Deck 15: Biotechnology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/71
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Biotechnology
1
A base-pair substitution carried by a measurable percentage of a population is called a ____.
A)single-nucleotide polymorphism
B)syndrome
C)gene
D)short tandem repeat
E)recombinant gene
A)single-nucleotide polymorphism
B)syndrome
C)gene
D)short tandem repeat
E)recombinant gene
A
2
On an SNP chip, a yellow dot indicates that the individual ____.
A)is homozygous dominant for two copies of the SNP
B)contains three different copies of the SNP
C)is homozygous recessive for two copies of the SNP
D)is heterozygous for the SNP
E)does not have the SNP
A)is homozygous dominant for two copies of the SNP
B)contains three different copies of the SNP
C)is homozygous recessive for two copies of the SNP
D)is heterozygous for the SNP
E)does not have the SNP
D
3
Many restriction enzymes leave single-stranded tails called ____ ends on DNA fragments.
A)sticky
B)blunt
C)cut
D)jagged
E)sharp
A)sticky
B)blunt
C)cut
D)jagged
E)sharp
A
4
Because it does not contain introns, researchers prefer to use ____ when working with human genes.
A)cDNA
B)cloned DNA
C)hybridized DNA
D)recombinant DNA
E)viral DNA
A)cDNA
B)cloned DNA
C)hybridized DNA
D)recombinant DNA
E)viral DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What serves as the template for the production of cDNA?
A)DNA
B)mRNA
C)rRNA
D)tRNA
E)protein
A)DNA
B)mRNA
C)rRNA
D)tRNA
E)protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
RNA can serve as a template for the production of complementary DNA via the action of ____.
A)DNA polymerase
B)RNA polymerase
C)reverse transcriptase
D)ligase
E)restriction endonuclease
A)DNA polymerase
B)RNA polymerase
C)reverse transcriptase
D)ligase
E)restriction endonuclease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
An organism's complete set of genetic material is its ____.
A)proteome
B)genome
C)DNA library
D)probe
E)transcriptome
A)proteome
B)genome
C)DNA library
D)probe
E)transcriptome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
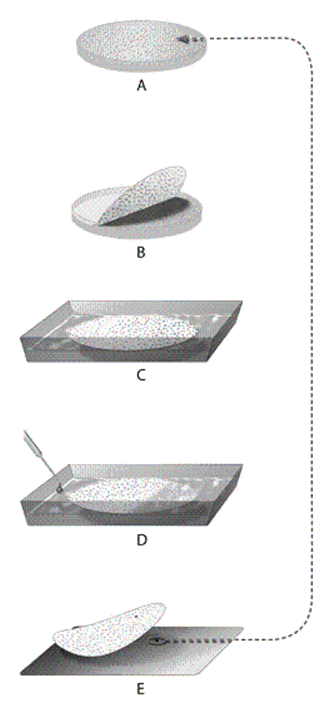
-In the accompanying figure, in which step is a radioactive probe base-pairing to the target gene?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Gene therapy is a promising therapeutic tool; however, some unwanted side effects can occur. What did some patients being treated for SCID-X1 develop after gene therapy?
A)a defective immune system
B)leukemia
C)myeloma
D)viral infection
E)diabetes
A)a defective immune system
B)leukemia
C)myeloma
D)viral infection
E)diabetes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In gel electrophoresis, the ____ the DNA fragment, the faster it moves through the gel.
A)more charged
B)longer
C)shorter
D)higher G-C content
E)higher A-T content
A)more charged
B)longer
C)shorter
D)higher G-C content
E)higher A-T content

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The "natural" use of restriction enzymes by bacteria is to ____.
A)integrate viral DNA
B)destroy viral DNA
C)repair "sticky ends"
D)copy the bacterial genes
E)clone DNA
A)integrate viral DNA
B)destroy viral DNA
C)repair "sticky ends"
D)copy the bacterial genes
E)clone DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Enzymes used to cut DNA molecules in recombinant DNA research are ____.
A)ligases
B)restriction enzymes
C)transcriptases
D)DNA polymerases
E)replicases
A)ligases
B)restriction enzymes
C)transcriptases
D)DNA polymerases
E)replicases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The polymerase used in PCR was isolated from ____, which typically lives in ____.
A)Escherichia coli; the mammalian gut
B)Haemophilus influenzae; hot springs
C)Homo sapiens; warm climates
D)Thermus aquaticus; hydrothermal vents
E)Streptococcus pneumoniae; mucous membranes
A)Escherichia coli; the mammalian gut
B)Haemophilus influenzae; hot springs
C)Homo sapiens; warm climates
D)Thermus aquaticus; hydrothermal vents
E)Streptococcus pneumoniae; mucous membranes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which genetically modified organisms currently make the majority of human insulin for medical purposes?
A)yeast
B)bacteria
C)rabbits
D)goats
E)plants
A)yeast
B)bacteria
C)rabbits
D)goats
E)plants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The modified nucleotides used in DNA sequencing have a(n) ____ instead of a hydroxyl group on the 3' carbon.
A)hydrogen
B)nitrogen
C)oxygen
D)amine group
E)phosphate group
A)hydrogen
B)nitrogen
C)oxygen
D)amine group
E)phosphate group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A cancer patient's cells are removed and a new gene is introduced into the cells during growth in cell culture. The cells are then reintroduced into the patient and the inserted gene directs the destruction of the cancer cells. This is an example of ____.
A)gene therapy
B)cloning
C)DNA profiling
D)DNA fingerprinting
E)cell replacement therapy
A)gene therapy
B)cloning
C)DNA profiling
D)DNA fingerprinting
E)cell replacement therapy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What treatment involves the transfer of a normal gene into cells of an individual with the intent to correct a genetic defect or treat a disease?
A)DNA cloning
B)DNA sequencing
C)gene replacement
D)gene therapy
E)reverse transcriptase
A)DNA cloning
B)DNA sequencing
C)gene replacement
D)gene therapy
E)reverse transcriptase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What commonly serves as a DNA cloning vector?
A)a reproducing bacterial population
B)a bacterial plasmid
C)an animal plasmid
D)a transgenic plant
E)restriction enzymes
A)a reproducing bacterial population
B)a bacterial plasmid
C)an animal plasmid
D)a transgenic plant
E)restriction enzymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
DNA is heated at the beginning of each PCR cycle to ____.
A)inactivate the DNA polymerase
B)allow primers to bind to template DNA
C)separate double-stranded DNA
D)allow a new nucleotide chain to be produced
E)denature contaminating proteins
A)inactivate the DNA polymerase
B)allow primers to bind to template DNA
C)separate double-stranded DNA
D)allow a new nucleotide chain to be produced
E)denature contaminating proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The enzyme used in the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is ____.
A)a restriction enzyme
B)reverse transcriptase
C)DNA polymerase
D)RNA replicase
E)ligase
A)a restriction enzyme
B)reverse transcriptase
C)DNA polymerase
D)RNA replicase
E)ligase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Reverse transcriptase produces a ____ molecule.
A)double-stranded DNA
B)single-stranded DNA
C)double-stranded RNA
D)single-stranded RNA
E)protein
A)double-stranded DNA
B)single-stranded DNA
C)double-stranded RNA
D)single-stranded RNA
E)protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
During the production of recombinant DNA, ____ seals the gaps between hybridized DNA fragments.
A)DNA polymerase
B)DNA ligase
C)RNA polymerase
D)ribosomes
E)DNA repair enzymes
A)DNA polymerase
B)DNA ligase
C)RNA polymerase
D)ribosomes
E)DNA repair enzymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
About ____ percent of an individual's genes are the same as in the general population.
A)19
B)29
C)59
D)79
E)99
A)19
B)29
C)59
D)79
E)99

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Imagine you have paid for a genetic test from a company that can report your probability of developing Alzheimer's disease based on the presence of a certain allele. This test would be examining your ____ profile.
A)chromosome number
B)introns
C)RNA
D)SNPs
E)mRNA expression
A)chromosome number
B)introns
C)RNA
D)SNPs
E)mRNA expression

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which biotechnology tool allows many copies of a specific section of DNA to be made very rapidly?
A)electrophoresis
B)DNA library production
C)DNA sequencing
D)polymerase chain reaction
E)DNA library screening
A)electrophoresis
B)DNA library production
C)DNA sequencing
D)polymerase chain reaction
E)DNA library screening

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Electrophoresis is used in DNA sequencing to separate DNA fragments based on their ____.
A)percentage of C-G base pairs
B)biochemical properties
C)colored pigment
D)length
E)number of copies
A)percentage of C-G base pairs
B)biochemical properties
C)colored pigment
D)length
E)number of copies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
DNA profiling is based on the slight differences that occur in ____ in the human genome.
A)sex chromosomes
B)base pairings
C)short tandem repeats
D)chromosome size
E)DNA/RNA pairing
A)sex chromosomes
B)base pairings
C)short tandem repeats
D)chromosome size
E)DNA/RNA pairing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Researchers clone a fragment of DNA by inserting it into a ____.
A)vector
B)CRISPR
C)restriction enzyme
D)chromosome
E)sister chromatid
A)vector
B)CRISPR
C)restriction enzyme
D)chromosome
E)sister chromatid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The laboratory technique used to separate the DNA fragments produced by automated DNA sequencing is ____.
A)the polymerase chain reaction
B)electrophoresis
C)ultracentrifugation
D)electron microscopy
E)fluorescence microscopy
A)the polymerase chain reaction
B)electrophoresis
C)ultracentrifugation
D)electron microscopy
E)fluorescence microscopy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What benefit does the bacterial gene encoding the Bt protein confer on genetically modified plants?
A)faster growth
B)slower metabolism
C)resistance to drought
D)vitamin enriched plant material
E)resistance to insects
A)faster growth
B)slower metabolism
C)resistance to drought
D)vitamin enriched plant material
E)resistance to insects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The human genome has approximately ____ protein-coding genes.
A)2,000
B)10,000
C)20,000
D)200,000
E)500,000
A)2,000
B)10,000
C)20,000
D)200,000
E)500,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
DNA sequencing gives a readout of 5' AATCGGTTG 3' based on the color-labeled nucleotides detected after gel electrophoresis. What is the sequence of the template strand?
A)5' AATCGGTTG 3'
B)5' CAACCGATT 3'
C)5' TTAGCCAAC 3'
D)5' GTTGGCTAA 3'
E)More information is required to determine the sequence of the template strand.
A)5' AATCGGTTG 3'
B)5' CAACCGATT 3'
C)5' TTAGCCAAC 3'
D)5' GTTGGCTAA 3'
E)More information is required to determine the sequence of the template strand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A collection of cells containing different fragments of foreign DNA, often representing an organism's entire genome, is called ____.
A)copied DNA
B)transcribed DNA
C)DNA amplification
D)a DNA library
E)plasmid DNA
A)copied DNA
B)transcribed DNA
C)DNA amplification
D)a DNA library
E)plasmid DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which nucleotides are used in DNA sequencing reactions?
A)deoxynucleotides only
B)dideoxynucleotides only
C)ribonucleotides only
D)deoxynucleotides and ribonucleotides
E)deoxynucleotides and dideoxynucleotides
A)deoxynucleotides only
B)dideoxynucleotides only
C)ribonucleotides only
D)deoxynucleotides and ribonucleotides
E)deoxynucleotides and dideoxynucleotides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
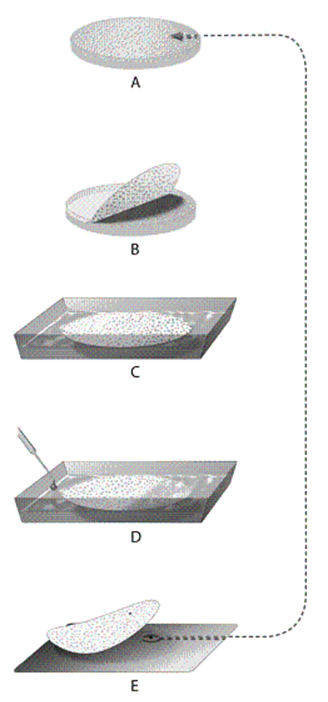
-In the accompanying figure, in which step are cells being ruptured to release their DNA?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Identifying an individual by analyzing the unique parts of his/her DNA is called ____.
A)sequencing
B)genomics
C)DNA profiling
D)electrophoresis
E)proteomics
A)sequencing
B)genomics
C)DNA profiling
D)electrophoresis
E)proteomics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The study of whole-genome structure and function is called ____.
A)electrophoresis
B)DNA sequencing
C)bioinformatics
D)genomics
E)proteomics
A)electrophoresis
B)DNA sequencing
C)bioinformatics
D)genomics
E)proteomics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Restriction enzyme cut ____.
A)specific RNA nucleotide sequences
B)specific DNA nucleotide sequences
C)nonspecific sites in mRNA
D)nonspecific sites in protein molecules
E)nonspecific sites in chromosomes
A)specific RNA nucleotide sequences
B)specific DNA nucleotide sequences
C)nonspecific sites in mRNA
D)nonspecific sites in protein molecules
E)nonspecific sites in chromosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The Ti plasmid from which plant pathogen is used to transfer genes into plants?
A)Agrobacterium tumefaciens
B)Escherichia coli
C)Haemophilus influenzae
D)Salmonella typhimurium
E)Streptococcus faecalis
A)Agrobacterium tumefaciens
B)Escherichia coli
C)Haemophilus influenzae
D)Salmonella typhimurium
E)Streptococcus faecalis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Probes for cloned genes of interest are ____.
A)complementary nucleotide sequences labeled with a tracer
B)certain media with specific antibodies
C)specific enzymes
D)certain bacteria sensitive to the genes
E)a labeled tracer gene from bacteria
A)complementary nucleotide sequences labeled with a tracer
B)certain media with specific antibodies
C)specific enzymes
D)certain bacteria sensitive to the genes
E)a labeled tracer gene from bacteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What happens directly after DNA polymerase adds a modified, colored nucleotide to the DNA strand during DNA sequencing?
A)The synthesis of the strand ends.
B)A normal nucleotide must be added next.
C)The DNA repair enzymes remove the nucleotide.
D)Restriction enzymes cut the DNA fragment.
E)The next nucleotide will be added at random.
A)The synthesis of the strand ends.
B)A normal nucleotide must be added next.
C)The DNA repair enzymes remove the nucleotide.
D)Restriction enzymes cut the DNA fragment.
E)The next nucleotide will be added at random.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Match each scenario with the type of genetic engineering that best describes it.
a.medical application
b.research application
c.agricultural application
Bacteria are genetically modified to produce human insulin.
a.medical application
b.research application
c.agricultural application
Bacteria are genetically modified to produce human insulin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Match each description with the most appropriate term.
a.cDNA
b.a restriction enzyme
c.reverse transcriptase
d.a DNA library
collections of DNA fragments incorporated into cloning vectors
a.cDNA
b.a restriction enzyme
c.reverse transcriptase
d.a DNA library
collections of DNA fragments incorporated into cloning vectors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Match each description with the most appropriate term.
a.polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
b.DNA cloning
c.DNA sequencing
d.DNA profiling
e.electrophoresis
f.probe
g.transgenic
analysis of the unique parts of a person's DNA
a.polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
b.DNA cloning
c.DNA sequencing
d.DNA profiling
e.electrophoresis
f.probe
g.transgenic
analysis of the unique parts of a person's DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Match each description with the most appropriate term.
a.polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
b.DNA cloning
c.DNA sequencing
d.DNA profiling
e.electrophoresis
f.probe
g.transgenic
technique that separates DNA fragments by size
a.polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
b.DNA cloning
c.DNA sequencing
d.DNA profiling
e.electrophoresis
f.probe
g.transgenic
technique that separates DNA fragments by size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Match each description with the most appropriate term.
a.polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
b.DNA cloning
c.DNA sequencing
d.DNA profiling
e.electrophoresis
f.probe
g.transgenic
method to determine the order of nucleotides in DNA
a.polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
b.DNA cloning
c.DNA sequencing
d.DNA profiling
e.electrophoresis
f.probe
g.transgenic
method to determine the order of nucleotides in DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Match each scenario with the type of genetic engineering that best describes it.
a.medical application
b.research application
c.agricultural application
Zebrafish are engineered to glow in places where BPA is present, to study the effects of the endocrine-disrupting chemical.
a.medical application
b.research application
c.agricultural application
Zebrafish are engineered to glow in places where BPA is present, to study the effects of the endocrine-disrupting chemical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Match each description with the most appropriate term.
a.cDNA
b.a restriction enzyme
c.reverse transcriptase
d.a DNA library
cuts apart foreign DNA as its primary function
a.cDNA
b.a restriction enzyme
c.reverse transcriptase
d.a DNA library
cuts apart foreign DNA as its primary function

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Match each description with the most appropriate term.
a.cDNA
b.a restriction enzyme
c.reverse transcriptase
d.a DNA library
catalyzes reactions to construct DNA strands from mRNA
a.cDNA
b.a restriction enzyme
c.reverse transcriptase
d.a DNA library
catalyzes reactions to construct DNA strands from mRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Match each description with the most appropriate term.
a.cDNA
b.a restriction enzyme
c.reverse transcriptase
d.a DNA library
any DNA copied from mRNA transcripts
a.cDNA
b.a restriction enzyme
c.reverse transcriptase
d.a DNA library
any DNA copied from mRNA transcripts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Match each scenario with the type of genetic engineering that best describes it.
a.medical application
b.research application
c.agricultural application
Genes that control glucose metabolism are inactivated to study diabetes.
a.medical application
b.research application
c.agricultural application
Genes that control glucose metabolism are inactivated to study diabetes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Explain the difference between a GMO and a transgenic organism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Match each scenario with the type of genetic engineering that best describes it.
a.medical application
b.research application
c.agricultural application
Cotton is genetically engineered for resistance to the herbicide glyphosate.
a.medical application
b.research application
c.agricultural application
Cotton is genetically engineered for resistance to the herbicide glyphosate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Match each description with the most appropriate term.
a.polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
b.DNA cloning
c.DNA sequencing
d.DNA profiling
e.electrophoresis
f.probe
g.transgenic
method that copies fragments of DNA using living cells
a.polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
b.DNA cloning
c.DNA sequencing
d.DNA profiling
e.electrophoresis
f.probe
g.transgenic
method that copies fragments of DNA using living cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Match each scenario with the type of genetic engineering that best describes it.
a.medical application
b.research application
c.agricultural application
Goats are genetically modified to produce an anti-clotting protein.
a.medical application
b.research application
c.agricultural application
Goats are genetically modified to produce an anti-clotting protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Match each description with the most appropriate term.
a.polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
b.DNA cloning
c.DNA sequencing
d.DNA profiling
e.electrophoresis
f.probe
g.transgenic
genetically modified organism that carries a gene from a different species
a.polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
b.DNA cloning
c.DNA sequencing
d.DNA profiling
e.electrophoresis
f.probe
g.transgenic
genetically modified organism that carries a gene from a different species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Match each description with the most appropriate term.
a.polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
b.DNA cloning
c.DNA sequencing
d.DNA profiling
e.electrophoresis
f.probe
g.transgenic
short fragment of DNA labeled with a tracer
a.polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
b.DNA cloning
c.DNA sequencing
d.DNA profiling
e.electrophoresis
f.probe
g.transgenic
short fragment of DNA labeled with a tracer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Match each description with the most appropriate term.
a.polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
b.DNA cloning
c.DNA sequencing
d.DNA profiling
e.electrophoresis
f.probe
g.transgenic
method that copies fragments of DNA and requires primers
a.polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
b.DNA cloning
c.DNA sequencing
d.DNA profiling
e.electrophoresis
f.probe
g.transgenic
method that copies fragments of DNA and requires primers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Describe how DNA sequencing is performed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Match each scenario with the type of genetic engineering that best describes it.
a.medical application
b.research application
c.agricultural application
An insect resistance gene is introduced into corn.
a.medical application
b.research application
c.agricultural application
An insect resistance gene is introduced into corn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Explain how CRISPR works and how it can be used in genome editing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What are some applications of GMOs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Explain how the Ti plasmid is used to genetically engineer plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
How were restriction enzymes discovered and why are they a useful tool for making recombinant DNA?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
How are the number of short tandem repeats in an individual measured and how can this information be used for DNA fingerprinting in criminal investigations?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Explain the significance of Taq polymerase for PCR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In DNA libraries, a cell that contains a particular DNA fragment of interest is mixed with thousands or millions of others that do not. How does the use of a probe allow for detection of the DNA fragment of interest?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Researchers are beginning the process of DNA cloning. They have chromosomal DNA, a plasmid cloning vector, restriction enzymes, and DNA ligase. What else is needed in order to perform DNA cloning? Why is this needed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Why is it more difficult to study the products of the human genome than to determine the genome sequence? What information can be obtained through studying the protein content of cells?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Why does DNA fingerprinting work for identifying humans?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Why is human insulin production by bacteria a beneficial use of genetic engineering?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



