Deck 6: Probability and Hypothesis Testing
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/116
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Probability and Hypothesis Testing
1
Mathematically, probability may be defined as ______.
A) the number of ways an outcome may occur divided by the total number of possible outcomes
B) the total number of possible outcomes minus the number of ways a particular outcome may occur
C) the likelihood of rejecting the null hypothesis
D) the number of ways an outcome may occur
A) the number of ways an outcome may occur divided by the total number of possible outcomes
B) the total number of possible outcomes minus the number of ways a particular outcome may occur
C) the likelihood of rejecting the null hypothesis
D) the number of ways an outcome may occur
the number of ways an outcome may occur divided by the total number of possible outcomes
2
Conceptually, probability is most similar to the concept of ______.
A) likelihood
B) hypothesis
C) samples
D) deductive reasoning
A) likelihood
B) hypothesis
C) samples
D) deductive reasoning
likelihood
3
An event may be defined as an action that ______.
A) may occur
B) is tested
C) is an outcome
D) takes place
A) may occur
B) is tested
C) is an outcome
D) takes place
takes place
4
Which of the following BEST addresses the addition rule of probability?
A) Which grocery store checkout line should I get in?
B) What are my chances of getting a parking ticket?
C) What are the chances of Barack Obama being elected president?
D) What is the likelihood one of the California professional football teams will win the Super Bowl?
A) Which grocery store checkout line should I get in?
B) What are my chances of getting a parking ticket?
C) What are the chances of Barack Obama being elected president?
D) What is the likelihood one of the California professional football teams will win the Super Bowl?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Imagine you are in the lobby of a hotel and are standing in front of several elevators. Which of the following in the BEST example of probability?
A) standing in front of the elevator you believe will be the first one to arrive
B) counting the number of elevators
C) taking the stairs instead of waiting for an elevator to arrive
D) pushing the 'up' button on the elevator even though it has already been pushed by someone else
A) standing in front of the elevator you believe will be the first one to arrive
B) counting the number of elevators
C) taking the stairs instead of waiting for an elevator to arrive
D) pushing the 'up' button on the elevator even though it has already been pushed by someone else

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following BEST addresses the addition rule of probability?
A) What's more likely to occur: being kidnapped or getting hit by lightning?
B) Is there intelligent life on other planets?
C) What is the probability of drawing an 8, 9, or 10 from a deck of cards?
D) Is there an equal chance of having a baby boy versus a baby girl?
A) What's more likely to occur: being kidnapped or getting hit by lightning?
B) Is there intelligent life on other planets?
C) What is the probability of drawing an 8, 9, or 10 from a deck of cards?
D) Is there an equal chance of having a baby boy versus a baby girl?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following BEST addresses the addition rule of probability?
A) What are the chances my checkout line in the grocery store will be the slowest?
B) Am I more likely to be in an automobile accident or a plane crash?
C) What is the likelihood of talking a policeman out of giving you a speeding ticket?
D) What are my chances of my test score being in the top third of the class?
A) What are the chances my checkout line in the grocery store will be the slowest?
B) Am I more likely to be in an automobile accident or a plane crash?
C) What is the likelihood of talking a policeman out of giving you a speeding ticket?
D) What are my chances of my test score being in the top third of the class?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The addition rule of probability states ______.
A) there are a number of ways an outcome can occur
B) the combined probability of mutually exclusive outcomes is the sum of their individual probabilities
C) the sum of the probabilities of all possible outcomes of an event equals 1.00
D) the outcome equals the number of ways the outcome can occur divided by the total possible outcomes
A) there are a number of ways an outcome can occur
B) the combined probability of mutually exclusive outcomes is the sum of their individual probabilities
C) the sum of the probabilities of all possible outcomes of an event equals 1.00
D) the outcome equals the number of ways the outcome can occur divided by the total possible outcomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following BEST addresses the addition rule of probability?
A) What is the probability of getting a score greater than the mean?
B) Is there life on Mars?
C) The probability of an outcome is a number between 0 and 1.
D) In rolling a pair of dice, is there an equal probability of rolling an 8 versus a 9?
A) What is the probability of getting a score greater than the mean?
B) Is there life on Mars?
C) The probability of an outcome is a number between 0 and 1.
D) In rolling a pair of dice, is there an equal probability of rolling an 8 versus a 9?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following BEST addresses the addition rule of probability?
A) Am I more likely to be killed in a plane crash or by terrorists?
B) What are my chances of getting at least 4 heads in 7 coin flips?
C) What is the probability of Hillary Clinton being elected president?
D) What type of car is most likely to be stolen?
A) Am I more likely to be killed in a plane crash or by terrorists?
B) What are my chances of getting at least 4 heads in 7 coin flips?
C) What is the probability of Hillary Clinton being elected president?
D) What type of car is most likely to be stolen?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is an important aspect of probability?
A) The sum of probabilities of all possible outcomes of an event equals 1.0.
B) All possible outcomes have the exact same probability of occurring.
C) Each outcome has a 50% chance of occurring.
D) Combined probabilities of events that occur at the same time is equal to 1.0.
A) The sum of probabilities of all possible outcomes of an event equals 1.0.
B) All possible outcomes have the exact same probability of occurring.
C) Each outcome has a 50% chance of occurring.
D) Combined probabilities of events that occur at the same time is equal to 1.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Conceptually, probability may be defined as ______.
A) the total number of possible outcomes divided by the total number of events
B) the total number of possible outcomes
C) the likelihood of the occurrence of a particular outcome of an event given all possible outcomes
D) the number of ways an outcome can occur plus the number of ways an outcome cannot occur
A) the total number of possible outcomes divided by the total number of events
B) the total number of possible outcomes
C) the likelihood of the occurrence of a particular outcome of an event given all possible outcomes
D) the number of ways an outcome can occur plus the number of ways an outcome cannot occur

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The concept of ______ refers to differences between statistics calculated from a sample and statistics pertaining to the population from which the sample is drawn.
A) sampling error
B) probability
C) random factors
D) statistical error
A) sampling error
B) probability
C) random factors
D) statistical error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following BEST addresses the addition rule of probability?
A) What are the chances of winning a gold medal in the Olympics?
B) How likely is it that my Toyota will be in a car accident?
C) What are the chances of my flight arriving within half an hour of the scheduled time?
D) What are my chances of having the highest test score in my class?
A) What are the chances of winning a gold medal in the Olympics?
B) How likely is it that my Toyota will be in a car accident?
C) What are the chances of my flight arriving within half an hour of the scheduled time?
D) What are my chances of having the highest test score in my class?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Probability is an important concept for researchers primarily because ______.
A) it is used to develop statistical hypotheses such as the null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis
B) it is used to prove a study's research hypotheses
C) it is used to evaluate data collected from samples
D) most research involves flipping coins and pulling aces out of a deck of cards
A) it is used to develop statistical hypotheses such as the null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis
B) it is used to prove a study's research hypotheses
C) it is used to evaluate data collected from samples
D) most research involves flipping coins and pulling aces out of a deck of cards

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An event may be defined as an action that ______, and outcomes are possible ______ of that event.
A) can occur; results
B) is collected; numbers
C) takes place; results
D) can occur; numbers
A) can occur; results
B) is collected; numbers
C) takes place; results
D) can occur; numbers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Conceptually, probability is most similar to the concept of ______.
A) certainty
B) likelihood
C) division
D) proof
A) certainty
B) likelihood
C) division
D) proof

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following BEST addresses the addition rule of probability?
A) What is the likelihood of getting hit by lightning?
B) Who will be the next President of the United States?
C) What is the probability of getting a score at least 10 points above the mean?
D) In rolling a pair of dice, is there an equal probability of rolling an 8 rather than a 9?
A) What is the likelihood of getting hit by lightning?
B) Who will be the next President of the United States?
C) What is the probability of getting a score at least 10 points above the mean?
D) In rolling a pair of dice, is there an equal probability of rolling an 8 rather than a 9?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following BEST addresses the addition rule of probability?
A) What is my chance of winning any type of prize on the state lottery?
B) Which type of cell phone is most likely to have mechanical problems?
C) What is the likelihood of a major earthquake hitting the Bay Area today?
D) Which is more likely to happen to a 30-year old woman: getting married or getting hit by lightning?
A) What is my chance of winning any type of prize on the state lottery?
B) Which type of cell phone is most likely to have mechanical problems?
C) What is the likelihood of a major earthquake hitting the Bay Area today?
D) Which is more likely to happen to a 30-year old woman: getting married or getting hit by lightning?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The addition rule of probability relates to ______.
A) the combined probabilities of mutually exclusive outcomes
B) the fact that the probability of an outcome is a number between 0 and 1.00
C) how researchers state the null and alternative hypotheses
D) determining the number of ways a particular outcome may occur
A) the combined probabilities of mutually exclusive outcomes
B) the fact that the probability of an outcome is a number between 0 and 1.00
C) how researchers state the null and alternative hypotheses
D) determining the number of ways a particular outcome may occur

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The null and alternative hypotheses ______.
A) are mutually exclusive from each other
B) contain values of a sample statistic such as the sample mean (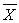 )
)
C) are two types of research hypotheses
D) state the critical values of a statistic needed to reject the null hypothesis
A) are mutually exclusive from each other
B) contain values of a sample statistic such as the sample mean (
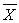 )
)C) are two types of research hypotheses
D) state the critical values of a statistic needed to reject the null hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In which of the following steps of analyzing data is probability most important?
A) calculating measures of central tendency such as the mean or median
B) developing research hypotheses
C) examining your data by creating tables and figures
D) calculating inferential statistics
A) calculating measures of central tendency such as the mean or median
B) developing research hypotheses
C) examining your data by creating tables and figures
D) calculating inferential statistics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A researcher finds that the mean income for her sample is $40,500 but the mean for the population from which the sample is drawn is believed to be $44,270. The difference between the two means can be attributed to ______.
A) nonrandom sampling
B) normal sampling
C) luck
D) sampling error
A) nonrandom sampling
B) normal sampling
C) luck
D) sampling error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The sum of the probabilities for the values of a binomial variable equals ______.
A) 1.00
B) .50
C) 2.00
D) zero
A) 1.00
B) .50
C) 2.00
D) zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A ______ is a statement about an expected outcome or relationship involving population parameters.
A) null hypothesis
B) statistical hypothesis
C) sampling error
D) alternative hypothesis
A) null hypothesis
B) statistical hypothesis
C) sampling error
D) alternative hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Sampling error refers to differences between ______.
A) statistics calculated from a sample and statistics pertaining to the population from which the sample is drawn
B) statistics calculated from two different populations
C) the likelihood of an occurrence of a particular outcome of an event and all possible outcomes
D) the likelihood of being in one category versus another category
A) statistics calculated from a sample and statistics pertaining to the population from which the sample is drawn
B) statistics calculated from two different populations
C) the likelihood of an occurrence of a particular outcome of an event and all possible outcomes
D) the likelihood of being in one category versus another category

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is the last step in the process of hypothesis testing?
A) make a decision regarding the null hypothesis
B) calculate the appropriate statistic
C) relate the result of the analysis to the research hypothesis
D) state the null and alternative hypothesis
A) make a decision regarding the null hypothesis
B) calculate the appropriate statistic
C) relate the result of the analysis to the research hypothesis
D) state the null and alternative hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In which of the following steps of the research process is probability most important?
A) developing a research hypothesis
B) collecting data
C) calculating descriptive statistics
D) calculating inferential statistics
A) developing a research hypothesis
B) collecting data
C) calculating descriptive statistics
D) calculating inferential statistics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A researcher finds that the mean number of arrests for juveniles in his sample is .39 whereas the mean number of arrests in the population is .15 The difference between the two means can be attributed to ______.
A) non-normal error
B) luck
C) a lack of planning
D) sampling error
A) non-normal error
B) luck
C) a lack of planning
D) sampling error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is an example of a binomial variable?
A) length of sentence
B) race (White or non-White)
C) age (in years)
D) education (
A) length of sentence
B) race (White or non-White)
C) age (in years)
D) education (

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is the correct order for the steps in hypothesis testing?
A) State the null and alternative hypotheses; make a decision about the null hypothesis; draw a conclusion; relate the results to the research hypothesis.
B) State the null and alternative hypotheses; make a decision about the null hypothesis; relate the results to the research hypothesis; draw a conclusion.
C) State the null and alternative hypotheses; draw a conclusion; make a decision about the null hypothesis; relate the results to the research hypothesis.
D) State the null and alternative hypotheses; draw a conclusion; relate the results to the research hypothesis; make a decision about the null hypothesis.
A) State the null and alternative hypotheses; make a decision about the null hypothesis; draw a conclusion; relate the results to the research hypothesis.
B) State the null and alternative hypotheses; make a decision about the null hypothesis; relate the results to the research hypothesis; draw a conclusion.
C) State the null and alternative hypotheses; draw a conclusion; make a decision about the null hypothesis; relate the results to the research hypothesis.
D) State the null and alternative hypotheses; draw a conclusion; relate the results to the research hypothesis; make a decision about the null hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Probability is an important concept for researchers primarily because ______.
A) it helps researchers prove their hypotheses
B) researchers collect data from samples rather than populations
C) researchers test hypotheses about samples by collecting data from populations
D) most research involves flipping coins and pulling aces out of a deck of cards
A) it helps researchers prove their hypotheses
B) researchers collect data from samples rather than populations
C) researchers test hypotheses about samples by collecting data from populations
D) most research involves flipping coins and pulling aces out of a deck of cards

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A researcher finds that the mean number of children in her sample is 3.48; however, the mean number of children in the population is 2.44. The difference between the two means can be attributed to ______.
A) systematic error
B) faulty logic
C) sampling error
D) non-random error
A) systematic error
B) faulty logic
C) sampling error
D) non-random error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A binomial distribution is used for a variable ______.
A) consisting of exactly two categories
B) consisting of only one category
C) consisting of three categories
D) that has zero categories
A) consisting of exactly two categories
B) consisting of only one category
C) consisting of three categories
D) that has zero categories

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In which of the following steps of the research process is probability most important?
A) testing research hypotheses
B) examining one's data
C) developing research hypotheses
D) reviewing the existing literature on the topic of interest
A) testing research hypotheses
B) examining one's data
C) developing research hypotheses
D) reviewing the existing literature on the topic of interest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If you were to draw 15 random samples of 100 residents in a city you may get 15 different means. These differences across samples may be defined as ______.
A) probability
B) random error
C) sampling error
D) normal error
A) probability
B) random error
C) sampling error
D) normal error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is the first step in hypothesis testing?
A) make a decision regarding the null hypothesis
B) calculate the appropriate statistic
C) relate the result of the analysis to the research hypothesis
D) state the null and alternative hypothesis
A) make a decision regarding the null hypothesis
B) calculate the appropriate statistic
C) relate the result of the analysis to the research hypothesis
D) state the null and alternative hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following variables would NOT be used for a binomial distribution?
A) age (over 65 or under 65)
B) gender (male or female)
C) jury verdict (guilty or not guilty
D) religion (Catholic, Protestant, Buddhist, etc.).
A) age (over 65 or under 65)
B) gender (male or female)
C) jury verdict (guilty or not guilty
D) religion (Catholic, Protestant, Buddhist, etc.).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is an example of a binomial variable?
A) religion (Christian, Buddhist, Catholic, Agnostic)
B) race (White, Asian, African American, Hispanic, Native American)
C) age (over 65 or under 65)
D) highest degree (high school diploma, some college, BA, professional degree)
A) religion (Christian, Buddhist, Catholic, Agnostic)
B) race (White, Asian, African American, Hispanic, Native American)
C) age (over 65 or under 65)
D) highest degree (high school diploma, some college, BA, professional degree)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following steps in the hypothesis testing process involves mathematical calculations?
A) state the null and alternative hypothesis
B) calculate the appropriate statistic
C) make a decision regarding the null hypothesis
D) draw a conclusion from the analysis
A) state the null and alternative hypothesis
B) calculate the appropriate statistic
C) make a decision regarding the null hypothesis
D) draw a conclusion from the analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following beliefs is the BEST example of an alternative hypothesis (H1)?
A) "It doesn't matter whether the President of the U.S. is a Democrat or a Republican."
B) "Men and women are looking for the same thing in their dating partners."
C) "Rubbing a good luck charm helps gamblers win more money."
D) "Cats are just as smart as dogs."
A) "It doesn't matter whether the President of the U.S. is a Democrat or a Republican."
B) "Men and women are looking for the same thing in their dating partners."
C) "Rubbing a good luck charm helps gamblers win more money."
D) "Cats are just as smart as dogs."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The statement " ≠ 8" is an example of a ______.
A) directional null hypothesis
B) non-directional null hypothesis
C) directional alternative hypothesis
D) non-directional alternative hypothesis
A) directional null hypothesis
B) non-directional null hypothesis
C) directional alternative hypothesis
D) non-directional alternative hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following beliefs is the BEST example of a null hypothesis (H0)?
A) "Men are smarter than women."
B) "There is life on Mars."
C) "Taking steroids does not help baseball players hit more home runs."
D) "McDonald's hamburgers taste better than Burger King hamburgers."
A) "Men are smarter than women."
B) "There is life on Mars."
C) "Taking steroids does not help baseball players hit more home runs."
D) "McDonald's hamburgers taste better than Burger King hamburgers."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following beliefs is most similar to an alternative hypothesis (H1)?
A) "Republicans and Democrats are equally likely to shoot their hunting partners."
B) "Men and women have the same beliefs regarding marriage."
C) "Hybrid cars get the same gas mileage as well-made traditional cars."
D) "Ipods are easier to use than other companies' MP3 players."
A) "Republicans and Democrats are equally likely to shoot their hunting partners."
B) "Men and women have the same beliefs regarding marriage."
C) "Hybrid cars get the same gas mileage as well-made traditional cars."
D) "Ipods are easier to use than other companies' MP3 players."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A statistical hypothesis that contains the ______ symbol may be defined as ______.
A) ≠; one-tailed
B) <; non-directional
C) <; one-tailed
D) ≠; directional
A) ≠; one-tailed
B) <; non-directional
C) <; one-tailed
D) ≠; directional

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following beliefs is the BEST example of a null hypothesis (H0)?
A) "Republicans are more likely to shoot their hunting partners than are Democrats."
B) "American Olympic skiers are not better than the rest of the world."
C) "Hybrid cars get better gas mileage than traditional cars."
D) "Apple Ipods are easier to use than other companies' MP3 players."
A) "Republicans are more likely to shoot their hunting partners than are Democrats."
B) "American Olympic skiers are not better than the rest of the world."
C) "Hybrid cars get better gas mileage than traditional cars."
D) "Apple Ipods are easier to use than other companies' MP3 players."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The "equals" sign can be found in which of the following hypotheses?
A) research hypothesis
B) null hypothesis
C) alternative hypothesis
D) all of these
A) research hypothesis
B) null hypothesis
C) alternative hypothesis
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The ______ hypothesis states that there is no difference or relationship among groups and the ______ hypothesis states that there is a difference or relationship among groups.
A) alternative; null
B) statistical; null
C) null; alternative
D) null; statistical
A) alternative; null
B) statistical; null
C) null; alternative
D) null; statistical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The statement ______ is an example of a ______ .
A) μ = 5; null hypothesis
B) μ = 5; alternative hypothesis
C) μ ≠ 5; null hypothesis
D) μ ≠ 5; research hypothesis
A) μ = 5; null hypothesis
B) μ = 5; alternative hypothesis
C) μ ≠ 5; null hypothesis
D) μ ≠ 5; research hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The difference between a statistical hypothesis and a research hypothesis is the research hypotheses ______.
A) involve concepts expressed with words and statistical hypotheses involve mathematical terms expressed with numbers
B) involve mathematical terms expressed with numbers and statistical hypotheses involve concepts expressed with words
C) involve population parameters while the statistical hypothesis involves sample parameters
D) can be tested while the statistical hypothesis cannot be
A) involve concepts expressed with words and statistical hypotheses involve mathematical terms expressed with numbers
B) involve mathematical terms expressed with numbers and statistical hypotheses involve concepts expressed with words
C) involve population parameters while the statistical hypothesis involves sample parameters
D) can be tested while the statistical hypothesis cannot be

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A researcher states a null hypothesis (H0) that μ = 25. Which of the following is the most likely source of this particular value for?
A) her personal beliefs
B) her review of the research literature
C) her own research
D) her intuition
A) her personal beliefs
B) her review of the research literature
C) her own research
D) her intuition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following beliefs is the BEST example of an alternative hypothesis (H1)?
A) "Boys and girls are equally likely to become obese as they age."
B) "Pepsi and Coke taste the same."
C) "Taking steroids help baseball players hit more home runs."
D) "Drugs such as Viagra do not improve the relationship between married couples."
A) "Boys and girls are equally likely to become obese as they age."
B) "Pepsi and Coke taste the same."
C) "Taking steroids help baseball players hit more home runs."
D) "Drugs such as Viagra do not improve the relationship between married couples."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following beliefs is the BEST example of a null hypothesis (H0)?
A) "Test prep courses such as Kaplan and the Princeton Review raise students' SAT scores."
B) "Women are more considerate than men."
C) "The higher the price of gas, the more people will consider buying a hybrid car."
D) "All politicians are the same."
A) "Test prep courses such as Kaplan and the Princeton Review raise students' SAT scores."
B) "Women are more considerate than men."
C) "The higher the price of gas, the more people will consider buying a hybrid car."
D) "All politicians are the same."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following beliefs is the BEST example of an alternative hypothesis (H1)?
A) "Caffeine doesn't affect my ability to fall asleep."
B) "Girls are just as good at sports as are boys."
C) "I'm more likely to buy a product if it's endorsed by my favorite actor."
D) "It doesn't matter what college I go to."
A) "Caffeine doesn't affect my ability to fall asleep."
B) "Girls are just as good at sports as are boys."
C) "I'm more likely to buy a product if it's endorsed by my favorite actor."
D) "It doesn't matter what college I go to."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is a correctly stated alternative hypothesis?
A) H1: μ ≠ 3
B) H1: μ = 3
C) H0: μ = 3
D) H1: μ > 3
A) H1: μ ≠ 3
B) H1: μ = 3
C) H0: μ = 3
D) H1: μ > 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The process of hypothesis testing starts with the assumption that ______.
A) the null hypothesis is yet to be defined
B) the null hypothesis is true
C) the alternative hypothesis is true unless the data proves otherwise
D) the research hypothesis is true
A) the null hypothesis is yet to be defined
B) the null hypothesis is true
C) the alternative hypothesis is true unless the data proves otherwise
D) the research hypothesis is true

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The statement ______ is an example of a ______.
A) μ ≠ 5; non-directional alternative hypothesis
B) μ = 5; directional alternative hypothesis
C) μ ≠ 5; null hypothesis
D) μ = 5; directional research hypothesis
A) μ ≠ 5; non-directional alternative hypothesis
B) μ = 5; directional alternative hypothesis
C) μ ≠ 5; null hypothesis
D) μ = 5; directional research hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A statistical hypothesis that contains the ______ symbol may be defined as ______.
A) <; two-tailed
B) >; non-directional
C) ≠; two-tailed
D) ≠; directional
A) <; two-tailed
B) >; non-directional
C) ≠; two-tailed
D) ≠; directional

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The statement " > 8" is an example of a ______.
A) directional null hypothesis
B) non-directional null hypothesis
C) directional alternative hypothesis
D) non-directional alternative hypothesis
A) directional null hypothesis
B) non-directional null hypothesis
C) directional alternative hypothesis
D) non-directional alternative hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The "not equals" sign (≠) can be found in which of the following hypotheses?
A) research hypothesis
B) null hypothesis
C) alternative hypothesis
D) all of these
A) research hypothesis
B) null hypothesis
C) alternative hypothesis
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
______ refers to the probability of a statistic needed to reject the null hypothesis.
A) ∞
B) μ
C) σ
D) α
A) ∞
B) μ
C) σ
D) α

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
______ separates the regions of rejection and non-rejection.
A) The alternative hypothesis
B) The population mean (μ)
C) A critical value
D) The median
A) The alternative hypothesis
B) The population mean (μ)
C) A critical value
D) The median

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Drawing distributions and shading in certain areas of the distribution corresponds MOST directly to ______.
A) stating the null hypothesis
B) the difference between statistics (such as s) and parameters (such as σ)
C) the effect of sample size on α
D) the concept of a 'critical value'
A) stating the null hypothesis
B) the difference between statistics (such as s) and parameters (such as σ)
C) the effect of sample size on α
D) the concept of a 'critical value'

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In this figure, the unshaded area represents ______. 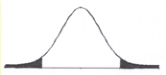
A) values of the statistic whose combined probability is less than 5%
B) the region of rejection
C) the region of non-rejection
D) alpha

A) values of the statistic whose combined probability is less than 5%
B) the region of rejection
C) the region of non-rejection
D) alpha

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In this figure, if the value of a calculated statistic falls in the ______ , you will ______. 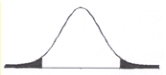
A) unshaded area; reject the null hypothesis
B) shaded area; reject the alternative hypothesis
C) shaded area; not reject the null hypothesis
D) unshaded area; not reject the null hypothesis

A) unshaded area; reject the null hypothesis
B) shaded area; reject the alternative hypothesis
C) shaded area; not reject the null hypothesis
D) unshaded area; not reject the null hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
______ is the value of a statistic that separates the regions of rejection and non-rejection.
A) The null hypothesis (H0)
B) A critical value
C) Alpha
D) A population parameter such as μ
A) The null hypothesis (H0)
B) A critical value
C) Alpha
D) A population parameter such as μ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
"The probability of a statistic needed to reject the null hypothesis" is represented by ______.
A) t
B) z
C) α
D)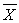
A) t
B) z
C) α
D)
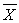

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The term "critical value" refers most specifically to ______.
A) how researchers define a 'low' probability
B) the value of a statistic needed to reject the null hypothesis
C) the minimum sample size needed to test a research hypothesis
D) the value of a population parameter such as µ
A) how researchers define a 'low' probability
B) the value of a statistic needed to reject the null hypothesis
C) the minimum sample size needed to test a research hypothesis
D) the value of a population parameter such as µ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The term "critical value" is used to define ______.
A) the minimum value of a statistic needed to reject the null hypothesis
B) the likelihood of rejecting the null hypothesis
C) the level of significance of a statistic
D) the probability of a statistic needed to reject the null hypothesis
A) the minimum value of a statistic needed to reject the null hypothesis
B) the likelihood of rejecting the null hypothesis
C) the level of significance of a statistic
D) the probability of a statistic needed to reject the null hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
α refers to ______.
A) the probability of accepting the null hypothesis
B) the probability of a statistic needed to reject the null hypothesis
C) the minimum value of a statistic needed to reject the null hypothesis
D) an example of a population parameter
A) the probability of accepting the null hypothesis
B) the probability of a statistic needed to reject the null hypothesis
C) the minimum value of a statistic needed to reject the null hypothesis
D) an example of a population parameter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A smaller alpha value indicates ______.
A) a higher likelihood of rejecting the null hypothesis
B) a lower likelihood of rejecting the null hypothesis
C) a lower likelihood of retaining the null hypothesis
D) a higher likelihood of retaining the alternative hypothesis
A) a higher likelihood of rejecting the null hypothesis
B) a lower likelihood of rejecting the null hypothesis
C) a lower likelihood of retaining the null hypothesis
D) a higher likelihood of retaining the alternative hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
α refers to ______.
A) the probability of accepting the null hypothesis
B) an example of a population parameter
C) the critical value of a statistic
D) the probability of a statistic needed to reject the null hypothesis
A) the probability of accepting the null hypothesis
B) an example of a population parameter
C) the critical value of a statistic
D) the probability of a statistic needed to reject the null hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
______ hypotheses ______.
A) Statistical; are stated when you analyze your data
B) Research; involve mathematical symbols
C) Statistical; are stated at the beginning of a research study
D) Research; are the null and alternative hypotheses
A) Statistical; are stated when you analyze your data
B) Research; involve mathematical symbols
C) Statistical; are stated at the beginning of a research study
D) Research; are the null and alternative hypotheses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
α refers to ______.
A) a statistical hypothesis
B) a population parameter
C) a critical value of a statistic
D) the probability of a statistic
A) a statistical hypothesis
B) a population parameter
C) a critical value of a statistic
D) the probability of a statistic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A 'critical value' is ______.
A) a rule
B) a probability
C) a hypothesis
D) a value of a statistic
A) a rule
B) a probability
C) a hypothesis
D) a value of a statistic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
______ hypotheses ______.
A) Research; are stated when you analyze your data
B) Statistical; are stated using concepts and variables
C) Research; are stated at the beginning of a research study
D) Research; are the null and alternative hypotheses
A) Research; are stated when you analyze your data
B) Statistical; are stated using concepts and variables
C) Research; are stated at the beginning of a research study
D) Research; are the null and alternative hypotheses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
α refers to ______.
A) the region of non-acceptance
B) the difference between a statistic (such as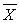 ) and a population parameter (such as μ)
) and a population parameter (such as μ)
C) the probability of a statistic needed to reject the null hypothesis
D) the likelihood of proving your research hypothesis is false
A) the region of non-acceptance
B) the difference between a statistic (such as
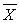 ) and a population parameter (such as μ)
) and a population parameter (such as μ)C) the probability of a statistic needed to reject the null hypothesis
D) the likelihood of proving your research hypothesis is false

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In this figure, the shaded areas represent ______. 
A) values of the statistic with a high probability of occurring
B) the region of rejection
C) the region of non-rejection
D) the null hypothesis

A) values of the statistic with a high probability of occurring
B) the region of rejection
C) the region of non-rejection
D) the null hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A 'critical value' ______.
A) is the same as α
B) is a population parameter
C) relates to the decision to reject the research hypothesis
D) separates the regions of rejection and non-rejection
A) is the same as α
B) is a population parameter
C) relates to the decision to reject the research hypothesis
D) separates the regions of rejection and non-rejection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The difference between the regions of rejection and non-rejection refers most directly to the concept of ______.
A) critical values
B) null hypotheses and research hypotheses
C) the difference between the standard deviation and the standard error of the mean
D) the difference between statistics and parameters
A) critical values
B) null hypotheses and research hypotheses
C) the difference between the standard deviation and the standard error of the mean
D) the difference between statistics and parameters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



