Deck 25: Phylogenies and the History of Life
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/37
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Phylogenies and the History of Life
1
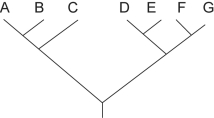 Figure 25.1
Figure 25.1Which of the following trees depicts the same relationship among species as shown in Figure 25.1?
A)
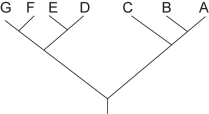
B)
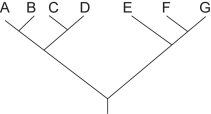
C)
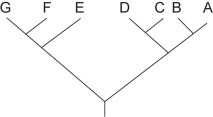
D) None; the above trees all depict a different relationship among species.
A
2
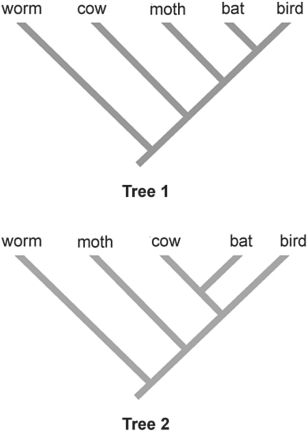 Figure 25.3
Figure 25.3Applying the principle of parsimony to the trait "ability to fly," which of the two phylogenetic trees above is most parsimonious?
A) Tree 1
B) Tree 2
C) Both trees are equally parsimonious.
A
3
Proposed number of Hox genes in some extant and extinct animal groups Which of the following is the most parsimonious explanation for the change in the number of Hox genes from the last common ancestor of insects and vertebrates to ancestral vertebrates, as shown in the table provided?
A) the occurrence of two distinct duplications of the entire seven-gene cluster, followed by the loss of one cluster
B) two distinct duplications of a three-gene cluster of Hox genes, followed by an independent duplication of an individual Hox gene
C) the occurrence of seven independent duplications of individual Hox genes
D) the occurrence of a single duplication of the entire seven-gene cluster
A) the occurrence of two distinct duplications of the entire seven-gene cluster, followed by the loss of one cluster
B) two distinct duplications of a three-gene cluster of Hox genes, followed by an independent duplication of an individual Hox gene
C) the occurrence of seven independent duplications of individual Hox genes
D) the occurrence of a single duplication of the entire seven-gene cluster
the occurrence of a single duplication of the entire seven-gene cluster
4
Which of the following statements best describes the rationale for applying the principle of parsimony in constructing phylogenetic trees?
A) Parsimony allows the researcher to "root" the tree.
B) Parsimony ensures there will be no homoplasous traits in the tree.
C) Similarity due to common ancestry should be more common than similarity due to convergent evolution.
D) Parsimony helps clarify the goals of evolution.
A) Parsimony allows the researcher to "root" the tree.
B) Parsimony ensures there will be no homoplasous traits in the tree.
C) Similarity due to common ancestry should be more common than similarity due to convergent evolution.
D) Parsimony helps clarify the goals of evolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Some beetles and flies have antler-like structures on their heads, much like male deer do. The existence of antlers in beetle, fly, and deer species with strong male-male competition is an example of
A) homology.
B) parsimony.
C) convergent evolution.
D) a synapomorphy.
A) homology.
B) parsimony.
C) convergent evolution.
D) a synapomorphy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements is true about a phylogeny, as represented by a phylogenetic tree?
A) A monophyletic group can be properly based on convergent features in addition to synapomorphies.
B) Descendant groups branches) from the same node do not necessarily share any derived characters.
C) The outgroup has mostly ancestral traits relative to the rest of the branches.
D) All of the above answers are correct.
E) None of the above answers are correct.
A) A monophyletic group can be properly based on convergent features in addition to synapomorphies.
B) Descendant groups branches) from the same node do not necessarily share any derived characters.
C) The outgroup has mostly ancestral traits relative to the rest of the branches.
D) All of the above answers are correct.
E) None of the above answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The cladistic approach to estimating phylogenetic trees is most like the approach of which species concept?
A) biological species concept
B) morphospecies concept
C) phylogenetic species concept
A) biological species concept
B) morphospecies concept
C) phylogenetic species concept

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
 Figure 25.1
Figure 25.1Which of the following would be useful in creating a phylogenetic tree of a taxon?
A) genetic sequences from living species
B) behavioral data from living species
C) morphological data from fossil species
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following would be least likely in the fossil record?
A) marine-dwelling species
B) burrowing species
C) marsh-dwelling species
D) desert-dwelling species
A) marine-dwelling species
B) burrowing species
C) marsh-dwelling species
D) desert-dwelling species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is an example of homoplasy?
A) chlorophyll in flowering plants and algae
B) scales in snakes and lizards
C) fur in bears and seals
D) cell walls in plants and fungi
A) chlorophyll in flowering plants and algae
B) scales in snakes and lizards
C) fur in bears and seals
D) cell walls in plants and fungi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is a monophyletic group?
A) fishes
B) dinosaurs excluding birds)
C) amphibians
D) mammals
E) all of the above
A) fishes
B) dinosaurs excluding birds)
C) amphibians
D) mammals
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
 Figure 25.1
Figure 25.1Your professor wants you to construct a phylogenetic tree of orchids. She gives you tissue from seven orchid species and one lily. What is the most likely reason she gave you the lily?
A) to see if it's a cryptic orchid species
B) to serve as an out-group
C) to see if the lily and the orchids show all the same shared derived characters synapomorphies)
D) to see if you were paying attention

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The Mesozoic era is nicknamed the Age of Reptiles and the Cenozoic era is nicknamed the Age of Mammals. What do these nicknames mean?
A) They indicate that the two eras are about the same length, because one lineage dominates the fauna of Earth only for a set period of time.
B) They identify the time of greatest diversity of these groups in the fossil record.
C) They identify the point of origin of these groups in the fossil record.
D) Both A and C are true.
E) Both B and C are true.
A) They indicate that the two eras are about the same length, because one lineage dominates the fauna of Earth only for a set period of time.
B) They identify the time of greatest diversity of these groups in the fossil record.
C) They identify the point of origin of these groups in the fossil record.
D) Both A and C are true.
E) Both B and C are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In plant communities today, leaf morphology is correlated with mean annual temperature, so paleobotanists use fossil leaf morphology to estimate the mean annual temperature of paleoclimates. However, the angiosperm fossil record contains an overabundance of samples fossilized near lakes or rivers where vines are especially common. Since vine leaves have a somewhat different association with temperature, use of data from vine-rich locations leads to mean average temperature estimates that are lower than actual recorded temperatures in modern plant communities. This potential bias in paleobotanical climate estimates is due to which type of bias in the fossil record? R. J. Burnham, N. C. A. Pitman, K. R. Johnson, and P. Wilf. 2001.
Habitat-related error in estimating temperature from leaf margins in a humid tropical forest. American Journal of Botany 88:1096-1102.)
A) Temporal bias
B) Habitat bias
C) Taxonomic bias
D) Abundance bias
Habitat-related error in estimating temperature from leaf margins in a humid tropical forest. American Journal of Botany 88:1096-1102.)
A) Temporal bias
B) Habitat bias
C) Taxonomic bias
D) Abundance bias

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Based on the table provided, which of the following traits is/are useful in generating a phylogeny for species W, Z?
A) Traits 2 and 3
B) Trait 2 only
C) Traits 1 and 2
D) Traits 1 and 3
E) Trait 3 only
A) Traits 2 and 3
B) Trait 2 only
C) Traits 1 and 2
D) Traits 1 and 3
E) Trait 3 only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
You find a new fossil deposit, containing many species with shells but no soft-bodied species. What is the most likely reason for this?
A) Soft-bodied species were rare or absent at this time and location.
B) There was a mass extinction event among hard-bodied, but not soft-bodied, species at this location.
C) Conditions were not right to fossilize soft-bodied organisms.
A) Soft-bodied species were rare or absent at this time and location.
B) There was a mass extinction event among hard-bodied, but not soft-bodied, species at this location.
C) Conditions were not right to fossilize soft-bodied organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following organisms would be most likely to fossilize?
A) a rare worm
B) a rare squirrel
C) a common squirrel
D) a common worm
A) a rare worm
B) a rare squirrel
C) a common squirrel
D) a common worm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
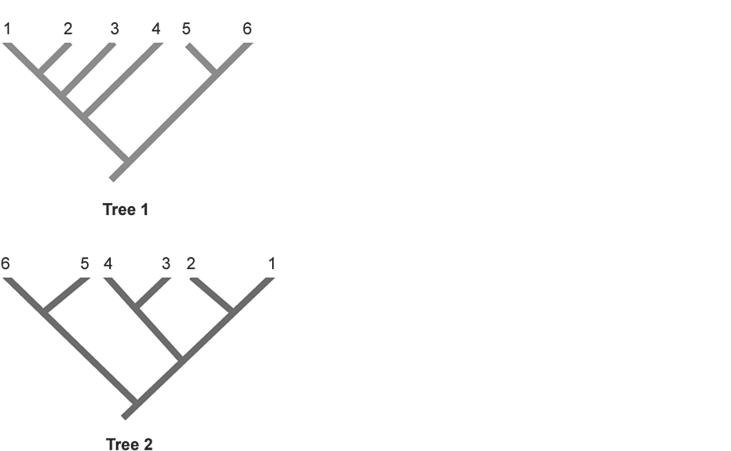 Figure 25.2
Figure 25.2In the phylogenetic trees above, numbers represent species and the same species are shown in both trees. Which two species are represented as sister species in Tree 2 but are not shown as sister species in Tree 1?
A) 1 and 2
B) 2 and 3
C) 3 and 4
D) 5 and 6
E) The two trees show all the same phylogenetic relationships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which listing of geological periods is in the correct order, from oldest to most recent?
A) Cambrian, Permian, Devonian, Cretaceous
B) Cambrian, Devonian, Permian, Cretaceous
C) Permian, Cambrian, Cretaceous, Devonian
D) Devonian, Cambrian, Permian, Cretaceous
A) Cambrian, Permian, Devonian, Cretaceous
B) Cambrian, Devonian, Permian, Cretaceous
C) Permian, Cambrian, Cretaceous, Devonian
D) Devonian, Cambrian, Permian, Cretaceous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
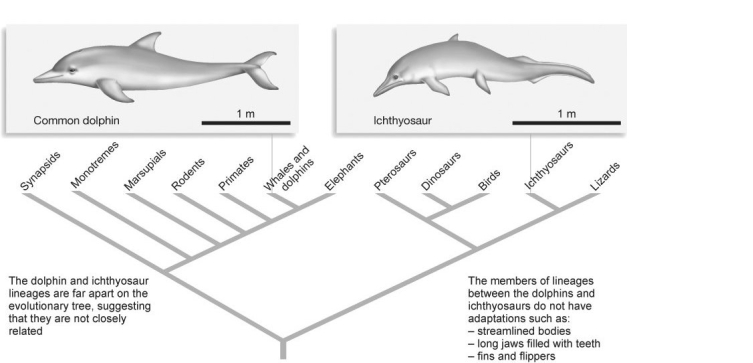 Figure 25.4
Figure 25.4For the streamlined bodies shown in Figure 25.4 above to be homologous instead of homoplasious, which of the following groups would you expect to also have streamlined bodies? Assume the trait was not lost in any of the lineages on the phylogenetic tree in Figure 25.4.
A) lizards and elephants
B) pterosaurs, dinosaurs, birds, and lizards
C) synapsids, monotremes, marsupials, elephants, primates, and rodents
D) all of the above
E) either B or C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
How do mass extinctions differ from background extinctions?
A) It is now recognized that mass extinctions but not background extinctions are generally caused by asteroid impacts.
B) Mass extinctions involve a relatively rapid extinction of a large proportion of organisms that were alive at that time.
C) Mass extinctions account for most species that have gone extinct in the history of life on Earth.
A) It is now recognized that mass extinctions but not background extinctions are generally caused by asteroid impacts.
B) Mass extinctions involve a relatively rapid extinction of a large proportion of organisms that were alive at that time.
C) Mass extinctions account for most species that have gone extinct in the history of life on Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following key adaptations is found in many animals from the Burgess Shale fauna, but not found in the Doushantuo and Ediacaran faunas?
A) segmentation
B) burrow formation
C) multicellularity
D) mouthparts
A) segmentation
B) burrow formation
C) multicellularity
D) mouthparts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
How did the pattern shown in the circled part of Figure 25.5 most likely arise?
A) allopatric speciation
B) background extinction
C) mass extinction
D) convergent evolution
E) adaptive radiation
A) allopatric speciation
B) background extinction
C) mass extinction
D) convergent evolution
E) adaptive radiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The largest extinction, measured as a percentage of species that disappeared, occurred at the end of which geological period?
A) Tertiary
B) Cretaceous
C) Permian
D) Devonian
E) Silurian
A) Tertiary
B) Cretaceous
C) Permian
D) Devonian
E) Silurian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Dicynodonts were pig-sized reptiles that lived during the Permian geologic period. An increase in dicynodont species diversity occurred soon after the Permian extinction. Given what you know of this period, this increase in dicynodont species diversity represents , most likely due to .
A) adaptive radiation; a morphological innovation among dicynodonts
B) competitive exclusion; the fact that they needed new food sources
C) adaptive radiation; the availability of previously unoccupied niches
D) competitive exclusion; intrasexual selection leading to anagenesis
A) adaptive radiation; a morphological innovation among dicynodonts
B) competitive exclusion; the fact that they needed new food sources
C) adaptive radiation; the availability of previously unoccupied niches
D) competitive exclusion; intrasexual selection leading to anagenesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is still lacking in the hypothesis of an asteroid impact as the cause of the end-Cretaceous mass extinction?
A) evidence that an asteroid hit Earth at the time of the extinctions 65 million years ago)
B) a convincing explanation of why mammals radiated after the event
C) evidence of the location where an asteroid hit Earth
D) a convincing explanation of why some lineages survived while others vanished
A) evidence that an asteroid hit Earth at the time of the extinctions 65 million years ago)
B) a convincing explanation of why mammals radiated after the event
C) evidence of the location where an asteroid hit Earth
D) a convincing explanation of why some lineages survived while others vanished

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following organisms would be most likely to fossilize?
A) a species of clam found in a shallow marine habitat
B) a species of rat that lives in the desert
C) a species of flower found in Ontario forests
D) a species of slug that lives in the rain forest
A) a species of clam found in a shallow marine habitat
B) a species of rat that lives in the desert
C) a species of flower found in Ontario forests
D) a species of slug that lives in the rain forest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
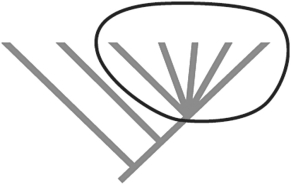 Figure 25.5
Figure 25.5-Which of the following words describes) the circled part of the phylogenetic tree in Figure 25.5?
I. monophyletic group
II. polyphyletic group
III. homoplasic trait
IV. polytomy
A) II, III, and IV
B) II only
C) I and IV
D) II and III
E) I only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Why would gene duplication events, such as those seen in the Hox gene complex, set the stage for adaptive radiation?
A) Without duplicated genes, species would be vulnerable to extinction.
B) The original gene copy is the out-group, and the new gene copies are the adaptive radiation.
C) There are more copies of genes, meaning speciation had occurred by polyploidy.
D) One copy of a gene can perform the original function while other copies are available to take on new functions.
A) Without duplicated genes, species would be vulnerable to extinction.
B) The original gene copy is the out-group, and the new gene copies are the adaptive radiation.
C) There are more copies of genes, meaning speciation had occurred by polyploidy.
D) One copy of a gene can perform the original function while other copies are available to take on new functions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following likely has the most Hox genes?
A) dolphins
B) bees
C) slugs
D) jellyfish
A) dolphins
B) bees
C) slugs
D) jellyfish

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The five mass extinctions occurred at the end of which periods?
A) Permian, Cretaceous, Devonian, Carboniferous, Silurian
B) Triassic, Devonian, Permian, Cretaceous, Ordovician
C) Jurassic, Cretaceous, Cambrian, Carboniferous, Silurian
D) Ordovician, Silurian, Cambrian, Devonian, Carboniferous
E) Devonian, Cambrian, Jurassic, Cretaceous, Permian
A) Permian, Cretaceous, Devonian, Carboniferous, Silurian
B) Triassic, Devonian, Permian, Cretaceous, Ordovician
C) Jurassic, Cretaceous, Cambrian, Carboniferous, Silurian
D) Ordovician, Silurian, Cambrian, Devonian, Carboniferous
E) Devonian, Cambrian, Jurassic, Cretaceous, Permian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A hypothetical island lies far from any other landmasses. There are many different types of plants, but only one animal-a beetle that can fly or walk from plant to plant and feeds by chewing leaves. Which morphological change would be most likely to trigger an adaptive radiation of the beetles?
A) a mouthpart that can pierce fruits and seeds
B) a change in wing shape that improves flight speed
C) an additional segment on a pair of legs
A) a mouthpart that can pierce fruits and seeds
B) a change in wing shape that improves flight speed
C) an additional segment on a pair of legs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Islands are well known for having many endemic species-species that are unique to that location. What isa likely explanation for this pattern?
A) Humans bring partly or fully domesticated species with them when they arrive on islands.
B) Colonizers encounter fewer competitors on an island, so they can diversify.
C) The type of organism that is a good colonizer has more than the average amount of genetic variability, so it's more likely to speciate.
D) Islands are more complex habitats than continents are, so they have more niches for specialization.
A) Humans bring partly or fully domesticated species with them when they arrive on islands.
B) Colonizers encounter fewer competitors on an island, so they can diversify.
C) The type of organism that is a good colonizer has more than the average amount of genetic variability, so it's more likely to speciate.
D) Islands are more complex habitats than continents are, so they have more niches for specialization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Dinosaurs were the largest land vertebrates during the eras).
A) Paleozoic
B) Cenozoic
C) Mesozoic
D) Paleozoic and Cenozoic
E) Precambrian
A) Paleozoic
B) Cenozoic
C) Mesozoic
D) Paleozoic and Cenozoic
E) Precambrian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
All of the following events can trigger an adaptive radiation EXCEPT
A) the evolution of a new morphological feature.
B) a vicariance event splitting the habitat.
C) the extinction of competitors.
D) gene duplication events.
E) the colonization of a new habitat.
A) the evolution of a new morphological feature.
B) a vicariance event splitting the habitat.
C) the extinction of competitors.
D) gene duplication events.
E) the colonization of a new habitat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following catastrophes is linked to the end-Permian mass extinction?
A) Earthquakes and tsunamis destroyed much of Earth's surface, killing most land-dwelling organisms.
B) Glaciers covered most of the land and shallow seas, preventing plant growth.
C) A meteor impact filled the atmosphere with ash and dust, blocking out the Sun and causing global cooling.
D) Volcanic eruptions cooled the planet by shading incoming solar radiation.
E) Flood basalts caused a massive spike in atmospheric CO2, leading to extreme global warming.
A) Earthquakes and tsunamis destroyed much of Earth's surface, killing most land-dwelling organisms.
B) Glaciers covered most of the land and shallow seas, preventing plant growth.
C) A meteor impact filled the atmosphere with ash and dust, blocking out the Sun and causing global cooling.
D) Volcanic eruptions cooled the planet by shading incoming solar radiation.
E) Flood basalts caused a massive spike in atmospheric CO2, leading to extreme global warming.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which statement best describes why the Cambrian explosion was important?
A) because plant and animal fossils were found together for the first time
B) because there was an explosion in ecological diversity among animals
C) because good fossils from this period are available to study
D) because there was an explosion in animal abundance
A) because plant and animal fossils were found together for the first time
B) because there was an explosion in ecological diversity among animals
C) because good fossils from this period are available to study
D) because there was an explosion in animal abundance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



