Deck 22: Adding Government and Trade to the Simple Macro Model
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/131
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Adding Government and Trade to the Simple Macro Model
1
Consider the government's budget balance.Suppose G = 2500 and the government's net tax revenue is equal to 0.2Y.When Y = 11 000,the government is running a budget
A)deficit of 1500.
B)surplus of 300.
C)balance.
D)deficit of 300.
E)surplus of 1500.
A)deficit of 1500.
B)surplus of 300.
C)balance.
D)deficit of 300.
E)surplus of 1500.
deficit of 300.
2
Consider the government's budget balance.Suppose G = 300 and the government's net tax revenue is equal to 0.14Y.When Y = 2000,the government is running a budget
A)deficit of 20.
B)surplus of 20.
C)balance.
D)deficit of -20.
E)surplus of 40.
A)deficit of 20.
B)surplus of 20.
C)balance.
D)deficit of -20.
E)surplus of 40.
deficit of 20.
3
Consider the government's budget balance.Suppose G = 500 and the government's net tax revenue is equal to 0.2Y.The government budget is balanced when Y equals
A)2000.
B)2200.
C)2400.
D)2500.
E)2800.
A)2000.
B)2200.
C)2400.
D)2500.
E)2800.
2500.
4
Consider the government's budget balance.Suppose G = 400 and the government's net tax revenue is 20% of national income (Y).Government saving is negative for all values of Y
A)above 10 000.
B)above 8000.
C)above 2000.
D)below 8000.
E)below 2000.
A)above 10 000.
B)above 8000.
C)above 2000.
D)below 8000.
E)below 2000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Consider the government's budget balance.Suppose G = 500 and the government's net tax revenue is equal to 0.25Y.When Y = 2920,the government is running a budget
A)deficit of 730.
B)surplus of 230.
C)balance.
D)deficit of 230.
E)surplus of 730.
A)deficit of 730.
B)surplus of 230.
C)balance.
D)deficit of 230.
E)surplus of 730.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Consider the government's budget balance.Suppose G = 300 and the government's net tax revenue is equal to 0.12Y.The government budget is balanced when Y equals
A)350.
B)1000.
C)2000.
D)2500.
E)3600.
A)350.
B)1000.
C)2000.
D)2500.
E)3600.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Consider the government's budget balance.Suppose G = 2500 and the government's net tax revenue is equal to 0.2Y.The government budget is balanced when Y equals
A)9500.
B)10 500.
C)11 500.
D)12 500.
E)13 500.
A)9500.
B)10 500.
C)11 500.
D)12 500.
E)13 500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Transfer payments made by the government affect its net tax revenues
A)directly.
B)indirectly through government purchases.
C)indirectly through net exports.
D)indirectly through the investment function.
E)indirectly through the consumption function.
A)directly.
B)indirectly through government purchases.
C)indirectly through net exports.
D)indirectly through the investment function.
E)indirectly through the consumption function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Consider the government's budget balance.Suppose G = 600 and the government's net tax revenue is 10% of Y.The government budget is balanced when Y equals
A)660.
B)1320.
C)3000.
D)4500.
E)6000.
A)660.
B)1320.
C)3000.
D)4500.
E)6000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Why are exports treated as autonomous expenditure in our simple macro model? Because
A)exports typically do not change as a result of a change in Canadian national income.
B)exports are always constant in dollar terms.
C)they are a component of net exports,which is autonomous in our model.
D)exports are a small component in the Canadian economy and are not significant in the model.
E)exports are a function of Canadian national income,which is autonomous in our model.
A)exports typically do not change as a result of a change in Canadian national income.
B)exports are always constant in dollar terms.
C)they are a component of net exports,which is autonomous in our model.
D)exports are a small component in the Canadian economy and are not significant in the model.
E)exports are a function of Canadian national income,which is autonomous in our model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the simple macro model,how do government transfer payments to individuals affect desired aggregate expenditure?
A)directly
B)through the consumption function
C)through business investment
D)through net exports
E)through the government's budget deficit
A)directly
B)through the consumption function
C)through business investment
D)through net exports
E)through the government's budget deficit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Consider the net tax rate,denoted by t.Which of the following correctly defines the net tax rate?
A)It is total tax revenue minus transfer payments.
B)It is the sum of the federal income tax rate plus an average of provincial income tax rates.
C)It is the increase in net tax revenue when national income rises by one dollar.
D)It is the sum of all government tax revenues.
E)Both A and C are correct.
A)It is total tax revenue minus transfer payments.
B)It is the sum of the federal income tax rate plus an average of provincial income tax rates.
C)It is the increase in net tax revenue when national income rises by one dollar.
D)It is the sum of all government tax revenues.
E)Both A and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Consider a simple macro model with a constant price level and demand-determined output.The inclusion of government in such a model affects desired aggregate expenditure directly through ________ and indirectly through ________.
A)the net taxes; the government purchases of goods and services
B)the net taxes; its effect on disposable income
C)the government purchases of goods and services; its effect on net exports
D)the government purchases of goods and services; its effect on disposable income
E)the government purchases of goods and services; its effect on investment
A)the net taxes; the government purchases of goods and services
B)the net taxes; its effect on disposable income
C)the government purchases of goods and services; its effect on net exports
D)the government purchases of goods and services; its effect on disposable income
E)the government purchases of goods and services; its effect on investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If the government's net tax rate increases,then for a given level of national income disposable income will ________ and net tax revenue will ________.
A)decrease; decrease
B)decrease; increase
C)increase; increase
D)increase; decrease
E)not change; increase
A)decrease; decrease
B)decrease; increase
C)increase; increase
D)increase; decrease
E)not change; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Suppose real national income (Y)is equal to 800 and government purchases are equal to 200.If the government's net tax revenues are equal to tY,where t is the net tax rate,then what is the value of t necessary for the government to have a balanced budget?
A)20%
B)25%
C)30%
D)35%
E)40%
A)20%
B)25%
C)30%
D)35%
E)40%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When economists use the term "budget surplus" they are referring to
A)net tax revenues minus government purchases.
B)national income minus transfer payments.
C)national income minus consumption.
D)disposable income minus consumption.
E)net tax revenues minus transfer payments.
A)net tax revenues minus government purchases.
B)national income minus transfer payments.
C)national income minus consumption.
D)disposable income minus consumption.
E)net tax revenues minus transfer payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Consider the government's budget balance.Suppose G = 300 and the government's net tax revenue is 0.3Y.The government budget is in surplus only when Y is
A)less than 350.
B)less than 1000.
C)greater than 1000.
D)greater than 2500.
E)greater than 3000.
A)less than 350.
B)less than 1000.
C)greater than 1000.
D)greater than 2500.
E)greater than 3000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Suppose Y = 400 and the government's net tax rate is 10%.If we are told that the government has a budget surplus,then government purchases must be
A)greater than 30.
B)less than 30.
C)greater than 40.
D)less than 40.
E)Not enough information to know.
A)greater than 30.
B)less than 30.
C)greater than 40.
D)less than 40.
E)Not enough information to know.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The G and T components in the national-income accounts measure purchases and net taxes collected by
A)all levels of government.
B)only provincial governments and the federal government.
C)only the federal government.
D)only provincial governments.
E)only local governments.
A)all levels of government.
B)only provincial governments and the federal government.
C)only the federal government.
D)only provincial governments.
E)only local governments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Why are government expenditures such as Old Age Security payments,employment insurance payments,or welfare benefits paid to individuals not considered part of G,the government component of aggregate expenditure?
A)These are transfer payments and place no direct demand on Canada's total output.
B)These payments are directly included as part of C,consumption,because they become consumption expenditure for the recipient.
C)Since the revenues from which these payments are made did not originate from tax collection,they are not considered part of G.
D)Since these expenditures are transfers from recipients to taxpayers,they are not included in G.
E)These payments are included in G only when the payments are made directly by the federal government.
A)These are transfer payments and place no direct demand on Canada's total output.
B)These payments are directly included as part of C,consumption,because they become consumption expenditure for the recipient.
C)Since the revenues from which these payments are made did not originate from tax collection,they are not considered part of G.
D)Since these expenditures are transfers from recipients to taxpayers,they are not included in G.
E)These payments are included in G only when the payments are made directly by the federal government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A decrease in domestic national income will cause a ________ the net export (NX)function.
A)movement to the left along
B)parallel downward shift of
C)parallel upward shift of
D)rotation upward in
E)rotation downward in
A)movement to the left along
B)parallel downward shift of
C)parallel upward shift of
D)rotation upward in
E)rotation downward in

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The net export (NX)function crosses the horizontal axis at a level of national income where the
A)X and IM curves intersect.
B)X curve reaches the horizontal axis.
C)IM curve reaches the horizontal axis.
D)X and IM curves are at their farthest distance apart.
E)X curve reaches its maximum.
A)X and IM curves intersect.
B)X curve reaches the horizontal axis.
C)IM curve reaches the horizontal axis.
D)X and IM curves are at their farthest distance apart.
E)X curve reaches its maximum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A fall in the Canadian-dollar price of foreign currency,other things being equal,causes Canada's net export (NX)function to shift ________ and ________.
A)upward; become flatter
B)upward; become steeper
C)downward; become flatter
D)downward; keep the same slope
E)downward; become steeper
A)upward; become flatter
B)upward; become steeper
C)downward; become flatter
D)downward; keep the same slope
E)downward; become steeper

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The diagrams below show the import,export,and net export functions for an economy. 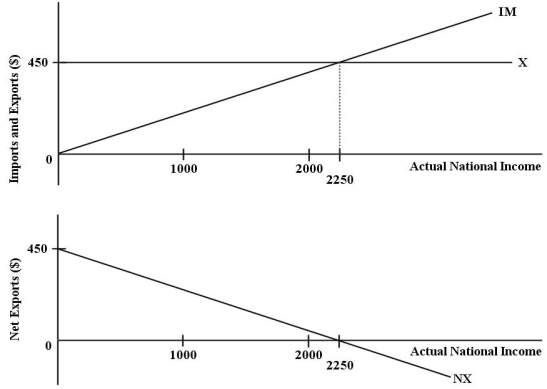 FIGURE 22-1 Refer to Figure 22-1.The function for desired imports for this economy can be expressed as
FIGURE 22-1 Refer to Figure 22-1.The function for desired imports for this economy can be expressed as
A)NX = 450 - Y.
B)IM = 450 - 0.5(Y).
C)NX = 0.5(Y).
D)IM = 0.5(Y).
E)IM = 0.2(Y).
 FIGURE 22-1 Refer to Figure 22-1.The function for desired imports for this economy can be expressed as
FIGURE 22-1 Refer to Figure 22-1.The function for desired imports for this economy can be expressed asA)NX = 450 - Y.
B)IM = 450 - 0.5(Y).
C)NX = 0.5(Y).
D)IM = 0.5(Y).
E)IM = 0.2(Y).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A rise in domestic prices relative to foreign prices,other things being equal,causes the net export (NX)function to shift ________ and ________.
A)upward; become flatter
B)upward; become steeper
C)downward; become flatter
D)downward; keep the same slope
E)downward; become steeper
A)upward; become flatter
B)upward; become steeper
C)downward; become flatter
D)downward; keep the same slope
E)downward; become steeper

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Consider the net export function.Suppose exports are $200 and imports are given by IM = 0.2Y.At what level of national income will net exports equal zero?
A)$0
B)$200
C)$250
D)$1000
E)$1250
A)$0
B)$200
C)$250
D)$1000
E)$1250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following can cause a parallel upward shift in the net export (NX)function?
A)an increase in domestic national income
B)an increase in foreign national income
C)an increase in domestic prices relative to foreign prices
D)a decrease in the Canadian-dollar price of foreign currency
E)a decrease in foreign prices relative to domestic prices
A)an increase in domestic national income
B)an increase in foreign national income
C)an increase in domestic prices relative to foreign prices
D)a decrease in the Canadian-dollar price of foreign currency
E)a decrease in foreign prices relative to domestic prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A fall in domestic prices relative to foreign prices,other things being equal,causes the net export (NX)function to shift ________ and ________.
A)upward; become flatter
B)upward; become steeper
C)downward; become flatter
D)downward; keep the same slope
E)downward; become steeper
A)upward; become flatter
B)upward; become steeper
C)downward; become flatter
D)downward; keep the same slope
E)downward; become steeper

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In a simple macro model,it is generally assumed that a country's exports
A)and imports are autonomous.
B)and imports are induced.
C)are autonomous,whereas imports are induced.
D)are induced,whereas imports are autonomous.
E)are always equal to investment.
A)and imports are autonomous.
B)and imports are induced.
C)are autonomous,whereas imports are induced.
D)are induced,whereas imports are autonomous.
E)are always equal to investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A movement along the net export (NX)function can be caused by a change in
A)domestic national income.
B)foreign national income.
C)domestic prices.
D)the exchange rate.
E)foreign prices.
A)domestic national income.
B)foreign national income.
C)domestic prices.
D)the exchange rate.
E)foreign prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A rise in the Canadian-dollar price of foreign currency,other things being equal,causes Canada's net export (NX)function to shift ________ and ________.
A)upward; become flatter
B)upward; become steeper
C)downward; become flatter
D)downward; keep the same slope
E)downward; become steeper
A)upward; become flatter
B)upward; become steeper
C)downward; become flatter
D)downward; keep the same slope
E)downward; become steeper

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Consider the net export function.Suppose exports are $1850 and imports are given by IM = 0.13Y.At what level of national income will net exports equal zero?
A)$0
B)$277
C)$1573
D)$14 231
E)$27 750
A)$0
B)$277
C)$1573
D)$14 231
E)$27 750

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Consider the net export function.An increase in domestic national income,other things being equal,is assumed to cause
A)the net export function to shift upward.
B)the net export function to pivot upward.
C)movement to the right along the net export function.
D)the net export function to pivot downward.
E)no effect on net exports.
A)the net export function to shift upward.
B)the net export function to pivot upward.
C)movement to the right along the net export function.
D)the net export function to pivot downward.
E)no effect on net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In a simple macro model,the net export (NX)function indicates a ________ relationship between net exports and ________.
A)positive; exports
B)positive; domestic national income
C)negative; imports
D)negative; domestic national income
E)negative; foreign national income
A)positive; exports
B)positive; domestic national income
C)negative; imports
D)negative; domestic national income
E)negative; foreign national income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Consider the net export function.Suppose exports are $940 and imports are given by IM = 0.1Y.At what level of national income will net exports equal zero?
A)$0
B)$9400
C)$15 730
D)$94
E)$27 750
A)$0
B)$9400
C)$15 730
D)$94
E)$27 750

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following can cause a downward shift and steepening of the net export (NX)function?
A)an increase in domestic national income
B)a decrease in foreign national income
C)an increase in domestic prices relative to foreign prices
D)a decrease in the Canadian-dollar price of foreign currency
E)both C and D are correct
A)an increase in domestic national income
B)a decrease in foreign national income
C)an increase in domestic prices relative to foreign prices
D)a decrease in the Canadian-dollar price of foreign currency
E)both C and D are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following can cause an upward shift and flattening of the net export (NX)function?
A)an increase in domestic national income
B)a decrease in foreign national income
C)a decrease in domestic prices relative to foreign prices
D)an increase in the Canadian-dollar price of foreign currency
E)both C and D are correct
A)an increase in domestic national income
B)a decrease in foreign national income
C)a decrease in domestic prices relative to foreign prices
D)an increase in the Canadian-dollar price of foreign currency
E)both C and D are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following can cause a parallel downward shift in the net export (NX)function?
A)an increase in domestic national income
B)a decrease in foreign national income
C)a decrease in domestic prices
D)an increase in the Canadian-dollar price of foreign currency
E)a decrease in foreign prices
A)an increase in domestic national income
B)a decrease in foreign national income
C)a decrease in domestic prices
D)an increase in the Canadian-dollar price of foreign currency
E)a decrease in foreign prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Consider the AE function in a simple macro model with government and foreign trade.It is generally assumed that as real national income
A)increases,exports will decrease.
B)increases,net exports will decrease.
C)increases,imports will decrease.
D)decreases,net exports will decrease.
E)decreases,exports will decrease.
A)increases,exports will decrease.
B)increases,net exports will decrease.
C)increases,imports will decrease.
D)decreases,net exports will decrease.
E)decreases,exports will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Consider the net export function (NX).An increase in foreign income,other things being equal,is assumed to cause the NX function to
A)shift parallel upward.
B)shift parallel downward.
C)pivot downward.
D)pivot upward.
E)remain stationary.
A)shift parallel upward.
B)shift parallel downward.
C)pivot downward.
D)pivot upward.
E)remain stationary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The diagrams below show the import,export,and net export functions for an economy. 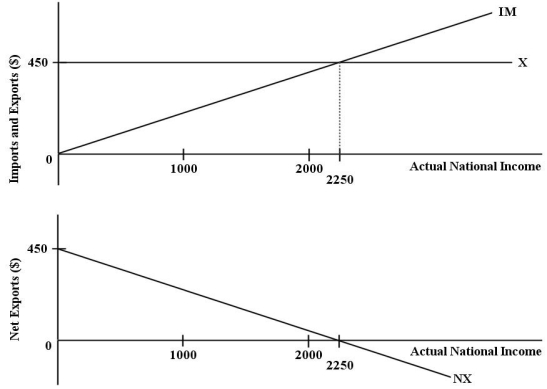 FIGURE 22-1 Refer to Figure 22-1.If actual national income is equal to $2000,then imports are equal to
FIGURE 22-1 Refer to Figure 22-1.If actual national income is equal to $2000,then imports are equal to
A)$0.
B)$200.
C)$400.
D)$450.
E)$1000.
 FIGURE 22-1 Refer to Figure 22-1.If actual national income is equal to $2000,then imports are equal to
FIGURE 22-1 Refer to Figure 22-1.If actual national income is equal to $2000,then imports are equal toA)$0.
B)$200.
C)$400.
D)$450.
E)$1000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The table below shows national income and imports.The level of exports is fixed at $300.All figures in the table and in the questions are in millions of dollars. 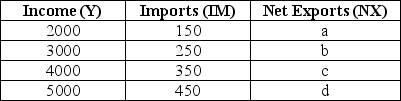 TABLE 22-1 Refer to Table 22-1.What are the correct values for the level of net exports (a,b,c,and d)at each level of national income?
TABLE 22-1 Refer to Table 22-1.What are the correct values for the level of net exports (a,b,c,and d)at each level of national income?
A)a = $150,b = $50,c = -$50,d = -$150
B)a = -$150,b = -$50,c = $50,d = $150
C)a = $150,b = $250,c = $350,d = $450
D)a = $300,b = $300,c = $300,d = $300
E)not enough data to determine
 TABLE 22-1 Refer to Table 22-1.What are the correct values for the level of net exports (a,b,c,and d)at each level of national income?
TABLE 22-1 Refer to Table 22-1.What are the correct values for the level of net exports (a,b,c,and d)at each level of national income?A)a = $150,b = $50,c = -$50,d = -$150
B)a = -$150,b = -$50,c = $50,d = $150
C)a = $150,b = $250,c = $350,d = $450
D)a = $300,b = $300,c = $300,d = $300
E)not enough data to determine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The AE function for an open economy with government can be written as
A)AE = C + I - G + (X - IM).
B)AE = C + I + G - (X - IM).
C)AE = C + I - G - (X + IM).
D)AE = C + I + S + (X + IM).
E)AE = C + I + G + (X - IM).
A)AE = C + I - G + (X - IM).
B)AE = C + I + G - (X - IM).
C)AE = C + I - G - (X + IM).
D)AE = C + I + S + (X + IM).
E)AE = C + I + G + (X - IM).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Consider the general form of the consumption function in a simple macro model.Once government and taxes are included in the model,desired consumption can be expressed as ________,where a = autonomous consumption,t = net tax rate,Y = national income, 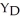 = disposable income,and MPC = marginal propensity to consume.
= disposable income,and MPC = marginal propensity to consume.
A)C = a + MPC(1 - t)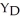
B)C = a - (1 - t)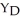
C)C = a + MPC ∙ Y
D)C = a + MPC ∙ t ∙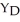
E)C = a + MPC(1 - t)Y
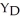 = disposable income,and MPC = marginal propensity to consume.
= disposable income,and MPC = marginal propensity to consume.A)C = a + MPC(1 - t)
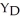
B)C = a - (1 - t)
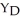
C)C = a + MPC ∙ Y
D)C = a + MPC ∙ t ∙
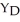
E)C = a + MPC(1 - t)Y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When compared to a simple macroeconomic model (with only consumption and investment),adding government and foreign trade to the AE function causes
A)the autonomous component of AE to increase.
B)the autonomous component of AE to fall.
C)the AE function to become downward sloping.
D)the AE function to become perfectly horizontal.
E)no change in the AE function.
A)the autonomous component of AE to increase.
B)the autonomous component of AE to fall.
C)the AE function to become downward sloping.
D)the AE function to become perfectly horizontal.
E)no change in the AE function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The table below shows national income and imports.The level of exports is fixed at $300.All figures in the table and in the questions are in millions of dollars. 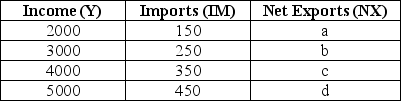 TABLE 22-1 Refer to Table 22-1.What is the marginal propensity to import?
TABLE 22-1 Refer to Table 22-1.What is the marginal propensity to import?
A)0.01
B)0.10
C)1.0
D)10.0
E)not enough data to determine
 TABLE 22-1 Refer to Table 22-1.What is the marginal propensity to import?
TABLE 22-1 Refer to Table 22-1.What is the marginal propensity to import?A)0.01
B)0.10
C)1.0
D)10.0
E)not enough data to determine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Consider a simple macro model with a constant price level and demand-determined output.The equations of the model are: C = 150 + 0.84Y,I = 400,G = 700,T = 0,X = 130,IM = 0.08Y.The marginal propensity to spend on national income,z,is
A)0.655.
B)0.760.
C)0.773.
D)0.840.
E)0.920.
A)0.655.
B)0.760.
C)0.773.
D)0.840.
E)0.920.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The table below shows national income and imports.The level of exports is fixed at $300.All figures in the table and in the questions are in millions of dollars. 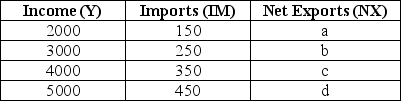 TABLE 22-1 Refer to Table 22-1.In this economy,if actual national income increases by $600,the level of imports will
TABLE 22-1 Refer to Table 22-1.In this economy,if actual national income increases by $600,the level of imports will
A)rise by $30.
B)rise by $60.
C)rise by $100.
D)fall by $100.
E)not change.
 TABLE 22-1 Refer to Table 22-1.In this economy,if actual national income increases by $600,the level of imports will
TABLE 22-1 Refer to Table 22-1.In this economy,if actual national income increases by $600,the level of imports willA)rise by $30.
B)rise by $60.
C)rise by $100.
D)fall by $100.
E)not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Consider a consumption function in a simple macro model with government and taxes.Given a marginal propensity to consume out of disposable income of 0.8 and a net tax rate of 20% of national income,the marginal propensity to consume out of national income is
A)0.36.
B)0.64.
C)0.80.
D)0.90.
E)1.00.
A)0.36.
B)0.64.
C)0.80.
D)0.90.
E)1.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The diagrams below show the import,export,and net export functions for an economy. 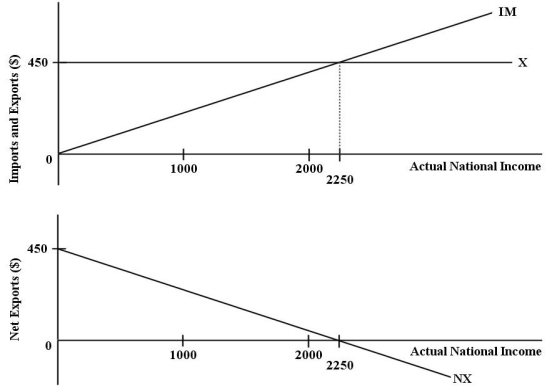 FIGURE 22-1 Refer to Figure 22-1.The net export function for this economy can be expressed as
FIGURE 22-1 Refer to Figure 22-1.The net export function for this economy can be expressed as
A)NX = 2250 - 450(Y).
B)NX = 450 - 0.2(Y).
C)NX = 2250 - 450.
D)NX = 0.2Y.
E)NX = 2250 - .2(IM).
 FIGURE 22-1 Refer to Figure 22-1.The net export function for this economy can be expressed as
FIGURE 22-1 Refer to Figure 22-1.The net export function for this economy can be expressed asA)NX = 2250 - 450(Y).
B)NX = 450 - 0.2(Y).
C)NX = 2250 - 450.
D)NX = 0.2Y.
E)NX = 2250 - .2(IM).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The table below shows national income and imports.The level of exports is fixed at $300.All figures in the table and in the questions are in millions of dollars. 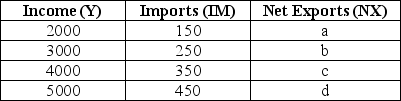 TABLE 22-1 Refer to Table 22-1.On a graph of the net export function for this economy,at what level of Y would the NX function intersect the horizontal axis?
TABLE 22-1 Refer to Table 22-1.On a graph of the net export function for this economy,at what level of Y would the NX function intersect the horizontal axis?
A)at $0
B)at $2000
C)at $3500
D)at $4000
E)at $5000
 TABLE 22-1 Refer to Table 22-1.On a graph of the net export function for this economy,at what level of Y would the NX function intersect the horizontal axis?
TABLE 22-1 Refer to Table 22-1.On a graph of the net export function for this economy,at what level of Y would the NX function intersect the horizontal axis?A)at $0
B)at $2000
C)at $3500
D)at $4000
E)at $5000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Consider an open economy that has a marginal propensity to import equal to 0.30.If national income rises by $2500,imports will rise by
A)$30.
B)$300.
C)$750.
D)$7500.
E)$8333.
A)$30.
B)$300.
C)$750.
D)$7500.
E)$8333.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In our simple macro model with government,consider the equation YD = (0.75)Y.Which of the following statements about this equation is correct?
A)If disposable income increases by $0.75,then national income increases by $1.00 and total tax revenue rises by $0.75.
B)Net tax revenue is equal to 75% of national income.
C)If national income increases by $1.00,then disposable income increases by $0.75 and net tax revenue increases by $0.25.
D)Net tax revenue is equal to 25% of disposable income.
E)If national income increases by $1.00,then disposable income increases by $0.25 and net tax revenue increases by $0.75.
A)If disposable income increases by $0.75,then national income increases by $1.00 and total tax revenue rises by $0.75.
B)Net tax revenue is equal to 75% of national income.
C)If national income increases by $1.00,then disposable income increases by $0.75 and net tax revenue increases by $0.25.
D)Net tax revenue is equal to 25% of disposable income.
E)If national income increases by $1.00,then disposable income increases by $0.25 and net tax revenue increases by $0.75.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Consider a consumption function in a simple macro model with government and taxes.Given a marginal propensity to consume out of disposable income of 0.9 and a net tax rate of 10% of national income,the marginal propensity to consume out of national income is
A)0.09.
B)0.72.
C)0.81.
D)0.90.
E)1.00.
A)0.09.
B)0.72.
C)0.81.
D)0.90.
E)1.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Consider a consumption function in a simple macro model with government and taxes.Given a marginal propensity to consume out of disposable income of 0.7 and a net tax rate of 30% of national income,the marginal propensity to consume out of national income is
A)0.49.
B)0.58.
C)0.70.
D)0.90.
E)1.00.
A)0.49.
B)0.58.
C)0.70.
D)0.90.
E)1.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Consider a simple macro model with a constant price level and demand-determined output.The marginal propensity to spend out of national income,z,can be expressed as ________ (where t = net tax rate and m = marginal propensity to import).
A)z = MPC(1 - t - m)
B)z = tY - mY
C)z = MPC - (1 - t- m)Y
D)z = MPC - (1 - t - m)
E)z = MPC(1 - t)- m
A)z = MPC(1 - t - m)
B)z = tY - mY
C)z = MPC - (1 - t- m)Y
D)z = MPC - (1 - t - m)
E)z = MPC(1 - t)- m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The diagrams below show the import,export,and net export functions for an economy. 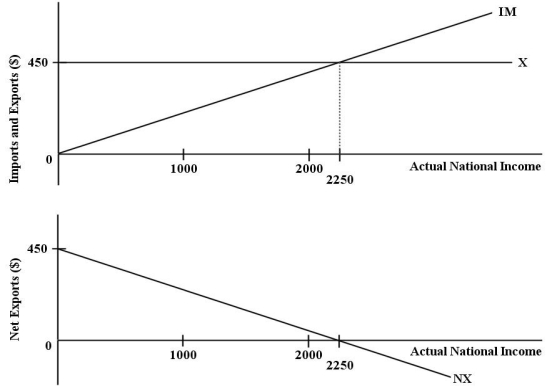 FIGURE 22-1 Refer to Figure 22-1.If actual national income in this economy is equal to $1000,then net exports are equal to
FIGURE 22-1 Refer to Figure 22-1.If actual national income in this economy is equal to $1000,then net exports are equal to
A)$90.
B)$200.
C)$250.
D)$375.
E)$400.
 FIGURE 22-1 Refer to Figure 22-1.If actual national income in this economy is equal to $1000,then net exports are equal to
FIGURE 22-1 Refer to Figure 22-1.If actual national income in this economy is equal to $1000,then net exports are equal toA)$90.
B)$200.
C)$250.
D)$375.
E)$400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In our simple macro model with government,consider the equation T = (0.2)Y.Which of the following statements about this equation is correct?
A)Total tax revenues are equal to 20% of disposable income.
B)Total tax revenues are equal to 20% of real GDP.
C)Net tax revenues are equal to 20% of disposable income.
D)If national income increases by $1.00,then net tax revenue increases by $0.20.
E)If total tax revenue increases by $0.20,then national income increases by $1.00.
A)Total tax revenues are equal to 20% of disposable income.
B)Total tax revenues are equal to 20% of real GDP.
C)Net tax revenues are equal to 20% of disposable income.
D)If national income increases by $1.00,then net tax revenue increases by $0.20.
E)If total tax revenue increases by $0.20,then national income increases by $1.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Suppose exports (X)= 100,real GDP (Y)= 500,and imports are equal to mY,where m is the marginal propensity to import.Net exports would be equal to zero if the marginal propensity to import were
A)1%.
B)5%.
C)10%.
D)20%.
E)50%.
A)1%.
B)5%.
C)10%.
D)20%.
E)50%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In our simple macro model with government and foreign trade,the marginal propensity to consume out of disposable income is ________ whereas the marginal propensity to consume out of national income is ________.
A)MPC; MPC(1 - t)
B)MPC(1 - t); MPC
C)MPC(1 - t)- m; MPC(1 - t)
D)MPC; MPC(1 - t)- m
E)MPC(1 - t); MPC(1 - t)- m
A)MPC; MPC(1 - t)
B)MPC(1 - t); MPC
C)MPC(1 - t)- m; MPC(1 - t)
D)MPC; MPC(1 - t)- m
E)MPC(1 - t); MPC(1 - t)- m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Consider the simplest macro model with demand-determined output.The equations are: C = 150 + 0.8Yd,Yd = Y-T,I = 400,G = 700,T = .2Y,X = 130,and IM = 0.14Y.Autonomous expenditures in this model are
A)1120.
B)1350.
C)1380.
D)2700.
E)5400.
A)1120.
B)1350.
C)1380.
D)2700.
E)5400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Consider a simple macro model with a constant price level and demand-determined output.The equations of the model are: C = 120 + 0.86Y,I = 300,G = 520,T = 0,X = 180,IM = 0.12Y.If national income is 2400,then desired aggregate expenditure is
A)1120.
B)1776.
C)2896.
D)3184.
E)3472.
A)1120.
B)1776.
C)2896.
D)3184.
E)3472.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Consider a simple macro model with a constant price level and demand-determined output.The equations of the model are: C = 60 + 0.43Y,I = 150,G = 260,T = 0,X = 90,IM = 0.06Y.A national income of 1200 results in desired aggregate expenditure of
A)560.
B)926.
C)1004.
D)1016.
E)1148.
A)560.
B)926.
C)1004.
D)1016.
E)1148.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The diagram below shows desired aggregate expenditure for a hypothetical economy.Assume the following features of this economy: • marginal propensity to consume (mpc)= 0.75
• net tax rate (t)= 0.20
• no foreign trade
• fixed price level
• all expenditure and income figures are in billions of dollars.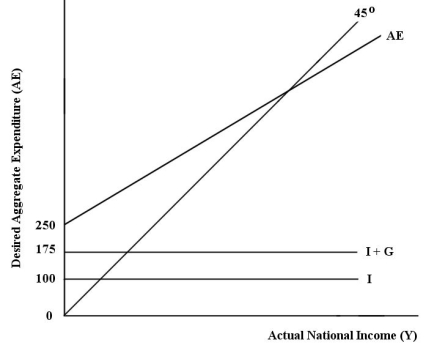 FIGURE 22-2
FIGURE 22-2
Refer to Figure 22-2.Which of the following equations describes the aggregate expenditure function for this economy?
A)AE = 250 + (0.6)Y
B)AE = 225 + (0.75)Y
C)AE = 250 +(0.15)Y
D)AE = 75 + (0.75)Y + (0.2)YD
E)AE = 250 +(0.75)Y + (0.2)YD
• net tax rate (t)= 0.20
• no foreign trade
• fixed price level
• all expenditure and income figures are in billions of dollars.
 FIGURE 22-2
FIGURE 22-2Refer to Figure 22-2.Which of the following equations describes the aggregate expenditure function for this economy?
A)AE = 250 + (0.6)Y
B)AE = 225 + (0.75)Y
C)AE = 250 +(0.15)Y
D)AE = 75 + (0.75)Y + (0.2)YD
E)AE = 250 +(0.75)Y + (0.2)YD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
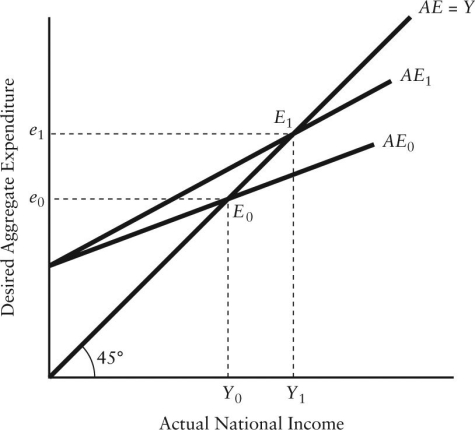 FIGURE 22-4 Refer to Figure 22-4.The rotation from AE1 to AE0 could be caused by
FIGURE 22-4 Refer to Figure 22-4.The rotation from AE1 to AE0 could be caused byA)an increase in the marginal propensity to consume out of disposable income.
B)a decrease in the marginal propensity to import.
C)an increase in the marginal propensity to import.
D)a decrease in the net tax rate.
E)a decrease in government purchases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Consider the simplest macro model with a constant price level and demand-determined output.The equations of the model are: C = 60 + 0.43Y,I = 150,G = 260,T = 0,X = 90,IM = 0.06Y.The marginal propensity to spend on national income,z,is
A)0.06.
B)0.37.
C)0.43.
D)0.49.
E)0.63.
A)0.06.
B)0.37.
C)0.43.
D)0.49.
E)0.63.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Consider the simplest macro model with demand-determined output.The equations are: C = 150 + 0.8Yd,Yd = Y -T,I = 400,G = 700,T = .2Y,X = 130,and IM = 0.14Y.The marginal propensity to spend on national income in this model is
A)0.50.
B)0.54.
C)0.64.
D)0.84.
E)0.86.
A)0.50.
B)0.54.
C)0.64.
D)0.84.
E)0.86.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Consider a simple macro model with a constant price level and demand-determined output.The equations of the model are: C = 120 + 0.86Y,I = 300,G = 520,T = 0,X = 180,IM = 0.12Y.Total autonomous spending in this model is
A)120.0.
B)1120.0.
C)420.0.
D)600.0.
E)828.8.
A)120.0.
B)1120.0.
C)420.0.
D)600.0.
E)828.8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The diagram below shows desired aggregate expenditure for a hypothetical economy.Assume the following features of this economy: • marginal propensity to consume (mpc)= 0.80
• net tax rate (t)= 0.15
• no foreign trade
• fixed price level
• all expenditure and income figures are in billions of dollars.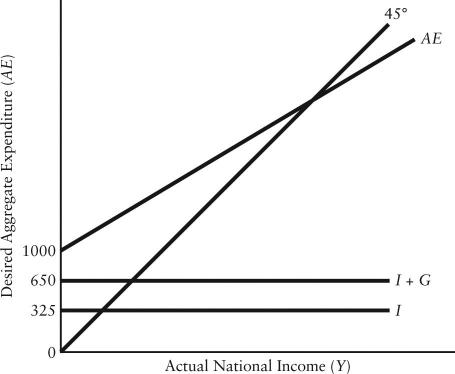 FIGURE 22-3
FIGURE 22-3
Refer to Figure 22-3.Which of the following correctly describes the consumption function for this economy?
A)C = 325 + (0.65)Y
B)C = 350 + (0.68)YD
C)C = 350 + (0.68)Y
D)C = 1000 + (0.80)
E)C = 1000 + (0.80)Y
• net tax rate (t)= 0.15
• no foreign trade
• fixed price level
• all expenditure and income figures are in billions of dollars.
 FIGURE 22-3
FIGURE 22-3Refer to Figure 22-3.Which of the following correctly describes the consumption function for this economy?
A)C = 325 + (0.65)Y
B)C = 350 + (0.68)YD
C)C = 350 + (0.68)Y
D)C = 1000 + (0.80)
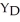
E)C = 1000 + (0.80)Y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Consider a simple macro model with a constant price level and demand-determined output.The equations of the model are: C = 120 + 0.86Y,I = 300,G = 520,T = 0,X = 180,IM = 0.12Y.The vertical intercept of the AE function is
A)120.0.
B)420.0.
C)600.0.
D)828.8.
E)1120.0.
A)120.0.
B)420.0.
C)600.0.
D)828.8.
E)1120.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Consider a simple macro model with a constant price level and demand-determined output.The equations of the model are: C = 60 + 0.43Y,I = 150,G = 260,T = 0,X = 90,IM = 0.06Y.The vertical intercept of the AE function is
A)60.0.
B)210.0.
C)300.0.
D)414.4.
E)560.0.
A)60.0.
B)210.0.
C)300.0.
D)414.4.
E)560.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The diagram below shows desired aggregate expenditure for a hypothetical economy.Assume the following features of this economy: • marginal propensity to consume (mpc)= 0.80
• net tax rate (t)= 0.15
• no foreign trade
• fixed price level
• all expenditure and income figures are in billions of dollars.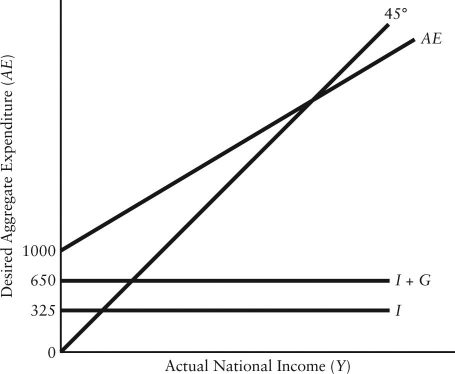 FIGURE 22-3
FIGURE 22-3
Refer to Figure 22-3.What is total autonomous expenditure?
A)$300
B)$325
C)$650
D)$1000
E)$1975
• net tax rate (t)= 0.15
• no foreign trade
• fixed price level
• all expenditure and income figures are in billions of dollars.
 FIGURE 22-3
FIGURE 22-3Refer to Figure 22-3.What is total autonomous expenditure?
A)$300
B)$325
C)$650
D)$1000
E)$1975

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
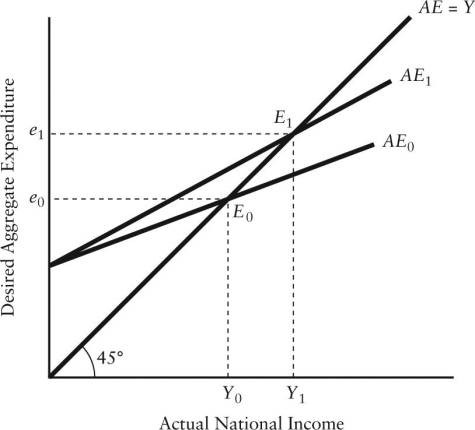 FIGURE 22-4 Refer to Figure 22-4.The rotation from AE0 to AE1 could be caused by
FIGURE 22-4 Refer to Figure 22-4.The rotation from AE0 to AE1 could be caused byA)a higher net tax rate.
B)a lower net tax rate.
C)a balanced budget.
D)lower government purchases.
E)higher government purchases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The diagram below shows desired aggregate expenditure for a hypothetical economy.Assume the following features of this economy: • marginal propensity to consume (mpc)= 0.75
• net tax rate (t)= 0.20
• no foreign trade
• fixed price level
• all expenditure and income figures are in billions of dollars.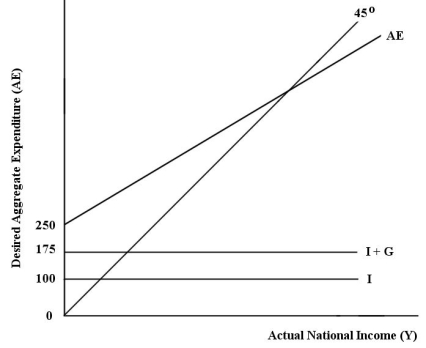 FIGURE 22-2
FIGURE 22-2
Refer to Figure 22-2.What is the level of autonomous consumption?
A)$0
B)$75
C)$100
D)$175
E)$250
• net tax rate (t)= 0.20
• no foreign trade
• fixed price level
• all expenditure and income figures are in billions of dollars.
 FIGURE 22-2
FIGURE 22-2Refer to Figure 22-2.What is the level of autonomous consumption?
A)$0
B)$75
C)$100
D)$175
E)$250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The diagram below shows desired aggregate expenditure for a hypothetical economy.Assume the following features of this economy: • marginal propensity to consume (mpc)= 0.75
• net tax rate (t)= 0.20
• no foreign trade
• fixed price level
• all expenditure and income figures are in billions of dollars.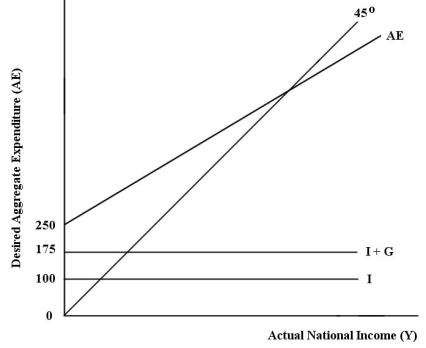 FIGURE 22-2
FIGURE 22-2
Refer to Figure 22-2.Which of the following correctly describes the consumption function for this economy?
A)C = (0.6)YD
B)Y = 250 + (0.75)YD
C)C = 75 + (0.75)YD
D)Y = 250 + (0.75)Y
E)C = 250 + (0.6)Y
• net tax rate (t)= 0.20
• no foreign trade
• fixed price level
• all expenditure and income figures are in billions of dollars.
 FIGURE 22-2
FIGURE 22-2Refer to Figure 22-2.Which of the following correctly describes the consumption function for this economy?
A)C = (0.6)YD
B)Y = 250 + (0.75)YD
C)C = 75 + (0.75)YD
D)Y = 250 + (0.75)Y
E)C = 250 + (0.6)Y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The diagram below shows desired aggregate expenditure for a hypothetical economy.Assume the following features of this economy: • marginal propensity to consume (mpc)= 0.75
• net tax rate (t)= 0.20
• no foreign trade
• fixed price level
• all expenditure and income figures are in billions of dollars.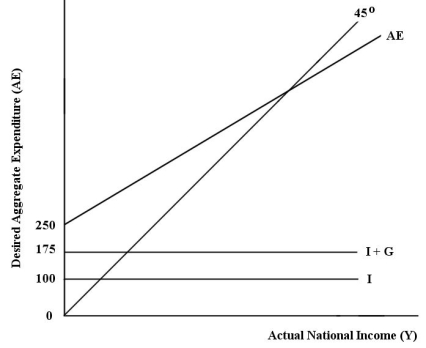 FIGURE 22-2
FIGURE 22-2
Refer to Figure 22-2.What is total autonomous expenditure?
A)$0
B)$75
C)$100
D)$175
E)$250
• net tax rate (t)= 0.20
• no foreign trade
• fixed price level
• all expenditure and income figures are in billions of dollars.
 FIGURE 22-2
FIGURE 22-2Refer to Figure 22-2.What is total autonomous expenditure?
A)$0
B)$75
C)$100
D)$175
E)$250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The diagram below shows desired aggregate expenditure for a hypothetical economy.Assume the following features of this economy: • marginal propensity to consume (mpc)= 0.80
• net tax rate (t)= 0.15
• no foreign trade
• fixed price level
• all expenditure and income figures are in billions of dollars.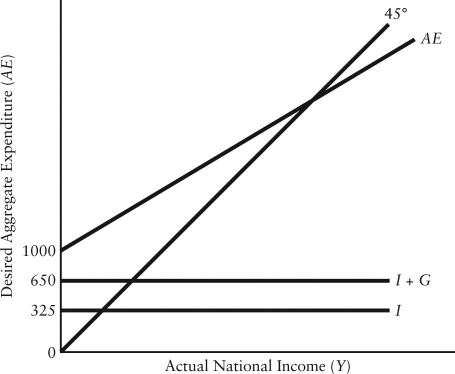 FIGURE 22-3
FIGURE 22-3
Refer to Figure 22-3.Which of the following equations describes the aggregate expenditure function for this economy?
A)AE = 1000 + (0.68)Y
B)AE = 1000 + (0.80)
C)AE = 1000 + (0.80)Y + 0.15 YD
D)AE = 1975 + (0.68)Y
E)AE = 1975 + (0.65)Y
• net tax rate (t)= 0.15
• no foreign trade
• fixed price level
• all expenditure and income figures are in billions of dollars.
 FIGURE 22-3
FIGURE 22-3Refer to Figure 22-3.Which of the following equations describes the aggregate expenditure function for this economy?
A)AE = 1000 + (0.68)Y
B)AE = 1000 + (0.80)
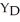
C)AE = 1000 + (0.80)Y + 0.15 YD
D)AE = 1975 + (0.68)Y
E)AE = 1975 + (0.65)Y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The diagram below shows desired aggregate expenditure for a hypothetical economy.Assume the following features of this economy: • marginal propensity to consume (mpc)= 0.80
• net tax rate (t)= 0.15
• no foreign trade
• fixed price level
• all expenditure and income figures are in billions of dollars.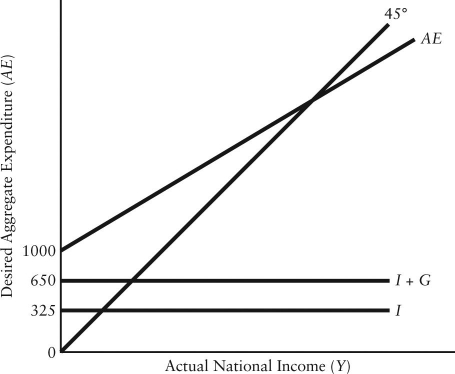 FIGURE 22-3
FIGURE 22-3
Refer to Figure 22-3.What is the marginal propensity to spend (z)in this economy?
A)0.45
B)0.48
C)0.65
D)0.68
E)0.80
• net tax rate (t)= 0.15
• no foreign trade
• fixed price level
• all expenditure and income figures are in billions of dollars.
 FIGURE 22-3
FIGURE 22-3Refer to Figure 22-3.What is the marginal propensity to spend (z)in this economy?
A)0.45
B)0.48
C)0.65
D)0.68
E)0.80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The diagram below shows desired aggregate expenditure for a hypothetical economy.Assume the following features of this economy: • marginal propensity to consume (mpc)= 0.80
• net tax rate (t)= 0.15
• no foreign trade
• fixed price level
• all expenditure and income figures are in billions of dollars.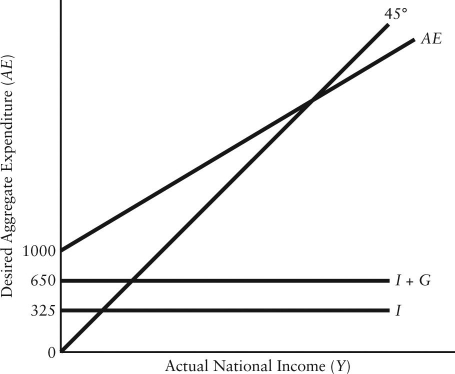 FIGURE 22-3
FIGURE 22-3
Refer to Figure 22-3.What is the level of autonomous consumption?
A)$0
B)$325
C)$350
D)$650
E)$1000
• net tax rate (t)= 0.15
• no foreign trade
• fixed price level
• all expenditure and income figures are in billions of dollars.
 FIGURE 22-3
FIGURE 22-3Refer to Figure 22-3.What is the level of autonomous consumption?
A)$0
B)$325
C)$350
D)$650
E)$1000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The diagram below shows desired aggregate expenditure for a hypothetical economy.Assume the following features of this economy: • marginal propensity to consume (mpc)= 0.75
• net tax rate (t)= 0.20
• no foreign trade
• fixed price level
• all expenditure and income figures are in billions of dollars.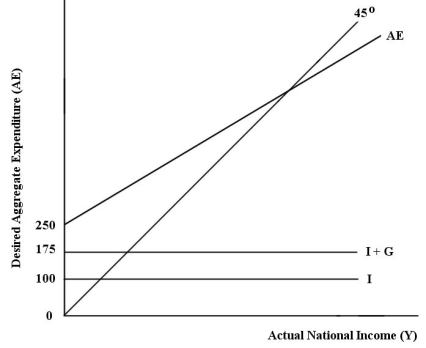 FIGURE 22-2
FIGURE 22-2
Refer to Figure 22-2.What is the marginal propensity to spend (z)in this economy?
A)0.15
B)0.20
C)0.40
D)0.60
E)0.75
• net tax rate (t)= 0.20
• no foreign trade
• fixed price level
• all expenditure and income figures are in billions of dollars.
 FIGURE 22-2
FIGURE 22-2Refer to Figure 22-2.What is the marginal propensity to spend (z)in this economy?
A)0.15
B)0.20
C)0.40
D)0.60
E)0.75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



