Deck 40: Water and Electrolyte Balance in Animals
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/41
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 40: Water and Electrolyte Balance in Animals
1
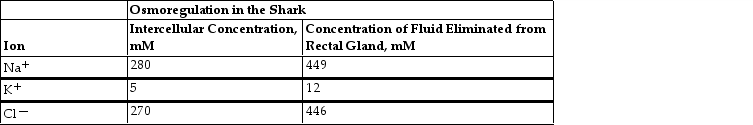 Table 40.1
Table 40.1What role does Na+/K+- ATPase play in salt excretion by the shark rectal gland?
A) Na+/K+- ATPase pumps sodium into and potassium out of cells across the basolateral membrane.
B) Na+/K+- ATPase pumps sodium out and potassium into cells across the basolateral membrane.
C) Na+/K+- ATPase pumps sodium out and potassium into cells across the apical membrane.
D) Na+/K+- ATPase pumps sodium into and potassium out of cells across the apical membrane.
B
2
The body fluids of an osmoconformer would be with its environment.
A) hyperosmotic; saltwater
B) isoosmotic; freshwater
C) hyperosmotic; freshwater
D) isoosmotic; saltwater
E) hypoosmotic; saltwater
A) hyperosmotic; saltwater
B) isoosmotic; freshwater
C) hyperosmotic; freshwater
D) isoosmotic; saltwater
E) hypoosmotic; saltwater
D
3
Marine vertebrates live in an) environment.
A) isotonic
B) hypertonic
C) hypotonic
D) osmotonic
A) isotonic
B) hypertonic
C) hypotonic
D) osmotonic
C
4
Salmon eggs hatch in freshwater. The fish then migrate to the ocean a hypertonic solution) and, after several years of feeding and growing, return to freshwater to breed. How can these organisms make the transition from freshwater to ocean water and back to freshwater?
A) Salmon surface to breathe oxygen, so there is no need for more than one mechanism of osmoregulation.
B) Different gill cells are involved in osmoregulation in freshwater than in salt water.
C) Their metabolism changes in salt water to degrade electrolytes.
D) The rectal gland functions in the ocean water, and chloride cells function in freshwater.
A) Salmon surface to breathe oxygen, so there is no need for more than one mechanism of osmoregulation.
B) Different gill cells are involved in osmoregulation in freshwater than in salt water.
C) Their metabolism changes in salt water to degrade electrolytes.
D) The rectal gland functions in the ocean water, and chloride cells function in freshwater.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A necropsy postmortem analysis) of a marine sea star that died after it was mistakenly placed in freshwater would likely show that it died because
A) its contractile vacuoles ruptured.
B) it was so hypertonic to the freshwater that it could not osmoregulate.
C) it was stressed and needed more time to acclimate to the new conditions.
D) its cells dehydrated and lost the ability to metabolize.
E) the sea star's kidneys could not handle the change in ionic content presented by the freshwater.
A) its contractile vacuoles ruptured.
B) it was so hypertonic to the freshwater that it could not osmoregulate.
C) it was stressed and needed more time to acclimate to the new conditions.
D) its cells dehydrated and lost the ability to metabolize.
E) the sea star's kidneys could not handle the change in ionic content presented by the freshwater.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Terrestrial organisms lose water through evaporation. Why are desert locusts and flour beetles good organisms to use in studying mechanisms to regulate water loss?
A) They have stoma that regulate water loss.
B) They live in environments where little to no water is available.
C) They are unable to ingest adequate amounts of sodium and chloride.
D) They have a relatively large surface area/volume relationship.
A) They have stoma that regulate water loss.
B) They live in environments where little to no water is available.
C) They are unable to ingest adequate amounts of sodium and chloride.
D) They have a relatively large surface area/volume relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following affects the osmolarity of a solution?
A) water concentration
B) salt concentration
C) glucose concentration
D) all of the above
A) water concentration
B) salt concentration
C) glucose concentration
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following mechanisms contributes to osmoregulation in both marine and freshwater bony fish?
A) gain of water through food
B) gain of salt through the gills via active transport
C) excretion of hyperosmotic urine
D) gain of water through the gills via osmosis
E) loss of salt through the gills via diffusion
A) gain of water through food
B) gain of salt through the gills via active transport
C) excretion of hyperosmotic urine
D) gain of water through the gills via osmosis
E) loss of salt through the gills via diffusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Tissues of sharks are isotonic to seawater, but their concentrations of sodium ions, potassium ions, and chloride ions in cells and extracellular fluids are similar to those of freshwater fishes. What can you infer about the movement of sodium and chloride in these animals?
A) To maintain homeostasis of sodium and chloride levels, the shark must take up additional sodium and chloride from seawater.
B) Sharks conserve sodium and chloride, limiting excretion.
C) Sodium and chloride must be eliminated through the gills.
D) Sodium and chloride will diffuse through shark gills from seawater down their concentration gradient.
A) To maintain homeostasis of sodium and chloride levels, the shark must take up additional sodium and chloride from seawater.
B) Sharks conserve sodium and chloride, limiting excretion.
C) Sodium and chloride must be eliminated through the gills.
D) Sodium and chloride will diffuse through shark gills from seawater down their concentration gradient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Sharks live in seawater. Their tissues are isotonic to seawater, but their concentrations of sodium ions, potassium ions, and chloride ions in cells and extracellular fluids are similar to those of freshwater fishes. How is that possible?
A) They excrete large quantities of electrolytes.
B) Metabolic intermediates of sharks tie up intracellular chloride and potassium ions.
C) Their blood is hypotonic to their tissues.
D) There are other compounds contributing to intra- and extracellular osmolarity in shark tissues.
A) They excrete large quantities of electrolytes.
B) Metabolic intermediates of sharks tie up intracellular chloride and potassium ions.
C) Their blood is hypotonic to their tissues.
D) There are other compounds contributing to intra- and extracellular osmolarity in shark tissues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following are soluble compounds that contribute to intracellular osmolarity in shark tissues?
A) urea and trimethylamine oxide
B) glucose and amino acids
C) excessively high levels of sodium and chloride
D) a proton pump
A) urea and trimethylamine oxide
B) glucose and amino acids
C) excessively high levels of sodium and chloride
D) a proton pump

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
African lungfish, which are often found in small, stagnant pools of freshwater, produce urea as a nitrogenous waste. What is the advantage of this adaptation?
A) Urea forms an insoluble precipitate.
B) Urea makes lungfish tissue hypoosmotic to the pool.
C) The highly toxic urea makes the pool uninhabitable to potential competitors.
D) Small, stagnant pools do not provide enough water to dilute the toxic ammonia.
E) Urea takes less energy to synthesize than ammonia.
A) Urea forms an insoluble precipitate.
B) Urea makes lungfish tissue hypoosmotic to the pool.
C) The highly toxic urea makes the pool uninhabitable to potential competitors.
D) Small, stagnant pools do not provide enough water to dilute the toxic ammonia.
E) Urea takes less energy to synthesize than ammonia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the function of the shark rectal gland?
A) It concentrates electrolytes necessary for homeostasis in a hypertonic environment.
B) It is involved in osmoregulation.
C) It secretes a hypotonic solution.
D) It is responsible for excretion of undigested residue.
A) It concentrates electrolytes necessary for homeostasis in a hypertonic environment.
B) It is involved in osmoregulation.
C) It secretes a hypotonic solution.
D) It is responsible for excretion of undigested residue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is an example of osmoregulation?
A) the contractile vacuole of a Paramecium
B) two solutions that are isotonic
C) type 2 diabetes mellitus
D) all of the above
A) the contractile vacuole of a Paramecium
B) two solutions that are isotonic
C) type 2 diabetes mellitus
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
 Table 40.1
Table 40.1The intercellular concentration of three electrolytes is compared with the concentration of these electrolytes in fluid eliminated from the shark rectal gland in Table 40.1. Based on the data, which of the following is a likely function of the rectal gland?
A) The rectal gland eliminates metabolic waste.
B) The rectal gland is able to concentrate Na+, K+, and Cl- .
C) There is very little potassium in sharks.
D) Chloride levels in seawater are similar to those in shark tissues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What role do chloride cells play in osmoregulation of marine fish with bony skeletons?
A) They are involved in excretion of excess salt.
B) They actively transport chloride into the gills.
C) They mediate the movement of salt from seawater through their gills.
D) They actively transport salt across the basolateral membrane of the rectal gland.
A) They are involved in excretion of excess salt.
B) They actively transport chloride into the gills.
C) They mediate the movement of salt from seawater through their gills.
D) They actively transport salt across the basolateral membrane of the rectal gland.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The force driving simple diffusion is
A) transmembrane pumps.
B) a concentration gradient.
C) phosphorylated protein carriers.
D) ATP.
A) transmembrane pumps.
B) a concentration gradient.
C) phosphorylated protein carriers.
D) ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Freshwater fish reside in hypotonic environments. They do not drink water, and they excrete large volumes of hypotonic urine in an effort to osmoregulate. How do they obtain an adequate supply of electrolytes?
A) There is an increase in Na+/K+- ATPase activity across the basolateral membrane.
B) Gill lamellae take up additional electrolytes from freshwater.
C) The rectal gland is specialized to produce the dilute hypotonic urine) and conserve ions.
D) Chloride cells transport additional electrolytes into the circulation of these organisms.
A) There is an increase in Na+/K+- ATPase activity across the basolateral membrane.
B) Gill lamellae take up additional electrolytes from freshwater.
C) The rectal gland is specialized to produce the dilute hypotonic urine) and conserve ions.
D) Chloride cells transport additional electrolytes into the circulation of these organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Freshwater fish live in a hypotonic environment. To maintain homeostasis in this environment, they must
A) excrete large quantities of water.
B) excrete large quantities of electrolytes.
C) consume large quantities of water.
D) take in electrolytes through simple diffusion.
A) excrete large quantities of water.
B) excrete large quantities of electrolytes.
C) consume large quantities of water.
D) take in electrolytes through simple diffusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
 Table 40.1
Table 40.1Refer to Table 40.1: Because the shark rectal gland functions only when ATP molecules are present, what can you infer about the movement of Na+, K+, and Cl- ?
A) Movement of these ions from circulation into the rectal gland is an active process.
B) These ions move into the rectal gland with their osmotic gradient.
C) Movement of these ions takes place from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
D) The rectal gland is unable to concentrate these ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The functional unit of the kidney is
A) the ureters.
B) the loop of Henle.
C) the renal corpuscle.
D) the nephron.
A) the ureters.
B) the loop of Henle.
C) the renal corpuscle.
D) the nephron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Insects maintain water and electrolyte balance through which anatomical structures?
A) chloride cells
B) rectal gland
C) Malpighian tubules
D) kidneys
A) chloride cells
B) rectal gland
C) Malpighian tubules
D) kidneys

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
There are microvilli on the luminal apical) surface of the epithelium that lines the lumen of the proximal tubule. Microvilli are structural features designed to
A) maximize surface area available for reabsorption of solutes from the renal tubule.
B) accommodate membrane proteins involved in active transport of substances into the rental tubule.
C) maximize surface area available to pump ions into the renal tubule.
D) provide adequate space to house membrane proteins involved in active transport of solutes out of the renal tubule.
A) maximize surface area available for reabsorption of solutes from the renal tubule.
B) accommodate membrane proteins involved in active transport of substances into the rental tubule.
C) maximize surface area available to pump ions into the renal tubule.
D) provide adequate space to house membrane proteins involved in active transport of solutes out of the renal tubule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Freshwater fish dilute ammonia and excrete it in a watery urine. Both freshwater and saltwater fish get rid of ammonia through diffusion across the gills. Humans convert ammonia to urea and excrete it in the urine. Birds convert ammonia to uric acid and excrete it. Why is it important for birds to get rid of ammonia?
A) It is insoluble in water.
B) It is toxic.
C) Ammonia interferes with water loss.
D) It is used to synthesize nonessential amino acids.
A) It is insoluble in water.
B) It is toxic.
C) Ammonia interferes with water loss.
D) It is used to synthesize nonessential amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Proper functioning of body cells and processes requires solute concentrations to be maintained within a narrow range. Which of the following solutes would be absorbed by the proximal tubule of the kidney nephron?
A) triglyceride
B) carbon dioxide
C) sodium
D) urea
A) triglyceride
B) carbon dioxide
C) sodium
D) urea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Through studies on the Malpighian tubules, researchers found that K+ accumulated on the inner face of the tubule, against its concentration gradient. What can you infer about the mechanism of transport?
A) Movement of potassium into the lumen of the Malpighian tubules is an energy- requiring process.
B) Sodium ions will follow potassium ions.
C) Potassium transport is a passive process.
D) Potassium moves out of the tubules at a faster rate than it moves into the lumen of the tubules.
A) Movement of potassium into the lumen of the Malpighian tubules is an energy- requiring process.
B) Sodium ions will follow potassium ions.
C) Potassium transport is a passive process.
D) Potassium moves out of the tubules at a faster rate than it moves into the lumen of the tubules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A potassium ion gradient is set up in the Malpighian tubules through an active transport process. As a result, potassium concentration is higher in the lumen of the tubules than in hemolymph. How would the potassium gradient affect water movement?
A) There would be a net movement of water into the lumen of the tubules.
B) Water would be conserved, forming a hypertonic solution in the Malpighian tubules.
C) The potassium gradient would have no effect on water movement.
D) Water would be forced out of the lumen of the Malpighian tubules through an osmotic gradient.
A) There would be a net movement of water into the lumen of the tubules.
B) Water would be conserved, forming a hypertonic solution in the Malpighian tubules.
C) The potassium gradient would have no effect on water movement.
D) Water would be forced out of the lumen of the Malpighian tubules through an osmotic gradient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Why do birds secrete uric acid as their nitrogenous waste? Because uric acid
A) is readily soluble in water, permitting its release in dilute urine.
B) is produced from their low- protein diet.
C) is metabolically intermediate to synthesize than other excretory products, balancing metabolic costs and water loss.
D) requires little water for nitrogenous waste disposal, thus conserving water and reducing body mass.
A) is readily soluble in water, permitting its release in dilute urine.
B) is produced from their low- protein diet.
C) is metabolically intermediate to synthesize than other excretory products, balancing metabolic costs and water loss.
D) requires little water for nitrogenous waste disposal, thus conserving water and reducing body mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
For filtration to take place through the fenestrated capillaries of the renal corpuscle,
A) there must be a larger concentration of proteins in the renal tubule than in the glomerulus.
B) there must be more than one capillary bed in the renal corpuscle.
C) concentration of ions must be greater in the capillaries the glomerulus) than in the renal tubule.
D) there must be a greater pressure inside the glomerulus than in the renal tubules.
A) there must be a larger concentration of proteins in the renal tubule than in the glomerulus.
B) there must be more than one capillary bed in the renal corpuscle.
C) concentration of ions must be greater in the capillaries the glomerulus) than in the renal tubule.
D) there must be a greater pressure inside the glomerulus than in the renal tubules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Reabsorption of water in the hindgut of insects is controlled by which of the following?
A) osmoregulators in the rectal gland
B) ion concentration of hemolymph
C) selective absorptive processes that take place in the Malpighian tubules
D) osmotic gradients created by ion pumps
A) osmoregulators in the rectal gland
B) ion concentration of hemolymph
C) selective absorptive processes that take place in the Malpighian tubules
D) osmotic gradients created by ion pumps

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The products of filtration in the renal corpuscle enter the renal tubule through which of the following structures?
A) Bowman's capsule
B) the proximal convoluted tubule
C) the loop of Henle
D) the collecting duct
A) Bowman's capsule
B) the proximal convoluted tubule
C) the loop of Henle
D) the collecting duct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the organ responsible for regulating water and electrolyte balance in terrestrial vertebrates?
A) kidneys
B) chloride cells
C) Malpighian tubules
D) rectal glands
A) kidneys
B) chloride cells
C) Malpighian tubules
D) rectal glands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
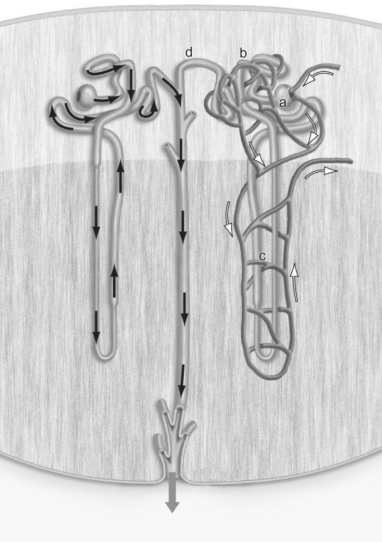 Figure 40.1
Figure 40.1-Where does filtration take place in the figure above?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is a function of antidiuretic hormone ADH)?
A) ADH alters the ion reabsorption by the loop of Henle.
B) ADH decreases the reabsorption of urea, creating a higher urea content in the urine.
C) ADH improves the reabsorption of glucose by the proximal convoluted tubule.
D) ADH triggers the insertion of water channels called aquaporins, thereby increasing the amount of water reabsorbed by the collecting duct.
E) ADH triggers the insertion of water channels called aquaporins, thereby reducing the amount of water reabsorbed by the collecting duct.
A) ADH alters the ion reabsorption by the loop of Henle.
B) ADH decreases the reabsorption of urea, creating a higher urea content in the urine.
C) ADH improves the reabsorption of glucose by the proximal convoluted tubule.
D) ADH triggers the insertion of water channels called aquaporins, thereby increasing the amount of water reabsorbed by the collecting duct.
E) ADH triggers the insertion of water channels called aquaporins, thereby reducing the amount of water reabsorbed by the collecting duct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Different habitats pose certain challenges to animal survival. For instance, terrestrial insects must maintain water balance by minimizing evaporation. How do insects minimize water loss?
A) Eat more plant material that is high in water content.
B) Excrete nitrogenous waste as urea.
C) Have a cuticle covered by a waxy hydrophobic layer.
D) Keep the spiracles open.
A) Eat more plant material that is high in water content.
B) Excrete nitrogenous waste as urea.
C) Have a cuticle covered by a waxy hydrophobic layer.
D) Keep the spiracles open.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In flour beetles and desert locusts, how is water conserved?
A) Water is transported into hindgut cells through endocytosis.
B) The pre- urine formed in the Malpighian tubules is hypertonic.
C) Sodium and chloride are actively transported out of pre- urine, and water follows, forming a hypertonic urine.
D) Urine that is formed is isotonic to hemolymph, but the muscle cells surrounding spiracles of these organisms are able to significantly limit water loss due to respiration.
A) Water is transported into hindgut cells through endocytosis.
B) The pre- urine formed in the Malpighian tubules is hypertonic.
C) Sodium and chloride are actively transported out of pre- urine, and water follows, forming a hypertonic urine.
D) Urine that is formed is isotonic to hemolymph, but the muscle cells surrounding spiracles of these organisms are able to significantly limit water loss due to respiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The loop of Henle dips into the renal cortex. This is an important feature of osmoregulation in terrestrial vertebrates because
A) the loop of Henle plays an important role in detoxification.
B) absorptive processes taking place in the loop of Henle are hormonally regulated.
C) differential permeabilities of ascending and descending limbs of the loop of Henle are important in establishing an osmotic gradient.
D) additional filtration takes place along the loop of Henle.
A) the loop of Henle plays an important role in detoxification.
B) absorptive processes taking place in the loop of Henle are hormonally regulated.
C) differential permeabilities of ascending and descending limbs of the loop of Henle are important in establishing an osmotic gradient.
D) additional filtration takes place along the loop of Henle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
How does ion composition of pre- urine differ from hemolymph?
A) Hemolymph is higher in osmolarity, conserving its Cl- .
B) Pre- urine is significantly higher in osmolarity especially with respect to Na+ and K+).
C) The protein pumps and channels of the Malpighian tubules concentrate Cl- in the pre- urine.
D) Pre- urine is similar to hemolymph in ion composition.
A) Hemolymph is higher in osmolarity, conserving its Cl- .
B) Pre- urine is significantly higher in osmolarity especially with respect to Na+ and K+).
C) The protein pumps and channels of the Malpighian tubules concentrate Cl- in the pre- urine.
D) Pre- urine is similar to hemolymph in ion composition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Water loss from insect surface is minimal due to which of the following structures?
A) a small surface area/volume relationship
B) a proteinaceous epidermis
C) chitin and the cuticle
D) tracheae and spiracles
A) a small surface area/volume relationship
B) a proteinaceous epidermis
C) chitin and the cuticle
D) tracheae and spiracles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Malpighian tubules form pre- urine, which is further processed by which of the following anatomical structures?
A) hemolymph
B) rectal gland
C) chloride cells
D) hindgut
A) hemolymph
B) rectal gland
C) chloride cells
D) hindgut

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Urine formation is involved in water and electrolyte balance in vertebrates. Which of the following statements is the most correct regarding urine formation?
A) The formation of the pre- urine is selective.
B) Water is actively pumped across cell membranes to create osmotic gradients.
C) Reabsorption is highly selective so that only ions that are needed are reabsorbed.
D) The Malpighian tubules form the pre- urine.
A) The formation of the pre- urine is selective.
B) Water is actively pumped across cell membranes to create osmotic gradients.
C) Reabsorption is highly selective so that only ions that are needed are reabsorbed.
D) The Malpighian tubules form the pre- urine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



