Deck 2: Examining Data: Tables and Figures
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/125
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Examining Data: Tables and Figures
1
Which of these is a reason why researchers examine data by creating tables and figures?
A) to test their research hypotheses
B) to define their population
C) to figure out which variable is the independent variable
D) to understand the shape of the distribution
A) to test their research hypotheses
B) to define their population
C) to figure out which variable is the independent variable
D) to understand the shape of the distribution
to understand the shape of the distribution
2
A researcher conducts a study on police effectiveness in reducing loitering. The respondents are asked to select from the answer choices "NOT effective, effective, or very effective." Which type of figure is most appropriate to illustrate the responses to the question?
A) pie chart
B) bar chart
C) histogram
D) frequency polygon
A) pie chart
B) bar chart
C) histogram
D) frequency polygon
bar chart
3
You would use a ______ to illustrate data for the variable "Age in years" while a ______ would be used to illustrate "15 to 24; 25 to 34; 35 to 44; etc."
A) frequency polygon; pie chart
B) histogram; pie chart
C) histogram; bar chart
D) frequency polygon; bar chart
A) frequency polygon; pie chart
B) histogram; pie chart
C) histogram; bar chart
D) frequency polygon; bar chart
histogram; bar chart
4
You would use a ______ to illustrate data for the variable "Number of cars per driver."
A) bar chart
B) histogram
C) frequency polygon
D) pie chart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of these is a reason why researchers examine data by creating tables and figures?
A) to calculate inferential statistics
B) to defend their research hypotheses
C) to gain an initial understanding of their data
D) to identify their independent and dependent variables
A) to calculate inferential statistics
B) to defend their research hypotheses
C) to gain an initial understanding of their data
D) to identify their independent and dependent variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
On the first day of class, students are asked to describe their plans after college (grad school, work, etc.); a ______ would be used to illustrate their responses to this question.
A) frequency polygon
B) normal distribution
C) histogram
D) bar chart
A) frequency polygon
B) normal distribution
C) histogram
D) bar chart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of these is a reason why researchers examine the data they have collected?
A) to detect outliers
B) to calculate measures of central tendency and variability
C) to test their research hypotheses
D) to draw inferences about populations
A) to detect outliers
B) to calculate measures of central tendency and variability
C) to test their research hypotheses
D) to draw inferences about populations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is a reason why researchers examine the data they have collected?
A) to calculate measures of central tendency and variability
B) to detect coding or data entry errors
C) to test their research hypotheses
D) to draw inferences about populations.
A) to calculate measures of central tendency and variability
B) to detect coding or data entry errors
C) to test their research hypotheses
D) to draw inferences about populations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of these is a reason why researchers examine data by creating tables and figures?
A) to prove a research hypothesis
B) to determine whether the population is skewed
C) to identify the modality of a distribution
D) to decide whether a variable is measured at the interval or ratio scale
A) to prove a research hypothesis
B) to determine whether the population is skewed
C) to identify the modality of a distribution
D) to decide whether a variable is measured at the interval or ratio scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
You would use a ______ to illustrate data for the variable "Number of siblings."
A) bar chart
B) histogram
C) frequency polygon
D) pie chart
A) bar chart
B) histogram
C) frequency polygon
D) pie chart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
______ are rare, extreme scores that lie outside of the range of the majority of scores in a set of data.
A) Distributions
B) Outliers
C) Data point
D) Data errors
A) Distributions
B) Outliers
C) Data point
D) Data errors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of these is a reason why researchers examine data by creating tables and figures?
A) to prove their research hypotheses
B) to define their independent and dependent variables
C) to detect outliers
D) to draw conclusions about populations
A) to prove their research hypotheses
B) to define their independent and dependent variables
C) to detect outliers
D) to draw conclusions about populations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of these is NOT a reason why researchers examine data they have collected?
A) to evaluate their research methodology
B) to assess the shape of the distribution of scores
C) to draw inferences about populations
D) to detect outliers
A) to evaluate their research methodology
B) to assess the shape of the distribution of scores
C) to draw inferences about populations
D) to detect outliers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is a reason why researchers examine the data before conducting statistical analyses on the data?
A) to draw inferences about the sample
B) to test the null hypothesis
C) to determine whether the data meet statistical criteria and assumptions
D) to make comparisons between the sample and population
A) to draw inferences about the sample
B) to test the null hypothesis
C) to determine whether the data meet statistical criteria and assumptions
D) to make comparisons between the sample and population

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
You would use a ______ to illustrate data for the variable "Cost per vehicle."
A) pie graph
B) bar chart
C) histogram
D) bar chart.
A) pie graph
B) bar chart
C) histogram
D) bar chart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
You would use a ______ to illustrate data for a variable measured at the ______ scale of measurement.
A) histogram; interval
B) frequency polygon; ordinal
C) pie graph; ratio
D) bar chart; ratio
A) histogram; interval
B) frequency polygon; ordinal
C) pie graph; ratio
D) bar chart; ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of these is NOT a reason why researchers examine data they have collected?
A) to evaluate their research methodology
B) to assess the shape of the distribution of scores
C) to detect outliers
D) to prove their research hypotheses
A) to evaluate their research methodology
B) to assess the shape of the distribution of scores
C) to detect outliers
D) to prove their research hypotheses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
You ask people to indicate the number of television sets in their residence (home, apartment, etc.). You would use a ______ to illustrate the data for this variable.
A) frequency polygon
B) histogram
C) bar chart
D) pie chart
A) frequency polygon
B) histogram
C) bar chart
D) pie chart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
You would use a ______ to illustrate data for a variable measured at the ______ scale of measurement.
A) pie graph; interval
B) frequency polygon; nominal
C) histogram; ordinal
D) bar chart; nominal
A) pie graph; interval
B) frequency polygon; nominal
C) histogram; ordinal
D) bar chart; nominal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
For a variable measured at the ______ scale of measurement, one would use a ______ to illustrate the data.
A) interval; pie graph
B) ratio; frequency polygon
C) nominal; histogram
D) ratio; bar chart
A) interval; pie graph
B) ratio; frequency polygon
C) nominal; histogram
D) ratio; bar chart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An instructor conducts a survey on the students to determine their religious preference. The data is measured at the ______ scale of measurement and therefore the instructor would use a ______ to illustrate the data.
A) nominal; pie graph
B) nominal; histogram
C) ordinal; bar chart
D) interval; pie graph
A) nominal; pie graph
B) nominal; histogram
C) ordinal; bar chart
D) interval; pie graph

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, ______ of the students predicted Candidate C will win the election; this represents ______ of the sample. 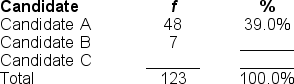
A) 68; .55%
B) 68; 55.3%
C) 75; 61.0%
D) Cannot be determined with information provided
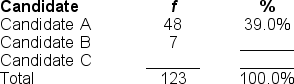
A) 68; .55%
B) 68; 55.3%
C) 75; 61.0%
D) Cannot be determined with information provided

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, ______ of the sample are married; this represents ______ of the sample. 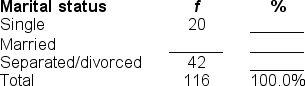
A) 54; 46.6%
B) 62; 53.8%
C) 116; 63.8%
D) 54; 63.8%
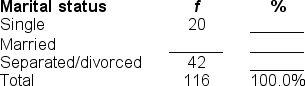
A) 54; 46.6%
B) 62; 53.8%
C) 116; 63.8%
D) 54; 63.8%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, ______ of this sample live in the 925 area code; this represents ______ of the sample. 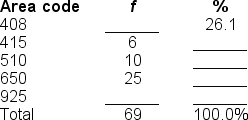
A) 10; .15%
B) 15; 10.0%
C) 10; 14.5%
D) Cannot be determined with information provided

A) 10; .15%
B) 15; 10.0%
C) 10; 14.5%
D) Cannot be determined with information provided

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
You would use a ______ to illustrate data for the 'Employment status' variable because it's measured at the ______ scale of measurement. 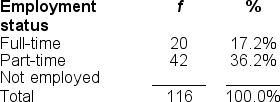
A) pie graph; ratio
B) frequency polygon; nominal
C) histogram; ordinal
D) bar chart; nominal
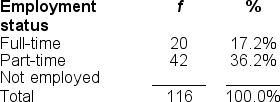
A) pie graph; ratio
B) frequency polygon; nominal
C) histogram; ordinal
D) bar chart; nominal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
You would use a ______ to illustrate the data in this frequency distribution table. 
A) pie graph
B) bar chart
C) histogram
D) frequency polygon

A) pie graph
B) bar chart
C) histogram
D) frequency polygon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
An instructor determines the number of students looking at Facebook or Twitter pages during five of her lectures. She would use a ______ to illustrate this data because this variable is measured at the ______ scale of measurement.
A) pie graph; interval
B) frequency polygon; nominal
C) histogram; ratio
D) bar chart; ordinal
A) pie graph; interval
B) frequency polygon; nominal
C) histogram; ratio
D) bar chart; ordinal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
You would use a ______ to illustrate the data in this frequency distribution table. 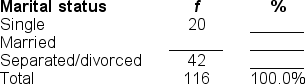
A) pie graph
B) frequency polygon
C) histogram
D) bar chart
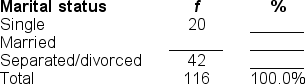
A) pie graph
B) frequency polygon
C) histogram
D) bar chart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
You would use a ______ to illustrate the data in this frequency distribution table. 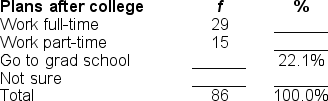
A) frequency polygon
B) bar chart
C) histogram
D) none of these is correct
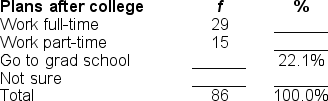
A) frequency polygon
B) bar chart
C) histogram
D) none of these is correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, ______ of this sample believed 9 or more drinks defined 'binge drinking'; this represents ______ of the sample. 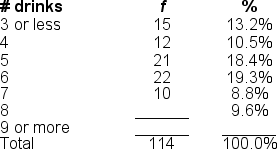
A) 35; 10.5%
B) 23; 20.2%
C) 12; 30.7%
D) Cannot be determined with information provided

A) 35; 10.5%
B) 23; 20.2%
C) 12; 30.7%
D) Cannot be determined with information provided

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, ______ of this sample work 0-10 hours per week; this represents ______ of the sample. 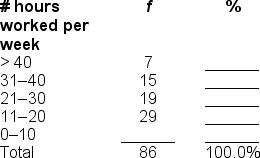
A) 16; .19%
B) 70; 81.8%
C) 16; 18.6%
D) Cannot be determined with information provided
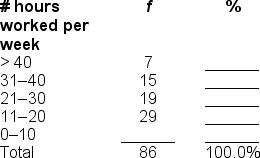
A) 16; .19%
B) 70; 81.8%
C) 16; 18.6%
D) Cannot be determined with information provided

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
You would use either a ______ to illustrate the data in this frequency distribution table. 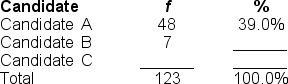
A) pie graph or frequency polygon
B) bar chart or pie graph
C) histogram or frequency polygon
D) bar chart or histogram
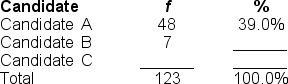
A) pie graph or frequency polygon
B) bar chart or pie graph
C) histogram or frequency polygon
D) bar chart or histogram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, ______ of the students had SAT Math scores between 200 and 400; this represents ______ of the class. 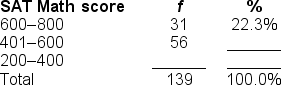
A) 37; 40.3%
B) 52; 37.4%
C) 52; .37%
D) Cannot be determined with information provided
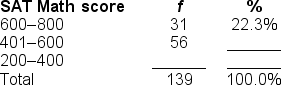
A) 37; 40.3%
B) 52; 37.4%
C) 52; .37%
D) Cannot be determined with information provided

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
You would use a ______ to illustrate the data in this frequency distribution table. 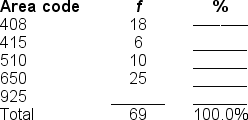
A) pie graph or frequency polygon
B) bar chart or histogram
C) histogram or frequency polygon
D) bar chart or pie graph

A) pie graph or frequency polygon
B) bar chart or histogram
C) histogram or frequency polygon
D) bar chart or pie graph

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
You would use a ______ to illustrate the data in this frequency distribution table. 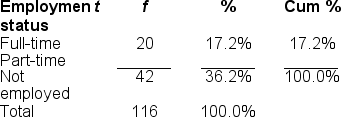
A) pie graph
B) frequency polygon
C) histogram
D) bar chart
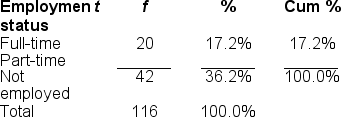
A) pie graph
B) frequency polygon
C) histogram
D) bar chart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, ______ of this sample are 'NOT sure' of their plans after finishing college; this represents ______ of the sample. 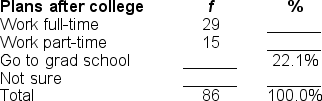
A) 20; 23.2%
B) 23; 26.8%
C) 42; 48.8%
D) Cannot be determined with information provided
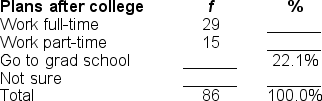
A) 20; 23.2%
B) 23; 26.8%
C) 42; 48.8%
D) Cannot be determined with information provided

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table,______ of the sample work part-time; this represents ______ of the sample. 
A) 54; 63.8%
B) 62; 53.8%
C) 116; 63.8%
D) 54; 46.6%

A) 54; 63.8%
B) 62; 53.8%
C) 116; 63.8%
D) 54; 46.6%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, ______ of this sample are NOT employed; this represents ______ of the sample. 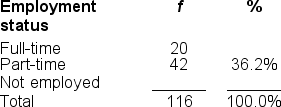
A) 54; 63.8%
B) 62; 53.8%
C) 54; 46.6%
D) 116; 63.8%
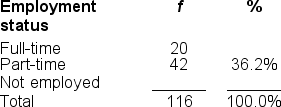
A) 54; 63.8%
B) 62; 53.8%
C) 54; 46.6%
D) 116; 63.8%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
You would use either a ______ to illustrate the data in this frequency distribution table. 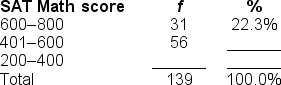
A) pie graph or frequency polygon
B) bar chart or pie graph
C) histogram or frequency polygon
D) bar chart or histogram
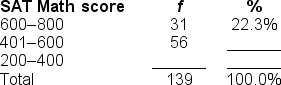
A) pie graph or frequency polygon
B) bar chart or pie graph
C) histogram or frequency polygon
D) bar chart or histogram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
You would use a ______ to illustrate the data in this frequency distribution table. 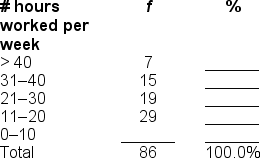
A) pie graph
B) bar chart
C) histogram
D) frequency polygon
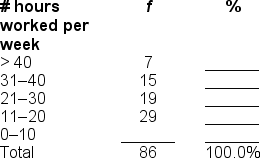
A) pie graph
B) bar chart
C) histogram
D) frequency polygon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, ______ of this sample preferred 'Yellow'; this represents ______ of the sample. 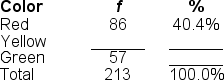
A) 70; 32.9%
B) 70; 59.6%
C) 143; 67.1%
D) 213; 32.9%
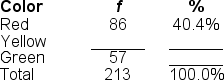
A) 70; 32.9%
B) 70; 59.6%
C) 143; 67.1%
D) 213; 32.9%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
You would use a ______ to illustrate the data in this frequency distribution table because the variable is measured at the ______ level of measurement 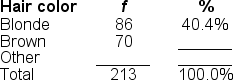
A) frequency polygon; ordinal
B) bar chart; nominal
C) histogram; interval
D) pie graph; ratio
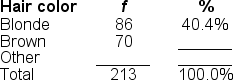
A) frequency polygon; ordinal
B) bar chart; nominal
C) histogram; interval
D) pie graph; ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, ______ of this sample owned 1 phone; this represents ______ of the sample. 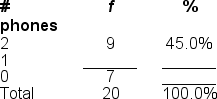
A) 4; 20.0%
B) 4; 55.0%
C) 16; 80.0%
D) 20; 20.0%
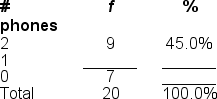
A) 4; 20.0%
B) 4; 55.0%
C) 16; 80.0%
D) 20; 20.0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, ______ of this sample took physics; on the other hand, ______took chemistry. 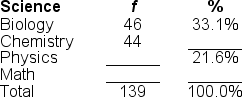
A) 49; 53.2%
B) 49; 35.3%
C) 30; 31.7%
D) 30; 45.3%
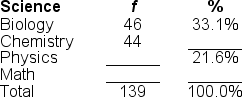
A) 49; 53.2%
B) 49; 35.3%
C) 30; 31.7%
D) 30; 45.3%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
You would use a ______ to illustrate the data in this frequency distribution table because the variable is measured at the ______ level of measurement 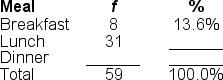
A) frequency polygon; ordinal
B) bar chart; nominal
C) histogram; interval
D) pie graph; ratio
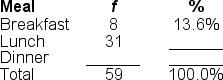
A) frequency polygon; ordinal
B) bar chart; nominal
C) histogram; interval
D) pie graph; ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, ______ of this sample selected 'Lunch'; this represents ______ of the sample. 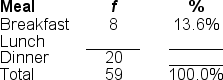
A) 31; 52.5%
B) 31; 86.4%
C) 28; 47.5%
D) 59; 52.5%
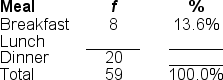
A) 31; 52.5%
B) 31; 86.4%
C) 28; 47.5%
D) 59; 52.5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, ______ of this sample took a math class; this represents ______ of the sample. 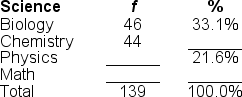
A) 19; 13.7%
B) 19; 45.3%
C) 49; 35.3%
D) 49; 13.7%
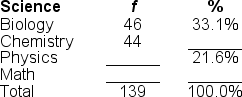
A) 19; 13.7%
B) 19; 45.3%
C) 49; 35.3%
D) 49; 13.7%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, ______ of this sample owned 0 phones; this represents ______ of the sample. 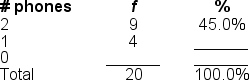
A) 7; 35.0%
B) 7; 55.0%
C) 13; 20.0%
D) 20; 35.0%
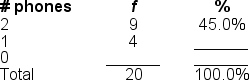
A) 7; 35.0%
B) 7; 55.0%
C) 13; 20.0%
D) 20; 35.0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, ______ of this sample had 'other' hair color; this represents ______ of the sample. 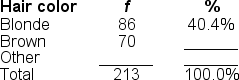
A) 57; 26.8%
B) 57; 59.6%
C) 156; 32.9%
D) 213; 26.8%
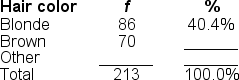
A) 57; 26.8%
B) 57; 59.6%
C) 156; 32.9%
D) 213; 26.8%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
You would use a ______ to illustrate the data in this frequency distribution table because the variable is measured at the ______ level of measurement 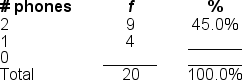
A) frequency polygon; nominal
B) bar chart; interval
C) histogram; ratio
D) pie graph; ordinal
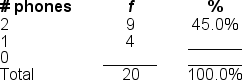
A) frequency polygon; nominal
B) bar chart; interval
C) histogram; ratio
D) pie graph; ordinal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
You would use a ______ to illustrate the data in this frequency distribution table because the variable is measured at the ______ level of measurement 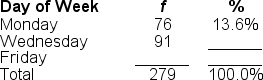
A) frequency polygon; ordinal
B) bar chart; nominal
C) histogram; interval
D) pie graph; ratio
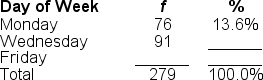
A) frequency polygon; ordinal
B) bar chart; nominal
C) histogram; interval
D) pie graph; ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A table that groups the values of a variable measured at the interval or ratio level of measurement into a small number of intervals is known as a ______.
A) percent distribution table
B) grouped frequency distribution table
C) cumulative frequency distribution table
D) cumulative percent distribution table
A) percent distribution table
B) grouped frequency distribution table
C) cumulative frequency distribution table
D) cumulative percent distribution table

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Given the nature of this variable, you would use a ______ to illustrate the data for this variable. 
A) pie chart
B) normal distribution
C) bar chart
D) frequency polygon

A) pie chart
B) normal distribution
C) bar chart
D) frequency polygon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which level of measurement of data would be BEST suited to construct a grouped frequency distribution?
A) dichotomous
B) nominal
C) ordinal
D) interval
A) dichotomous
B) nominal
C) ordinal
D) interval

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
You would use a ______ to illustrate the data in this frequency distribution table because the variable is measured at the ______ level of measurement 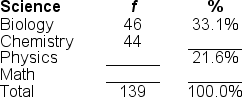
A) frequency polygon; ordinal
B) bar chart; nominal
C) histogram; interval
D) pie graph; ratio
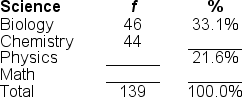
A) frequency polygon; ordinal
B) bar chart; nominal
C) histogram; interval
D) pie graph; ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, ______ of this sample selected 'Dinner'; this represents ______ of the sample. 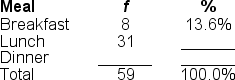
A) 20; 33.9%
B) 20; 86.4%
C) 39; 52.5%
D) 59; 33.9%
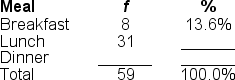
A) 20; 33.9%
B) 20; 86.4%
C) 39; 52.5%
D) 59; 33.9%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, ______ of this sample had 0 jobs; this represents ______ of the sample. 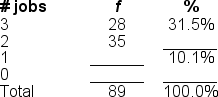
A) 17; 19.1%
B) 17; 58.4%
C) 26; 29.2%
D) 26; 19.1%

A) 17; 19.1%
B) 17; 58.4%
C) 26; 29.2%
D) 26; 19.1%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Grouped frequency distribution tables are created to summarize data for variables measured at the ______ level of measurement.
A) nominal or interval
B) nominal or ordinal
C) ordinal or ratio
D) interval or ratio
A) nominal or interval
B) nominal or ordinal
C) ordinal or ratio
D) interval or ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, ______ of this sample had 1 job; on the other hand, ______had 2 jobs. 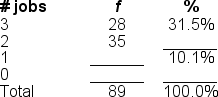
A) 9; 39.3%
B) 9; 58.4%
C) 26; 49.4%
D) 26; 29.2%

A) 9; 39.3%
B) 9; 58.4%
C) 26; 49.4%
D) 26; 29.2%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
You would use a ______ to illustrate the data in this frequency distribution table because the variable is measured at the ______ level of measurement 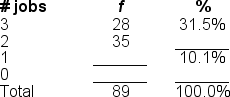
A) frequency polygon; nominal
B) bar chart; interval
C) histogram; ratio
D) pie graph; ordinal
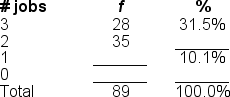
A) frequency polygon; nominal
B) bar chart; interval
C) histogram; ratio
D) pie graph; ordinal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, the percentage ('%') for 2 arrests is ______; the cumulative percent ('Cum %') associated with 2 arrests is ______. 
A) 17.5%; 87.5%
B) 70.0%; 20.0%
C) 20.0%; 70.0%
D) 87.5%; 17.5%

A) 17.5%; 87.5%
B) 70.0%; 20.0%
C) 20.0%; 70.0%
D) 87.5%; 17.5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, the cumulative percent ('Cum %') associated with a B grade is ______. 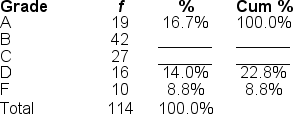
A) 46.5%
B) 36.8%
C) 60.5%
D) 83.3%

A) 46.5%
B) 36.8%
C) 60.5%
D) 83.3%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, the percentage ('%') for 10th grade is ______; the cumulative percent ('Cum %') associated with 10th grade is ______. 
A) 15.8%; 78.9%
B) 18.4%; 78.9%
C) 34.2%; 94.7%
D) 78.9%; 18.4%

A) 15.8%; 78.9%
B) 18.4%; 78.9%
C) 34.2%; 94.7%
D) 78.9%; 18.4%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following is TRUE statement regarding intervals in a grouped frequency distribution table?
A) The intervals should be of equal size.
B) The intervals should overlap.
C) Many of the intervals should have a frequency of zero.
D) All of the intervals should have the same frequencies.
A) The intervals should be of equal size.
B) The intervals should overlap.
C) Many of the intervals should have a frequency of zero.
D) All of the intervals should have the same frequencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
For which of these variables would you create a grouped frequency distribution table to summarize data you've collected?
A) number of calories
B) type of salad dressing
C) favorite restaurant
D) day of week
A) number of calories
B) type of salad dressing
C) favorite restaurant
D) day of week

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The intervals created for a grouped frequency distribution table should represent the nature of the data as ______ as possible.
A) redundantly
B) accurately
C) arbitrarily
D) simplistically
A) redundantly
B) accurately
C) arbitrarily
D) simplistically

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The smallest values of a variable that would be grouped into a particular interval are ______.
A) real limits
B) real lower limits
C) real upper limits
D) grouped frequency distribution
A) real limits
B) real lower limits
C) real upper limits
D) grouped frequency distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, the cumulative percent ('Cum %') associated with 11th grade is ______. 
A) 15.8%
B) 34.2%
C) 78.9%
D) 94.7%

A) 15.8%
B) 34.2%
C) 78.9%
D) 94.7%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The largest values of a variable that would be grouped into a particular interval are ______.
A) real limits
B) real lower limits
C) real upper limits
D) grouped frequency distribution
A) real limits
B) real lower limits
C) real upper limits
D) grouped frequency distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
For which of these variables would you create a grouped frequency distribution table to summarize data you've collected?
A) type of music
B) quality of video
C) number of downloads
D) favorite singer
A) type of music
B) quality of video
C) number of downloads
D) favorite singer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
For which of these variables would you create a grouped frequency distribution table to summarize data you've collected?
A) type of automobile
B) miles per gallon
C) color of automobile
D) type of gasoline
A) type of automobile
B) miles per gallon
C) color of automobile
D) type of gasoline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Real limits are ______.
A) the values of a variable that fall halfway between the top of one interval and the bottom of the next interval
B) the smallest value of a variable that would be grouped into a particular interval
C) the largest value of a variable that would be grouped into a particular interval
D) a small number of intervals that provide the frequencies within each interval
A) the values of a variable that fall halfway between the top of one interval and the bottom of the next interval
B) the smallest value of a variable that would be grouped into a particular interval
C) the largest value of a variable that would be grouped into a particular interval
D) a small number of intervals that provide the frequencies within each interval

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
For which of these variables would you create a grouped frequency distribution table to summarize data you've collected?
A) college major
B) year in school
C) type of housing
D) distance from campus (miles)
A) college major
B) year in school
C) type of housing
D) distance from campus (miles)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When creating a grouped frequency distribution table, the number of intervals depends on ______.
A) the size of the population
B) the difference between the sample and the population
C) the distribution of data in the sample
D) arbitrary cutpoints
A) the size of the population
B) the difference between the sample and the population
C) the distribution of data in the sample
D) arbitrary cutpoints

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Real upper limits are ______.
A) the values of a variable that fall halfway between the top of one interval and the bottom of the next interval
B) the smallest value of a variable that would be grouped into a particular level
C) the largest value of a variable that would be grouped into a particular interval
D) a small number of intervals that provide the frequencies within each interval
A) the values of a variable that fall halfway between the top of one interval and the bottom of the next interval
B) the smallest value of a variable that would be grouped into a particular level
C) the largest value of a variable that would be grouped into a particular interval
D) a small number of intervals that provide the frequencies within each interval

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Real lower limits are ______.
A) the values of a variable that fall halfway between the top of one interval and the bottom of the next interval
B) the smallest value of a variable that would be grouped into a particular level
C) the largest value of a variable that would be grouped into a particular interval
D) a small number of intervals that provide the frequencies within each interval
A) the values of a variable that fall halfway between the top of one interval and the bottom of the next interval
B) the smallest value of a variable that would be grouped into a particular level
C) the largest value of a variable that would be grouped into a particular interval
D) a small number of intervals that provide the frequencies within each interval

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following is NOT a guideline for creating grouped frequency distribution tables?
A) The number of intervals should accurately represent the data.
B) Intervals should be of equal size.
C) Intervals should not overlap.
D) The data are grouped into arbitrary intervals.
A) The number of intervals should accurately represent the data.
B) Intervals should be of equal size.
C) Intervals should not overlap.
D) The data are grouped into arbitrary intervals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, the cumulative percent ('Cum %') associated with 3 victimization is ______. 
A) 17.5%
B) 20.0%
C) 50.0%
D) 87.5%

A) 17.5%
B) 20.0%
C) 50.0%
D) 87.5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, the percentage ('%') for 2 arrests is ______; the cumulative percent ('Cum %') associated with 2 arrests is ______. 
A) 5.0%; 90.0%
B) 15.0%; 90.0%
C) 20.0%; 95.0%
D) 90.0%; 15.0%

A) 5.0%; 90.0%
B) 15.0%; 90.0%
C) 20.0%; 95.0%
D) 90.0%; 15.0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Filling in the blanks in this frequency distribution table, the cumulative percent ('Cum %') associated with 3 arrests is ______. 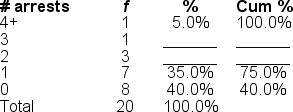
A) 5.0%
B) 20.0%
C) 90.0%
D) 95.0%
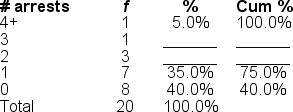
A) 5.0%
B) 20.0%
C) 90.0%
D) 95.0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



