Deck 13: A Macroeconomic Theory of the Small Open Economy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/195
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: A Macroeconomic Theory of the Small Open Economy
1
If a country's exports are greater than its imports, what is the country said to have?
A) a trade surplus
B) a trade deficit
C) a comparative advantage
D) an absolute advantage
A) a trade surplus
B) a trade deficit
C) a comparative advantage
D) an absolute advantage
a trade surplus
2
In an open economy, what does the market for loanable funds equate national saving with?
A) domestic investment
B) net capital outflow
C) the sum of national consumption and net exports
D) the sum of domestic investment and net capital outflow
A) domestic investment
B) net capital outflow
C) the sum of national consumption and net exports
D) the sum of domestic investment and net capital outflow
the sum of domestic investment and net capital outflow
3
Suppose a foreign energy company wants to build a number of new solar parks in Canada. How does this affect the Canadian market for loanable funds?
A) The supply of loanable funds increases.
B) The demand for loanable funds increases.
C) The supply of loanable funds decreases.
D) The demand for loanable funds decreases.
A) The supply of loanable funds increases.
B) The demand for loanable funds increases.
C) The supply of loanable funds decreases.
D) The demand for loanable funds decreases.
The supply of loanable funds decreases.
4
In an open economy, what does the market for loanable funds take as given?
A) saving
B) investment
C) exchange rate
D) real interest rate
A) saving
B) investment
C) exchange rate
D) real interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which statement could be prompted by an interest rate that is temporarily higher in Canada than in the rest of the world?
A) A Bahamian bank purchases a Canadian bond instead of the British bond it had considered purchasing.
B) Canadian firms decide, because interest rates are higher, to do more investment spending.
C) Cole, a Canadian resident, decides to spend his savings on a trip to Hawaii.
D) Canadian net capital outflow increases.
A) A Bahamian bank purchases a Canadian bond instead of the British bond it had considered purchasing.
B) Canadian firms decide, because interest rates are higher, to do more investment spending.
C) Cole, a Canadian resident, decides to spend his savings on a trip to Hawaii.
D) Canadian net capital outflow increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which statement best describes the effects of a decrease in the real interest rate?
A) It discourages people from saving and so increases the quantity of loanable funds demanded.
B) It discourages people from saving and so decreases the quantity of loanable funds demanded.
C) It encourages people to save and so increases the quantity of loanable funds supplied.
D) It encourages people to save and so decreases the quantity of loanable funds supplied.
A) It discourages people from saving and so increases the quantity of loanable funds demanded.
B) It discourages people from saving and so decreases the quantity of loanable funds demanded.
C) It encourages people to save and so increases the quantity of loanable funds supplied.
D) It encourages people to save and so decreases the quantity of loanable funds supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Peter and Wendy are co-owners of the Canadian firm, Tick Tock Airlines. Peter borrows money to build airplanes in Quebec. Wendy borrows money to build airplanes in England. How does this affect the market for loanable funds in Canada?
A) Peter increases the demand for loanable funds.
B) Wendy increases the demand for loanable funds.
C) Peter increases the supply for loanable funds.
D) Wendy increases the supply of loanable funds.
A) Peter increases the demand for loanable funds.
B) Wendy increases the demand for loanable funds.
C) Peter increases the supply for loanable funds.
D) Wendy increases the supply of loanable funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the open-economy macroeconomic model, where does the demand for loanable funds come from?
A) domestic investment
B) net exports
C) net capital outflow
D) the sum of net capital outflow and domestic investment
A) domestic investment
B) net exports
C) net capital outflow
D) the sum of net capital outflow and domestic investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which statement best describes the effects of an increase in real interest rates in Canada?
A) It discourages both Canadian and foreign residents from buying Canadian assets.
B) It encourages both Canadian and foreign residents to buy Canadian assets.
C) It encourages Canadian residents to buy Canadian assets, but discourages foreign residents from buying Canadian assets.
D) It encourages foreign residents to buy Canadian assets, but discourages Canadian residents from buying Canadian assets.
A) It discourages both Canadian and foreign residents from buying Canadian assets.
B) It encourages both Canadian and foreign residents to buy Canadian assets.
C) It encourages Canadian residents to buy Canadian assets, but discourages foreign residents from buying Canadian assets.
D) It encourages foreign residents to buy Canadian assets, but discourages Canadian residents from buying Canadian assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What does the open-economy macroeconomic model examine?
A) the determination of output growth rate and the real interest rate
B) the determination of unemployment rates and the exchange rate
C) the determination of output growth rate and the inflation rate
D) the determination of the trade balance and the exchange rate
A) the determination of output growth rate and the real interest rate
B) the determination of unemployment rates and the exchange rate
C) the determination of output growth rate and the inflation rate
D) the determination of the trade balance and the exchange rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What macroeconomic measures are considered fixed in our open-economy model?
A) the exchange rate, GDP, and the world real interest rate
B) the exchange rate, world real interest rate, and the inflation rate
C) net capital outflow, the inflation rate, and the price level
D) GDP, the price level, and the world real interest rate
A) the exchange rate, GDP, and the world real interest rate
B) the exchange rate, world real interest rate, and the inflation rate
C) net capital outflow, the inflation rate, and the price level
D) GDP, the price level, and the world real interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What effect does a fall in the real interest rate have on the quantity of loanable funds?
A) It increases the quantity demanded and decreases the quantity supplied.
B) It decreases both the quantity demanded and supplied.
C) It increases both the quantity demanded and supplied.
D) It decreases the quantity demanded and increases the quantity supplied.
A) It increases the quantity demanded and decreases the quantity supplied.
B) It decreases both the quantity demanded and supplied.
C) It increases both the quantity demanded and supplied.
D) It decreases the quantity demanded and increases the quantity supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What are the main elements of our open-economy macroeconomic model?
A) the market for loanable funds, the foreign-currency market, and the price level
B) the market for goods and services, the price level, and GDP
C) the market for goods and services, net exports, and GDP
D) the market for loanable funds, net capital outflow, and the foreign-currency market
A) the market for loanable funds, the foreign-currency market, and the price level
B) the market for goods and services, the price level, and GDP
C) the market for goods and services, net exports, and GDP
D) the market for loanable funds, net capital outflow, and the foreign-currency market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What does the open-economy macroeconomic model take as given?
A) GDP, but not the price level
B) the price level, but not GDP
C) both the price level and GDP
D) the exchange rate
A) GDP, but not the price level
B) the price level, but not GDP
C) both the price level and GDP
D) the exchange rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In an open economy, what are the determinants of the prevailing real interest rate?
A) domestic supply and domestic demand for loanable funds
B) world supply and domestic demand for loanable funds
C) world supply and world demand for loanable funds
D) domestic supply and world demand for loanable funds
A) domestic supply and domestic demand for loanable funds
B) world supply and domestic demand for loanable funds
C) world supply and world demand for loanable funds
D) domestic supply and world demand for loanable funds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the open-economy macroeconomic model, how can the market for loanable funds identity be written?
A) S = I
B) S = NCO - I
C) S = I + NCO
D) S + I = NCO
A) S = I
B) S = NCO - I
C) S = I + NCO
D) S + I = NCO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the effect of an increase in the Canadian real interest rate above the world interest rate?
A) Canadians buy more foreign assets, which increases Canadian net capital outflow.
B) Canadians buy more foreign assets, which reduces Canadian net capital outflow.
C) Foreigners buy more Canadian assets, which reduces Canadian net capital outflow.
D) Foreigners buy more Canadian assets, which increases Canadian net capital outflow.
A) Canadians buy more foreign assets, which increases Canadian net capital outflow.
B) Canadians buy more foreign assets, which reduces Canadian net capital outflow.
C) Foreigners buy more Canadian assets, which reduces Canadian net capital outflow.
D) Foreigners buy more Canadian assets, which increases Canadian net capital outflow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What does a higher real interest rate lower the quantity of?
A) national saving
B) net capital outflow
C) loanable funds demanded
D) loanable funds supplied
A) national saving
B) net capital outflow
C) loanable funds demanded
D) loanable funds supplied

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What does a lower real interest rate decrease the quantity of?
A) loanable funds demanded
B) loanable funds supplied
C) domestic investment
D) net capital outflow
A) loanable funds demanded
B) loanable funds supplied
C) domestic investment
D) net capital outflow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the open-economy macroeconomic model, where does the supply of loanable funds come from?
A) national saving
B) private saving
C) public saving
D) the sum of domestic investment and net capital outflow
A) national saving
B) private saving
C) public saving
D) the sum of domestic investment and net capital outflow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What would make the equilibrium interest rate decrease and the equilibrium quantity of funds increase?
A) The supply of loanable funds shifts right.
B) The supply of loanable funds shifts left.
C) The demand for loanable funds shifts right.
D) The demand for loanable funds shifts left.
A) The supply of loanable funds shifts right.
B) The supply of loanable funds shifts left.
C) The demand for loanable funds shifts right.
D) The demand for loanable funds shifts left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If the quantity of loanable funds supplied is greater than the quantity demanded, what best describes the difference?
A) There is a surplus of loanable funds, and the interest rate will fall.
B) There is a shortage of loanable funds, and the interest rate will rise.
C) There is a surplus of loanable funds that is used to buy foreign assets.
D) There is a shortage of loanable funds that is used to buy foreign assets.
A) There is a surplus of loanable funds, and the interest rate will fall.
B) There is a shortage of loanable funds, and the interest rate will rise.
C) There is a surplus of loanable funds that is used to buy foreign assets.
D) There is a shortage of loanable funds that is used to buy foreign assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What would make both the equilibrium interest rate and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds decrease?
A) The demand for loanable funds shifts right.
B) The demand for loanable funds shifts left.
C) The supply of loanable funds shifts right.
D) The supply of loanable funds shifts left.
A) The demand for loanable funds shifts right.
B) The demand for loanable funds shifts left.
C) The supply of loanable funds shifts right.
D) The supply of loanable funds shifts left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
At the equilibrium interest rate in the open-macroeconomic model, what is the amount that people want to save?
A) the desired quantity of net capital outflow
B) the desired quantity of domestic investment
C) the desired quantity of net capital outflow plus domestic investment
D) the desired quantity of net capital outflow minus domestic investment
A) the desired quantity of net capital outflow
B) the desired quantity of domestic investment
C) the desired quantity of net capital outflow plus domestic investment
D) the desired quantity of net capital outflow minus domestic investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What changes will a shortage of loanable funds induce in a savings-investment diagram in a closed economy?
A) The demand for loanable funds curve will shift right, so the interest rate will rise.
B) The supply of loanable funds curve will shift left, so the interest rate will fall.
C) There will be no shifts of the curves, but the interest rate will rise.
D) There will be no shifts of the curves, but the interest rate will fall.
A) The demand for loanable funds curve will shift right, so the interest rate will rise.
B) The supply of loanable funds curve will shift left, so the interest rate will fall.
C) There will be no shifts of the curves, but the interest rate will rise.
D) There will be no shifts of the curves, but the interest rate will fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the world real interest rate is less than the real interest rate that would occur in Canada if there was no trade, what should we expect to happen in the supply and demand for loanable funds graph?
A) the supply curve to shift to the left
B) the demand curve to shift to the right
C) net capital outflow to remain unchanged
D) net capital outflow to decrease
A) the supply curve to shift to the left
B) the demand curve to shift to the right
C) net capital outflow to remain unchanged
D) net capital outflow to decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Figure 13-1 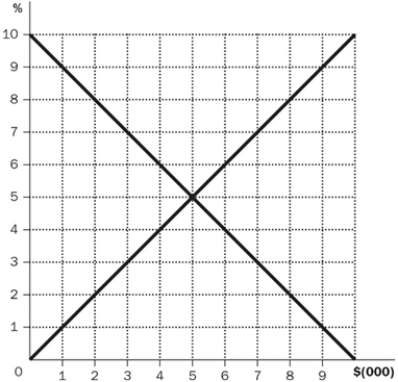
Refer to Figure 13-1. In the figure shown, if the world real interest rate went from 7 to 6 percent, what changes would occur?
A) There would be an increase in net capital outflow.
B) The demand for loanable funds curve to shift right.
C) The supply for loanable funds curve to shift left.
D) There would be a decrease in net capital outflow.

Refer to Figure 13-1. In the figure shown, if the world real interest rate went from 7 to 6 percent, what changes would occur?
A) There would be an increase in net capital outflow.
B) The demand for loanable funds curve to shift right.
C) The supply for loanable funds curve to shift left.
D) There would be a decrease in net capital outflow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Figure 13-1 
Refer to Figure 13-1. If the world interest rate equals 3 percent, what is the net capital outflow?
A) -$4000
B) -$2000
C) $2000
D) $4000

Refer to Figure 13-1. If the world interest rate equals 3 percent, what is the net capital outflow?
A) -$4000
B) -$2000
C) $2000
D) $4000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Figure 13-1 
Refer to Figure 13-1. If the world interest rate equals 7 percent, what is the net capital outflow?
A) -$4000
B) -$2000
C) $2000
D) $4000

Refer to Figure 13-1. If the world interest rate equals 7 percent, what is the net capital outflow?
A) -$4000
B) -$2000
C) $2000
D) $4000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In an open economy, what best identifies the sources of loanable funds?
A) Canadians who consume less than their income and government budget deficit
B) Canadians who consume less than their income and government budget surplus
C) foreigners who buy Canadian bonds and shares of stock and Canadian government surplus
D) foreigners who invest in Canada and Canadian government surplus
A) Canadians who consume less than their income and government budget deficit
B) Canadians who consume less than their income and government budget surplus
C) foreigners who buy Canadian bonds and shares of stock and Canadian government surplus
D) foreigners who invest in Canada and Canadian government surplus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In an open economy, where does the demand for loanable funds come from?
A) from those who want to borrow funds to buy domestic capital goods
B) from those who want to borrow funds to buy foreign assets
C) from those who want to borrow funds to buy either domestic capital goods or foreign assets
D) from those who want to borrow funds to buy Canadian bonds or shares of stock in Canadian companies
A) from those who want to borrow funds to buy domestic capital goods
B) from those who want to borrow funds to buy foreign assets
C) from those who want to borrow funds to buy either domestic capital goods or foreign assets
D) from those who want to borrow funds to buy Canadian bonds or shares of stock in Canadian companies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If the world real interest rate was lower than the interest rate that would occur if the Canadian economy were closed, then what would the Canadian net capital outflow be?
A) positive
B) negative
C) decreasing
D) increasing
A) positive
B) negative
C) decreasing
D) increasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Figure 13-1 
Refer to Figure 13-1. In the figure shown, if the real interest rate is 7 percent, what is the result?
A) surplus of $4000
B) surplus of $2000
C) shortage of $4000
D) shortage of $2000

Refer to Figure 13-1. In the figure shown, if the real interest rate is 7 percent, what is the result?
A) surplus of $4000
B) surplus of $2000
C) shortage of $4000
D) shortage of $2000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In an open economy, what does net capital outflow equal?
A) imports
B) net exports
C) exports
D) net imports
A) imports
B) net exports
C) exports
D) net imports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which statement is consistent with negative net exports?
A) Exports are greater than imports.
B) Net capital outflow is positive.
C) Exports are less than imports.
D) Net capital outflow is zero.
A) Exports are greater than imports.
B) Net capital outflow is positive.
C) Exports are less than imports.
D) Net capital outflow is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In the market for foreign-currency exchange in the open-economy macroeconomic model, what does the amount of net capital outflow represent?
A) the quantity of dollars supplied for the purpose of selling assets domestically
B) the quantity of dollars supplied for the purpose of buying assets abroad
C) the quantity of dollars demanded for the purpose of buying Canadian exports of goods and services
D) the quantity of dollars demanded for the purpose of importing foreign goods and services
A) the quantity of dollars supplied for the purpose of selling assets domestically
B) the quantity of dollars supplied for the purpose of buying assets abroad
C) the quantity of dollars demanded for the purpose of buying Canadian exports of goods and services
D) the quantity of dollars demanded for the purpose of importing foreign goods and services

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Figure 13-1 
Refer to Figure 13-1. In the figure shown, if the real interest rate is 3 percent, what is the quantity of loanable funds demanded?
A) $3000
B) $5000
C) $7000
D) $10000

Refer to Figure 13-1. In the figure shown, if the real interest rate is 3 percent, what is the quantity of loanable funds demanded?
A) $3000
B) $5000
C) $7000
D) $10000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which statement is consistent with negative net exports?
A) Net capital outflow is positive, so foreign assets bought by Canadians are greater than Canadian assets bought by foreigners.
B) Net capital outflow is positive, so Canadian assets bought by foreigners are greater than foreign assets bought by Canadians.
C) Net capital outflow is negative, so foreign assets bought by Canadians are greater than Canadian assets bought by foreigners.
D) Net capital outflow is negative, so Canadian assets bought by foreigners are greater than foreign assets bought by Canadians.
A) Net capital outflow is positive, so foreign assets bought by Canadians are greater than Canadian assets bought by foreigners.
B) Net capital outflow is positive, so Canadian assets bought by foreigners are greater than foreign assets bought by Canadians.
C) Net capital outflow is negative, so foreign assets bought by Canadians are greater than Canadian assets bought by foreigners.
D) Net capital outflow is negative, so Canadian assets bought by foreigners are greater than foreign assets bought by Canadians.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If there is a surplus of loanable funds, what best describes the difference?
A) The quantity demanded is less than the quantity supplied, and the interest rate will rise.
B) The quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied, and the interest rate will fall.
C) The quantity demanded is less than the quantity supplied, and the excess is the net capital outflow
D) The quantity demanded is less than the quantity supplied, and the shortage is the net capital inflow.
A) The quantity demanded is less than the quantity supplied, and the interest rate will rise.
B) The quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied, and the interest rate will fall.
C) The quantity demanded is less than the quantity supplied, and the excess is the net capital outflow
D) The quantity demanded is less than the quantity supplied, and the shortage is the net capital inflow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In the open-economy macroeconomic model, what is net capital outflow equal to?
A) the quantity of dollars supplied in the foreign exchange market
B) the quantity of dollars demanded in the foreign exchange market
C) the quantity of funds supplied in the loanable funds market
D) the quantity of funds demanded in the loanable funds market
A) the quantity of dollars supplied in the foreign exchange market
B) the quantity of dollars demanded in the foreign exchange market
C) the quantity of funds supplied in the loanable funds market
D) the quantity of funds demanded in the loanable funds market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is included in the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange in the open-economy macroeconomic model?
A) An oil company in Nigeria wants to buy oil rigging equipment from a Canadian manufacturer.
B) A Canadian bank loans dollars to Makena, a Canadian resident, who wants to purchase a new car made in Canada.
C) A Canadian-based mutual fund wants to purchase shares issued by a Polish company.
D) A Canadian resident imports a car made in Sweden.
A) An oil company in Nigeria wants to buy oil rigging equipment from a Canadian manufacturer.
B) A Canadian bank loans dollars to Makena, a Canadian resident, who wants to purchase a new car made in Canada.
C) A Canadian-based mutual fund wants to purchase shares issued by a Polish company.
D) A Canadian resident imports a car made in Sweden.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following would tend to shift the supply of dollars in the foreign-currency exchange market model to the left?
A) The exchange rate rises.
B) The exchange rate falls.
C) The expected rate of return on Canadian assets rises.
D) The expected rate of return on Canadian assets falls.
A) The exchange rate rises.
B) The exchange rate falls.
C) The expected rate of return on Canadian assets rises.
D) The expected rate of return on Canadian assets falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What does the value of net exports equal?
A) the value of national saving-net capital outflow
B) the value of public saving
C) the value of national saving minus imports
D) the value of national saving minus domestic investment
A) the value of national saving-net capital outflow
B) the value of public saving
C) the value of national saving minus imports
D) the value of national saving minus domestic investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which statement is consistent with a below-the-equilibrium exchange rate of the dollar?
A) The quantity of dollars supplied is less than the quantity demanded, and the dollar will appreciate.
B) The quantity of dollars supplied is less than the quantity demanded, and the dollar will depreciate.
C) The quantity of dollars supplied is greater than the quantity demanded, and the dollar will appreciate.
D) The quantity of dollars supplied is greater than the quantity demanded, and the dollar will depreciate.
A) The quantity of dollars supplied is less than the quantity demanded, and the dollar will appreciate.
B) The quantity of dollars supplied is less than the quantity demanded, and the dollar will depreciate.
C) The quantity of dollars supplied is greater than the quantity demanded, and the dollar will appreciate.
D) The quantity of dollars supplied is greater than the quantity demanded, and the dollar will depreciate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which statement is consistent with a depreciation of the dollar?
A) Canadian goods become less expensive relative to foreign goods, which makes exports rise and imports fall.
B) Canadian goods become less expensive relative to foreign goods, which makes exports fall and imports rise.
C) Canadian goods become more expensive relative to foreign goods, which makes exports rise and imports fall.
D) Canadian goods become more expensive relative to foreign goods, which makes exports fall and imports rise.
A) Canadian goods become less expensive relative to foreign goods, which makes exports rise and imports fall.
B) Canadian goods become less expensive relative to foreign goods, which makes exports fall and imports rise.
C) Canadian goods become more expensive relative to foreign goods, which makes exports rise and imports fall.
D) Canadian goods become more expensive relative to foreign goods, which makes exports fall and imports rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
According to the theory of purchasing-power parity, what is the shape of the demand curve for foreign-currency exchange?
A) downward sloping
B) upward sloping
C) horizontal
D) vertical
A) downward sloping
B) upward sloping
C) horizontal
D) vertical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What does the identity "net capital outflow = net exports" imply?
A) The supply of dollars equals the demand for dollars in the foreign-currency market.
B) National saving equals domestic investment.
C) The volume of exports equals the volume of imports.
D) Canadian investment abroad is equal to foreign investment in Canada.
A) The supply of dollars equals the demand for dollars in the foreign-currency market.
B) National saving equals domestic investment.
C) The volume of exports equals the volume of imports.
D) Canadian investment abroad is equal to foreign investment in Canada.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the real exchange rate equal to?
A) the relative price of domestic and foreign currency
B) the relative price of domestic and foreign goods
C) the ratio between the domestic and foreign interest rates
D) the nominal exchange rate minus the inflation rate
A) the relative price of domestic and foreign currency
B) the relative price of domestic and foreign goods
C) the ratio between the domestic and foreign interest rates
D) the nominal exchange rate minus the inflation rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Where does the supply of dollars in the foreign-currency exchange market come from?
A) from Canadian national saving
B) from Canadian net capital outflow
C) from domestic investment
D) from foreign demand for Canadian goods
A) from Canadian national saving
B) from Canadian net capital outflow
C) from domestic investment
D) from foreign demand for Canadian goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is the variable that links the loanable funds market and the foreign-currency exchange market?
A) net capital outflow
B) national saving
C) exports
D) imports
A) net capital outflow
B) national saving
C) exports
D) imports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which statement is consistent with an above-the-equilibrium exchange rate of the dollar?
A) The quantity of dollars supplied is greater than the quantity demanded, and the dollar will appreciate.
B) The quantity of dollars supplied is greater than the quantity demanded, and the dollar will depreciate.
C) The quantity of dollars supplied is less than the quantity demanded, and the dollar will appreciate.
D) The quantity of dollars supplied is less than the quantity demanded, and the dollar will depreciate.
A) The quantity of dollars supplied is greater than the quantity demanded, and the dollar will appreciate.
B) The quantity of dollars supplied is greater than the quantity demanded, and the dollar will depreciate.
C) The quantity of dollars supplied is less than the quantity demanded, and the dollar will appreciate.
D) The quantity of dollars supplied is less than the quantity demanded, and the dollar will depreciate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In the market for foreign-currency exchange in the open-economy macroeconomic model, which of the following results from a higher real exchange rate?
A) It makes Canadian goods more expensive relative to foreign goods and reduces the quantity of dollars supplied.
B) It makes Canadian goods more expensive relative to foreign goods and reduces the quantity of dollars demanded.
C) It makes foreign goods more expensive relative to Canadian goods and reduces the quantity of dollars supplied.
D) It makes foreign goods more expensive relative to Canadian goods and reduces the quantity of dollars demanded.
A) It makes Canadian goods more expensive relative to foreign goods and reduces the quantity of dollars supplied.
B) It makes Canadian goods more expensive relative to foreign goods and reduces the quantity of dollars demanded.
C) It makes foreign goods more expensive relative to Canadian goods and reduces the quantity of dollars supplied.
D) It makes foreign goods more expensive relative to Canadian goods and reduces the quantity of dollars demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What is net capital outflow equal to?
A) national saving minus the net exports
B) domestic investment plus national saving
C) national saving minus domestic investment
D) domestic investment minus national saving
A) national saving minus the net exports
B) domestic investment plus national saving
C) national saving minus domestic investment
D) domestic investment minus national saving

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is included in the demand for dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange in the open-market macroeconomic model?
A) A firm in the United States wants to buy softwood lumber from a Canadian firm.
B) A Bahamian bank desires to purchase Canadian government securities.
C) A Canadian citizen wants to buy a bond issued by a Swiss corporation.
D) A Canadian citizen exchanges dollars for UK pounds.
A) A firm in the United States wants to buy softwood lumber from a Canadian firm.
B) A Bahamian bank desires to purchase Canadian government securities.
C) A Canadian citizen wants to buy a bond issued by a Swiss corporation.
D) A Canadian citizen exchanges dollars for UK pounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In the open-economy macroeconomic model, what is the key determinant of net capital outflow?
A) the nominal exchange rate
B) the nominal interest rate
C) the real exchange rate
D) the real interest rate
A) the nominal exchange rate
B) the nominal interest rate
C) the real exchange rate
D) the real interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which statement is consistent with an appreciation of the dollar?
A) Canadian goods become less expensive relative to foreign goods, which makes exports rise and imports fall.
B) Canadian goods become less expensive relative to foreign goods, which makes exports fall and imports rise.
C) Canadian goods become more expensive relative to foreign goods, which makes exports rise and imports fall.
D) Canadian goods become more expensive relative to foreign goods, which makes exports fall and imports rise.
A) Canadian goods become less expensive relative to foreign goods, which makes exports rise and imports fall.
B) Canadian goods become less expensive relative to foreign goods, which makes exports fall and imports rise.
C) Canadian goods become more expensive relative to foreign goods, which makes exports rise and imports fall.
D) Canadian goods become more expensive relative to foreign goods, which makes exports fall and imports rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following would tend to shift the supply of dollars in the foreign-currency exchange market model to the right?
A) The exchange rate rises.
B) The exchange rate falls.
C) The expected rate of return on Canadian assets rises.
D) The expected rate of return on Canadian assets falls.
A) The exchange rate rises.
B) The exchange rate falls.
C) The expected rate of return on Canadian assets rises.
D) The expected rate of return on Canadian assets falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What is the price that balances supply and demand in the market for foreign-currency exchange in the open-economy macroeconomic model?
A) the nominal exchange rate
B) the nominal interest rate
C) the real exchange rate
D) the real interest rate
A) the nominal exchange rate
B) the nominal interest rate
C) the real exchange rate
D) the real interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What is the supply and demand for loanable funds equation in an open economy?
A) S = I
B) S = NX + NCO
C) S = NCO
D) S = I + NCO
A) S = I
B) S = NX + NCO
C) S = NCO
D) S = I + NCO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In the open-economy macroeconomic model, what does the quantity of dollars demanded in the foreign-currency exchange market depend on?
A) the real exchange rate and import quotas
B) the real exchange rate and government deficit
C) the real interest rate and import quotas
D) the real interest rate and government deficit
A) the real exchange rate and import quotas
B) the real exchange rate and government deficit
C) the real interest rate and import quotas
D) the real interest rate and government deficit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If Canadian citizens decide to save a smaller fraction of their incomes, which statement would best describe the effects?
A) Canadian domestic investment increases, and Canadian net capital outflow increases.
B) Canadian domestic investment increases, and Canadian net capital outflow decreases.
C) Canadian domestic investment decreases, and Canadian net capital outflow increases.
D) Canadian domestic investment decreases, and Canadian net capital outflow decreases.
A) Canadian domestic investment increases, and Canadian net capital outflow increases.
B) Canadian domestic investment increases, and Canadian net capital outflow decreases.
C) Canadian domestic investment decreases, and Canadian net capital outflow increases.
D) Canadian domestic investment decreases, and Canadian net capital outflow decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In the open-economy macroeconomic model, what would make Trinidad's net capital outflow decrease?
A) a decrease in Canadian interest rates
B) a decrease in Trinidadian interest rates
C) an appreciation of the Trinidadian dollar
D) an increase in Trinidad's net exports
A) a decrease in Canadian interest rates
B) a decrease in Trinidadian interest rates
C) an appreciation of the Trinidadian dollar
D) an increase in Trinidad's net exports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What are the effects of an increase in the supply of loanable funds?
A) Net capital outflow and the real exchange rate both increase.
B) Net capital outflow and the real exchange rate both decrease.
C) Net capital outflow increases, and the real exchange rate decreases.
D) Net capital outflow decreases, and the real exchange rate increases.
A) Net capital outflow and the real exchange rate both increase.
B) Net capital outflow and the real exchange rate both decrease.
C) Net capital outflow increases, and the real exchange rate decreases.
D) Net capital outflow decreases, and the real exchange rate increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If Canadian citizens decide to purchase more foreign assets at each interest rate, which statement would best describe the effects?
A) The real interest rate increases, the real exchange rate of the dollar appreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow decreases.
B) The real interest rate increases, the real exchange rate of the dollar depreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow increases.
C) The real interest rate decreases, the real exchange rate of the dollar depreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow decreases.
D) The real interest rate decreases, the real exchange rate of the dollar appreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow increases.
A) The real interest rate increases, the real exchange rate of the dollar appreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow decreases.
B) The real interest rate increases, the real exchange rate of the dollar depreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow increases.
C) The real interest rate decreases, the real exchange rate of the dollar depreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow decreases.
D) The real interest rate decreases, the real exchange rate of the dollar appreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Suppose that Peru has a budget surplus, and then goes into deficit. Which statement best predicts the consequences?
A) National saving would increase, and Peru's supply of loanable funds would shift to the left.
B) National saving would increase, and Peru's demand for loanable funds would shift to the right.
C) National saving would decrease, and Peru's supply of loanable funds would shift to the left.
D) National saving would decrease, and Peru's demand for loanable funds would shift to the right.
A) National saving would increase, and Peru's supply of loanable funds would shift to the left.
B) National saving would increase, and Peru's demand for loanable funds would shift to the right.
C) National saving would decrease, and Peru's supply of loanable funds would shift to the left.
D) National saving would decrease, and Peru's demand for loanable funds would shift to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If Canadian firms decide to invest more domestically at each interest rate, which statement would best describe the results?
A) The real interest rate decreases, the real exchange rate of the dollar depreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow decreases.
B) The real interest rate decreases, the real exchange rate of the dollar appreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow increases.
C) The real interest rate increases, the real exchange rate of the dollar appreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow decreases.
D) The real interest rate increases, the real exchange rate of the dollar depreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow increases.
A) The real interest rate decreases, the real exchange rate of the dollar depreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow decreases.
B) The real interest rate decreases, the real exchange rate of the dollar appreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow increases.
C) The real interest rate increases, the real exchange rate of the dollar appreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow decreases.
D) The real interest rate increases, the real exchange rate of the dollar depreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which statement best predicts the effects of an increase in the supply of loanable funds?
A) The interest rate and the real exchange rate both increase.
B) The interest rate and the real exchange rate both decrease.
C) The interest rate increases, and the real exchange rate decreases.
D) The interest rate decreases, and the real exchange rate increases.
A) The interest rate and the real exchange rate both increase.
B) The interest rate and the real exchange rate both decrease.
C) The interest rate increases, and the real exchange rate decreases.
D) The interest rate decreases, and the real exchange rate increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If Canadian citizens decide to save a larger fraction of their incomes, which statement would best identify the effects?
A) The real interest rate decreases, the real exchange rate of the dollar depreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow increases.
B) The real interest rate decreases, the real exchange rate of the dollar appreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow decreases.
C) The real interest rate increases, the real exchange rate of the dollar appreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow decreases.
D) The real interest rate increases, the real exchange rate of the dollar depreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow increases.
A) The real interest rate decreases, the real exchange rate of the dollar depreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow increases.
B) The real interest rate decreases, the real exchange rate of the dollar appreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow decreases.
C) The real interest rate increases, the real exchange rate of the dollar appreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow decreases.
D) The real interest rate increases, the real exchange rate of the dollar depreciates, and Canadian net capital outflow increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The People's Republic of China has had a large trade surplus in recent years. What is the most likely explanation of this surplus?
A) China has a high rate of inflation, which reduces the value of its currency.
B) China has a large supply of labour, so low wages give it a competitive edge.
C) China has many trade barriers, which restrict the ability of other countries to sell their products in China.
D) China has a large amount of saving relative to domestic investment.
A) China has a high rate of inflation, which reduces the value of its currency.
B) China has a large supply of labour, so low wages give it a competitive edge.
C) China has many trade barriers, which restrict the ability of other countries to sell their products in China.
D) China has a large amount of saving relative to domestic investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which statement best predicts the effects of a fall in the Canadian real interest rate?
A) Owning Canadian assets becomes less attractive, and net capital outflow rises.
B) Owning Canadian assets becomes less attractive, and net capital outflow falls.
C) Owning Canadian assets becomes more attractive, and net capital outflow rises.
D) Owning Canadian assets becomes more attractive, and net capital outflow falls.
A) Owning Canadian assets becomes less attractive, and net capital outflow rises.
B) Owning Canadian assets becomes less attractive, and net capital outflow falls.
C) Owning Canadian assets becomes more attractive, and net capital outflow rises.
D) Owning Canadian assets becomes more attractive, and net capital outflow falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If a government increases its budget deficit, which statement would best describe the consequences?
A) Interest rates and domestic investment rise.
B) Interest rates and domestic investment fall.
C) Interest rates rise, and domestic investment falls.
D) Interest rates fall, and domestic investment rises.
A) Interest rates and domestic investment rise.
B) Interest rates and domestic investment fall.
C) Interest rates rise, and domestic investment falls.
D) Interest rates fall, and domestic investment rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If a country went from a government budget deficit to a surplus, which statement would best predict the consequences?
A) National saving would increase, shifting the supply of loanable funds right.
B) National saving would increase, shifting the supply of loanable funds left.
C) National saving would decrease, shifting the demand for loanable funds right.
D) National saving would decrease, shifting the demand for loanable funds left.
A) National saving would increase, shifting the supply of loanable funds right.
B) National saving would increase, shifting the supply of loanable funds left.
C) National saving would decrease, shifting the demand for loanable funds right.
D) National saving would decrease, shifting the demand for loanable funds left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If a government increases its budget deficit, which statement would best predict the effects?
A) Interest rates rise, and the real exchange rate appreciates.
B) Interest rates fall, and the real exchange rate depreciates.
C) Interest rates rise, and the real exchange rate depreciates.
D) Interest rates fall, and the real exchange rate appreciates.
A) Interest rates rise, and the real exchange rate appreciates.
B) Interest rates fall, and the real exchange rate depreciates.
C) Interest rates rise, and the real exchange rate depreciates.
D) Interest rates fall, and the real exchange rate appreciates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which statement best predicts the effects of an increase in a country's real interest rate?
A) Its net capital outflow and the real exchange rate increase.
B) Its net capital outflow and the real exchange rate decrease.
C) Its net capital outflow increases, and the real exchange rate decreases.
D) Its net capital outflow decreases, and the real exchange rate increases.
A) Its net capital outflow and the real exchange rate increase.
B) Its net capital outflow and the real exchange rate decrease.
C) Its net capital outflow increases, and the real exchange rate decreases.
D) Its net capital outflow decreases, and the real exchange rate increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which statement best predicts the effects of an increase in the Canadian real interest rate?
A) Canadian net capital outflow and net capital outflow of other countries would rise.
B) Canadian net capital outflow and net capital outflow of other countries would fall.
C) Canadian net capital outflow would rise, while net capital outflow of other countries would fall.
D) Canadian net capital outflow would fall, while net capital outflow of other countries would rise.
A) Canadian net capital outflow and net capital outflow of other countries would rise.
B) Canadian net capital outflow and net capital outflow of other countries would fall.
C) Canadian net capital outflow would rise, while net capital outflow of other countries would fall.
D) Canadian net capital outflow would fall, while net capital outflow of other countries would rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If the government of Barbados implemented a policy that reduced national saving, which statement would best predict the consequences?
A) Its real exchange rate would depreciate, and Barbadian net exports would rise.
B) Its real exchange rate would depreciate, and Barbadian net exports would fall.
C) Its real exchange rate would appreciate, and Barbadian net exports would rise.
D) Its real exchange rate would appreciate, and Barbadian net exports would fall.
A) Its real exchange rate would depreciate, and Barbadian net exports would rise.
B) Its real exchange rate would depreciate, and Barbadian net exports would fall.
C) Its real exchange rate would appreciate, and Barbadian net exports would rise.
D) Its real exchange rate would appreciate, and Barbadian net exports would fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If the government of Pakistan made policy changes that increased national saving, which statement would best predict the consequences?
A) The real exchange rate of the rupee would depreciate, and Pakistan net exports would rise.
B) The real exchange rate of the rupee would depreciate, and Pakistan net exports would fall.
C) The real exchange rate of the rupee would appreciate, and Pakistan net exports would rise.
D) The real exchange rate of the rupee would appreciate, and Pakistan net exports would fall.
A) The real exchange rate of the rupee would depreciate, and Pakistan net exports would rise.
B) The real exchange rate of the rupee would depreciate, and Pakistan net exports would fall.
C) The real exchange rate of the rupee would appreciate, and Pakistan net exports would rise.
D) The real exchange rate of the rupee would appreciate, and Pakistan net exports would fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Suppose that the government of Jordan raises its budget deficit. Which statement best predicts the effects of this action?
A) The real exchange rate of the Jordanian dinar would depreciate, and Jordanian net exports would rise.
B) The real exchange rate of the Jordanian dinar would depreciate, and Jordanian net exports would fall.
C) The real exchange rate of the Jordanian dinar would appreciate, and Jordanian net exports would rise.
D) The real exchange rate of the Jordanian dinar would appreciate, and Jordanian net exports would fall.
A) The real exchange rate of the Jordanian dinar would depreciate, and Jordanian net exports would rise.
B) The real exchange rate of the Jordanian dinar would depreciate, and Jordanian net exports would fall.
C) The real exchange rate of the Jordanian dinar would appreciate, and Jordanian net exports would rise.
D) The real exchange rate of the Jordanian dinar would appreciate, and Jordanian net exports would fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
How does a change in government budget affect national saving?
A) An increase in budget deficit increases national saving.
B) An increase in budget surplus increases national saving.
C) A decrease in budget surplus increases national saving.
D) A decrease in budget deficit does not affect national saving.
A) An increase in budget deficit increases national saving.
B) An increase in budget surplus increases national saving.
C) A decrease in budget surplus increases national saving.
D) A decrease in budget deficit does not affect national saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
How does the supply or demand for loanable funds shift when a country decreases its budget deficit?
A) The supply of loanable funds shifts right.
B) The supply of loanable funds shifts left.
C) The demand for loanable funds shifts right.
D) The demand for loanable funds shifts left.
A) The supply of loanable funds shifts right.
B) The supply of loanable funds shifts left.
C) The demand for loanable funds shifts right.
D) The demand for loanable funds shifts left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



