependent on the North for food products.
C) Southern legislatures could not create banking systems.
D) Southern governments increased the income tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
"Jesus Christ recognized this institution [slavery] as one that was lawful among men, and regulated its relative duties. . . . I affirm then, first, (and no man denies,) that Jesus Christ has not abolished slavery by a prohibitory command: and second, I affirm, he has introduced no new moral principle which can work its destruction, under the gospel dispensation; and that the principle relied on for this purpose, is a fundamental principle of the Mosaic law, under which slavery was instituted by Jehovah himself. . . . To the church at Colosse . . . Paul in his letter to them, recognizes the three relations of wives and husbands, parents and children, servants and masters, as relations existing among the members . . . and to the servants and masters he thus writes: 'Servants obey in all things your masters, according to the flesh: not with eye service, as men pleasers, but in singleness of heart, fearing God: and whatsoever you do, do it heartily, as to the Lord and not unto men; knowing that of the Lord ye shall receive the reward of the inheritance, for ye serve the Lord Christ. . . . Masters give unto your servants that which is just and equal, knowing that you also have a master in heaven.'"
According to Reverend Thornton Stringfellow, who initially established the institution of slavery?
A) Jehovah
B) Moses
C) Jesus
D) Paul
According to Reverend Thornton Stringfellow, who initially established the institution of slavery?
A) Jehovah
B) Moses
C) Jesus
D) Paul

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which staple crop was grown almost exclusively along a narrow strip of coast stretching from the Carolinas into Georgia?
A) Tobacco
B) Sugar
C) Hemp
D) Rice
A) Tobacco
B) Sugar
C) Hemp
D) Rice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What was the primary cause of the growth in the southern slave population between 1790 and 1869?
A) The importation of slaves from Africa
B) Natural reproduction
C) Miscegenation
D) Southerners buying slaves from the North
A) The importation of slaves from Africa
B) Natural reproduction
C) Miscegenation
D) Southerners buying slaves from the North

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
"Be it good or bad, it [slavery] has grown up with our society and institutions, and is so interwoven with them, that to destroy it would be to destroy us as a people. But let me not be understood as admitting, even by implication, that the existing relations between the two races in the slaveholding States is an evil: far otherwise; I hold it to be a good. . . . I appeal to facts. Never before has the black race of Central Africa, from the dawn of history to the present day, attained a condition so civilized and so improved, not only physically, but morally and intellectually. It came to us in a low, degraded, and savage condition, and in the course of a few generations, it has grown up under the fostering care of our institutions, reviled they have been, to its present comparatively civilized condition. This, with the rapid increase of numbers, is conclusive proof of the general happiness of the race, in spite of all the exaggerated tales to the contrary. . . . I may say with truth, that in few countries so much is left to the share of the laborer, and so little exacted from him, or where there is more kind attention paid to him in sickness or infirmities of age. Compare his condition with the tenants of the poor houses in the more civilized portions of Europe-look at the sick, and the old and infirm slave, on one hand, in the midst of his family and friends, under the kind superintending care of his master and mistress, and compare it with the forlorn and wretched condition of the pauper in the poor house."
Which of the following did John Calhoun give as a justification to allow the South to remain a slave society?
A) Slavery improved slaves' spiritual lives by teaching them Christianity.
B) Slavery was still legal in other countries.
C) Slaves were better off than their laboring counterparts in Europe.
D) Without slavery, poor whites would have no way to distinguish themselves from blacks.
Which of the following did John Calhoun give as a justification to allow the South to remain a slave society?
A) Slavery improved slaves' spiritual lives by teaching them Christianity.
B) Slavery was still legal in other countries.
C) Slaves were better off than their laboring counterparts in Europe.
D) Without slavery, poor whites would have no way to distinguish themselves from blacks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What did plantation owners mean when they described the master-slave relationship in terms of "paternalism"?
A) Masters had no direct contact with their slaves.
B) A slave's labor and obedience were exchanged for the master's care and guidance.
C) The master's relationship with his slave mirrored his relationship with God.
D) The relationship between master and slave was like that of government and citizen.
A) Masters had no direct contact with their slaves.
B) A slave's labor and obedience were exchanged for the master's care and guidance.
C) The master's relationship with his slave mirrored his relationship with God.
D) The relationship between master and slave was like that of government and citizen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What did mid-nineteenth-century southern men need in order to achieve high social standing and success in the world of politics?
A) A reputation for using violence on their slaves
B) A strong education from a reputable school
C) Connections to northern industry
D) An honorable reputation
A) A reputation for using violence on their slaves
B) A strong education from a reputable school
C) Connections to northern industry
D) An honorable reputation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How did slaves manipulate planters' emphasis on paternalism?
A) They sometimes negotiated concessions like small garden plots.
B) They convinced masters to abandon violence in the fields.
C) They often negotiated the terms of their own freedom.
D) They convinced masters to teach them to read and write.
A) They sometimes negotiated concessions like small garden plots.
B) They convinced masters to abandon violence in the fields.
C) They often negotiated the terms of their own freedom.
D) They convinced masters to teach them to read and write.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Historians use the term planter to identify whites who owned at least how many slaves?
A) Five
B) Ten
C) Twenty
D) Fifty
A) Five
B) Ten
C) Twenty
D) Fifty

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
How did white Virginians respond to the violence of Nat Turner's rebellion?
A) Many emancipated their slaves.
B) The legislature passed laws to encourage more lenient treatment of slaves.
C) They blamed the revolt on outside agitators.
D) Planters started to openly criticize the institution of slavery.
A) Many emancipated their slaves.
B) The legislature passed laws to encourage more lenient treatment of slaves.
C) They blamed the revolt on outside agitators.
D) Planters started to openly criticize the institution of slavery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
By 1860, the southern slave system existed
A) exclusively on plantations.
B) in almost every industry.
C) only on farms.
D) in rural but not urban areas.
A) exclusively on plantations.
B) in almost every industry.
C) only on farms.
D) in rural but not urban areas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The economy of the upcountry South depended on
A) slave ownership.
B) cash crops.
C) servant labor.
D) barter.
A) slave ownership.
B) cash crops.
C) servant labor.
D) barter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What happened to slave men when they became elderly?
A) They were allowed to retire from the plantation.
B) They primarily worked in the big house.
C) They became supervisors of the younger slaves.
D) They moved on to new jobs, like cleaning stables.
A) They were allowed to retire from the plantation.
B) They primarily worked in the big house.
C) They became supervisors of the younger slaves.
D) They moved on to new jobs, like cleaning stables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Why were open slave revolts uncommon in the South?
A) Heavily armed whites outnumbered blacks two to one by 1860.
B) The majority of slaves believed slavery was better than being free and poor.
C) Slave religion discouraged open revolt.
D) Slaves lacked the organizational skills needed to stage a revolt.
A) Heavily armed whites outnumbered blacks two to one by 1860.
B) The majority of slaves believed slavery was better than being free and poor.
C) Slave religion discouraged open revolt.
D) Slaves lacked the organizational skills needed to stage a revolt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The rarest job on the plantation for slaves was that of driver, the person who
A) transported the slaves to the fields from their quarters.
B) worked alongside the carpenter, driving in nails.
C) sat in the farm equipment and managed the animals that pulled it.
D) made sure all slaves worked hard.
A) transported the slaves to the fields from their quarters.
B) worked alongside the carpenter, driving in nails.
C) sat in the farm equipment and managed the animals that pulled it.
D) made sure all slaves worked hard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which statement characterizes how southern plain folk viewed religion?
A) They typically avoided it.
B) Most embraced Catholicism.
C) They enjoyed religious revivals.
D) They attended traditional church services each week without fail.
A) They typically avoided it.
B) Most embraced Catholicism.
C) They enjoyed religious revivals.
D) They attended traditional church services each week without fail.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What percentage of non-slaveholding rural white men were landless and very poor?
A) 5 percent
B) 25 percent
C) 50 percent
D) 75 percent
A) 5 percent
B) 25 percent
C) 50 percent
D) 75 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The majority of plantation slaves worked as
A) skilled artisans.
B) field hands.
C) house servants.
D) tobacco farmers.
A) skilled artisans.
B) field hands.
C) house servants.
D) tobacco farmers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What does the drawing titled "Camp Meeting, Mid-Nineteenth Century" suggest about those who attended camp meetings and revivals? 
A) They possessed a relatively low-class status.
B) They were slaves.
C) They were wealthy.
D) They were a racially and economically diverse group.

A) They possessed a relatively low-class status.
B) They were slaves.
C) They were wealthy.
D) They were a racially and economically diverse group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Why did planters promote Christianity in the slave quarters?
A) They didn't want infidels playing with their children.
B) They hoped that religion would help the slaves live longer.
C) They believed Christianity would make slaves more obedient.
D) Evangelicals were advocating Christianizing the slaves.
A) They didn't want infidels playing with their children.
B) They hoped that religion would help the slaves live longer.
C) They believed Christianity would make slaves more obedient.
D) Evangelicals were advocating Christianizing the slaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which statement describes the daily lives of southern women on the plantation?
A) Elite women had few responsibilities.
B) They worked long hours performing plantation duties.
C) Women's only responsibility was to bear children.
D) They were only responsible for educating their children.
A) Elite women had few responsibilities.
B) They worked long hours performing plantation duties.
C) Women's only responsibility was to bear children.
D) They were only responsible for educating their children.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Most runaway slaves
A) escaped to Canada.
B) found refuge in the free North.
C) were caught and returned.
D) were executed by angry owners.
A) escaped to Canada.
B) found refuge in the free North.
C) were caught and returned.
D) were executed by angry owners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following was the most common way slaves reacted to their bondage?
A) Quiet suffering
B) Suicide
C) Small-scale resistance
D) Organized rebellions
A) Quiet suffering
B) Suicide
C) Small-scale resistance
D) Organized rebellions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Most plantation mistresses kept their opinions on issues to themselves, but the diarist Mary Boykin Chesnut echoed most women in railing against
A) miscegenation.
B) racial discrimination.
C) the institution of slavery.
D) the South's lack of public schools.
A) miscegenation.
B) racial discrimination.
C) the institution of slavery.
D) the South's lack of public schools.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which statement describes slave marriages?
A) Some were long-lasting.
B) They were protected by law.
C) Masters were obligated to honor the bonds of marriage.
D) Slaves did not marry.
A) Some were long-lasting.
B) They were protected by law.
C) Masters were obligated to honor the bonds of marriage.
D) Slaves did not marry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The typical plantation belt yeoman aspired to
A) overthrow slavery.
B) move up to the planter class.
C) leave the farm and open a shop in town.
D) earn an education.
A) overthrow slavery.
B) move up to the planter class.
C) leave the farm and open a shop in town.
D) earn an education.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Most upcountry yeomen focused on cultivating
A) cotton.
B) food.
C) tobacco.
D) indigo.
A) cotton.
B) food.
C) tobacco.
D) indigo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
African American Christianity, created by slaves themselves,
A) emphasized justice.
B) delivered the same message taught by white preachers.
C) resembled Catholicism more than Evangelical Protestantism.
D) focused on passive resistance.
A) emphasized justice.
B) delivered the same message taught by white preachers.
C) resembled Catholicism more than Evangelical Protestantism.
D) focused on passive resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
How did southern men's emphasis on chivalry affect southern law?
A) Women could more easily seek divorce in the South than in the North.
B) White women kept their own property after they married.
C) Laws protected women from unfair treatment by their husbands.
D) Southern laws affirmed the paramount rights of husbands.
A) Women could more easily seek divorce in the South than in the North.
B) White women kept their own property after they married.
C) Laws protected women from unfair treatment by their husbands.
D) Southern laws affirmed the paramount rights of husbands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
How did yeomen in the South's plantation belt feel about wealthy planters?
A) They relied on planters to ship and sell their cotton for them.
B) Most raged at the oppression of the planter regime.
C) They tried to avoid their richer neighbors and carve out their own market niche.
D) Most were opposed to slavery in principle.
A) They relied on planters to ship and sell their cotton for them.
B) Most raged at the oppression of the planter regime.
C) They tried to avoid their richer neighbors and carve out their own market niche.
D) Most were opposed to slavery in principle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Explain how plain folk in both the plantation belt and the upcountry viewed the idea of white supremacy, and what led them to adopt these views.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following restrictions was placed on the 260,000 free blacks in the South by 1860?
A) They could not legally marry.
B) They could not participate in politics.
C) They could not own any property.
D) They could not own slaves.
A) They could not legally marry.
B) They could not participate in politics.
C) They could not own any property.
D) They could not own slaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What did the Whig and Democratic parties have in common?
A) Both supported state-run banks.
B) Both opposed state support of railroads.
C) Both emphasized the importance of education.
D) Both declared allegiance to republican equality.
A) Both supported state-run banks.
B) Both opposed state support of railroads.
C) Both emphasized the importance of education.
D) Both declared allegiance to republican equality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
List and describe the various kinds of jobs that slaves held outside of plantations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
After 1820, the South began passing strict slave codes and put a great deal of effort into justifying the institution of slavery. What were some of the defenses southerners used to justify slavery?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Explain how the politics of slavery helped knit together all of white society in the South.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Why did the South remain agricultural when the economy of the North was diversifying?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which statement describes the life of free black elites in southern cities?
A) They worshiped in white churches.
B) They had the right to vote.
C) They still lived in ghettoes.
D) They never left the state of their birth.
A) They worshiped in white churches.
B) They had the right to vote.
C) They still lived in ghettoes.
D) They never left the state of their birth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The majority of poor white men in the mid-nineteenth-century South would agree on which statement?
A) The South should promote agriculture.
B) They system of slavery benefitted only the rich.
C) Women workers deserved the same rights as men.
D) Planter politicians should be overthrown.
A) The South should promote agriculture.
B) They system of slavery benefitted only the rich.
C) Women workers deserved the same rights as men.
D) Planter politicians should be overthrown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Why was the cotton kingdom also a slave empire?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
How did powerful whites defend slavery from attacks by critics?
A) They triumphed in public debates.
B) They acknowledged the diversity of opinions.
C) They argued that all slaves would eventually gain freedom.
D) They used intimidation tactics to silence critics.
A) They triumphed in public debates.
B) They acknowledged the diversity of opinions.
C) They argued that all slaves would eventually gain freedom.
D) They used intimidation tactics to silence critics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
How did southern whites view free blacks in the antebellum period? What kinds of legislation did southern whites pass in regard to the rights of free blacks?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Why did southerners move westward in 1815? Where did they tend to settle?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Elite southerners maintained their power over the yeoman majority by
A) using violent intimidation to gain votes.
B) convincing yeomen of their shared interests.
C) raising voter requirements to weed out poor voters.
D) proclaiming their moral superiority.
A) using violent intimidation to gain votes.
B) convincing yeomen of their shared interests.
C) raising voter requirements to weed out poor voters.
D) proclaiming their moral superiority.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The goal of most free blacks in the South was to
A) become slaveholders.
B) raise a slave rebellion.
C) preserve their own freedom.
D) move to Africa.
A) become slaveholders.
B) raise a slave rebellion.
C) preserve their own freedom.
D) move to Africa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Most free blacks in the antebellum South
A) lived in cities.
B) worked as skilled laborers.
C) gradually assimilated into the rural white society.
D) lacked education.
A) lived in cities.
B) worked as skilled laborers.
C) gradually assimilated into the rural white society.
D) lacked education.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The large numbers of blacks in the antebellum South had profound effects on the region. Give several examples of how blacks influenced southern culture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
By the 1850s, the political system of the white South
A) had extended suffrage for all adult white males.
B) had restricted suffrage to keep yeomen from holding office.
C) was characterized by poor voter turnout.
D) was largely free from partisan voting.
A) had extended suffrage for all adult white males.
B) had restricted suffrage to keep yeomen from holding office.
C) was characterized by poor voter turnout.
D) was largely free from partisan voting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Discuss the roles and responsibilities of plantation mistresses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
How did the democratization of politics in the South change the shape of government?
A) Planters' power became more proportionate to their population.
B) Yeomen captured the majority of political offices.
C) Most new legislators did not own slaves.
D) Democratization changed the voter rolls more than the officeholders.
A) Planters' power became more proportionate to their population.
B) Yeomen captured the majority of political offices.
C) Most new legislators did not own slaves.
D) Democratization changed the voter rolls more than the officeholders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
There were some free blacks in the South during the antebellum years. Describe them, and include in your answer (a) how they were treated by whites, (b) what their status was in society, (c) what kinds of labor they performed, and (d) whether they owned any slaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match the term with the definition.
Farmers who owned and worked on their own small plots of land. Those living within the plantation belt were more dependent on planters than were those in the upcountry, where small farmers dominated.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen
Farmers who owned and worked on their own small plots of land. Those living within the plantation belt were more dependent on planters than were those in the upcountry, where small farmers dominated.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Besides planters and their slaves, the population of the antebellum South included plantation belt yeomen, upcountry yeomen, and poor whites. Characterize each group, describing their relationship to the planter class, their aspirations, and their views on slavery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Match the term with the definition.
The South's romantic ideal of male-female relationships. The ideal's underlying assumptions about the weakness of white women and the protective authority of men resembled the paternalistic defense of slavery.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen
The South's romantic ideal of male-female relationships. The ideal's underlying assumptions about the weakness of white women and the protective authority of men resembled the paternalistic defense of slavery.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Match the term with the definition.
A surveyor's mark that had established the boundary between Maryland and Pennsylvania in colonial times. By the 1830s, the boundary divided the free North and the slave South.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen
A surveyor's mark that had established the boundary between Maryland and Pennsylvania in colonial times. By the 1830s, the boundary divided the free North and the slave South.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Match the term with the definition.
Interracial sex. Proslavery spokesmen played on the fears of whites when they suggested that giving blacks equal rights would lead to interracial sex. In reality, slavery led to considerable sexual abuse of black women by their white masters.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen
Interracial sex. Proslavery spokesmen played on the fears of whites when they suggested that giving blacks equal rights would lead to interracial sex. In reality, slavery led to considerable sexual abuse of black women by their white masters.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Match the term with the definition.
Large farm worked by twenty or more slaves. Although small farms were more numerous, these large farms produced more than 75 percent of the South's export crops.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen
Large farm worked by twenty or more slaves. Although small farms were more numerous, these large farms produced more than 75 percent of the South's export crops.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Match the term with the definition.
Laws enacted in southern states in the 1820s and 1830s that required the total submission of slaves. Attacks by antislavery activists and by slaves convinced southern legislators that they had to do everything in their power to strengthen the institution.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen
Laws enacted in southern states in the 1820s and 1830s that required the total submission of slaves. Attacks by antislavery activists and by slaves convinced southern legislators that they had to do everything in their power to strengthen the institution.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Match the term with the definition.
The hills and mountains of the South whose higher elevation, colder climate, rugged terrain, and poor transportation made the region less hospitable than the flatlands to slavery and large plantations.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen
The hills and mountains of the South whose higher elevation, colder climate, rugged terrain, and poor transportation made the region less hospitable than the flatlands to slavery and large plantations.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Match the term with the definition.
Term that reflected the dominance in the southern economy of cotton, the cultivation of which was the key factor in the growth of slavery.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen
Term that reflected the dominance in the southern economy of cotton, the cultivation of which was the key factor in the growth of slavery.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Match the term with the definition.
The theory of slavery that emphasized reciprocal duties and obligations between masters and their slaves, with slaves providing labor and obedience and masters providing basic care and direction. Whites used this theory to deny that the slave system was brutal and exploitative.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen
The theory of slavery that emphasized reciprocal duties and obligations between masters and their slaves, with slaves providing labor and obedience and masters providing basic care and direction. Whites used this theory to deny that the slave system was brutal and exploitative.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Discuss the southern concepts of paternalism and chivalry. Identify the similarities between them and compare the complex relationship between subordinated women and oppressed slaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Match the term with the definition.
An African American who was not enslaved. Southern whites worried about the increasing numbers of these individuals. In the 1820s and 1830s, state legislatures stemmed the growth of this population and shrank their liberty.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen
An African American who was not enslaved. Southern whites worried about the increasing numbers of these individuals. In the 1820s and 1830s, state legislatures stemmed the growth of this population and shrank their liberty.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Match the term with the definition.
Flatlands that spread from South Carolina to east Texas and were dominated by large plantations.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen
Flatlands that spread from South Carolina to east Texas and were dominated by large plantations.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Match the term with the definition.
A substantial landowner who tilled his estate with twenty or more slaves. These wealthy landowners dominated the social and political world of the South. Their values and ideology influenced the values of all southern whites.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen
A substantial landowner who tilled his estate with twenty or more slaves. These wealthy landowners dominated the social and political world of the South. Their values and ideology influenced the values of all southern whites.
A)chivalry
B)cotton kingdom
C)free black
D)Mason-Dixon line
E)miscegenation
F)paternalism
G)plantation
H)plantation belt
I)planter
J)slave codes
K)upcountry
L)yeomen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Although a new nation was created under the Constitution in 1789, there were already significant differences between the North and the South. Discuss the evolution of the South as a distinctive region economically. What role did slavery play? How did white southerners enforce slavery and argue its positive aspects?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Describe in detail the family, religious, and community life of slaves. Were slaves able to retain any of their African culture?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



