Deck 10: The Citrate Cycle
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: The Citrate Cycle
1
Where do citrate cycle reactions in eukaryotic cells take place?
A) cytosol
B) mitochondrial matrix
C) endoplasmic reticulum
D) nucleus
A) cytosol
B) mitochondrial matrix
C) endoplasmic reticulum
D) nucleus
mitochondrial matrix
2
Identify the strongest reductant in the table below. 
A) O2
B) oxaloacetate
C) pyruvate
D) ferredoxin

A) O2
B) oxaloacetate
C) pyruvate
D) ferredoxin
ferredoxin
3
Calculate the G ' of a redox reaction of pyruvate and hydrogen under standard conditions using the table below. 
A) 18.33 kJ/mol
B) 36.66 kJ/mol
C) 54.99 kJ/mol
D) 73.32 kJ/mol

A) 18.33 kJ/mol
B) 36.66 kJ/mol
C) 54.99 kJ/mol
D) 73.32 kJ/mol
36.66 kJ/mol
4
Which molecule in the net reaction of the citrate cycle contributes to the inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase?
A) FAD
B) H2O
C) H+
D) NADH
A) FAD
B) H2O
C) H+
D) NADH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Identify the strongest oxidant in the table below. 
A) O2
B) oxaloacetate
C) pyruvate
D) ferredoxin

A) O2
B) oxaloacetate
C) pyruvate
D) ferredoxin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How many ATP are produced from two turns of the citrate cycle?
A) 9
B) 10
C) 18
D) 20
A) 9
B) 10
C) 18
D) 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The primary function of NAD+ in the citrate cycle is that it
A) functions as an electron donor.
B) is oxidized to produce GTP.
C) acts as an electron acceptor.
D) phosphorylates ADP.
A) functions as an electron donor.
B) is oxidized to produce GTP.
C) acts as an electron acceptor.
D) phosphorylates ADP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Calculate the E ' of a coupled redox reaction with O2 and ferredoxin (Fe2+) using the table below. 
A) "-1.25"
B) "-0.39"
C) "0.39"
D) "1.25"

A) "-1.25"
B) "-0.39"
C) "0.39"
D) "1.25"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which enzyme requires CoASH to produce acetyl-CoA?
A) "pyruvate dehydrogenase"
B) "citrate synthase"
C) "isocitrate dehydrogenase"
D) " -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase"
A) "pyruvate dehydrogenase"
B) "citrate synthase"
C) "isocitrate dehydrogenase"
D) " -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The primary function of the citrate cycle is to oxidize
A) glucose.
B) pyruvate.
C) acetyl-CoA.
D) citrate.
A) glucose.
B) pyruvate.
C) acetyl-CoA.
D) citrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In two turns of the citrate cycle, how many electrons are transferred from the citrate cycle intermediates to NAD+ and FAD?
A) 4
B) 8
C) 12
D) 16
A) 4
B) 8
C) 12
D) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is a reactant in the net reaction of the citrate cycle?
A) CO2
B) H2O
C) GTP
D) CoA
A) CO2
B) H2O
C) GTP
D) CoA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which enzyme in the citrate cycle produces NADH?
A) aconitase
B) citrate synthase
C) isocitrate dehydrogenase
D) fumarase
A) aconitase
B) citrate synthase
C) isocitrate dehydrogenase
D) fumarase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is a product of the net reaction of the citrate cycle?
A) FAD
B) H2O
C) H+
D) NAD+
A) FAD
B) H2O
C) H+
D) NAD+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which enzyme of the citrate cycle catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation reaction that produces CO2, NADH, and succinyl-CoA?
A) "pyruvate dehydrogenase"
B) "citrate synthase"
C) "isocitrate dehydrogenase"
D) " -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase"
A) "pyruvate dehydrogenase"
B) "citrate synthase"
C) "isocitrate dehydrogenase"
D) " -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which enzyme regulates the flux of acetyl-CoA through the citrate cycle?
A) "pyruvate dehydrogenase"
B) "citrate synthase"
C) "isocitrate dehydrogenase"
D) " -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase"
A) "pyruvate dehydrogenase"
B) "citrate synthase"
C) "isocitrate dehydrogenase"
D) " -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which molecules function as electron acceptors in the citrate cycle?
A) NAD+, FAD
B) NADH, FADH2
C) GDP, ADP
D) GTP, ATP
A) NAD+, FAD
B) NADH, FADH2
C) GDP, ADP
D) GTP, ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The poison compound 1080 converts fluoroacetate to fluorocitrate. Which enzyme in the citrate cycle is inhibited by this poison?
A) "aconitase"
B) "citrate synthase"
C) "isocitrate dehydrogenase"
D) " -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase"
A) "aconitase"
B) "citrate synthase"
C) "isocitrate dehydrogenase"
D) " -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which enzyme in the citrate cycle is activated by CoA?
A) "pyruvate dehydrogenase"
B) "citrate synthase"
C) "isocitrate dehydrogenase"
D) " -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase"
A) "pyruvate dehydrogenase"
B) "citrate synthase"
C) "isocitrate dehydrogenase"
D) " -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Regeneration of NAD+ and FAD inside the mitochondrial matrix is required because
A) anabolic reactions generally require them.
B) they produce GDP through the citrate cycle.
C) they transport pyruvate through the matrix.
D) they maintain flux through the citrate cycle.
A) anabolic reactions generally require them.
B) they produce GDP through the citrate cycle.
C) they transport pyruvate through the matrix.
D) they maintain flux through the citrate cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the purpose of the first 3 steps in the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction?
A) regenerate the oxidized form of lipoamide
B) form NADH
C) transfer electrons
D) form acetyl-CoA
A) regenerate the oxidized form of lipoamide
B) form NADH
C) transfer electrons
D) form acetyl-CoA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Identify the E2 subunit in the reaction schematic of the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction below. 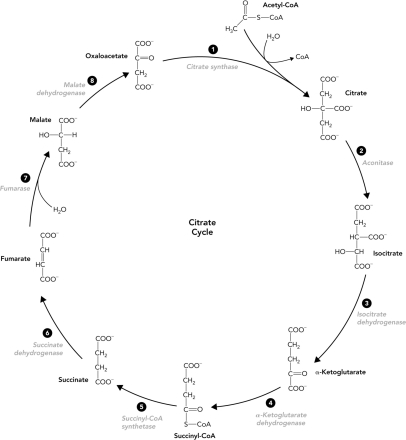
A) pyruvate dehydrogenase
B) dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase
C) dihydrolipopyl acetyltransferase
D) flavin adenine dinucleotide

A) pyruvate dehydrogenase
B) dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase
C) dihydrolipopyl acetyltransferase
D) flavin adenine dinucleotide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A patient seeks medical attention for ulcerous skin lesions. The patient is diagnosed with
A) arsenic exposure.
B) a deficiency in vitamin B3.
C) beriberi.
D) cheilosis.
A) arsenic exposure.
B) a deficiency in vitamin B3.
C) beriberi.
D) cheilosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The disease beriberi is a result of which vitamin deficiency?
A) thiamine
B) pantothenic acid
C) riboflavin
D) niacin
A) thiamine
B) pantothenic acid
C) riboflavin
D) niacin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which coenzyme in the citrate cycle is affected by arsenic?
A) coenzyme A
B) thiamine pyrophosphate
C) dihydrolipopyl acetyltransferase
D) flavin adenine dinucleotide
A) coenzyme A
B) thiamine pyrophosphate
C) dihydrolipopyl acetyltransferase
D) flavin adenine dinucleotide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
How would an increase in Ca2+ be expected to affect the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction?
A) The pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase enzyme activity would increase, resulting in an inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase activity.
B) The last step of the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction is blocked, resulting in a decrease in activity.
C) The E1 subunit is phosphorylated by pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, and the catalytic activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase decreases.
D) The pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase-1 enzyme would increase, resulting in pyruvate dehydrogenase activation at an accelerated rate.
A) The pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase enzyme activity would increase, resulting in an inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase activity.
B) The last step of the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction is blocked, resulting in a decrease in activity.
C) The E1 subunit is phosphorylated by pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, and the catalytic activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase decreases.
D) The pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase-1 enzyme would increase, resulting in pyruvate dehydrogenase activation at an accelerated rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Identify the coenzyme that provides a reactive disulfide that participates in the redox reaction in the active site of pyruvate dehydrogenase.
A) NAD+
B) coenzyme A
C) lipoamide
D) thiamine pyrophosphate
A) NAD+
B) coenzyme A
C) lipoamide
D) thiamine pyrophosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Coenzyme A is derived from which of the following vitamins?
A) thiamine
B) pantothenic acid
C) riboflavin
D) niacin
A) thiamine
B) pantothenic acid
C) riboflavin
D) niacin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which vitamin is the precursor to the coenzyme that functions as a reductant in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in the final step of the reaction?
A) thiamine
B) pantothenic acid
C) riboflavin
D) niacin
A) thiamine
B) pantothenic acid
C) riboflavin
D) niacin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If acetyl-CoA is not metabolized by the citrate cycle, the molecule in the cell
A) undergoes fatty acid metabolism.
B) is transported across the cell membrane.
C) is used to synthesize amino acids.
D) is used during glycolysis.
A) undergoes fatty acid metabolism.
B) is transported across the cell membrane.
C) is used to synthesize amino acids.
D) is used during glycolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Identify the E1 subunit in the reaction schematic of the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction below. 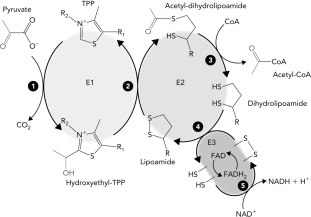
A) pyruvate dehydrogenase
B) dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase
C) dihydrolipopyl acetyltransferase
D) flavin adenine dinucleotide

A) pyruvate dehydrogenase
B) dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase
C) dihydrolipopyl acetyltransferase
D) flavin adenine dinucleotide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which two enzymes in the citrate cycle are affected by arsenic poisoning?
A) pyruvate dehydrogenase and succinate dehydrogenase
B) pyruvate dehydrogenase and -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
C) malate dehydrogenase and succinate dehydrogenase
D) malate dehydrogenase and -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
A) pyruvate dehydrogenase and succinate dehydrogenase
B) pyruvate dehydrogenase and -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
C) malate dehydrogenase and succinate dehydrogenase
D) malate dehydrogenase and -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Classify the reaction that occurs at step 5 in the reaction schematic of the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction below. 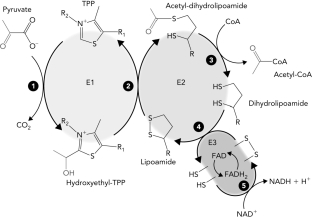
A) isomerization
B) addition
C) oxidation reduction
D) decarboxylation

A) isomerization
B) addition
C) oxidation reduction
D) decarboxylation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Classify the reaction that occurs at step 4 in the reaction schematic of the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction below. 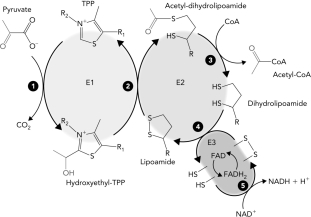
A) isomerization
B) addition
C) oxidation reduction
D) decarboxylation

A) isomerization
B) addition
C) oxidation reduction
D) decarboxylation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Pantothenic acid is essential for life because it is the vitamin precursor to the molecule that
A) provides a reactive disulfide that can participate in redox reactions within the enzyme active site of pyruvate dehydrogenase.
B) can accept one or two electrons in redox reactions in the cell.
C) is involved in at least 200 redox reactions in the cell.
D) is a cofactor in the biosynthetic pathways that produce fatty acids, acetylcholine, heme, and cholesterol.
A) provides a reactive disulfide that can participate in redox reactions within the enzyme active site of pyruvate dehydrogenase.
B) can accept one or two electrons in redox reactions in the cell.
C) is involved in at least 200 redox reactions in the cell.
D) is a cofactor in the biosynthetic pathways that produce fatty acids, acetylcholine, heme, and cholesterol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Arsenite affects the lipoamide coenzymes of the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction by
A) acting as a competitive inhibitor.
B) covalently modifying the coenzyme.
C) being a noncompetitive inhibitor.
D) modifying the coenzyme through electrostatic interactions.
A) acting as a competitive inhibitor.
B) covalently modifying the coenzyme.
C) being a noncompetitive inhibitor.
D) modifying the coenzyme through electrostatic interactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In linked metabolic pathways, the oxidants in subsequent reactions must
A) result in negative E ' values at each reaction step.
B) result in positive G ' values at each reaction step.
C) have progressively lower standard reduction potentials.
D) have progressively higher standard reduction potentials.
A) result in negative E ' values at each reaction step.
B) result in positive G ' values at each reaction step.
C) have progressively lower standard reduction potentials.
D) have progressively higher standard reduction potentials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Classify the reaction that occurs at step 1 in the reaction schematic of the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction below. 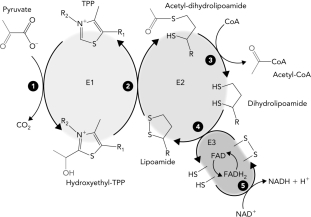
A) isomerization
B) addition
C) oxidation reduction
D) decarboxylation

A) isomerization
B) addition
C) oxidation reduction
D) decarboxylation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is the cause of the irreversible blockage of the catalytic activity of lipoamide-containing enzymes?
A) cheilosis
B) pellagra
C) beriberi
D) arsenic poisoning
A) cheilosis
B) pellagra
C) beriberi
D) arsenic poisoning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Thiamine pyrophosphate functions as a coenzyme in which reactions in the citrate cycle?
A) pyruvate dehydrogenase and succinate dehydrogenase
B) pyruvate dehydrogenase and -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
C) malate dehydrogenase and succinate dehydrogenase
D) malate dehydrogenase and -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
A) pyruvate dehydrogenase and succinate dehydrogenase
B) pyruvate dehydrogenase and -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
C) malate dehydrogenase and succinate dehydrogenase
D) malate dehydrogenase and -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which reaction in the citrate cycle produces NADH? 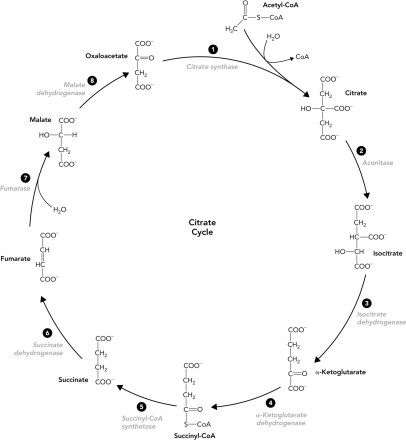
A) 4
B) 5
C) 6
D) 7

A) 4
B) 5
C) 6
D) 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Why is the G ' of the condensation of oxaloacetate and acetyl-CoA highly favorable?
A) The addition of inorganic phosphate provides energy, resulting in the highly favorable nature of this reaction.
B) Allosteric regulations of the reaction cause a release of energy, making the reaction thermodynamically favorable.
C) The iron-sulfur cluster in the enzyme reduces the activation energy of the reaction, resulting in the favorable G ' .
D) The hydrolysis of the thioester bond in citryl-CoA results in the highly exergonic reaction.
A) The addition of inorganic phosphate provides energy, resulting in the highly favorable nature of this reaction.
B) Allosteric regulations of the reaction cause a release of energy, making the reaction thermodynamically favorable.
C) The iron-sulfur cluster in the enzyme reduces the activation energy of the reaction, resulting in the favorable G ' .
D) The hydrolysis of the thioester bond in citryl-CoA results in the highly exergonic reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How is the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction regulated?
A) pH and enzyme conformation
B) pH and the protonation state of the active site
C) allosteric control and covalent modification
D) product inhibition
A) pH and enzyme conformation
B) pH and the protonation state of the active site
C) allosteric control and covalent modification
D) product inhibition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which reaction in the citrate cycle produces FADH2? 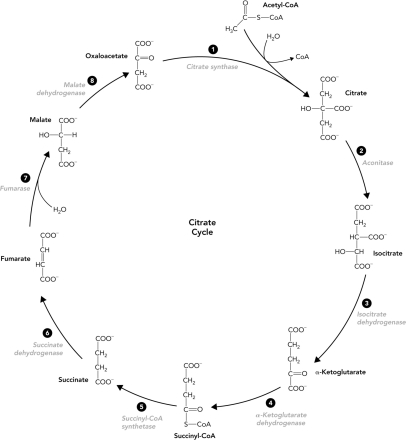
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6

A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An in vitro study shows that -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase is inhibited in the citrate cycle. What is a possible explanation for this inhibition?
A) high levels of ATP
B) low levels of Ca2+
C) low levels of NADH
D) high levels of ADP
A) high levels of ATP
B) low levels of Ca2+
C) low levels of NADH
D) high levels of ADP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In the citrate cycle, a high concentration of NADH would result in
A) activation of citrate synthase.
B) inhibition of -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase.
C) inhibition of fumarase.
D) activation of -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase.
A) activation of citrate synthase.
B) inhibition of -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase.
C) inhibition of fumarase.
D) activation of -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The reaction catalyzed by __________ is the most exergonic reaction in the citrate cycle.
A) "citrate synthase"
B) "fumarase"
C) "isocitrate dehydrogenase"
D) " -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase"
A) "citrate synthase"
B) "fumarase"
C) "isocitrate dehydrogenase"
D) " -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A high concentration of which molecule would inhibit citrate synthase in the citrate cycle?
A) AMP
B) ADP
C) NAD+
D) ATP
A) AMP
B) ADP
C) NAD+
D) ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which reactions in the citrate cycle produce CO2? 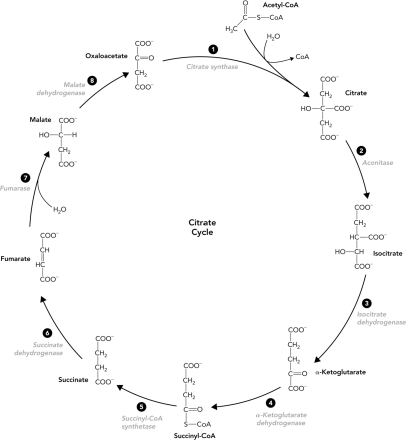
A) 1 and 2
B) 2 and 3
C) 3 and 4
D) 4 and 5

A) 1 and 2
B) 2 and 3
C) 3 and 4
D) 4 and 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which reaction in the citrate cycle produces CO2? 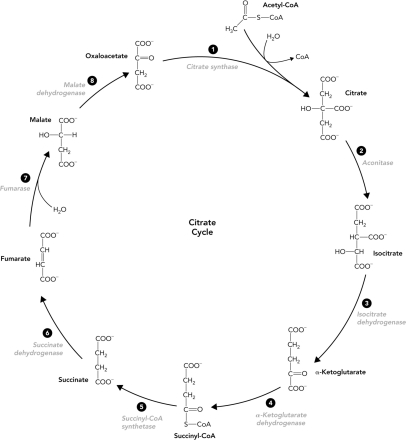
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 5

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which reaction in the citrate cycle produces GTP? 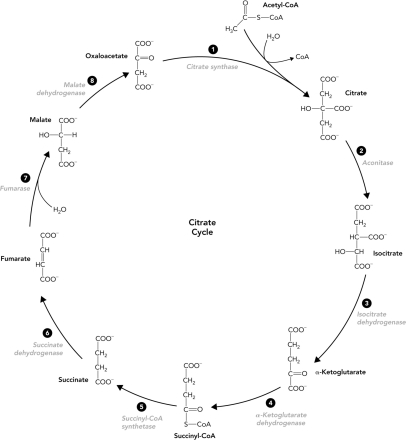
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6

A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
According to the G ' , which of the following exergonic reactions is most likely irreversible under normal cellular conditions and is considered to be the rate-limiting step of the citrate cycle?
A) "citrate synthase"
B) "fumarase"
C) "isocitrate dehydrogenase"
D) " -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase"
A) "citrate synthase"
B) "fumarase"
C) "isocitrate dehydrogenase"
D) " -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which reactions in the citrate cycle produce NADH? 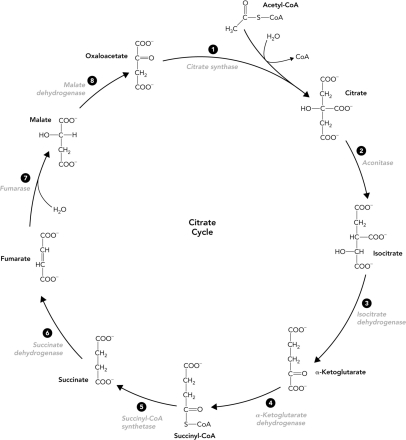
A) 1, 2, and 4
B) 3, 4, and 8
C) 3, 6, and 7
D) 5, 6, and 8

A) 1, 2, and 4
B) 3, 4, and 8
C) 3, 6, and 7
D) 5, 6, and 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The reaction catalyzed by __________is the most endergonic reaction in the citrate cycle.
A) fumarase
B) succinate dehydrogenase
C) malate dehydrogenase
D) aconitase
A) fumarase
B) succinate dehydrogenase
C) malate dehydrogenase
D) aconitase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What enzyme in the citrate cycle is activated by high concentrations of AMP?
A) "isocitrate dehydrogenase"
B) " -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase"
C) "citrate synthase"
D) "succinyl-CoA synthetase"
A) "isocitrate dehydrogenase"
B) " -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase"
C) "citrate synthase"
D) "succinyl-CoA synthetase"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The reaction catalyzed by is likely to be reversible under cellular conditions according to the G ' .
A) "malate dehydrogenase"
B) "citrate synthase"
C) "succinate dehydrogenase"
D) " -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase"
A) "malate dehydrogenase"
B) "citrate synthase"
C) "succinate dehydrogenase"
D) " -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
How would a high NADH to NAD+ ratio be expected to affect the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction?
A) The pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase enzyme activity would increase, resulting in an increase in pyruvate dehydrogenase activity.
B) The last step of the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction is blocked, resulting in a decrease in activity.
C) The E1 subunit is phosphorylated by pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, and the catalytic activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase decreases.
D) The pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase-1 enzyme would increase, resulting in pyruvate dehydrogenase activation at an accelerated rate.
A) The pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase enzyme activity would increase, resulting in an increase in pyruvate dehydrogenase activity.
B) The last step of the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction is blocked, resulting in a decrease in activity.
C) The E1 subunit is phosphorylated by pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, and the catalytic activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase decreases.
D) The pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase-1 enzyme would increase, resulting in pyruvate dehydrogenase activation at an accelerated rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
How would an increased level of acetyl-CoA be expected to affect the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction?
A) The pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase enzyme activity would increase, resulting in an inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase activity.
B) The last step of the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction would be blocked, resulting in a decrease in activity.
C) The E1 subunit would be phosphorylated by pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, and the catalytic activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase would decrease.
D) The pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase-1 enzyme would increase, resulting in pyruvate dehydrogenase activation at an accelerated rate.
A) The pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase enzyme activity would increase, resulting in an inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase activity.
B) The last step of the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction would be blocked, resulting in a decrease in activity.
C) The E1 subunit would be phosphorylated by pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, and the catalytic activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase would decrease.
D) The pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase-1 enzyme would increase, resulting in pyruvate dehydrogenase activation at an accelerated rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
An in vitro study shows that isocitrate dehydrogenase is activated in the citrate cycle. What is a possible explanation for the activation?
A) high levels of ATP
B) low levels of ATP
C) high levels of NADH
D) low levels of AMP
A) high levels of ATP
B) low levels of ATP
C) high levels of NADH
D) low levels of AMP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
High levels of ATP would result in the inhibition of which enzyme in the citrate cycle?
A) succinate dehydrogenase
B) isocitrate dehydrogenase
C) malate dehydrogenase
D) fumarase
A) succinate dehydrogenase
B) isocitrate dehydrogenase
C) malate dehydrogenase
D) fumarase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 A. The electrochemical cell shown here is measuring the reduction potential of Fe2+/Fe3+ using a reference hydrogen half reaction. Write each half reaction on the figure and show the flow of electrons.
A. The electrochemical cell shown here is measuring the reduction potential of Fe2+/Fe3+ using a reference hydrogen half reaction. Write each half reaction on the figure and show the flow of electrons.
B. Do these oxidants have a higher or lower affinity for electrons compared with H+? Explain how you know this using information from the experiment.
 A. The electrochemical cell shown here is measuring the reduction potential of Fe2+/Fe3+ using a reference hydrogen half reaction. Write each half reaction on the figure and show the flow of electrons.
A. The electrochemical cell shown here is measuring the reduction potential of Fe2+/Fe3+ using a reference hydrogen half reaction. Write each half reaction on the figure and show the flow of electrons.B. Do these oxidants have a higher or lower affinity for electrons compared with H+? Explain how you know this using information from the experiment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which citrate cycle intermediate is also used in gluconeogenesis?
A) "oxaloacetate"
B) " -ketoglutarate"
C) "fumarate"
D) "succinate"
A) "oxaloacetate"
B) " -ketoglutarate"
C) "fumarate"
D) "succinate"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
When the citrate cycle is inhibited, which two metabolites are exported to the cytosol for fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis?
A) "malate and succinyl-CoA"
B) "succinyl-CoA and -ketoglutarate"
C) " -ketoglutarate and citrate"
D) "citrate and malate"
A) "malate and succinyl-CoA"
B) "succinyl-CoA and -ketoglutarate"
C) " -ketoglutarate and citrate"
D) "citrate and malate"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A low NADH to NAD+ ratio would activate which enzyme in the citrate cycle?
A) succinyl-CoA synthetase
B) fumarase
C) citrate synthase
D) succinate dehydrogenase
A) succinyl-CoA synthetase
B) fumarase
C) citrate synthase
D) succinate dehydrogenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The citrate cycle is considered to be a(n) pathway.
A) anabolic
B) catabolic
C) anaplerotic
D) amphibolic
A) anabolic
B) catabolic
C) anaplerotic
D) amphibolic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Describe the fate of NADH and FADH2 produced in the citrate cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Use the overall net reaction of the citrate cycle to explain why excess NADH inhibits the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Predict the fate of succinyl-CoA in the cell when it is not in the citrate cycle.
A) cholesterol synthesis
B) heme synthesis
C) gluconeogenesis
D) amino acid synthesis
A) cholesterol synthesis
B) heme synthesis
C) gluconeogenesis
D) amino acid synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which citrate cycle intermediate is siphoned off the citrate cycle during starvation?
A) "succinyl-CoA"
B) "malate"
C) " -ketoglutarate"
D) "fumarate"
A) "succinyl-CoA"
B) "malate"
C) " -ketoglutarate"
D) "fumarate"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What two features of the citrate cycle make it unique compared with linear metabolic pathways?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The anaplerotic reaction catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase requires which coenzyme?
A) niacin
B) biotin
C) riboflavin
D) thiamine
A) niacin
B) biotin
C) riboflavin
D) thiamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
An in vitro study shows that citrate synthase is inhibited in the citrate cycle. What is a possible explanation for this inhibition?
A) high levels of ADP
B) low levels of succinyl-CoA
C) high levels of NADH
D) high levels of AMP
A) high levels of ADP
B) low levels of succinyl-CoA
C) high levels of NADH
D) high levels of AMP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What is the fate of oxaloacetate when it is not used in the citrate cycle?
A) cholesterol synthesis
B) heme synthesis
C) amino acid synthesis
D) gluconeogenesis
A) cholesterol synthesis
B) heme synthesis
C) amino acid synthesis
D) gluconeogenesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which anaplerotic reactions do plants, yeast, and bacteria use to generate oxaloacetate?
A) pyruvate carboxylase
B) malic enzyme
C) phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
D) malate dehydrogenase
A) pyruvate carboxylase
B) malic enzyme
C) phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
D) malate dehydrogenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which citrate cycle metabolite is used as a precursor for heme biosynthesis?
A) "succinyl Co-A"
B) "oxaloacetate"
C) " -ketoglutarate"
D) "malate"
A) "succinyl Co-A"
B) "oxaloacetate"
C) " -ketoglutarate"
D) "malate"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The regulatory mechanism in the citrate cycle involving the NADH to NAD+ ratio is considered to be an example of regulation by
A) pH and protonation state.
B) product inhibition.
C) covalent modification.
D) pH and enzyme conformation.
A) pH and protonation state.
B) product inhibition.
C) covalent modification.
D) pH and enzyme conformation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A high NADH to NAD+ ratio would inhibit which enzyme in the citrate cycle?
A) succinate dehydrogenase
B) succinyl-CoA synthetase
C) aconitase
D) isocitrate dehydrogenase
A) succinate dehydrogenase
B) succinyl-CoA synthetase
C) aconitase
D) isocitrate dehydrogenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which anaplerotic reaction balances the input of oxaloacetate with acetyl-CoA in the citrate cycle by converting pyruvate into oxaloacetate?
A) pyruvate carboxylase
B) malate dehydrogenase
C) malic enzyme
D) pyruvate kinase
A) pyruvate carboxylase
B) malate dehydrogenase
C) malic enzyme
D) pyruvate kinase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Predict the fate of -ketoglutarate when it is not used in the citrate cycle.
A) cholesterol synthesis
B) heme synthesis
C) gluconeogenesis
D) amino acid synthesis
A) cholesterol synthesis
B) heme synthesis
C) gluconeogenesis
D) amino acid synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Compare and contrast the functions of NAD+ and FAD in the citrate cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



