Deck 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/155
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory
1
Use Lewis theory to determine the chemical formula for the compound formed between Rb and S.
A) RbS
B) RbS2
C) Rb2S
D) Rb2S3
E) Rb3S2
A) RbS
B) RbS2
C) Rb2S
D) Rb2S3
E) Rb3S2
Rb2S
2
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) An ionic bond is much stronger than most covalent bonds.
B) An ionic bond is formed through the sharing of electrons.
C) Ionic compounds at room temperature typically conduct electricity.
D) Once dissolved in water, ionic compounds rarely conduct electricity.
E) None of the above is true.
A) An ionic bond is much stronger than most covalent bonds.
B) An ionic bond is formed through the sharing of electrons.
C) Ionic compounds at room temperature typically conduct electricity.
D) Once dissolved in water, ionic compounds rarely conduct electricity.
E) None of the above is true.
An ionic bond is much stronger than most covalent bonds.
3
Use Lewis theory to determine the chemical formula for the compound formed between Ca and N.
A) CaN
B) Ca3N2
C) CaN2
D) Ca2N
E) Ca2N3
A) CaN
B) Ca3N2
C) CaN2
D) Ca2N
E) Ca2N3
Ca3N2
4
Which of the following represent the Lewis structure for Ca2⁺?
A)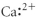
B)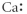
C)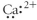
D)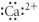
E)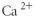
A)
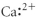
B)
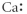
C)
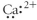
D)
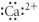
E)
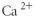

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following represent the Lewis structure for Cl?
A)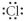
B)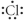
C)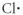
D)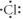
E)
A)
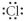
B)
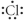
C)
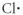
D)
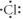
E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Identify the compound with ionic bonding.
A) NaCl
B) CH4
C) H2O
D) H2
E) CO2
A) NaCl
B) CH4
C) H2O
D) H2
E) CO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Identify an ionic bond.
A) Electrons are pooled.
B) Electrons are shared.
C) Electrons are transferred.
D) Electrons are gained.
E) Electrons are lost.
A) Electrons are pooled.
B) Electrons are shared.
C) Electrons are transferred.
D) Electrons are gained.
E) Electrons are lost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Identify the compound with covalent bonding.
A) NaF
B) CaO
C) CH3NH2
D) K2O
E) SrBr2
A) NaF
B) CaO
C) CH3NH2
D) K2O
E) SrBr2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Identify the compound or element with metallic bonding.
A) NaCl
B) Li
C) H2O
D) He
E) S
A) NaCl
B) Li
C) H2O
D) He
E) S

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following represent the Lewis structure for Br⁻?
A)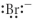
B)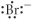
C)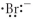
D)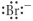
E)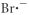
A)
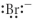
B)
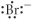
C)
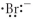
D)
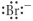
E)
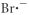

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following represent the Lewis structure for Mg?
A)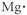
B)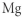
C)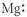
D)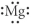
E)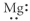
A)
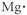
B)
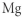
C)
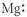
D)
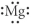
E)
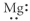

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following represent the Lewis structure for S2⁻?
A)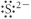
B)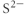
C)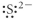
D)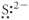
E)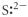
A)
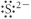
B)
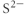
C)
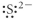
D)
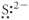
E)
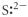

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Identify the compound with ionic bonding.
A) H2O
B) CH4
C) H2
D) CO2
E) RbF
A) H2O
B) CH4
C) H2
D) CO2
E) RbF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) A covalent bond is formed through the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
B) A pair of electrons involved in a covalent bond are sometimes referred to as "lone pairs."
C) It is not possible for two atoms to share more than two electrons.
D) Single bonds are shorter than double bonds.
E) A covalent bond has a lower potential energy than the two separate atoms.
A) A covalent bond is formed through the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
B) A pair of electrons involved in a covalent bond are sometimes referred to as "lone pairs."
C) It is not possible for two atoms to share more than two electrons.
D) Single bonds are shorter than double bonds.
E) A covalent bond has a lower potential energy than the two separate atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Identify the compound with covalent bonding.
A) NaCl
B) KCl
C) H2O
D) CaO
E) SrBr2
A) NaCl
B) KCl
C) H2O
D) CaO
E) SrBr2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Use Lewis theory to determine the chemical formula for the compound formed between Mg and Br.
A) MgBr
B) Mg2Br3
C) Mg3Br2
D) MgBr2
E) Mg2Br
A) MgBr
B) Mg2Br3
C) Mg3Br2
D) MgBr2
E) Mg2Br

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Identify the substance that conducts electricity.
A) NaCl dissolved in water
B) solid NaCl
C) water
D) solid sugar
E) sugar dissolved in water
A) NaCl dissolved in water
B) solid NaCl
C) water
D) solid sugar
E) sugar dissolved in water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Identify the compound with covalent bonding.
A) Li2S
B) SrO
C) CaI2
D) C2Cl4
E) SrBr2
A) Li2S
B) SrO
C) CaI2
D) C2Cl4
E) SrBr2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Identify the compound with ionic bonding.
A) SrBr2
B) CH3CH2CH3
C) CH4
D) H2
E) CO2
A) SrBr2
B) CH3CH2CH3
C) CH4
D) H2
E) CO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following represent the Lewis structure for N?
A)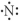
B)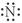
C)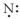
D)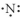
E)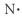
A)
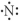
B)
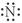
C)
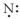
D)
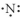
E)
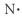

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Identify the compound with the highest magnitude of lattice energy.
A) CsF
B) BaO
C) SrO
D) CaO
A) CsF
B) BaO
C) SrO
D) CaO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Place the following in order of increasing magnitude of lattice energy. MgO LiI CaS
A) CaS < MgO < LiI
B) LiI < CaS < MgO
C) MgO < CaS < LiI
D) LiI < MgO < CaS
E) MgO < LiI < CaS
A) CaS < MgO < LiI
B) LiI < CaS < MgO
C) MgO < CaS < LiI
D) LiI < MgO < CaS
E) MgO < LiI < CaS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Use Lewis theory to determine the chemical formula for the compound formed between Al and O.
A) Al3O2
B) Al2O3
C) AlO2
D) Al2O
E) AlO
A) Al3O2
B) Al2O3
C) AlO2
D) Al2O
E) AlO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Place the following in order of increasing magnitude of lattice energy. CaO MgO SrS
A) MgO < CaO < SrS
B) SrS < MgO < CaO
C) SrS < CaO < MgO
D) CaO < MgO < SrS
E) CaO < SrS < MgO
A) MgO < CaO < SrS
B) SrS < MgO < CaO
C) SrS < CaO < MgO
D) CaO < MgO < SrS
E) CaO < SrS < MgO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Identify the compound with the lowest magnitude of lattice energy.
A) CsF
B) BaO
C) SrO
D) CaO
A) CsF
B) BaO
C) SrO
D) CaO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Choose the compound below that should have the highest melting point according to the ionic bonding model.
A) AlN
B) MgO
C) NaF
D) CaS
E) RbI
A) AlN
B) MgO
C) NaF
D) CaS
E) RbI

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Choose the compound below that should have the lowest melting point according to the ionic bonding model.
A) LiF
B) NaCl
C) CsI
D) KBr
E) RbI
A) LiF
B) NaCl
C) CsI
D) KBr
E) RbI

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Identify the compound with the lowest magnitude of lattice energy.
A) KCl
B) KBr
C) SrO
D) CaO
A) KCl
B) KBr
C) SrO
D) CaO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Place the following in order of decreasing magnitude of lattice energy. NaF RbBr KCl
A) RbBr > NaF > KCl
B) NaF > KCl > RbBr
C) KCl > NaF > RbBr
D) NaF > RbBr > KCl
E) RbBr > KCl > NaF
A) RbBr > NaF > KCl
B) NaF > KCl > RbBr
C) KCl > NaF > RbBr
D) NaF > RbBr > KCl
E) RbBr > KCl > NaF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Identify the compound with the highest magnitude of lattice energy.
A) MgO
B) BaO
C) SrO
D) CaO
A) MgO
B) BaO
C) SrO
D) CaO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following reactions is associated with the lattice energy of RbI (Δr)?
A) Rb(s) +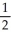 I2(g) → RbI(s)
I2(g) → RbI(s)
B) RbI(s) → Rb⁺(g) + I⁻(g)
C) RbI(s) → Rb(s) +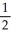 I2(g)
I2(g)
D) RbI(s) → Rb⁺(aq) + I⁻(aq)
E) Rb⁺(g) + I⁻(g) → RbI(s)
A) Rb(s) +
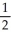 I2(g) → RbI(s)
I2(g) → RbI(s)B) RbI(s) → Rb⁺(g) + I⁻(g)
C) RbI(s) → Rb(s) +
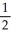 I2(g)
I2(g)D) RbI(s) → Rb⁺(aq) + I⁻(aq)
E) Rb⁺(g) + I⁻(g) → RbI(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Choose the compound below that should have the highest melting point according to the ionic bonding model.
A) SrI2
B) MgF2
C) CaCl2
D) SrF2
E) SrBr2
A) SrI2
B) MgF2
C) CaCl2
D) SrF2
E) SrBr2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Place the following in order of decreasing magnitude of lattice energy. KF MgS RbI
A) RbI > KF > MgS
B) RbI > MgS > KF
C) MgS > RbI > KF
D) KF > RbI > MgS
E) MgS > KF > RbI
A) RbI > KF > MgS
B) RbI > MgS > KF
C) MgS > RbI > KF
D) KF > RbI > MgS
E) MgS > KF > RbI

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Identify the complete electronic configuration for Br-.
A) 1s22s22p63s23p64s24p6
B) 1s22s22p63s23p64s24d104p6
C) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p6
D) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p5
E) 1s22s2p63s2p64s23d104p6
A) 1s22s22p63s23p64s24p6
B) 1s22s22p63s23p64s24d104p6
C) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p6
D) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p5
E) 1s22s2p63s2p64s23d104p6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following reactions is associated with the lattice energy of Li2O (Δr)?
A) Li2O(s) → 2Li⁺(g) + O2⁻(g)
B) 2Li⁺(aq) + O2⁻(aq) → Li2O(s)
C) 2Li⁺(g) + O2⁻(g) → Li2O(s)
D) Li2O(s) → 2Li⁺(aq) + O2⁻(aq)
E) 2Li(s) +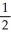 O2(g) → Li2O(s)
O2(g) → Li2O(s)
A) Li2O(s) → 2Li⁺(g) + O2⁻(g)
B) 2Li⁺(aq) + O2⁻(aq) → Li2O(s)
C) 2Li⁺(g) + O2⁻(g) → Li2O(s)
D) Li2O(s) → 2Li⁺(aq) + O2⁻(aq)
E) 2Li(s) +
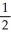 O2(g) → Li2O(s)
O2(g) → Li2O(s)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Identify the compound with the lowest magnitude of lattice energy.
A) BaO
B) MgO
C) SrO
D) CaO
A) BaO
B) MgO
C) SrO
D) CaO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Identify the compound with the highest magnitude of lattice energy.
A) NaCl
B) KCl
C) LiCl
D) CsCl
A) NaCl
B) KCl
C) LiCl
D) CsCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following reactions is associated with the lattice energy of CaS (Δr)?
A) Ca(s) + S(s) → CaS(s)
B) CaS(s) → Ca(s) + S(s)
C) Ca2⁺(aq) + S2⁻(aq) → CaS(s)
D) Ca2⁺(g) + S2⁻(g) → CaS(s)
E) CaS(s) → Ca2⁺(aq) + S2⁻(aq)
A) Ca(s) + S(s) → CaS(s)
B) CaS(s) → Ca(s) + S(s)
C) Ca2⁺(aq) + S2⁻(aq) → CaS(s)
D) Ca2⁺(g) + S2⁻(g) → CaS(s)
E) CaS(s) → Ca2⁺(aq) + S2⁻(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Use Lewis theory to determine the chemical formula for the compound formed between K and I.
A) KI2
B) K2I
C) KI
D) K2I2
A) KI2
B) K2I
C) KI
D) K2I2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Place the following in order of decreasing magnitude of lattice energy. K2O Rb2S Li2O
A) Li2O > K2O > Rb2S
B) Li2O > Rb2S > K2O
C) Rb2S > K2O > Li2O
D) Rb2S > Li2O > K2O
E) K2O > Li2O > Rb2S
A) Li2O > K2O > Rb2S
B) Li2O > Rb2S > K2O
C) Rb2S > K2O > Li2O
D) Rb2S > Li2O > K2O
E) K2O > Li2O > Rb2S

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Use the data given below to construct a Born-Haber cycle to determine the lattice energy of CaO. ΔH°(kJ mol-1)
Ca(s) → Ca(g) 193
Ca(g) → Ca⁺(g) + e⁻ 590
Ca⁺(g) → Ca2⁺(g) + e⁻ 1010
2O(g) → O2(g) -498
O(g) + e⁻ → O⁻(g) -141
O⁻(g) + e⁻ → O2⁻(g) 878
Ca(s) +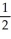 O2(g) → CaO(s) -635
O2(g) → CaO(s) -635
A) -3414 kJ mol-1
B) +1397 kJ mol-1
C) -2667 kJ mol-1
D) +3028 kJ mol-1
E) -2144 kJ mol-1
Ca(s) → Ca(g) 193
Ca(g) → Ca⁺(g) + e⁻ 590
Ca⁺(g) → Ca2⁺(g) + e⁻ 1010
2O(g) → O2(g) -498
O(g) + e⁻ → O⁻(g) -141
O⁻(g) + e⁻ → O2⁻(g) 878
Ca(s) +
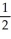 O2(g) → CaO(s) -635
O2(g) → CaO(s) -635A) -3414 kJ mol-1
B) +1397 kJ mol-1
C) -2667 kJ mol-1
D) +3028 kJ mol-1
E) -2144 kJ mol-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Choose the best Lewis structure for NO3⁻.
A)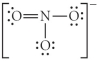
B)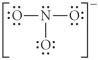
C)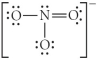
D)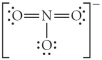
E)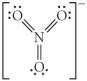
A)
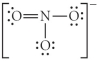
B)
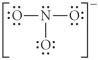
C)
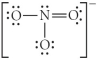
D)
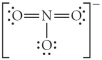
E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Identify the longest bond.
A) single covalent bond
B) double covalent bond
C) triple covalent bond
D) All of the above bonds are the same length.
A) single covalent bond
B) double covalent bond
C) triple covalent bond
D) All of the above bonds are the same length.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Choose the best Lewis structure for CH2Cl2.
A)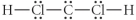
B)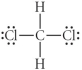
C)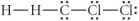
D)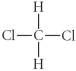
E)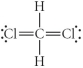
A)
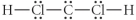
B)

C)
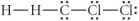
D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A double covalent bond contains ________ of electrons.
A) 0 pairs
B) 1 pair
C) 2 pairs
D) 3 pairs
E) 4 pairs
A) 0 pairs
B) 1 pair
C) 2 pairs
D) 3 pairs
E) 4 pairs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Use the data given below to construct a Born-Haber cycle to determine the heat of formation of KCl. ΔH°(kJ mol-1)
K(s) → K(g) 89
K(g) → K⁺(g) + e⁻ 418
Cl2(g) → 2Cl(g) 244
Cl(g) + e⁻ → Cl⁻(g) -349
KCl(s) → K⁺(g) + Cl⁻(g) 717
A) -1119 kJ mol-1
B) -997 kJ mol-1
C) -437 kJ mol-1
D) +631 kJ mol-1
E) +158 kJ mol-1
K(s) → K(g) 89
K(g) → K⁺(g) + e⁻ 418
Cl2(g) → 2Cl(g) 244
Cl(g) + e⁻ → Cl⁻(g) -349
KCl(s) → K⁺(g) + Cl⁻(g) 717
A) -1119 kJ mol-1
B) -997 kJ mol-1
C) -437 kJ mol-1
D) +631 kJ mol-1
E) +158 kJ mol-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Use the data given below to construct a Born-Haber cycle to determine the bond energy of O2. ΔH°(kJ mol-1)
Na(s) → Na(g) 107
Na(g) → Na⁺(g) + e⁻ 496
O(g) + e⁻ → O⁻(g) -141
O⁻(g) + e⁻ → O2⁻(g) 878
2Na(s) +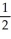 O2(g) → Na2O(s) -416
O2(g) → Na2O(s) -416
2Na⁺(g) + O2⁻(g) → Na2O(s) -2608
A) 426 kJ mol-1
B) 249 kJ mol-1
C) 852 kJ mol-1
D) 498 kJ mol-1
E) 356 kJ mol-1
Na(s) → Na(g) 107
Na(g) → Na⁺(g) + e⁻ 496
O(g) + e⁻ → O⁻(g) -141
O⁻(g) + e⁻ → O2⁻(g) 878
2Na(s) +
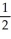 O2(g) → Na2O(s) -416
O2(g) → Na2O(s) -4162Na⁺(g) + O2⁻(g) → Na2O(s) -2608
A) 426 kJ mol-1
B) 249 kJ mol-1
C) 852 kJ mol-1
D) 498 kJ mol-1
E) 356 kJ mol-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Identify the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons in water.
A) 1 bonding pair and 1 lone pair
B) 1 bonding pair and 2 lone pairs
C) 2 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs
D) 2 bonding pairs and 1 lone pair
E) 3 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs
A) 1 bonding pair and 1 lone pair
B) 1 bonding pair and 2 lone pairs
C) 2 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs
D) 2 bonding pairs and 1 lone pair
E) 3 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Choose the bond below that is the strongest.
A) N=O
B) N-I
C) N-O
D) N-S
E) N=N
A) N=O
B) N-I
C) N-O
D) N-S
E) N=N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Identify the complete electronic configuration for S2-.
A) 1s22s22p63s24p6
B) 1s22s22p63s23p6
C) 1s22s22p63s23p5
D) 1s22s23p64s25p6
E) 1s22s2p63s2p6
A) 1s22s22p63s24p6
B) 1s22s22p63s23p6
C) 1s22s22p63s23p5
D) 1s22s23p64s25p6
E) 1s22s2p63s2p6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use the data given below to construct a Born-Haber cycle to determine the second ionization energy of Ca. ΔH°(kJ mol-1)
Ca(s) → Ca(g) 193
Ca(g) → Ca⁺(g) + e⁻ 590.
2O(g) → O2(g) -498
O(g) + e⁻ → O⁻(g) -141
O⁻(g) + e⁻ → O2⁻(g) 878
Ca(s) +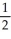 O2(g) → CaO(s) -635
O2(g) → CaO(s) -635
Ca2⁺(g) + O2⁻(g) → CaO(s) -3414
A) 1010 kJ mol-1
B) 1757 kJ mol-1
C) 1508 kJ mol-1
D) -3027 kJ mol-1
E) -1514 kJ mol-1
Ca(s) → Ca(g) 193
Ca(g) → Ca⁺(g) + e⁻ 590.
2O(g) → O2(g) -498
O(g) + e⁻ → O⁻(g) -141
O⁻(g) + e⁻ → O2⁻(g) 878
Ca(s) +
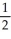 O2(g) → CaO(s) -635
O2(g) → CaO(s) -635Ca2⁺(g) + O2⁻(g) → CaO(s) -3414
A) 1010 kJ mol-1
B) 1757 kJ mol-1
C) 1508 kJ mol-1
D) -3027 kJ mol-1
E) -1514 kJ mol-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A single covalent bond contains ________ of electrons.
A) 0 pairs
B) 1 pair
C) 2 pairs
D) 3 pairs
E) 4 pairs
A) 0 pairs
B) 1 pair
C) 2 pairs
D) 3 pairs
E) 4 pairs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Choose the bond below that is the strongest.
A) C-F
B) C=O
C) C-I
D) I-I
E) C≡N
A) C-F
B) C=O
C) C-I
D) I-I
E) C≡N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Use the data given below to construct a Born-Haber cycle to determine the electron affinity of Br. ΔH°(kJ mol-1)
K(s) → K(g) 89
K(g) → K⁺(g) + e⁻ 419
Br2(g) → 2Br(g) 193
K(s) +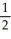 Br2(g) → KBr (s) -394
Br2(g) → KBr (s) -394
KBr(s) → K⁺(g) + Br⁻(g) 674
A) -885 kJ mol-1
B) -325 kJ mol-1
C) +367 kJ mol-1
D) -464 kJ mol-1
E) +246 kJ mol-1
K(s) → K(g) 89
K(g) → K⁺(g) + e⁻ 419
Br2(g) → 2Br(g) 193
K(s) +
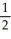 Br2(g) → KBr (s) -394
Br2(g) → KBr (s) -394KBr(s) → K⁺(g) + Br⁻(g) 674
A) -885 kJ mol-1
B) -325 kJ mol-1
C) +367 kJ mol-1
D) -464 kJ mol-1
E) +246 kJ mol-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Identify the complete electronic configuration for Ca2+.
A) 1s22s22p63s24p6
B) 1s22s22p63s23p6
C) 1s22s22p63s23p5
D) 1s22s23p64s25p6
E) 1s22s2p63s2p6
A) 1s22s22p63s24p6
B) 1s22s22p63s23p6
C) 1s22s22p63s23p5
D) 1s22s23p64s25p6
E) 1s22s2p63s2p6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Identify the weakest bond.
A) single covalent bond
B) double covalent bond
C) triple covalent bond
D) All of the above bonds are the same strength.
A) single covalent bond
B) double covalent bond
C) triple covalent bond
D) All of the above bonds are the same strength.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A triple covalent bond contains ________ of electrons.
A) 0 pairs
B) 1 pair
C) 2 pairs
D) 3 pairs
E) 4 pairs
A) 0 pairs
B) 1 pair
C) 2 pairs
D) 3 pairs
E) 4 pairs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Identify the strongest bond.
A) single covalent bond
B) double covalent bond
C) triple covalent bond
D) All of the above bonds are the same strength.
A) single covalent bond
B) double covalent bond
C) triple covalent bond
D) All of the above bonds are the same strength.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Choose the best Lewis structure for NH4⁺.
A)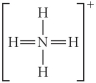
B)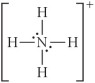
C)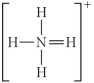
D)
E)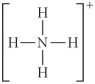
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Identify the shortest bond.
A) single covalent bond
B) double covalent bond
C) triple covalent bond
D) All of the above bonds are the same length.
A) single covalent bond
B) double covalent bond
C) triple covalent bond
D) All of the above bonds are the same length.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Place the following in order of increasing bond length. C-F C-S C-Cl
A) C-S < C-Cl < C-F
B) C-Cl < C-F < C-S
C) C-F < C-S < C-Cl
D) C-F < C-Cl < C-S
E) C-S < C-F < C-Cl
A) C-S < C-Cl < C-F
B) C-Cl < C-F < C-S
C) C-F < C-S < C-Cl
D) C-F < C-Cl < C-S
E) C-S < C-F < C-Cl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Place the following elements in order of decreasing electronegativity. S Cl Se
A) Se > S > Cl
B) Cl > Se > S
C) Se > Cl > S
D) S > Cl > Se
E) Cl > S > Se
A) Se > S > Cl
B) Cl > Se > S
C) Se > Cl > S
D) S > Cl > Se
E) Cl > S > Se

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Place the following in order of decreasing XO bond length, where "X" represents the central atom in each of the following compounds or ions: SiO32⁻ CO2 CO32⁻
A) CO2 > SiO32⁻ > CO32⁻
B) CO2 > CO32⁻ > SiO32⁻
C) CO32⁻ > CO2 > SiO32⁻
D) CO32⁻ > SiO32⁻ > CO2
E) SiO32⁻ > CO32⁻ > CO2
A) CO2 > SiO32⁻ > CO32⁻
B) CO2 > CO32⁻ > SiO32⁻
C) CO32⁻ > CO2 > SiO32⁻
D) CO32⁻ > SiO32⁻ > CO2
E) SiO32⁻ > CO32⁻ > CO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which compound has the highest carbon-carbon bond strength?
A) CH3CH3
B) CH2CH2
C) HCCH
D) All bond strengths are the same.
A) CH3CH3
B) CH2CH2
C) HCCH
D) All bond strengths are the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the bond energies provided to estimate ?rH° for the reaction below. XeF2 +2F2 ? XeF6 ?rH°= ?
Bond Bond Energy (kJ mol-1)
Xe-F 147
F-F 159
A) -429 kJ mol-1
B) +159 kJ mol-1
C) -660 kJ mol-1
D) +176 kJ mol-1
E) -270 kJ mol-1
Bond Bond Energy (kJ mol-1)
Xe-F 147
F-F 159
A) -429 kJ mol-1
B) +159 kJ mol-1
C) -660 kJ mol-1
D) +176 kJ mol-1
E) -270 kJ mol-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Choose the bond below that is the weakest.
A) Na-Cl
B) I-I
C) C=N
D) Li-F
E) C=O
A) Na-Cl
B) I-I
C) C=N
D) Li-F
E) C=O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Place the following in order of decreasing bond length. H-F H-I H-Br
A) H-F > H-Br > H-I
B) H-I > H-F > H-Br
C) H-I > H-Br > H-F
D) H-Br > H-F > H-I
E) H-F > H-I > H-Br
A) H-F > H-Br > H-I
B) H-I > H-F > H-Br
C) H-I > H-Br > H-F
D) H-Br > H-F > H-I
E) H-F > H-I > H-Br

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use the bond energies provided to estimate ΔrH° for the reaction below. 2Br2(l) + C2H2(g) → C2H2Br4(l) ΔrH° = ?
Bond Bond Energy (kJ mol-1)
Br-Br 193
C≡C 837
C-C 347
C-Br 276
C-H 414
A) +407 kJ mol-1
B) -324 kJ mol-1
C) -228 kJ mol-1
D) +573 kJ mol-1
E) -648 kJ mol-1
Bond Bond Energy (kJ mol-1)
Br-Br 193
C≡C 837
C-C 347
C-Br 276
C-H 414
A) +407 kJ mol-1
B) -324 kJ mol-1
C) -228 kJ mol-1
D) +573 kJ mol-1
E) -648 kJ mol-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Place the following elements in order of increasing electronegativity. K Cs P
A) P < K < Cs
B) K < P < Cs
C) Cs < P < K
D) Cs < K < P
E) P < Cs < K
A) P < K < Cs
B) K < P < Cs
C) Cs < P < K
D) Cs < K < P
E) P < Cs < K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Rank the following molecules in decreasing bond energy. Cl2 Br2 F2 I2
A) I2 > Br2 > Cl2 > F2
B) Cl2 > Br2 > F2 > I2
C) I2 > Cl2 > Br2 > F2
D) Cl2 > I2 > F2 > Br2
A) I2 > Br2 > Cl2 > F2
B) Cl2 > Br2 > F2 > I2
C) I2 > Cl2 > Br2 > F2
D) Cl2 > I2 > F2 > Br2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Place the following in order of increasing bond length. NO2⁻ NO3⁻ NO
A) NO < NO2⁻ < NO3⁻
B) NO2⁻ < NO3⁻ < NO
C) NO3⁻ < NO < NO2⁻
D) NO < NO3⁻ < NO2⁻
E) NO3⁻ < NO2⁻ < NO
A) NO < NO2⁻ < NO3⁻
B) NO2⁻ < NO3⁻ < NO
C) NO3⁻ < NO < NO2⁻
D) NO < NO3⁻ < NO2⁻
E) NO3⁻ < NO2⁻ < NO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following processes is exothermic?
A) the second ionization energy of Mg
B) the sublimation of Li
C) the breaking of the bond of I2
D) the formation of NaBr from its constituent elements in their standard state
E) None of the above processes is exothermic
A) the second ionization energy of Mg
B) the sublimation of Li
C) the breaking of the bond of I2
D) the formation of NaBr from its constituent elements in their standard state
E) None of the above processes is exothermic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following processes is endothermic?
A) K⁺(g) + I⁻(g) → KI(s)
B) 2Br(g) → Br2(g)
C) Ca(s) → Ca(g)
D) 2Na(s) +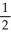 O2(g) → Na2O(s)
O2(g) → Na2O(s)
E) None of the above processes is endothermic.
A) K⁺(g) + I⁻(g) → KI(s)
B) 2Br(g) → Br2(g)
C) Ca(s) → Ca(g)
D) 2Na(s) +
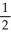 O2(g) → Na2O(s)
O2(g) → Na2O(s)E) None of the above processes is endothermic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Use the bond energies provided to estimate ΔrH° for the reaction below. PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) → PCl5(l) ΔrH° = ?
Bond Bond Energy (kJ mol-1)
Cl-Cl 243
P-Cl 331
A) -243 kJ mol-1
B) -419 kJ mol-1
C) -662 kJ mol-1
D) -67 kJ mol-1
E) -905 kJ mol-1
Bond Bond Energy (kJ mol-1)
Cl-Cl 243
P-Cl 331
A) -243 kJ mol-1
B) -419 kJ mol-1
C) -662 kJ mol-1
D) -67 kJ mol-1
E) -905 kJ mol-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following processes is exothermic?
A) Cl2(g) → 2Cl(g)
B) Br(g) + e⁻ → Br⁻(g)
C) Li(s) → Li(g)
D) NaF(s) → Na⁺(g) + F⁻(g)
E) None of the above processes is exothermic.
A) Cl2(g) → 2Cl(g)
B) Br(g) + e⁻ → Br⁻(g)
C) Li(s) → Li(g)
D) NaF(s) → Na⁺(g) + F⁻(g)
E) None of the above processes is exothermic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Choose the bond below that is the weakest.
A) C≡O
B) N≡N
C) C-I
D) C=S
E) K-Cl
A) C≡O
B) N≡N
C) C-I
D) C=S
E) K-Cl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following processes is endothermic?
A) the reaction associated with the lattice energy of LiCl
B) the reaction associated with the ionization energy of potassium
C) the reaction associated with the heat of formation of CaS
D) the formation of F2 from its elements in their standard states
E) None of the above processes is endothermic.
A) the reaction associated with the lattice energy of LiCl
B) the reaction associated with the ionization energy of potassium
C) the reaction associated with the heat of formation of CaS
D) the formation of F2 from its elements in their standard states
E) None of the above processes is endothermic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Use the bond energies provided to estimate ΔrH° for the reaction below. CH3OH(l) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) ΔrH° = ?
Bond Bond Energy (kJ mol-1)
C-H 414
C-O 360
C=O 799
O=O 498
O-H 464
A) +473 kJ mol-1
B) -91 kJ mol-1
C) -486 kJ mol-1
D) -392 kJ mol-1
E) +206 kJ mol-1
Bond Bond Energy (kJ mol-1)
C-H 414
C-O 360
C=O 799
O=O 498
O-H 464
A) +473 kJ mol-1
B) -91 kJ mol-1
C) -486 kJ mol-1
D) -392 kJ mol-1
E) +206 kJ mol-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which compound has the longest carbon-carbon bond length?
A) CH3CH3
B) CH2CH2
C) HCCH
D) All bond lengths are the same.
A) CH3CH3
B) CH2CH2
C) HCCH
D) All bond lengths are the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Use the bond energies provided to estimate ?rH° for the reaction below. C2H4(g) + H2(g) ? C2H6(g) ?rH°= ?
Bond Bond Energy (kJ mol-1)
C-C 347
C-H 414
C=C 611
C?C 837
H-H 436
A) -128 kJ mol-1
B) +98 kJ mol-1
C) +700 kJ mol-1
D) -102 kJ mol-1
E) -166 kJ mol-1
Bond Bond Energy (kJ mol-1)
C-C 347
C-H 414
C=C 611
C?C 837
H-H 436
A) -128 kJ mol-1
B) +98 kJ mol-1
C) +700 kJ mol-1
D) -102 kJ mol-1
E) -166 kJ mol-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



