Deck 19: Radioactivity and Nuclear Chemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/116
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Radioactivity and Nuclear Chemistry
1
Describe what changes occur in the atomic nucleus during positron emission.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number decreases.
D) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number increases.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number decreases.
D) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number increases.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.
The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number decreases.
2
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the alpha decay of 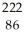 Rn.
Rn.
A)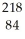 Po
Po
B)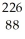 Ra
Ra
C)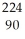 Th
Th
D) Rn
Rn
E) At
At
 Rn.
Rn.A)
 Po
PoB)
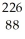 Ra
RaC)
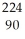 Th
ThD)
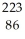 Rn
RnE)
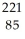 At
At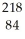 Po
Po 3
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the alpha decay of  Th.
Th.
A) U
U
B) Pa
Pa
C)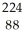 Ra
Ra
D)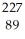 Ac
Ac
E)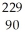 Th
Th
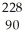 Th.
Th.A)
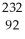 U
UB)
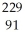 Pa
PaC)
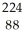 Ra
RaD)
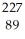 Ac
AcE)
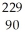 Th
Th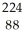 Ra
Ra 4
Identify the radioactive green light that glows in the dark.
A) phenolphthalein
B) radioactivity
C) phosphorescence
D) gamma radiation
E) neon
A) phenolphthalein
B) radioactivity
C) phosphorescence
D) gamma radiation
E) neon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the alpha decay of  Po.
Po.
A)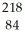 Po
Po
B) Hg
Hg
C) At
At
D) Pb
Pb
E) Rn
Rn
 Po.
Po.A)
 Po
PoB)
 Hg
HgC)
 At
AtD)
 Pb
PbE)
 Rn
Rn
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Describe what changes occur in the atomic nucleus during electron capture.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number decreases.
D) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number increases.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number decreases.
D) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number increases.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which radiation has the highest penetrating power?
A) alpha rays
B) beta rays
C) gamma rays
D) positron emission
E) electron capture
A) alpha rays
B) beta rays
C) gamma rays
D) positron emission
E) electron capture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Positrons are similar in ionizing power and penetrating power to alpha particles.
B) A positron is the antiparticle of the protons.
C) Alpha particles are the heaviest particles of radioactive decay and as such have the highest penetrating power.
D) An alpha particle is a helium 2+ ion.
E) A simultaneous emission of alpha and beta rays is called gamma radiation.
A) Positrons are similar in ionizing power and penetrating power to alpha particles.
B) A positron is the antiparticle of the protons.
C) Alpha particles are the heaviest particles of radioactive decay and as such have the highest penetrating power.
D) An alpha particle is a helium 2+ ion.
E) A simultaneous emission of alpha and beta rays is called gamma radiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the alpha decay of  Po.
Po.
A) Rn
Rn
B) Pb
Pb
C) Ra
Ra
D) Hg
Hg
E) At
At
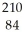 Po.
Po.A)
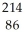 Rn
RnB)
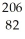 Pb
PbC)
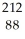 Ra
RaD)
 Hg
HgE)
 At
At
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Write a nuclear equation for the alpha decay of  Am.
Am.
A) Am →
Am → 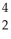 He +
He +  Np
Np
B) Am →
Am → 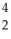 He +
He + 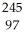 Bk
Bk
C)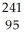 Am →
Am →  e +
e + 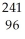 Cm
Cm
D)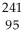 Am →
Am → 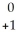 e +
e + 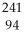 Pu
Pu
E)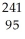 Am →
Am →  n +
n + 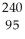 Am
Am
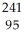 Am.
Am.A)
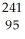 Am →
Am → 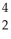 He +
He +  Np
NpB)
 Am →
Am → 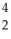 He +
He + 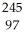 Bk
BkC)
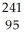 Am →
Am → 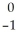 e +
e + 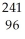 Cm
CmD)
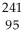 Am →
Am → 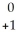 e +
e + 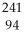 Pu
PuE)
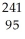 Am →
Am → 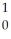 n +
n + 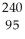 Am
Am
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Write a nuclear equation for the alpha decay of 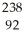 U.
U.
A)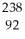 U →
U → 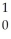 n +
n + 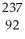 U
U
B)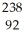 U →
U → 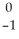 e +
e + 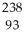 Np
Np
C)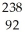 U →
U → 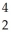 He +
He + 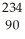 Th
Th
D)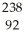 U →
U → 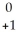 e +
e + 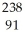 Pa
Pa
E)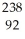 U →
U →  He +
He + 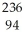 Pu
Pu
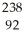 U.
U.A)
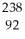 U →
U → 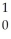 n +
n + 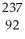 U
UB)
 U →
U →  e +
e + 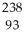 Np
NpC)
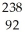 U →
U → 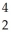 He +
He + 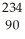 Th
ThD)
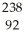 U →
U → 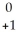 e +
e + 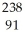 Pa
PaE)
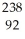 U →
U → 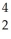 He +
He + 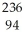 Pu
Pu
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Write the nuclear equation for the beta decay of 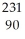 Th.
Th.
A)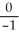 e +
e + 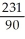 Th →
Th → 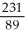 Ac
Ac
B)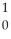 n +
n + 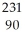 Th →
Th → 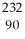 Th
Th
C)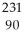 Th →
Th → 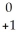 e +
e + 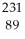 Ac
Ac
D)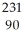 Th →
Th →  He +
He + 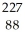 Ra
Ra
E)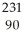 Th →
Th → 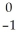 e +
e +  Pa
Pa
 Th.
Th.A)
 e +
e + 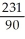 Th →
Th → 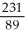 Ac
AcB)
 n +
n + 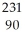 Th →
Th → 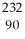 Th
ThC)
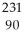 Th →
Th → 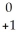 e +
e + 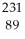 Ac
AcD)
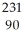 Th →
Th →  He +
He +  Ra
RaE)
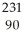 Th →
Th → 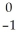 e +
e + 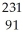 Pa
Pa
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Describe what changes occur in the atomic nucleus during beta decay.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number decreases.
D) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number increases.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number decreases.
D) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number increases.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Describe what changes occur in the atomic nucleus during gamma ray emission.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number decreases.
D) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number increases.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number decreases.
D) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number increases.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Describe what changes occur in the atomic nucleus during alpha decay.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number decreases.
D) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number increases.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number decreases.
D) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number increases.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Gamma rays have the lowest ionizing power of any radioactivity.
B) Alpha radiation has the highest penetrating power of any radioactivity.
C) Beta emitters will do more damage than alpha emitters within the body.
D) Beta radiation has the highest ionizing power of any radioactivity.
E) Gamma radiation has the lowest penetrating power.
A) Gamma rays have the lowest ionizing power of any radioactivity.
B) Alpha radiation has the highest penetrating power of any radioactivity.
C) Beta emitters will do more damage than alpha emitters within the body.
D) Beta radiation has the highest ionizing power of any radioactivity.
E) Gamma radiation has the lowest penetrating power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the alpha decay of 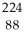 Ra.
Ra.
A)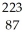 Fr
Fr
B)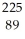 Ac
Ac
C)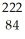 Po
Po
D)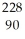 Th
Th
E)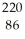 Rn
Rn
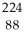 Ra.
Ra.A)
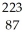 Fr
FrB)
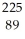 Ac
AcC)
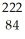 Po
PoD)
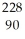 Th
ThE)
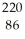 Rn
Rn
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which particle has the lowest penetrating power?
A) alpha particle
B) beta particle
C) gamma rays
D) positron emission
E) electron capture
A) alpha particle
B) beta particle
C) gamma rays
D) positron emission
E) electron capture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Write the nuclear equation for the alpha decay of 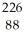 Ra.
Ra.
A)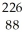 Ra +
Ra + 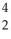 He →
He →  Th
Th
B) Ra →
Ra →  n +
n + 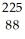 Ra
Ra
C)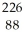 Ra →
Ra → 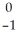 e +
e + 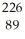 Ac
Ac
D) Ra +
Ra +  e →
e →  Ac
Ac
E) Ra →
Ra →  He +
He +  Rn
Rn
 Ra.
Ra.A)
 Ra +
Ra +  He →
He →  Th
ThB)
 Ra →
Ra →  n +
n + 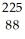 Ra
RaC)
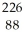 Ra →
Ra → 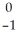 e +
e + 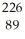 Ac
AcD)
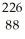 Ra +
Ra + 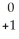 e →
e →  Ac
AcE)
 Ra →
Ra →  He +
He +  Rn
Rn
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Write a nuclear equation for the alpha decay of 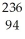 Pu.
Pu.
A)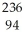 Pu →
Pu → 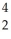 He +
He + 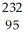 Pu
Pu
B)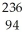 Pu →
Pu → 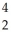 He +
He + 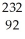 U
U
C)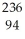 Pu →
Pu → 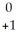 e +
e + 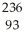 Np
Np
D)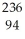 Pu →
Pu →  n +
n + 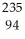 Pu
Pu
E)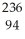 Pu →
Pu → 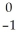 e +
e + 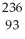 Np
Np
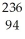 Pu.
Pu.A)
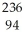 Pu →
Pu → 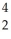 He +
He +  Pu
PuB)
 Pu →
Pu →  He +
He + 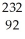 U
UC)
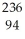 Pu →
Pu → 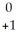 e +
e + 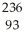 Np
NpD)
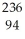 Pu →
Pu →  n +
n + 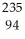 Pu
PuE)
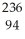 Pu →
Pu → 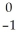 e +
e + 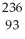 Np
Np
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the beta decay of 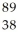 Sr.
Sr.
A)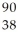 Sr
Sr
B)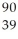 Y
Y
C)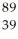 Y
Y
D)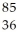 Kr
Kr
E)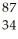 Se
Se
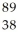 Sr.
Sr.A)
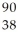 Sr
SrB)
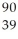 Y
YC)
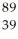 Y
YD)
 Kr
KrE)
 Se
Se
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the beta decay of 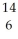 C.
C.
A)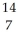 N
N
B)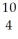 Be
Be
C)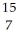 N
N
D)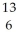 C
C
E)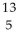 B
B
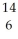 C.
C.A)
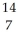 N
NB)
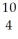 Be
BeC)
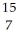 N
ND)
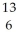 C
CE)
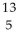 B
B
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the positron emission of 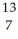 N.
N.
A)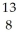 O
O
B)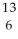 C
C
C)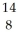 O
O
D)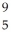 B
B
E)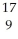 F
F
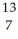 N.
N.A)
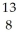 O
OB)
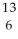 C
CC)
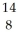 O
OD)
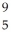 B
BE)
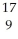 F
F
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear equation: 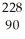 Th →
Th → 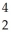 He + ?
He + ?
A)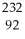 U
U
B)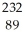 Ac
Ac
C)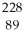 Ac
Ac
D)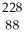 Ra
Ra
E)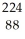 Ra
Ra
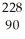 Th →
Th → 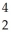 He + ?
He + ?A)
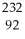 U
UB)
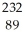 Ac
AcC)
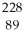 Ac
AcD)
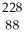 Ra
RaE)
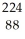 Ra
Ra
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the electron capture by 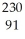 Pa.
Pa.
A)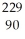 Th
Th
B)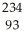 Np
Np
C)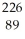 Ac
Ac
D)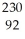 U
U
E)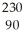 Th
Th
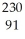 Pa.
Pa.A)
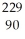 Th
ThB)
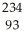 Np
NpC)
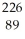 Ac
AcD)
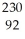 U
UE)
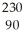 Th
Th
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the positron emission of 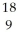 F.
F.
A)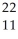 Na
Na
B)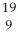 F
F
C)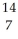 N
N
D)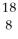 O
O
E)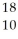 Ne
Ne
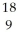 F.
F.A)
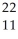 Na
NaB)
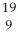 F
FC)
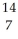 N
ND)
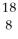 O
OE)
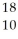 Ne
Ne
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the positron emission of 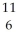 C.
C.
A)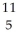 B
B
B)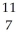 N
N
C)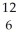 C
C
D)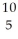 B
B
E)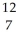 N
N
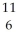 C.
C.A)
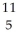 B
BB)
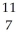 N
NC)
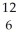 C
CD)
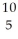 B
BE)
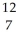 N
N
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the positron emission of 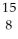 O.
O.
A)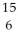 C
C
B)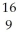 F
F
C)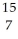 N
N
D)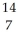 N
N
E) C
C
 O.
O.A)
 C
CB)
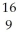 F
FC)
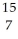 N
ND)
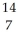 N
NE)
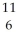 C
C
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the beta decay of 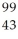 Tc.
Tc.
A)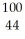 Ru
Ru
B)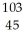 Rh
Rh
C)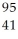 Nb
Nb
D)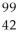 Mo
Mo
E)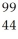 Ru
Ru
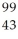 Tc.
Tc.A)
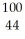 Ru
RuB)
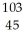 Rh
RhC)
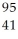 Nb
NbD)
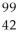 Mo
MoE)
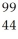 Ru
Ru
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the beta decay of 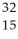 P.
P.
A)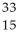 P
P
B)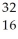 S
S
C)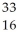 S
S
D)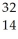 Si
Si
E)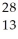 Al
Al
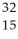 P.
P.A)
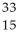 P
PB)
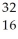 S
SC)
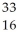 S
SD)
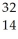 Si
SiE)
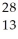 Al
Al
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the beta decay of  Pb.
Pb.
A) Pt
Pt
B) Tl
Tl
C) Hg
Hg
D)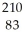 Bi
Bi
E)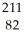 Pb
Pb
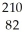 Pb.
Pb.A)
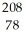 Pt
PtB)
 Tl
TlC)
 Hg
HgD)
 Bi
BiE)
 Pb
Pb
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The following reaction represents what nuclear process? 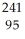 Am →
Am →  He +
He +  Np
Np
A) beta emission
B) neutron bombardment
C) alpha emission
D) electron capture
E) positron emission
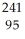 Am →
Am → 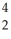 He +
He + 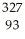 Np
NpA) beta emission
B) neutron bombardment
C) alpha emission
D) electron capture
E) positron emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the electron capture by  Cl.
Cl.
A) Ar
Ar
B)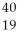 K
K
C)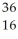 S
S
D)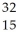 P
P
E)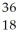 Ar
Ar
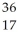 Cl.
Cl.A)
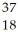 Ar
ArB)
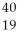 K
KC)
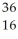 S
SD)
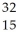 P
PE)
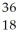 Ar
Ar
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear equation: 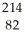 Pb →
Pb → 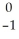 e + ?
e + ?
A)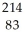 Bi
Bi
B) Tl
Tl
C) Pb
Pb
D) Pb
Pb
E) Tl
Tl
 Pb →
Pb →  e + ?
e + ?A)
 Bi
BiB)
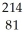 Tl
TlC)
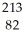 Pb
PbD)
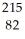 Pb
PbE)
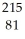 Tl
Tl
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the positron emission of 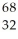 Ge.
Ge.
A)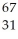 Ga
Ga
B)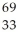 As
As
C)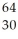 Zn
Zn
D)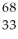 As
As
E)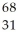 Ga
Ga
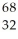 Ge.
Ge.A)
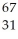 Ga
GaB)
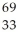 As
AsC)
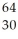 Zn
ZnD)
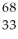 As
AsE)
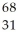 Ga
Ga
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The following reaction represents what nuclear process? 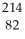 Pb →
Pb → 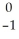 e +
e + 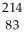 Bi
Bi
A) alpha emission
B) gamma emission
C) electron capture
D) neutron bombardment
E) beta emission
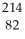 Pb →
Pb → 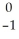 e +
e +  Bi
BiA) alpha emission
B) gamma emission
C) electron capture
D) neutron bombardment
E) beta emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the electron capture by  Be.
Be.
A)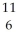 C
C
B)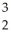 He
He
C)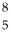 B
B
D)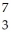 Li
Li
E) B
B
 Be.
Be.A)
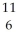 C
CB)
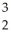 He
HeC)
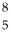 B
BD)
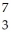 Li
LiE)
 B
B
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the electron capture by 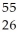 Fe.
Fe.
A)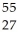 Co
Co
B)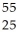 Mn
Mn
C)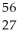 Co
Co
D)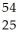 Mn
Mn
E)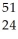 Cr
Cr
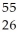 Fe.
Fe.A)
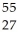 Co
CoB)
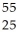 Mn
MnC)
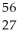 Co
CoD)
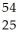 Mn
MnE)
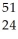 Cr
Cr
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The following reaction represents what nuclear process? 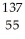 Cs +
Cs + 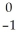 e →
e → 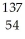 Xe
Xe
A) beta emission
B) positron emission
C) gamma emission
D) electron capture
E) alpha capture
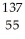 Cs +
Cs + 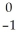 e →
e → 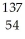 Xe
XeA) beta emission
B) positron emission
C) gamma emission
D) electron capture
E) alpha capture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the electron capture by 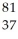 Rb.
Rb.
A)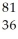 Kr
Kr
B)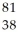 Sr
Sr
C)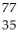 Br
Br
D) Y
Y
E) Kr
Kr
 Rb.
Rb.A)
 Kr
KrB)
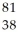 Sr
SrC)
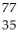 Br
BrD)
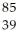 Y
YE)
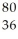 Kr
Kr
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following nuclides are most likely to decay via beta decay?
A) I-131
B) Ar-40
C) F-18
D) Zr-90
E) Pb-206
A) I-131
B) Ar-40
C) F-18
D) Zr-90
E) Pb-206

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Identify the nuclide that has the longest half-life.
A) U
U
B)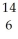 C
C
C)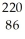 Rn
Rn
D)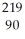 Th
Th
E)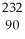 Th
Th
A)
 U
UB)
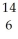 C
CC)
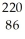 Rn
RnD)
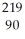 Th
ThE)
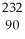 Th
Th
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following nuclides are most likely to decay via positron emission?
A) Cs-137
B) I-131
C) Al-24
D) K-42
E) N-14
A) Cs-137
B) I-131
C) Al-24
D) K-42
E) N-14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Give the maximum age that can be estimated from radiocarbon dating.
A) 100 000 years
B) 1 000 000 years
C) 50 000 years
D) 5000 years
E) 10 000 years
A) 100 000 years
B) 1 000 000 years
C) 50 000 years
D) 5000 years
E) 10 000 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Identify the nuclide that has the shortest half-life.
A)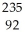 U
U
B)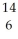 C
C
C)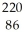 Rn
Rn
D)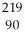 Th
Th
E)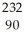 Th
Th
A)
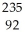 U
UB)
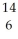 C
CC)
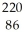 Rn
RnD)
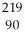 Th
ThE)
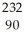 Th
Th
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following nuclides are most likely to decay via beta decay?
A) I-126
B) Al-24
C) N-13
D) Cs-137
E) Na-20
A) I-126
B) Al-24
C) N-13
D) Cs-137
E) Na-20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Nuclides above the valley of stability can become more stable through which of the following processes?
A) beta emission
B) positron emission
C) gamma emission
D) electron capture
E) neutron bombardment
A) beta emission
B) positron emission
C) gamma emission
D) electron capture
E) neutron bombardment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear equation: 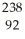 U → ? +
U → ? + 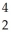 He + 2
He + 2  g
g
A) Th
Th
B) Ra
Ra
C) Pu
Pu
D)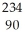 Th
Th
E)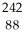 Ra
Ra
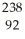 U → ? +
U → ? + 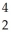 He + 2
He + 2 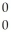 g
gA)
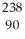 Th
ThB)
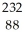 Ra
RaC)
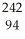 Pu
PuD)
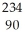 Th
ThE)
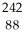 Ra
Ra
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) If the N/Z ratio is too high, there are too many neutrons and the nuclide will convert a neutron to a proton via beta decay.
B) If the N/Z ratio lies somewhere below 1, the nuclide is stable.
C) If the N/Z ratio is too low, there are too many neutrons and the nuclide will undergo beta decay.
D) The valley of stability is the geographic location where many of the known nuclides were first discovered.
E) All stable nuclei have an N/Z ratio equal to 1.
A) If the N/Z ratio is too high, there are too many neutrons and the nuclide will convert a neutron to a proton via beta decay.
B) If the N/Z ratio lies somewhere below 1, the nuclide is stable.
C) If the N/Z ratio is too low, there are too many neutrons and the nuclide will undergo beta decay.
D) The valley of stability is the geographic location where many of the known nuclides were first discovered.
E) All stable nuclei have an N/Z ratio equal to 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Identify the instrument used to detect radiation.
A) cathode ray tube
B) Geiger counter
C) oscillation counter
D) X-ray tube
E) nuclear magnetic resonance instruments
A) cathode ray tube
B) Geiger counter
C) oscillation counter
D) X-ray tube
E) nuclear magnetic resonance instruments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Atoms with Z > ________ are radioactive and decay in one or more steps involving mostly alpha and beta decay.
A) 60
B) 100
C) 83
D) 160
E) 40
A) 60
B) 100
C) 83
D) 160
E) 40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following equations shows the correct relationship between the half-life of a nuclide and the radioactive decay rate constant?
A) ln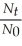 = -
= - 
B)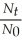 = - ln
= - ln 
C)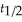 = 0.693 × k
= 0.693 × k
D)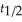 =
= 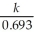
E)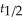 =
= 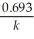
A) ln
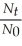 = -
= - 
B)
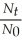 = - ln
= - ln 
C)
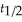 = 0.693 × k
= 0.693 × kD)
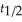 =
= 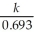
E)
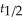 =
= 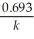

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear equation: 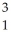 H +
H + 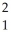 H →
H → 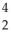 He + ? +
He + ? + 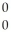 g
g
A)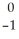 e
e
B)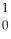 n
n
C)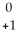 e
e
D)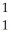 H
H
E)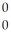 g
g
 H +
H +  H →
H →  He + ? +
He + ? + 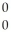 g
gA)
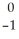 e
eB)
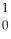 n
nC)
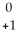 e
eD)
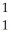 H
HE)
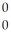 g
g
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following nuclides are most likely to decay via positron emission?
A) Na-26
B) I-121
C) Ca-42
D) S-30
E) Sb-122
A) Na-26
B) I-121
C) Ca-42
D) S-30
E) Sb-122

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What is the correct technique used in radiometric dating of rocks?
A) uranium-238 to lead-206
B) potassium-40 to argon-40
C) carbon-14 to nitrogen-14
D) bismuth-206 to uranium-238
E) calcium-41 to argon-42
A) uranium-238 to lead-206
B) potassium-40 to argon-40
C) carbon-14 to nitrogen-14
D) bismuth-206 to uranium-238
E) calcium-41 to argon-42

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Nuclides below the valley of stability can become more stable through which of the following processes?
A) gamma emission
B) beta emission
C) positron emission
D) neutron emission
E) neutron bombardment
A) gamma emission
B) beta emission
C) positron emission
D) neutron emission
E) neutron bombardment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Stable isotopes with low atomic numbers have an N/Z ratio of 1. What does that imply?
A) The number of neutrons equals the number of protons.
B) The number of neutrons equals the number of electrons plus protons.
C) The number of protons equals the number of electrons.
D) The atomic number equals the atomic mass.
E) The number of protons equals the number of electrons plus neutrons.
A) The number of neutrons equals the number of protons.
B) The number of neutrons equals the number of electrons plus protons.
C) The number of protons equals the number of electrons.
D) The atomic number equals the atomic mass.
E) The number of protons equals the number of electrons plus neutrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear equation: 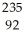 U →
U → 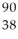 Sr + ? + 2
Sr + ? + 2 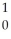 n + 4
n + 4 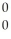 g
g
A) Te
Te
B) Xe
Xe
C)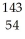 Xe
Xe
D)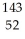 Te
Te
E)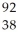 Sr
Sr
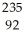 U →
U → 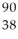 Sr + ? + 2
Sr + ? + 2 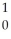 n + 4
n + 4 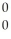 g
gA)
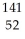 Te
TeB)
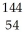 Xe
XeC)
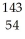 Xe
XeD)
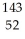 Te
TeE)
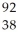 Sr
Sr
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Above what atomic number are there no stable isotopes of any element?
A) 20
B) 92
C) 83
D) 40
E) 89
A) 20
B) 92
C) 83
D) 40
E) 89

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The radioactive decay of ________ is the single greatest source of human exposure to radiation.
A) radon
B) uranium
C) ozone
D) carbon
E) thorium
A) radon
B) uranium
C) ozone
D) carbon
E) thorium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Calculate the mass defect in Fe-56 if the mass of an Fe-56 nucleus is 55.921 u. The mass of a proton is 1.00728 u and the mass of a neutron is 1.008665 u.
A) 0.528 u
B) 3.507 u
C) 0.564 u
D) 1.056 u
E) 0.079 u
A) 0.528 u
B) 3.507 u
C) 0.564 u
D) 1.056 u
E) 0.079 u

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The following reaction represents what nuclear process? 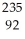 U +
U + 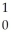 n →
n → 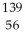 Ba +
Ba + 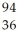 Kr + 3
Kr + 3 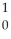 n
n
A) nuclear fission
B) nuclear fusion
C) electron capture
D) alpha decay
E) beta emission
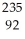 U +
U + 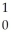 n →
n → 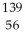 Ba +
Ba + 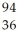 Kr + 3
Kr + 3 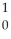 n
nA) nuclear fission
B) nuclear fusion
C) electron capture
D) alpha decay
E) beta emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The following reaction represents which nuclear process? 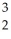 He +
He + 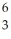 Li → 2
Li → 2 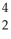 He + p+
He + p+
A) nuclear fission
B) nuclear fusion
C) electron capture
D) alpha decay
E) beta emission
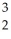 He +
He + 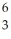 Li → 2
Li → 2 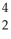 He + p+
He + p+A) nuclear fission
B) nuclear fusion
C) electron capture
D) alpha decay
E) beta emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Determine how many neutrons are produced during the neutron-induced fission of 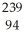 Pu to form
Pu to form 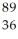 Kr and
Kr and 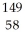 Ce.
Ce.
A) 2
B) 0
C) 3
D) 1
E) 4
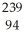 Pu to form
Pu to form 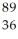 Kr and
Kr and 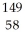 Ce.
Ce.A) 2
B) 0
C) 3
D) 1
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The splitting of the uranium atom is called ________.
A) radioactive cleavage
B) nuclear fission
C) nuclear fusion
D) radioactive merge
E) recombination
A) radioactive cleavage
B) nuclear fission
C) nuclear fusion
D) radioactive merge
E) recombination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Determine the binding energy of an O-16 nucleus. The O-16 nucleus has a mass of 15.9905 u. A proton has a mass of 1.00728 u, a neutron has a mass of 1.008665 u, and 1 u is equivalent to 931 MeV of energy.
A) 8.84 MeV
B) 128 MeV
C) 138 MeV
D) 78.1 MeV
E) 38.2 MeV
A) 8.84 MeV
B) 128 MeV
C) 138 MeV
D) 78.1 MeV
E) 38.2 MeV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A geological sample is found to have a Pb-206/U-238 mass ratio of 0.337/1.00. Assuming there was no Pb-206 present when the sample was formed, how old is it? The half-life of U-238 is 4.5 × 109 years.
A) 7.3 × 1011 years
B) 1.4 × 1010 years
C) 2.4 × 1010 years
D) 2.1 × 109 years
E) 7.1 × 109 years
A) 7.3 × 1011 years
B) 1.4 × 1010 years
C) 2.4 × 1010 years
D) 2.1 × 109 years
E) 7.1 × 109 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The age of an ancient tree trunk is estimated using radiocarbon dating. If the trunk has a C-14 decay rate that is 34% of what it is in living plants, how old is the trunk? The half-life of C-14 is 5730 years.
A) 2.92 × 104 years
B) 1.94 × 104 years
C) 8.92 × 103 years
D) 5.31 × 103 years
E) 1.74 × 102 years
A) 2.92 × 104 years
B) 1.94 × 104 years
C) 8.92 × 103 years
D) 5.31 × 103 years
E) 1.74 × 102 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Determine the binding energy per nucleon of a Mg-24 nucleus. The Mg-24 nucleus has a mass of 23.985042 u. A proton has a mass of 1.00728 u, a neutron has a mass of 1.008665 u, and 1 u is equivalent to 931 MeV of energy.
A) 192 MeV
B) 8.83 MeV
C) 0.113 MeV
D) 106 MeV
E) 4.41 MeV
A) 192 MeV
B) 8.83 MeV
C) 0.113 MeV
D) 106 MeV
E) 4.41 MeV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The following reaction represents what nuclear process? 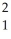 H +
H + 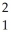 H →
H → 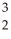 He +
He + 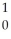 n
n
A) nuclear fusion
B) alpha emission
C) beta emission
D) nuclear fission
E) neutron capture
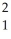 H +
H + 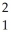 H →
H → 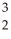 He +
He + 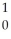 n
nA) nuclear fusion
B) alpha emission
C) beta emission
D) nuclear fission
E) neutron capture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The combination of two light nuclei to form a heavier nuclei is called ________.
A) radioactive cleavage
B) nuclear fission
C) nuclear fusion
D) radioactive merge
E) recombination
A) radioactive cleavage
B) nuclear fission
C) nuclear fusion
D) radioactive merge
E) recombination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Calculate the mass defect in Mo-96 if the mass of a Mo-96 nucleus is 95.962 u. The mass of a proton is 1.00728 u and the mass of a neutron is 1.008665 u.
A) 0.197 u
B) 0.795 u
C) 0.212 u
D) 0.812 u
E) 0.188 u
A) 0.197 u
B) 0.795 u
C) 0.212 u
D) 0.812 u
E) 0.188 u

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Determine how many neutrons are produced during the spontaneous fission of 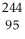 Am to form I-134 and Mo-107.
Am to form I-134 and Mo-107.
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
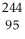 Am to form I-134 and Mo-107.
Am to form I-134 and Mo-107.A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Complete the following equation of nuclear fusion. 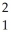 H +
H + 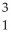 H →
H → 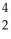 He + ________
He + ________
A)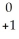 e
e
B)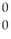 g
g
C)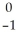 e
e
D)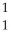 H
H
E)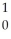 n
n
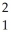 H +
H +  H →
H →  He + ________
He + ________A)
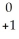 e
eB)
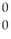 g
gC)
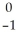 e
eD)
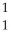 H
HE)
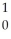 n
n
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Determine the binding energy of a F-19 nucleus. The F-19 nucleus has a mass of 18.99840325 u. A proton has a mass of 1.00728 u, a neutron has a mass of 1.008665 u, and 1 u is equivalent to 931 MeV of energy.
A) 142 MeV
B) 796 MeV
C) 1080 MeV
D) 143 MeV
E) 145 MeV
A) 142 MeV
B) 796 MeV
C) 1080 MeV
D) 143 MeV
E) 145 MeV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Determine the half-life of a nuclide that loses 38.0% of its mass in 387 hours.
A) 277 hours
B) 455 hour
C) 561 hours
D) 639 hours
E) 748 hours
A) 277 hours
B) 455 hour
C) 561 hours
D) 639 hours
E) 748 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Fluorine-18 undergoes positron emission with a half-life of 1.10 × 102 minutes. If a patient is given a 248 mg dose for a PET scan, how long will it take for the amount of fluorine-18 to drop to 83 mg? (Assume that none of the fluorine is excreted from the body.)
A) 99 minutes
B) 1.7 × 102 minutes
C) 1.3 × 102 minutes
D) 3.0 × 102 minutes
E) 2.1 × 102 minutes
A) 99 minutes
B) 1.7 × 102 minutes
C) 1.3 × 102 minutes
D) 3.0 × 102 minutes
E) 2.1 × 102 minutes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Calculate the mass defect in Ni-59 if the mass of a Ni-59 nucleus is 58.69344 u. The mass of a proton is 1.00728 u and the mass of a neutron is 1.008665 u.
A) 0.23212 u
B) 0.77902 u
C) 0.23041 u
D) 0.77589 u
E) 0.22198 u
A) 0.23212 u
B) 0.77902 u
C) 0.23041 u
D) 0.77589 u
E) 0.22198 u

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Write a nuclear equation to describe the neutron-induced fission of U-235 to form Xe-134 and Sr-100. Determine how many neutrons are produced in the reaction.
A) 4
B) 3
C) 1
D) 0
E) 2
A) 4
B) 3
C) 1
D) 0
E) 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The nuclide As-76 has a half-life of 26.0 hours. If a sample of As-76 weighs 344 g, what mass of As-76 remains after 538 minutes?
A) 67.8 g
B) 271 g
C) 144 g
D) 437 g
E) 251 g
A) 67.8 g
B) 271 g
C) 144 g
D) 437 g
E) 251 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



