Deck 22: The Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/82
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: The Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
1
Which of the following is the general formula for an alkali metal hydride? (M = metal)
A) MH
B) M(OH)2
C) MH2
D) MH3
E) MOH
A) MH
B) M(OH)2
C) MH2
D) MH3
E) MOH
MH
2
Which two elements are most abundant in our solar system?
A) hydrogen and helium
B) hydrogen and oxygen
C) helium and iron
D) hydrogen and iron
E) carbon and oxygen
A) hydrogen and helium
B) hydrogen and oxygen
C) helium and iron
D) hydrogen and iron
E) carbon and oxygen
hydrogen and helium
3
What is the oxidation state of the common ion formed from Na?
A) 1+
B) 2+
C) 3−
D) 2−
E) 1−
A) 1+
B) 2+
C) 3−
D) 2−
E) 1−
1−
4
What is the formula of the common oxide formed from Group 5A elements? (E = main group element)
A) EO
B) EO2
C) EO3
D) E4O10
E) E2O7
A) EO
B) EO2
C) EO3
D) E4O10
E) E2O7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Approximately 300 billion liters of hydrogen is produced annually.The majority of the hydrogen is used in the production of ____.
A) ammonia
B) hydrogen chloride
C) methane
D) sulfuric acid
E) water
A) ammonia
B) hydrogen chloride
C) methane
D) sulfuric acid
E) water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the highest oxidation state possible for elements from Group 5A?
A) 2+
B) 4+
C) 5+
D) 6+
E) 7+
A) 2+
B) 4+
C) 5+
D) 6+
E) 7+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is the second most abundant (by mass)element in the earth's crust,oceans,and atmosphere?
A) hydrogen
B) oxygen
C) carbon
D) aluminum
E) silicon
A) hydrogen
B) oxygen
C) carbon
D) aluminum
E) silicon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Metal hydrides are used to remove traces of water from nonpolar solvents.Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction of lithium hydride and water.
A) LiH2(s)+ 2 H2O(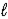 )→ Li(s)+ 2 H3O+(aq)
)→ Li(s)+ 2 H3O+(aq)
B) 2 LiH(s)+ 2 H2O(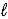 )→ 2 LiOH(s)+ H2(g)
)→ 2 LiOH(s)+ H2(g)
C) 2 LiH(s)+ H2O(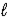 )→ Li2O(s)+ 2 H2(g)
)→ Li2O(s)+ 2 H2(g)
D) 2 LiH(s)+ H2O(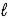 )→ Li2O(s)+ 4 H+(aq)
)→ Li2O(s)+ 4 H+(aq)
E) LiH(s)+ H2O(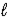 )→ Li(s)+ H3O+(aq)
)→ Li(s)+ H3O+(aq)
A) LiH2(s)+ 2 H2O(
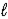 )→ Li(s)+ 2 H3O+(aq)
)→ Li(s)+ 2 H3O+(aq)B) 2 LiH(s)+ 2 H2O(
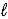 )→ 2 LiOH(s)+ H2(g)
)→ 2 LiOH(s)+ H2(g)C) 2 LiH(s)+ H2O(
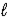 )→ Li2O(s)+ 2 H2(g)
)→ Li2O(s)+ 2 H2(g)D) 2 LiH(s)+ H2O(
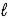 )→ Li2O(s)+ 4 H+(aq)
)→ Li2O(s)+ 4 H+(aq)E) LiH(s)+ H2O(
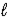 )→ Li(s)+ H3O+(aq)
)→ Li(s)+ H3O+(aq)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Use your knowledge of group properties to predict the chemical formula for selenic acid.
A) HSeO2
B) H2SeO3
C) H2SeO4
D) H3SeO3
E) H3SeO4
A) HSeO2
B) H2SeO3
C) H2SeO4
D) H3SeO3
E) H3SeO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following reactions does not represent a commercial method for the large-scale production of hydrogen gas?
A) CH4(g)+ H2O(g)→ CO(g)+ 3 H2(g)
B) C(s)+ H2O(g)→ CO(g)+ H2(g)
C) 2 H2O(l)→ 2 H2(g)+ O2(g)
D) CO(g)+ H2O(g)→ CO2(g)+ H2(g)
E) None of the above
A) CH4(g)+ H2O(g)→ CO(g)+ 3 H2(g)
B) C(s)+ H2O(g)→ CO(g)+ H2(g)
C) 2 H2O(l)→ 2 H2(g)+ O2(g)
D) CO(g)+ H2O(g)→ CO2(g)+ H2(g)
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The oxidation state per each nitrogen,given in parentheses,is correct in all the following cases except
A) HN3 (1).
B) N2O3 (-6).
C) HNO3 (5).
D) NH4+ (-3).
E) N2O (1).
A) HN3 (1).
B) N2O3 (-6).
C) HNO3 (5).
D) NH4+ (-3).
E) N2O (1).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following reactions describes the formation of a molecular compound of hydrogen?
A) 2K(s)+ H2(g)→ 2KH(s)
B) 2Na(s)+ H2(g)→ 2NaH(s)
C) Sr(s)+ H2(g)→ SrH2(s)
D) Si(s)+ 2H2(g)→ SiH(g)
E) 2Al(s)+ 3H2(g)→ 2AlH3(s)
A) 2K(s)+ H2(g)→ 2KH(s)
B) 2Na(s)+ H2(g)→ 2NaH(s)
C) Sr(s)+ H2(g)→ SrH2(s)
D) Si(s)+ 2H2(g)→ SiH(g)
E) 2Al(s)+ 3H2(g)→ 2AlH3(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is the most abundant metal on earth?
A) calcium
B) iron
C) copper
D) aluminum
E) zinc
A) calcium
B) iron
C) copper
D) aluminum
E) zinc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which list contains the three most abundant elements in the Earth's crust?
A) hydrogen,helium,and lithium
B) sodium,calcium,and iron
C) oxygen,nitrogen,and iron
D) carbon,nitrogen,and oxygen
E) oxygen,aluminum,and silicon
A) hydrogen,helium,and lithium
B) sodium,calcium,and iron
C) oxygen,nitrogen,and iron
D) carbon,nitrogen,and oxygen
E) oxygen,aluminum,and silicon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following compounds is a common oxide for phosphorus?
A) PO
B) P2O3
C) PO3
D) PO5
E) P4O10
A) PO
B) P2O3
C) PO3
D) PO5
E) P4O10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following chemical equations shows the production of synthesis gas?
A) 2 H2O(g)→ 2 H2(g)+ O2(g)
B) 16 CH4(g)+ 7 O2(g)→ 2 C8H18(g)+ 14 H2O(g)
C) C(s)+ 2 H2(g)→ CH4(g)
D) CO(g)+ H2O(g)→ CO2(g)+ H2(g)
E) C(s)+ H2O(g)→ H2(g)+ CO(g)
A) 2 H2O(g)→ 2 H2(g)+ O2(g)
B) 16 CH4(g)+ 7 O2(g)→ 2 C8H18(g)+ 14 H2O(g)
C) C(s)+ 2 H2(g)→ CH4(g)
D) CO(g)+ H2O(g)→ CO2(g)+ H2(g)
E) C(s)+ H2O(g)→ H2(g)+ CO(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Predict the formula of the product resulting from reaction of elemental forms of Mg and P.
A) MgP
B) MgP2
C) Mg2P
D) MgP3
E) Mg3P2
A) MgP
B) MgP2
C) Mg2P
D) MgP3
E) Mg3P2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the oxidation state of each nitrogen in dinitrogen oxide?
A) 4
B) 1
C) 0
D) 3
E) -3
A) 4
B) 1
C) 0
D) 3
E) -3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Catalytic steam reformation of hydrocarbons (such as methane)produce a mixture of
A) CO2 and H2O.
B) C and H2.
C) O2 and H2.
D) CH4 and H2O.
E) CO and H2.
A) CO2 and H2O.
B) C and H2.
C) O2 and H2.
D) CH4 and H2O.
E) CO and H2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is not a likely oxidation number for iodine?
A) −1
B) 0
C) +1
D) +2
E) +7
A) −1
B) 0
C) +1
D) +2
E) +7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What mass of CO2 would be produced by heating a 600.-kg sample of limestone that is 68.9% CaCO3? Assume complete reaction and no other source of carbon dioxide.
A) 182 kg
B) 413 kg
C) 264 kg
D) 30.3 kg
E) 600 kg
A) 182 kg
B) 413 kg
C) 264 kg
D) 30.3 kg
E) 600 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Aluminum is resistant to corrosion because:
A) its surface is coated with unreactive AlN.
B) its surface is coated with unreactive Al2O3.
C) it is a noble metal.
D) it has the greatest density of all naturally occurring metals.
E) it has a high positive standard reduction potential.
A) its surface is coated with unreactive AlN.
B) its surface is coated with unreactive Al2O3.
C) it is a noble metal.
D) it has the greatest density of all naturally occurring metals.
E) it has a high positive standard reduction potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which group 1A metal is the strongest reducing agent?
A) Li
B) Na
C) K
D) Rb
E) Cs
A) Li
B) Na
C) K
D) Rb
E) Cs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following calcium compounds is an important reactant in the commercial production of phosphoric acid?
A) Apatites
B) Fluorites
C) Limestone
D) Slaked lime
E) Gypsum
A) Apatites
B) Fluorites
C) Limestone
D) Slaked lime
E) Gypsum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following methods is used for the commercial production of sodium metal?
A) Electrolysis of molten Na2CO3
B) Electrolysis of NaCl(aq)
C) Electrolysis of molten NaCl using a Downs Cell
D) Reaction of potassium metal vapor with molten NaCl
E) Reduction of NaOH with carbon
A) Electrolysis of molten Na2CO3
B) Electrolysis of NaCl(aq)
C) Electrolysis of molten NaCl using a Downs Cell
D) Reaction of potassium metal vapor with molten NaCl
E) Reduction of NaOH with carbon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What mass of MgO would be produced by heating a 300.-kg sample that is 53.0% Mg(OH)2? Assume complete reaction and no other source of magnesium.
A) 111 kg
B) 237 kg
C) 2.73 kg
D) 434 kg
E) 207 kg
A) 111 kg
B) 237 kg
C) 2.73 kg
D) 434 kg
E) 207 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which one of the following elements would react with chlorine most rapidly?
A) Li
B) Na
C) K
D) Rb
E) Cs
A) Li
B) Na
C) K
D) Rb
E) Cs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is the general valence shell electron configuration of Group 3A elements?
A) [Noble Gas Core]ns1
B) [Noble Gas Core]ns2np1
C) [Noble Gas Core]ns2np3
D) [Noble Gas Core]ns2np2
E) [Noble Gas Core]ns2np4
A) [Noble Gas Core]ns1
B) [Noble Gas Core]ns2np1
C) [Noble Gas Core]ns2np3
D) [Noble Gas Core]ns2np2
E) [Noble Gas Core]ns2np4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Write a balanced chemical equation for the electrolysis of brine (salt water).
A) 2 NaCl(aq)+ 2 H2O(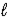 )→ 2 Na(s)+ 2 HCl(aq)+ O2(g)
)→ 2 Na(s)+ 2 HCl(aq)+ O2(g)
B) 2 NaCl(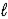 )→ 2 Na(
)→ 2 Na( 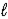 )+ Cl2(g)
)+ Cl2(g)
C) 2 NaCl(aq)+ O2(g)→ Na2O2(s)+ Cl2(g)
D) 4 NaCl(aq)+ O2(g)→ 4 Na(s)+ 2 OCl2(g)
E) 2 NaCl(aq)+ 2 H2O(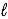 )→ Cl2(g)+ 2 NaOH(aq)+ H2(g)
)→ Cl2(g)+ 2 NaOH(aq)+ H2(g)
A) 2 NaCl(aq)+ 2 H2O(
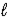 )→ 2 Na(s)+ 2 HCl(aq)+ O2(g)
)→ 2 Na(s)+ 2 HCl(aq)+ O2(g)B) 2 NaCl(
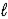 )→ 2 Na(
)→ 2 Na( 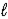 )+ Cl2(g)
)+ Cl2(g)C) 2 NaCl(aq)+ O2(g)→ Na2O2(s)+ Cl2(g)
D) 4 NaCl(aq)+ O2(g)→ 4 Na(s)+ 2 OCl2(g)
E) 2 NaCl(aq)+ 2 H2O(
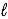 )→ Cl2(g)+ 2 NaOH(aq)+ H2(g)
)→ Cl2(g)+ 2 NaOH(aq)+ H2(g)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The primary source material for the commercial production of magnesium is
A) ores rich in MgCO3.
B) ores rich in MgCl2.
C) seashells.
D) seawater.
E) limestone.
A) ores rich in MgCO3.
B) ores rich in MgCl2.
C) seashells.
D) seawater.
E) limestone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following elements does not produce hydrogen gas when it reacts with water?
A) Na(s)
B) MgH2(s)
C) Ca(s)
D) LiH(s)
E) CaO(s)
A) Na(s)
B) MgH2(s)
C) Ca(s)
D) LiH(s)
E) CaO(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT?
A) Diagnostic imaging of the human digestive tract often requires a patient to consume a slurry of BaSO4(s),a compound that contains the toxic Ba2+ ion.
B) Hydroxyapatite is a calcium containing compound that is the main component of tooth enamel.
C) Beryllium is toxic.Exposure (by breathing)to beryllium can cause berylliosis.
D) Most magnesium is obtained from seawater,where it is present at a roughly 0.05 M concentration.
E) Calcium is the central element in chlorophyll.
A) Diagnostic imaging of the human digestive tract often requires a patient to consume a slurry of BaSO4(s),a compound that contains the toxic Ba2+ ion.
B) Hydroxyapatite is a calcium containing compound that is the main component of tooth enamel.
C) Beryllium is toxic.Exposure (by breathing)to beryllium can cause berylliosis.
D) Most magnesium is obtained from seawater,where it is present at a roughly 0.05 M concentration.
E) Calcium is the central element in chlorophyll.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction of potassium and water.
A) K(s)+ H2O(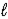 )→ KO(s)+ H2(g)
)→ KO(s)+ H2(g)
B) 2 K(s)+ 2 H2O(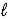 )→ 2 KOH(aq)+ H2(g)
)→ 2 KOH(aq)+ H2(g)
C) 2 K(s)+ 2 H2O(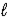 )→ K2O2(s)+ 2 H2(g)
)→ K2O2(s)+ 2 H2(g)
D) 2 K(s)+ H2O(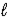 )→ K2O(s)+ H2(g)
)→ K2O(s)+ H2(g)
E) 4 K(s)+ 2 H2O(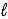 )→ 4 KH(s)+ O2(g)
)→ 4 KH(s)+ O2(g)
A) K(s)+ H2O(
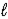 )→ KO(s)+ H2(g)
)→ KO(s)+ H2(g)B) 2 K(s)+ 2 H2O(
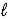 )→ 2 KOH(aq)+ H2(g)
)→ 2 KOH(aq)+ H2(g)C) 2 K(s)+ 2 H2O(
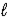 )→ K2O2(s)+ 2 H2(g)
)→ K2O2(s)+ 2 H2(g)D) 2 K(s)+ H2O(
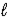 )→ K2O(s)+ H2(g)
)→ K2O(s)+ H2(g)E) 4 K(s)+ 2 H2O(
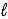 )→ 4 KH(s)+ O2(g)
)→ 4 KH(s)+ O2(g)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Oxides of the alkaline earth family form ____ upon reaction with water.
A) basic solutions
B) acidic solutions
C) alkaline earth hydrides
D) oxygen gas
E) hydrogen gas
A) basic solutions
B) acidic solutions
C) alkaline earth hydrides
D) oxygen gas
E) hydrogen gas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The primary product from the reaction of potassium and oxygen is _____.
A) KO
B) K2O
C) KO4
D) KO2
E) KO3
A) KO
B) K2O
C) KO4
D) KO2
E) KO3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Elemental sodium is commercially produced by electrolysis of ____.A valuable by-product,____,is simultaneously produced during the electrolysis.
A) NaCl(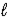 ),Cl2(g)
),Cl2(g)
B) NaH(g),H2(g)
C) NaCl(aq),NaOH(aq)
D) Na2O2(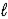 ),O2(g)
),O2(g)
E) Na2S(s),S8(s)
A) NaCl(
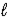 ),Cl2(g)
),Cl2(g)B) NaH(g),H2(g)
C) NaCl(aq),NaOH(aq)
D) Na2O2(
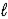 ),O2(g)
),O2(g)E) Na2S(s),S8(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction of lime and water to form slaked lime.
A) CaO(s)+ 2 H2O(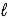 )→ CaCO3(s)+ 2 H2(g)
)→ CaCO3(s)+ 2 H2(g)
B) CaO(s)+ H2O(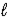 )⇋ Ca(OH)2(s)
)⇋ Ca(OH)2(s)
C) Ca3(PO4)2(s)+ 2 H2O(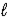 )→ 2 CaHPO4(aq)+ Ca(OH)2(aq)
)→ 2 CaHPO4(aq)+ Ca(OH)2(aq)
D) CaCO3(s)+ H2O(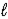 )⇋ Ca(s)+ H3O+(aq)+ CO2(g)
)⇋ Ca(s)+ H3O+(aq)+ CO2(g)
E) CaCO3(s)+ H2O(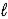 )→ CaO(s)+ H2CO3(aq)
)→ CaO(s)+ H2CO3(aq)
A) CaO(s)+ 2 H2O(
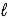 )→ CaCO3(s)+ 2 H2(g)
)→ CaCO3(s)+ 2 H2(g)B) CaO(s)+ H2O(
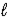 )⇋ Ca(OH)2(s)
)⇋ Ca(OH)2(s)C) Ca3(PO4)2(s)+ 2 H2O(
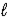 )→ 2 CaHPO4(aq)+ Ca(OH)2(aq)
)→ 2 CaHPO4(aq)+ Ca(OH)2(aq)D) CaCO3(s)+ H2O(
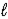 )⇋ Ca(s)+ H3O+(aq)+ CO2(g)
)⇋ Ca(s)+ H3O+(aq)+ CO2(g)E) CaCO3(s)+ H2O(
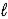 )→ CaO(s)+ H2CO3(aq)
)→ CaO(s)+ H2CO3(aq)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following balanced chemical equations represents the decomposition of limestone at high temperature?
A) Ca(OH)2(s)→ CaO(s)+ H2O(g)
B) 2 CaO(s)→ 2 Ca(s)+ O2(g)
C) CaCO3(s)→ CaO(s)+ CO2(g)
D) Ca(OH)2(s)→ CaH2(s)+ O2(g)
E) 2 CaCO3(s)→ 2 Ca(s)+ O2(g)+ CO2(g)
A) Ca(OH)2(s)→ CaO(s)+ H2O(g)
B) 2 CaO(s)→ 2 Ca(s)+ O2(g)
C) CaCO3(s)→ CaO(s)+ CO2(g)
D) Ca(OH)2(s)→ CaH2(s)+ O2(g)
E) 2 CaCO3(s)→ 2 Ca(s)+ O2(g)+ CO2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The products of the reaction of strontium hydride and water are
A) SrOH + H2.
B) Sr2O + H2.
C) Sr(OH)2 + H2.
D) SrO + H2.
E) SrOH + O2.
A) SrOH + H2.
B) Sr2O + H2.
C) Sr(OH)2 + H2.
D) SrO + H2.
E) SrOH + O2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
All of the following statements concerning sodium are correct EXCEPT
A) most sodium compounds are water soluble.
B) sodium is soft and easily cut with a knife.
C) sodium is usually found in nature as the reduced metal or as a sulfide salt.
D) sodium ions help regulate osmotic pressure in the human body.
E) sodium is commercially prepared by electrolysis of molten NaCl.
A) most sodium compounds are water soluble.
B) sodium is soft and easily cut with a knife.
C) sodium is usually found in nature as the reduced metal or as a sulfide salt.
D) sodium ions help regulate osmotic pressure in the human body.
E) sodium is commercially prepared by electrolysis of molten NaCl.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Who developed the process for obtaining aluminum from bauxite ore?
A) Antoine Lavoisier
B) Fritz Haber
C) Michael Faraday
D) Herman Frasch
E) Charles Hall
A) Antoine Lavoisier
B) Fritz Haber
C) Michael Faraday
D) Herman Frasch
E) Charles Hall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the total number of valence electrons in N2?
A) 16
B) 17
C) 34
D) 11
E) 22
A) 16
B) 17
C) 34
D) 11
E) 22

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The Ostwald process is an industrial method of producing ____ from the oxidation of ____.
A) nitric acid,ammonia
B) ammonia,nitric acid
C) ammonia,nitrogen
D) nitric acid,nitrogen
E) dinitrogen monoxide,nitrogen
A) nitric acid,ammonia
B) ammonia,nitric acid
C) ammonia,nitrogen
D) nitric acid,nitrogen
E) dinitrogen monoxide,nitrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The active ingredients in "strike anywhere" matches are _____ and the powerful oxidizing agent,KClO3(s).
A) N2H4
B) P4O10
C) Mg3N2
D) P4S3
E) (HPO3)3
A) N2H4
B) P4O10
C) Mg3N2
D) P4S3
E) (HPO3)3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In what way is cryolite (Na3AlF6)used in the production of aluminum?
A) Cryolite is a catalyst,it increases the rate of aluminum reduction.
B) Cryolite-bauxite mixtures melt at lower temperatures than pure bauxite.
C) Cryolite makes aluminum more corrosion resistant.
D) Cryolite is reduced to aluminum at the cathode.
E) Cryolite is oxidized to F2(g)at the anode.
A) Cryolite is a catalyst,it increases the rate of aluminum reduction.
B) Cryolite-bauxite mixtures melt at lower temperatures than pure bauxite.
C) Cryolite makes aluminum more corrosion resistant.
D) Cryolite is reduced to aluminum at the cathode.
E) Cryolite is oxidized to F2(g)at the anode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Dinitrogen monoxide (laughing gas)can be produced by the careful decomposition of ammonium nitrate at 250 °C.Choose the correct balanced equation for this reaction.
A) NH4NO3(s)→ N2O(g)+ 2 H2(g)+ O2(g)
B) NH4NO3(s)+ 2 N2(g)→ 3 N2O(g)+ 2 H2(g)
C) NH4NO3(s)→ N2O(g)+ 2 H2O(g)
D) 2 NH4NO3(s)→ N2O(g)+ 2 HNO2(g)+ H2O(g)+ 2 H2(g)
E) 3 NH4NO3(s)→ N2O(g)+ 2 N2(g)+ 8 H2O(g)
A) NH4NO3(s)→ N2O(g)+ 2 H2(g)+ O2(g)
B) NH4NO3(s)+ 2 N2(g)→ 3 N2O(g)+ 2 H2(g)
C) NH4NO3(s)→ N2O(g)+ 2 H2O(g)
D) 2 NH4NO3(s)→ N2O(g)+ 2 HNO2(g)+ H2O(g)+ 2 H2(g)
E) 3 NH4NO3(s)→ N2O(g)+ 2 N2(g)+ 8 H2O(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following statements concerning boron compounds is incorrect?
A) More than 20 neutral boron hydrides (general formula BxHy)are known.
B) The two boron atoms in B2H6 are connected by three-center,two-electron B-H-B bridges.
C) Borax,Na2B4O7⋅10 H2O,is used as a low-melting flux in metallurgy.
D) Sodium borohydride,NaBH4,is a reducing agent used in organic chemistry.
E) Diborane,B2H6,is used as an oxidizing agent in organic chemistry.
A) More than 20 neutral boron hydrides (general formula BxHy)are known.
B) The two boron atoms in B2H6 are connected by three-center,two-electron B-H-B bridges.
C) Borax,Na2B4O7⋅10 H2O,is used as a low-melting flux in metallurgy.
D) Sodium borohydride,NaBH4,is a reducing agent used in organic chemistry.
E) Diborane,B2H6,is used as an oxidizing agent in organic chemistry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the oxidation state of nitrogen in nitrogen dioxide?
A) 5
B) 4
C) 0
D) 1
E) -3
A) 5
B) 4
C) 0
D) 1
E) -3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT?
A) Carbon is classified as a nonmetal.
B) Silicon is classified as a metalloid.
C) Germanium is classified as a metal.
D) Tin is classified as a metal.
E) Lead is classified as a metal.
A) Carbon is classified as a nonmetal.
B) Silicon is classified as a metalloid.
C) Germanium is classified as a metal.
D) Tin is classified as a metal.
E) Lead is classified as a metal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Nitric acid decomposes slowly in sunlight with nitrogen dioxide and oxygen as reduction and oxidation products,respectively.Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
A) HNO3(aq)→ NO2(g)+ 1/2 O2(g)
B) HNO3(aq)→ NO2(g)+ 1/2 O2(g)+ H+(aq)
C) 2 HNO3(aq)→ 2 NO2(g)+ O2(g)+ H2(g)
D) 4 HNO3(aq)→ 2 NO2(g)+ + N2(g)+ 3 O2(g)+ 2 H2O(g)
E) 4 HNO3(aq)→ 4 NO2(g)+ O2(g)+ 2 H2O(g)
A) HNO3(aq)→ NO2(g)+ 1/2 O2(g)
B) HNO3(aq)→ NO2(g)+ 1/2 O2(g)+ H+(aq)
C) 2 HNO3(aq)→ 2 NO2(g)+ O2(g)+ H2(g)
D) 4 HNO3(aq)→ 2 NO2(g)+ + N2(g)+ 3 O2(g)+ 2 H2O(g)
E) 4 HNO3(aq)→ 4 NO2(g)+ O2(g)+ 2 H2O(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following nitrogen oxides are free radicals: NO,N2O,NO2,and/or N2O3?
A) NO and N2O
B) N2O and NO2
C) NO2 and N2O3
D) NO and NO2
E) N2O and N2O3
A) NO and N2O
B) N2O and NO2
C) NO2 and N2O3
D) NO and NO2
E) N2O and N2O3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The building block of silicate minerals is the
A) linear SiO unit.
B) the bent SiO2 unit.
C) trigonal-bipyramidal SiO5 unit.
D) tetrahedral SiO4 unit.
E) the linear SiO2 unit.
A) linear SiO unit.
B) the bent SiO2 unit.
C) trigonal-bipyramidal SiO5 unit.
D) tetrahedral SiO4 unit.
E) the linear SiO2 unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Molten Al2O3 is reduced by electrolysis at low potentials and high currents.If 7.5 × 103 amperes of current is passed through molten Al2O3 for 12.0 hours,what mass of Al is produced? Assume 100% current efficiency.
A) 5.0 × 102 g
B) 3.0 × 104 g
C) 9.1 × 104 g
D) 2.7 × 105 g
E) 3.1 × 106 g
A) 5.0 × 102 g
B) 3.0 × 104 g
C) 9.1 × 104 g
D) 2.7 × 105 g
E) 3.1 × 106 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT?
A) Quartz is a form of silicon dioxide that is used for controlling the frequency of radio and television transmissions.
B) Silica gel,a noncrystalline for of SiO2,is used to keep electronics dry.
C) Passing beer through a bed of silica gel removes small particles that cause cloudiness.
D) Gaseous SiO2 is a linear molecule with silicon-oxygen double bonds and a boiling point slight below 0 °C.
E) Silicon dioxide is resistant to attack from all acids except HF.
A) Quartz is a form of silicon dioxide that is used for controlling the frequency of radio and television transmissions.
B) Silica gel,a noncrystalline for of SiO2,is used to keep electronics dry.
C) Passing beer through a bed of silica gel removes small particles that cause cloudiness.
D) Gaseous SiO2 is a linear molecule with silicon-oxygen double bonds and a boiling point slight below 0 °C.
E) Silicon dioxide is resistant to attack from all acids except HF.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Phosphorus was first isolated in 1669 by Hennig Brandt,a German alchemist.Brandt was able to isolate approximately 30 grams of phosphorus from 60 gallons of ________.
A) sea water
B) Chilean saltpeter
C) urea
D) honey
E) urine
A) sea water
B) Chilean saltpeter
C) urea
D) honey
E) urine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The only acid that decomposes silicon dioxide is ____.
A) CF3CO2H
B) H2SO4
C) HBr
D) HF
E) HClO4
A) CF3CO2H
B) H2SO4
C) HBr
D) HF
E) HClO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Bauxite ore is the primary source material in the commercial production of ___.
A) B
B) Al
C) Na3AlF6
D) NaOH
E) B2H6
A) B
B) Al
C) Na3AlF6
D) NaOH
E) B2H6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT?
A) Phosphoric acid gives a tart taste to carbonated beverages such as colas.
B) Sodium phosphate,Na3PO4,is a relatively strong base used in paint strippers.
C) Ca(H2PO4)2⋅H2O is used as an acid leavening agent in baking powder.
D) Ca3(PO4)2 is a dark green compound used in latex paints.
E) Calcium monohydrogen phosphate is an abrasive and polishing agent in toothpaste.
A) Phosphoric acid gives a tart taste to carbonated beverages such as colas.
B) Sodium phosphate,Na3PO4,is a relatively strong base used in paint strippers.
C) Ca(H2PO4)2⋅H2O is used as an acid leavening agent in baking powder.
D) Ca3(PO4)2 is a dark green compound used in latex paints.
E) Calcium monohydrogen phosphate is an abrasive and polishing agent in toothpaste.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Quartz is a pure crystalline form of _____.
A) silica,SiO2
B) sodium silicate,NaSiO4
C) calcium orthosilicate,Ca2SiO4
D) silicon tetrachloride,SiCl4
E) silicon carbide,SiC
A) silica,SiO2
B) sodium silicate,NaSiO4
C) calcium orthosilicate,Ca2SiO4
D) silicon tetrachloride,SiCl4
E) silicon carbide,SiC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Hydrazine,N2H4,is produced by the Raschig process−the oxidation of ammonia with alkaline ____.
A) HNO3(aq)
B) NaOCl(aq)
C) N2(g)
D) HPO42-(aq)
E) N2O(g)
A) HNO3(aq)
B) NaOCl(aq)
C) N2(g)
D) HPO42-(aq)
E) N2O(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following elements is least likely to form a stable oxide?
A) Fe
B) Ca
C) S8
D) P4
E) He
A) Fe
B) Ca
C) S8
D) P4
E) He

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is the outer shell ground state electron configuration of At?
A) 6s26p4
B) 7s27p5
C) 7s27p6
D) 6s26p5
E) 6s26p6
A) 6s26p4
B) 7s27p5
C) 7s27p6
D) 6s26p5
E) 6s26p6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following does not contain sulfur?
A) Acid rain
B) Egg protein
C) Amines
D) Volcanic gases
E) Barite
A) Acid rain
B) Egg protein
C) Amines
D) Volcanic gases
E) Barite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The primary product of the reaction of potassium and oxygen is ________.This compound is used in oxygen generators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Write a balanced chemical equation for the roasting of CuS.
A) CuS(s)+ 2 HCl(aq)→ CuCl2(aq)+ H2(g)+ S(s)
B) CuS(s)+ O2(g)→ CuO2(s)+ S(s)
C) CuS(s)+ O2(g)→ CuO(s)+ SO(g)
D) CuS(s)+ 2 HCl(aq)→ CuCl2(aq)+ H2S(g)
E) 2 CuS(s)+ 2 O2(g)→ 2 CuO(s)+ SO2(g)
A) CuS(s)+ 2 HCl(aq)→ CuCl2(aq)+ H2(g)+ S(s)
B) CuS(s)+ O2(g)→ CuO2(s)+ S(s)
C) CuS(s)+ O2(g)→ CuO(s)+ SO(g)
D) CuS(s)+ 2 HCl(aq)→ CuCl2(aq)+ H2S(g)
E) 2 CuS(s)+ 2 O2(g)→ 2 CuO(s)+ SO2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A(n)________ reaction is one where an element or compound is simultaneously oxidized and reduced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Anhydrous hydrogen fluoride is used in all of the following applications EXCEPT
A) etching fluorescent light bulbs.
B) the production of refrigerants.
C) the reduction of alkali and alkaline earth metals.
D) the production of plastics.
E) the production of herbicides.
A) etching fluorescent light bulbs.
B) the production of refrigerants.
C) the reduction of alkali and alkaline earth metals.
D) the production of plastics.
E) the production of herbicides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In the United States,most sulfur is obtained from
A) the reduction of cinnabar,HgS.
B) S8 deposits along the Gulf of Mexico.
C) the reduction of iron pyrite,FeS2.
D) the reduction of copper sulfide,CuS.
E) the oxidation of H2S gas.
A) the reduction of cinnabar,HgS.
B) S8 deposits along the Gulf of Mexico.
C) the reduction of iron pyrite,FeS2.
D) the reduction of copper sulfide,CuS.
E) the oxidation of H2S gas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following occurs uncombined in nature?
A) Cl
B) P
C) Ar
D) F
E) Br
A) Cl
B) P
C) Ar
D) F
E) Br

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Concentrated nitric acid reacts with copper to form NO2(g).Dilute nitric acid reacts with copper to form NO(g).Why does the reaction involving the dilute acid give a different nitrogen oxide than the concentrated acid?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
One commercial method of producing Cl2 is by electrolysis of aqueous NaCl.
NaCl(aq)+ 2 H2O(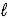 )→ Cl2(g)+ 2 NaOH(aq)+ H2(g)
)→ Cl2(g)+ 2 NaOH(aq)+ H2(g)
Owing to environmental concerns,some manufacturers are shifting to the soda-lime method for NaOH production.Explain why this method is environmentally preferred.Write a balanced chemical equation for the production of NaOH from soda ash and lime.
NaCl(aq)+ 2 H2O(
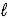 )→ Cl2(g)+ 2 NaOH(aq)+ H2(g)
)→ Cl2(g)+ 2 NaOH(aq)+ H2(g)Owing to environmental concerns,some manufacturers are shifting to the soda-lime method for NaOH production.Explain why this method is environmentally preferred.Write a balanced chemical equation for the production of NaOH from soda ash and lime.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Pure oxygen can be produced by the catalyzed decomposition of potassium chlorate.Choose the correct balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
A) KClO3(s)→ KClO(s)+ O2(g)
B) 2 KClO3(s)→ 2 K(s)+ Cl2(g)+ 3 O2(g)
C) 2 KClO3(s)→ 2 KCl(s)+ 3 O2(g)
D) 2 KClO3(s)→ 2 KClO2(s)+ O2(g)
E) KClO3(s)→ K(s)+ ClO(g)+ O2(g)
A) KClO3(s)→ KClO(s)+ O2(g)
B) 2 KClO3(s)→ 2 K(s)+ Cl2(g)+ 3 O2(g)
C) 2 KClO3(s)→ 2 KCl(s)+ 3 O2(g)
D) 2 KClO3(s)→ 2 KClO2(s)+ O2(g)
E) KClO3(s)→ K(s)+ ClO(g)+ O2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The most reactive nonmetallic element is _____.This element has been shown to form compounds with every other element except He and Ne.
A) oxygen
B) fluorine
C) chlorine
D) phosphorus
E) carbon
A) oxygen
B) fluorine
C) chlorine
D) phosphorus
E) carbon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Arrange the following in order of increasing ease of oxidation: At−,Cl−,I−,Br−
A) At− < Cl− < Br− < I−
B) Cl− < I− < At− < Br−
C) At− < Br− < I− < Cl−
D) Cl− < Br− < I− < At−
E) Br− < Cl− < I− < At−
A) At− < Cl− < Br− < I−
B) Cl− < I− < At− < Br−
C) At− < Br− < I− < Cl−
D) Cl− < Br− < I− < At−
E) Br− < Cl− < I− < At−

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Silicon is purified in a process called ________,where a narrow segment of a silicon rod is melted and allowed to slowly recrystallize.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Based on the following data,what is the I-I bond energy? 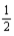 H2(g)+
H2(g)+ 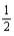 I2(g)→ HI(g); ΔrH° = 26.36 kJ/mol-rxn Bond
I2(g)→ HI(g); ΔrH° = 26.36 kJ/mol-rxn Bond
Bond Energy (kJ/mol)
H-H
435
H-I
295
A) 365 kJ/mol
B) 208 kJ/mol
C) -208 kJ/mol
D) -155 kJ/mol
E) 155 kJ/mol
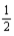 H2(g)+
H2(g)+ 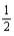 I2(g)→ HI(g); ΔrH° = 26.36 kJ/mol-rxn Bond
I2(g)→ HI(g); ΔrH° = 26.36 kJ/mol-rxn BondBond Energy (kJ/mol)
H-H
435
H-I
295
A) 365 kJ/mol
B) 208 kJ/mol
C) -208 kJ/mol
D) -155 kJ/mol
E) 155 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
What is the molecular formula of chlorous acid?
A) HClO
B) HClO2
C) HClO3
D) HClO4
E) HCl
A) HClO
B) HClO2
C) HClO3
D) HClO4
E) HCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A class of aluminosilicate,called a(n)________,contains regularly spaced holes and cavities.This type of aluminosilicate is often used as a catalyst.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Give two examples of the allotropes of elemental oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Ammonium perchlorate can decompose violently according to the chemical equation below. 2 NH4ClO4(s)→ N2(g)+ Cl2(g)+ 2 O2(g)+ 4 H2O(g)
What volume of chlorine gas is produced by the decomposition of 120 g NH4ClO4 at 650 K and 1.0 atm? (R = 0.08206 L⋅atm/K⋅mol)
A) 27 L
B) 54 L
C) 91 L
D) 110 L
E) 3200 L
What volume of chlorine gas is produced by the decomposition of 120 g NH4ClO4 at 650 K and 1.0 atm? (R = 0.08206 L⋅atm/K⋅mol)
A) 27 L
B) 54 L
C) 91 L
D) 110 L
E) 3200 L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



