Deck 6: Consumer Behaviour
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/73
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Consumer Behaviour
1
The marginal rate of substitution
A)is the amount of one good the consumer is willing to give up in exchange for another so as to keep total satisfaction unchanged.
B)is constant as one moves along a particular indifference curve.
C)is the amount of one good the consumer is willing to give up in exchange for another so as to keep total expenditure unchanged.
D)is equal to the price ratio on the budget line.
E)always has a positive algebraic value.
A)is the amount of one good the consumer is willing to give up in exchange for another so as to keep total satisfaction unchanged.
B)is constant as one moves along a particular indifference curve.
C)is the amount of one good the consumer is willing to give up in exchange for another so as to keep total expenditure unchanged.
D)is equal to the price ratio on the budget line.
E)always has a positive algebraic value.
A
2
FIGURE 6- 12 Sophie consumes two goods - paperback novels and visits to the movies.
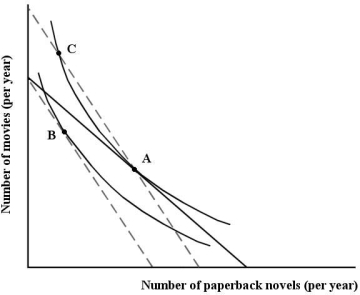
Refer to Figure 6- 12.Sophie's movement from point A to point B is the
A)income effect of an increase in the price of paperback novels.
B)result of a change in her preferences between movies an paperback novels.
C)total effect of a decrease in income.
D)substitution effect of a decrease in the price of paperback novels.
E)total effect of an increase in the price of paperback novels.

Refer to Figure 6- 12.Sophie's movement from point A to point B is the
A)income effect of an increase in the price of paperback novels.
B)result of a change in her preferences between movies an paperback novels.
C)total effect of a decrease in income.
D)substitution effect of a decrease in the price of paperback novels.
E)total effect of an increase in the price of paperback novels.
E
3
Given a particular market demand curve,consumer surplus is
A)less the lower the price and the larger the output.
B)greater the higher the price and the smaller the output.
C)greater the lower the price and the larger the output.
D)less the lower the price and the smaller the output.
E)greater the lower the price and the smaller the output.
A)less the lower the price and the larger the output.
B)greater the higher the price and the smaller the output.
C)greater the lower the price and the larger the output.
D)less the lower the price and the smaller the output.
E)greater the lower the price and the smaller the output.
C
4
The table below shows the quantities of toffee bars and bags of cashews that a consumer could consume over a 1- week period. TABLE 6- 1
-Suppose a utility- maximizing person consumes only two goods,hamburgers and milkshakes.Suppose the price of milkshakes rises and all other variables remain constant.As a result,this person will certainly
A)not increase his consumption of both milkshakes and hamburgers.
B)increase his/her consumption of milkshakes.
C)purchase more milkshakes and fewer hamburgers.
D)consume more hamburgers and the same amount of milkshakes.
E)reduce his/her consumption of both milkshakes and hamburgers.
-Suppose a utility- maximizing person consumes only two goods,hamburgers and milkshakes.Suppose the price of milkshakes rises and all other variables remain constant.As a result,this person will certainly
A)not increase his consumption of both milkshakes and hamburgers.
B)increase his/her consumption of milkshakes.
C)purchase more milkshakes and fewer hamburgers.
D)consume more hamburgers and the same amount of milkshakes.
E)reduce his/her consumption of both milkshakes and hamburgers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The diagram below shows a set of budget lines facing a household.
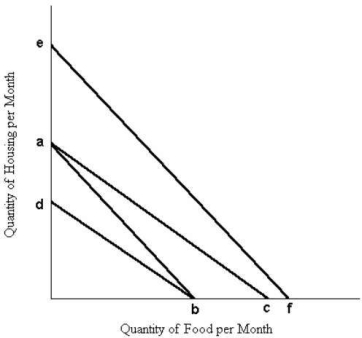 FIGURE 6- 8
FIGURE 6- 8
Refer to Figure 6- 8.The movement of the budget line from ab to ef could be caused by
A)a decrease in money income.
B)an equal percentage increase in the price of both food and housing.
C)a decrease in the price of either food or housing.
D)an equal percentage decrease in the price of both food and housing.
E)an increase in the price of either food or housing.
 FIGURE 6- 8
FIGURE 6- 8Refer to Figure 6- 8.The movement of the budget line from ab to ef could be caused by
A)a decrease in money income.
B)an equal percentage increase in the price of both food and housing.
C)a decrease in the price of either food or housing.
D)an equal percentage decrease in the price of both food and housing.
E)an increase in the price of either food or housing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An equal proportional increase in money income and all money prices will
A)shift the budget line to the right parallel to the original budget line.
B)rotate the budget line inward from the horizontal axis.
C)rotate the budget line inward from the vertical axis.
D)shift the budget line to the left parallel to the original budget line.
E)leave the position of the budget line unchanged.
A)shift the budget line to the right parallel to the original budget line.
B)rotate the budget line inward from the horizontal axis.
C)rotate the budget line inward from the vertical axis.
D)shift the budget line to the left parallel to the original budget line.
E)leave the position of the budget line unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Assume an individual with a downward- sloping demand curve is paying a single price for each unit of some commodity.He will experience consumer surplus on
A)all units that were not bought at that particular price.
B)none of the units.
C)all of the units bought.
D)the first unit only.
E)all units bought with the possible exception of the last unit.
A)all units that were not bought at that particular price.
B)none of the units.
C)all of the units bought.
D)the first unit only.
E)all units bought with the possible exception of the last unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Assume a person reveals the following demand conditions.At a price of $10,quantity demanded is zero; and at a price of $1,quantity demanded is 10 units.
A)The consumer surplus will be zero at a price of $10.
B)Demand decreases as the price decreases.
C)The lower the price the smaller the consumer surplus.
D)The consumer surplus is zero at a price of $1.
E)The consumer surplus will be the area under the entire demand curve.
A)The consumer surplus will be zero at a price of $10.
B)Demand decreases as the price decreases.
C)The lower the price the smaller the consumer surplus.
D)The consumer surplus is zero at a price of $1.
E)The consumer surplus will be the area under the entire demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The Smith family is allocating its monthly household expenditure between only two goods,food and clothing.Suppose that the price of food is $5 per unit,and the price of clothing is $10 per unit and that the marginal utility that the family is receiving from its consumption of food is currently 25.What is the family's marginal utility from its consumption of clothing if it is maximizing its utility?
A)10
B)50
C)25
D)5
E)12.5
A)10
B)50
C)25
D)5
E)12.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Economists use the term "marginal utility" to describe the
A)inverse of the measure of total utility.
B)average utility of each unit of a good consumed.
C)change in total satisfaction caused by consumption of an additional unit of a good.
D)price paid for every unit consumed.
E)total satisfaction received from consumption of a good.
A)inverse of the measure of total utility.
B)average utility of each unit of a good consumed.
C)change in total satisfaction caused by consumption of an additional unit of a good.
D)price paid for every unit consumed.
E)total satisfaction received from consumption of a good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose the price of potatoes falls and we observe a decrease in an individual's purchases of potatoes.Which of the following can we infer?
A)The substitution effect outweighs the income effect.
B)The income effect just offsets the substitution effect.
C)The income effect is negative and outweighs the substitution effect.
D)The income effect is positive and exceeds the substitution effect.
E)The income effect is negative and reinforces the substitution effect.
A)The substitution effect outweighs the income effect.
B)The income effect just offsets the substitution effect.
C)The income effect is negative and outweighs the substitution effect.
D)The income effect is positive and exceeds the substitution effect.
E)The income effect is negative and reinforces the substitution effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Consider the income and substitution effects of price changes.The income effect refers to the change in quantity demanded that occurs as a result of a change in
A)relative prices,with real income held constant.
B)money income,with relative prices held constant.
C)marginal utility,with real income held constant.
D)preferences,with real income held constant.
E)real income,with relative prices held constant.
A)relative prices,with real income held constant.
B)money income,with relative prices held constant.
C)marginal utility,with real income held constant.
D)preferences,with real income held constant.
E)real income,with relative prices held constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The substitution effect of a price change
A)is equal to the income effect for normal goods.
B)will result in the consumer buying less of a good at a lower price.
C)will result in the consumer buying less of a good at a higher price.
D)is equal to the income effect for inferior goods.
E)outweighs the income effect for Giffen goods.
A)is equal to the income effect for normal goods.
B)will result in the consumer buying less of a good at a lower price.
C)will result in the consumer buying less of a good at a higher price.
D)is equal to the income effect for inferior goods.
E)outweighs the income effect for Giffen goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An indifference curve plotted for two different goods on the axes
A)shows the different combinations of two goods that the same income can purchase.
B)shows all combinations of the two goods that give the same level of utility.
C)changes its slope as the relative prices of the two goods change.
D)shifts when real income changes.
E)shows the combinations of the two goods that will just use up a consumer's income.
A)shows the different combinations of two goods that the same income can purchase.
B)shows all combinations of the two goods that give the same level of utility.
C)changes its slope as the relative prices of the two goods change.
D)shifts when real income changes.
E)shows the combinations of the two goods that will just use up a consumer's income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In which of the following situations will an individual's purchasing power be unaffected?
A)money income falls and the price of one good falls
B)money income is cut in half and prices of all goods and services remain constant
C)money income doubles and the prices of all goods and services are cut in half
D)money income is cut in half and the prices of all goods and services fall by 50%
E)money income doubles and the prices of all goods and services remain constant
A)money income falls and the price of one good falls
B)money income is cut in half and prices of all goods and services remain constant
C)money income doubles and the prices of all goods and services are cut in half
D)money income is cut in half and the prices of all goods and services fall by 50%
E)money income doubles and the prices of all goods and services remain constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The total value that Doug places on his consumption of computer games equals
A)the price multiplied by quantity demanded.
B)the total amount he pays for all the games he purchases.
C)price times marginal value.
D)his marginal utility multiplied by quantity demanded.
E)his total expenditure on computer games plus his consumer surplus.
A)the price multiplied by quantity demanded.
B)the total amount he pays for all the games he purchases.
C)price times marginal value.
D)his marginal utility multiplied by quantity demanded.
E)his total expenditure on computer games plus his consumer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The market demand curve is derived from
A)a weighted average of the quantity demanded of all individuals in the economy at each price.
B)the vertical summation of individual demand curves.
C)market data provided by Statistics Canada.
D)the average quantity demanded of all individuals in the economy.
E)the horizontal summation of individual demand curves.
A)a weighted average of the quantity demanded of all individuals in the economy at each price.
B)the vertical summation of individual demand curves.
C)market data provided by Statistics Canada.
D)the average quantity demanded of all individuals in the economy.
E)the horizontal summation of individual demand curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The table below shows the total value (in dollars)that Andrew gets from playing 9- hole rounds of golf. TABLE 6- 3
-Refer to Table 6- 3.Andrew values the 4th round of golf at a marginal value of
A)$92.
B)$310.
C)$16.
D)$430.
E)$108.
-Refer to Table 6- 3.Andrew values the 4th round of golf at a marginal value of
A)$92.
B)$310.
C)$16.
D)$430.
E)$108.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The table below shows the quantities of toffee bars and bags of cashews that a consumer could consume over a 1- week period. TABLE 6- 1
-Refer to Table 6- 1.If the prices of both toffee bars and bags of cashews are $2 and this consumer has $14 per week to spend on these two snacks,what is the maximum total utility achievable?
A)15
B)10
C)57
D)45
E)33
-Refer to Table 6- 1.If the prices of both toffee bars and bags of cashews are $2 and this consumer has $14 per week to spend on these two snacks,what is the maximum total utility achievable?
A)15
B)10
C)57
D)45
E)33

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Consider the income and substitution effects of price changes.For a product with an income elasticity greater than one,a price increase will cause the consumer's real income to
A)rise and the quantity purchased to rise.
B)fall and the quantity purchased to rise.
C)remain constant.
D)fall and the quantity purchased to fall.
E)rise and the quantity purchased to fall.
A)rise and the quantity purchased to rise.
B)fall and the quantity purchased to rise.
C)remain constant.
D)fall and the quantity purchased to fall.
E)rise and the quantity purchased to fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The substitution effect is
A)the change in quantity demanded that occurs when one good is substituted for another.
B)the change in quantity demanded that occurs as a result of a change in absolute prices,with real income held constant.
C)the change in quantity demanded that occurs as a result of a change in relative prices with money income held constant.
D)the change in quantity demanded that occurs as a result of a change in relative prices with real income held constant.
E)the change in the relative prices of two or more goods.
A)the change in quantity demanded that occurs when one good is substituted for another.
B)the change in quantity demanded that occurs as a result of a change in absolute prices,with real income held constant.
C)the change in quantity demanded that occurs as a result of a change in relative prices with money income held constant.
D)the change in quantity demanded that occurs as a result of a change in relative prices with real income held constant.
E)the change in the relative prices of two or more goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Indifference theory is based on the assumption that
A)consumers can always say which of two consumption bundles they prefer without having to say by how much they prefer it.
B)the consumer is able to quantify the difference in total utility received from two different consumption bundles.
C)the consumer has equated the marginal utilities of all products,and is therefore indifferent between consumption bundles.
D)the consumer receives the same utility and is therefore indifferent between any two consumption bundles.
E)consumers are not able to rank consumption bundles in order of preference.
A)consumers can always say which of two consumption bundles they prefer without having to say by how much they prefer it.
B)the consumer is able to quantify the difference in total utility received from two different consumption bundles.
C)the consumer has equated the marginal utilities of all products,and is therefore indifferent between consumption bundles.
D)the consumer receives the same utility and is therefore indifferent between any two consumption bundles.
E)consumers are not able to rank consumption bundles in order of preference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
At a garage sale,Ken purchases a used bicycle for $8 when he was willing to pay $25.If the bicycle costs $75 new,Ken's consumer surplus is
A)$50.
B)$67.
C)$17.
D)$33.
E)$0.
A)$50.
B)$67.
C)$17.
D)$33.
E)$0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If all consumers in an economy have maximized their utility,and they face a given set of market prices,then each consumer will have identical
A)total utilities for each good.
B)consumption of each good.
C)marginal utilities per unit of each good.
D)marginal utilities for each good.
E)ratios of marginal utility to price for each good.
A)total utilities for each good.
B)consumption of each good.
C)marginal utilities per unit of each good.
D)marginal utilities for each good.
E)ratios of marginal utility to price for each good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If consumption of an extra unit of some good generates a marginal utility of zero,then consumption of that additional unit would mean that total utility would
A)be negative.
B)also be zero.
C)be increasing.
D)be decreasing.
E)not change.
A)be negative.
B)also be zero.
C)be increasing.
D)be decreasing.
E)not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Given a typical downward- sloping demand curve in a market that has reached its equilibrium,the consumer surplus
A)is calculated as the product of market price and quantity consumed.
B)is measured by the area above the market price and under the demand curve.
C)is measured by the area below the market price and under the demand curve.
D)is measured by the area immediately above the demand curve.
E)cannot be measured given the information.
A)is calculated as the product of market price and quantity consumed.
B)is measured by the area above the market price and under the demand curve.
C)is measured by the area below the market price and under the demand curve.
D)is measured by the area immediately above the demand curve.
E)cannot be measured given the information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Suppose a consumer can purchase only two goods,pasta and cheese.Let the quantity of pasta be measured on the vertical axis and the quantity of cheese be measured on the horizontal axis.If the price of pasta falls,with no change in the price of cheese or in the consumer's money income,then the budget line for the consumer will rotate
A)outward parallel to the existing budget line.
B)toward the origin and become steeper.
C)away from the origin and become steeper.
D)away from the origin and become flatter.
E)toward the origin and become flatter.
A)outward parallel to the existing budget line.
B)toward the origin and become steeper.
C)away from the origin and become steeper.
D)away from the origin and become flatter.
E)toward the origin and become flatter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Suppose Arun consumes only 2 goods - books and CDs - and has a set of downward sloping indifference curves.As Arun moves from one point to another on a particular indifference curve,
A)Arun is consuming the same combination of goods,but with varying levels of income.
B)the combination of books and CDs will vary,but the level of utility remains constant.
C)the combination of books and CDs that Arun prefers will remain constant,but the level of satisfaction will vary.
D)Arun's level of satisfaction will vary as the combinations of books and CDs varies.
E)the combination of books and CDs and Arun's income level will remain constant.
A)Arun is consuming the same combination of goods,but with varying levels of income.
B)the combination of books and CDs will vary,but the level of utility remains constant.
C)the combination of books and CDs that Arun prefers will remain constant,but the level of satisfaction will vary.
D)Arun's level of satisfaction will vary as the combinations of books and CDs varies.
E)the combination of books and CDs and Arun's income level will remain constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Laurie spends all of her money buying bread and cheese.The marginal utility she receives from the last loaf of bread is 60 and from the last block of cheese is 30.The price of bread is $3 and the price of cheese is $2.Laurie
A)should buy more cheese and less bread in order to maximize her utility.
B)should buy more bread and more cheese in order to maximize her utility.
C)should buy more bread and less cheese in order to maximize her utility.
D)is buying bread and cheese in utility- maximizing amounts.
E)is spending too much money on bread and cheese.
A)should buy more cheese and less bread in order to maximize her utility.
B)should buy more bread and more cheese in order to maximize her utility.
C)should buy more bread and less cheese in order to maximize her utility.
D)is buying bread and cheese in utility- maximizing amounts.
E)is spending too much money on bread and cheese.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A consumer maximizes his or her utility when expenditures are allocated such that
A)the utility received per dollar spent on the last unit of each good is equal.
B)the marginal utility is zero for each good consumed utility.
C)the utility received from the last unit of each good is equal.
D)the total number of dollars spent on each good is equal.
E)the total utility from each good is equal.
A)the utility received per dollar spent on the last unit of each good is equal.
B)the marginal utility is zero for each good consumed utility.
C)the utility received from the last unit of each good is equal.
D)the total number of dollars spent on each good is equal.
E)the total utility from each good is equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When a consumer's marginal rate of substitution between X and Y is equal to the ratio of prices for X and Y,and when the consumer is spending all available income,then
A)the consumer is not maximizing his utility.
B)the budget line is tangent to the indifference curve at all quantities of X and Y.
C)a higher indifference curve can be reached given the existing budget line.
D)all budget lines are tangent to all indifference curves.
E)the budget line is tangent to an indifference curve.
A)the consumer is not maximizing his utility.
B)the budget line is tangent to the indifference curve at all quantities of X and Y.
C)a higher indifference curve can be reached given the existing budget line.
D)all budget lines are tangent to all indifference curves.
E)the budget line is tangent to an indifference curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Bjorn is a student with a monthly budget of $500,which he allocates between transportation services and "all other goods." Suppose the price of transportation is $5 per unit,and the price of "all other goods" is $20 per unit.The marginal utility he currently receives from his consumption of transportation services is 60.What is his marginal utility from the consumption of "all other goods" if he is maximizing his utility?
A)200
B)240
C)5
D)20
E)25
A)200
B)240
C)5
D)20
E)25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The paradox in "the paradox of value" refers to the
A)fact that goods with high total values command high prices.
B)situation where a good with a low total value can command a high price,while a good with a high total value can command a low price.
C)situation where a good that is necessary to sustain life is "more valuable" than a decorative,luxury item.
D)fact that goods with low total values command low prices.
E)confusion between supply curves and demand curves.
A)fact that goods with high total values command high prices.
B)situation where a good with a low total value can command a high price,while a good with a high total value can command a low price.
C)situation where a good that is necessary to sustain life is "more valuable" than a decorative,luxury item.
D)fact that goods with low total values command low prices.
E)confusion between supply curves and demand curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Suppose a consumer can purchase only two goods,beef and chicken.If the price of beef falls (with all other variables held constant),and the consumption of chicken increases,we can conclude that the increased consumption of chicken is due to
A)a change in the consumer's preference toward chicken.
B)neither the income effect nor the substitution effect.
C)the substitution effect only.
D)both the income effect and the substitution effect.
E)the income effect only.
A)a change in the consumer's preference toward chicken.
B)neither the income effect nor the substitution effect.
C)the substitution effect only.
D)both the income effect and the substitution effect.
E)the income effect only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the income effect of a price change is negative and larger in absolute terms than the substitution effect,then the demand curve will be
A)of indeterminate slope.
B)downward sloping.
C)horizontal.
D)vertical.
E)upward sloping.
A)of indeterminate slope.
B)downward sloping.
C)horizontal.
D)vertical.
E)upward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An individual's consumer surplus from some product can be eliminated entirely by: 1.raising the price until very few units are bought.
2.charging a price for each unit that is equal to the individual's marginal value for each unit.
3.raising the price until zero units are purchased.
A)1 only
B)2 only
C)3 only
D)2 or 3
E)1 or 2,but not 3.
2.charging a price for each unit that is equal to the individual's marginal value for each unit.
3.raising the price until zero units are purchased.
A)1 only
B)2 only
C)3 only
D)2 or 3
E)1 or 2,but not 3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In economics,the term "utility" is defined as the
A)usefulness of a good.
B)usefulness of a theory to explain price determination.
C)total consumer satisfaction received from consumption of a good.
D)a service such as sewer and water or electricity.
E)system of basing the price of a good on its usefulness to society.
A)usefulness of a good.
B)usefulness of a theory to explain price determination.
C)total consumer satisfaction received from consumption of a good.
D)a service such as sewer and water or electricity.
E)system of basing the price of a good on its usefulness to society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Given a particular consumer's indifference map,the further the indifference curve is from the origin
A)the higher the marginal rate of substitution.
B)the higher the level of satisfaction.
C)the more goods are included.
D)the lower the marginal rate of substitution.
E)the lower the level of satisfaction.
A)the higher the marginal rate of substitution.
B)the higher the level of satisfaction.
C)the more goods are included.
D)the lower the marginal rate of substitution.
E)the lower the level of satisfaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
At a garage sale,Dominique purchases a sewing machine for $30 when she was willing to pay $55.If the sewing machine costs $200 new,Dominique's consumer surplus would be
A)$25.
B)$0.
C)$145.
D)$170.
E)$120.
A)$25.
B)$0.
C)$145.
D)$170.
E)$120.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Consider the income and substitution effects of price changes.The substitution effect is the change in quantity demanded that occurs
A)when one good is substituted for another.
B)with a change in the relative prices of two or more goods.
C)as a result of a change in relative prices,with real income held constant.
D)as a result of a change in relative prices with money income held constant.
E)as a result of a change in absolute prices,with real income held constant.
A)when one good is substituted for another.
B)with a change in the relative prices of two or more goods.
C)as a result of a change in relative prices,with real income held constant.
D)as a result of a change in relative prices with money income held constant.
E)as a result of a change in absolute prices,with real income held constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The figures below show Chris's consumption of specialty coffee per week.
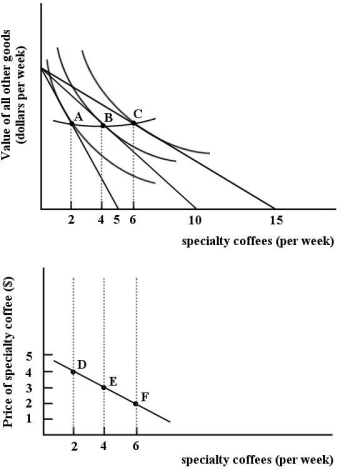 FIGURE 6- 10
FIGURE 6- 10
Refer to Figure 6- 10.The two diagrams in Figure 6- 10 are showing
A)that Chris is indifferent between bundles A,B and C.
B)the derivation of Chris's demand curve for specialty coffee.
C)the derivation of Chris's indifference curve for specialty coffee.
D)that Chris is indifferent between points D,E and F.
E)the change in Chris's preferences toward specialty coffee.
 FIGURE 6- 10
FIGURE 6- 10Refer to Figure 6- 10.The two diagrams in Figure 6- 10 are showing
A)that Chris is indifferent between bundles A,B and C.
B)the derivation of Chris's demand curve for specialty coffee.
C)the derivation of Chris's indifference curve for specialty coffee.
D)that Chris is indifferent between points D,E and F.
E)the change in Chris's preferences toward specialty coffee.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In indifference curve analysis,the consumer's utility- maximizing point is where
A)the indifference curve farthest from the origin intersects with the budget line that is farthest from the origin.
B)the consumer's marginal utility curve is tangent to the relevant budget line.
C)the price- consumption line is tangent to the budget line.
D)one indifference curve is tangent to the relevant budget line.
E)each indifference curve has the same slope as the relevant budget line.
A)the indifference curve farthest from the origin intersects with the budget line that is farthest from the origin.
B)the consumer's marginal utility curve is tangent to the relevant budget line.
C)the price- consumption line is tangent to the budget line.
D)one indifference curve is tangent to the relevant budget line.
E)each indifference curve has the same slope as the relevant budget line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Assume you are consuming two goods,X and Y.Suppose that the money prices for X and Y remain unchanged,but your income increases by 20%.What happens to your consumption of good X?
A)it stays the same
B)it increases
C)it increases or decreases,depending on whether it is normal or inferior
D)it increases by 20%
E)it decreases
A)it stays the same
B)it increases
C)it increases or decreases,depending on whether it is normal or inferior
D)it increases by 20%
E)it decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Consider the pizza market,with a downward- sloping demand curve and an upward- sloping supply curve.Suppose 100 pizzas are purchased at the free- market equilibrium price.The consumer surplus on the 100th pizza is
A)positive.
B)zero.
C)negative.
D)unknown.
E)non- negative.
A)positive.
B)zero.
C)negative.
D)unknown.
E)non- negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Since there is a limited supply of diamonds in the world,the consumption of diamonds
A)is no less important than consumption of water.
B)takes priority over some other good.
C)takes place at relatively low marginal value.
D)should be regulated by the government.
E)takes place at relatively high marginal value.
A)is no less important than consumption of water.
B)takes priority over some other good.
C)takes place at relatively low marginal value.
D)should be regulated by the government.
E)takes place at relatively high marginal value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The marginal rate of substitution measures the tradeoff between the
A)different values that two consumers place on a good.
B)prices of two goods along a budget line.
C)amount of one good the consumer is willing to purchase and its own price.
D)different indifference curves.
E)amount of one good the consumer is willing to give up in exchange for another good along an indifference curve.
A)different values that two consumers place on a good.
B)prices of two goods along a budget line.
C)amount of one good the consumer is willing to purchase and its own price.
D)different indifference curves.
E)amount of one good the consumer is willing to give up in exchange for another good along an indifference curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Suppose a consumer can purchase only two goods,soap and apples.If the price of soap falls and the consumption of apples increases,we can conclude that the increased consumption of apples is due to
A)the income effect only.
B)the substitution effect only.
C)the deflation effect.
D)both the income effect and the substitution effect.
E)neither the income effect nor the substitution effect.
A)the income effect only.
B)the substitution effect only.
C)the deflation effect.
D)both the income effect and the substitution effect.
E)neither the income effect nor the substitution effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A basic hypothesis of marginal utility theory is that the utility a consumer derives from successive units of a good diminishes as total consumption of the good increases.This hypothesis is known as
A)the utility theory of demand.
B)the law of diminishing marginal utility.
C)utility maximization.
D)the law of diminishing total utility.
E)the paradox of value.
A)the utility theory of demand.
B)the law of diminishing marginal utility.
C)utility maximization.
D)the law of diminishing total utility.
E)the paradox of value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The table below shows the quantities of toffee bars and bags of cashews that a consumer could consume over a 1- week period. TABLE 6- 1
-If total utility from the consumption of some product is decreasing as more units are consumed,then marginal utility must be
A)decreasing.
B)increasing at a decreasing rate.
C)decreasing at an increasing rate.
D)positive.
E)negative.
-If total utility from the consumption of some product is decreasing as more units are consumed,then marginal utility must be
A)decreasing.
B)increasing at a decreasing rate.
C)decreasing at an increasing rate.
D)positive.
E)negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The figures below show Chris's consumption of specialty coffee per week.
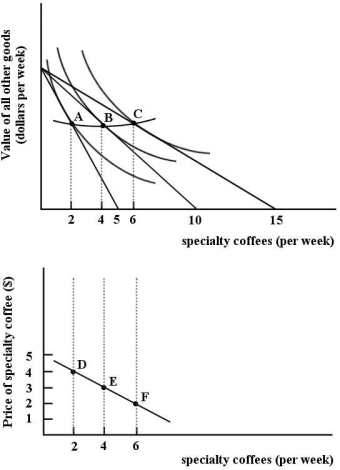 FIGURE 6- 10
FIGURE 6- 10
Refer to Figure 6- 10.The line connecting points A,B and C is _.The line connecting points D,E and F is .
A)the demand curve; the budget line
B)the income- consumption line; the budget line
C)the price- consumption line; the demand curve
D)the budget line; the price- consumption line
E)the income- consumption line; the demand curve
 FIGURE 6- 10
FIGURE 6- 10Refer to Figure 6- 10.The line connecting points A,B and C is _.The line connecting points D,E and F is .
A)the demand curve; the budget line
B)the income- consumption line; the budget line
C)the price- consumption line; the demand curve
D)the budget line; the price- consumption line
E)the income- consumption line; the demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The table below shows the quantities of toffee bars and bags of cashews that a consumer could consume over a 1- week period. TABLE 6- 1
-Refer to Table 6- 1.If the price of toffee bars is $1 each,bags of cashews are $2 each,and this consumer has $7 per week to spend on these two snacks,how many of each will he/she purchase to maximize utility?
A)3 toffee bars and 2 bags of cashews
B)0 toffee bars and 3 bags of cashews
C)7 toffee bars and 0 bags of cashews
D)1 toffee bars and 3 bags of cashews
E)2 toffee bars and 2 bags of cashews
-Refer to Table 6- 1.If the price of toffee bars is $1 each,bags of cashews are $2 each,and this consumer has $7 per week to spend on these two snacks,how many of each will he/she purchase to maximize utility?
A)3 toffee bars and 2 bags of cashews
B)0 toffee bars and 3 bags of cashews
C)7 toffee bars and 0 bags of cashews
D)1 toffee bars and 3 bags of cashews
E)2 toffee bars and 2 bags of cashews

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The "law" of diminishing marginal utility implies that the
A)first unit of a good consumed will contribute most to the consumer's satisfaction.
B)last unit of a good consumed will contribute most to the consumer's satisfaction.
C)marginal utility of a good diminishes over time.
D)total utility is constant as more units are consumed.
E)total utility is negative.
A)first unit of a good consumed will contribute most to the consumer's satisfaction.
B)last unit of a good consumed will contribute most to the consumer's satisfaction.
C)marginal utility of a good diminishes over time.
D)total utility is constant as more units are consumed.
E)total utility is negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The table below shows the total value (in dollars)that Andrew gets from playing 9- hole rounds of golf. TABLE 6- 3
-Refer to Table 6- 3.If the price of a 9- hole round of golf is $16,and Andrew is maximizing his utility,then his consumer surplus will be
A)$310.
B)$92.
C)$108.
D)$16.
E)$44.
-Refer to Table 6- 3.If the price of a 9- hole round of golf is $16,and Andrew is maximizing his utility,then his consumer surplus will be
A)$310.
B)$92.
C)$108.
D)$16.
E)$44.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The table below shows the total value (in dollars)that Andrew gets from playing 9- hole rounds of golf. TABLE 6- 3
-Consumer surplus is
A)the total value that a consumer receives from the purchase of a particular good.
B)the consumption of a commodity above and beyond the amount required by the consumer.
C)a measure of the gains that a consumer forgoes by buying this product rather than another.
D)the difference between what the consumer is willing to pay for all the units consumed and what he or she actually paid.
E)the sum of the marginal values to the consumer.
-Consumer surplus is
A)the total value that a consumer receives from the purchase of a particular good.
B)the consumption of a commodity above and beyond the amount required by the consumer.
C)a measure of the gains that a consumer forgoes by buying this product rather than another.
D)the difference between what the consumer is willing to pay for all the units consumed and what he or she actually paid.
E)the sum of the marginal values to the consumer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
FIGURE 6- 2 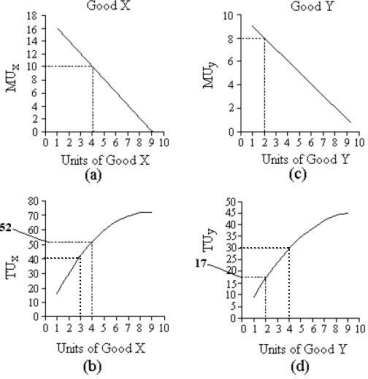
As a consumer moves along an indifference curve
A)the combination of goods and the consumer's income level will remain constant.
B)the combination of goods will vary,but the level of money income remains constant.
C)the combination of goods will vary but the level of utility remains constant.
D)his level of utility will vary as the combinations of goods varies.
E)the combination of goods he prefers will remain constant,but the level of satisfaction will vary.

As a consumer moves along an indifference curve
A)the combination of goods and the consumer's income level will remain constant.
B)the combination of goods will vary,but the level of money income remains constant.
C)the combination of goods will vary but the level of utility remains constant.
D)his level of utility will vary as the combinations of goods varies.
E)the combination of goods he prefers will remain constant,but the level of satisfaction will vary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Christine is allocating her household expenditure between cleaning services and gardening services in order to maximize the household's total utility.For the quantities of cleaning and gardening services she has chosen,an increase in the price of cleaning service will,ceteris paribus,
A)increase the marginal utility of a unit of cleaning service.
B)have no effect on the marginal utility per dollar spent on cleaning service.
C)reduce the marginal utility of a unit of cleaning service.
D)reduce the marginal utility per dollar spent on cleaning service.
E)increase the marginal utility per dollar spent on cleaning service.
A)increase the marginal utility of a unit of cleaning service.
B)have no effect on the marginal utility per dollar spent on cleaning service.
C)reduce the marginal utility of a unit of cleaning service.
D)reduce the marginal utility per dollar spent on cleaning service.
E)increase the marginal utility per dollar spent on cleaning service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Suppose there are only two goods,A and B,and that consumer income is constant.If the price of good A falls and the consumption of good B rises,we can conclude that
A)both A and B are normal goods.
B)A is a normal good.
C)B is an inferior good.
D)B is a normal good.
E)A is an inferior good.
A)both A and B are normal goods.
B)A is a normal good.
C)B is an inferior good.
D)B is a normal good.
E)A is an inferior good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The table below shows the quantities of toffee bars and bags of cashews that a consumer could consume over a 1- week period. TABLE 6- 1
-Refer to Table 6- 1.If the prices of toffee bars and bags of cashews are both $1 and this consumer has $7 per week to spend on these two snacks,how many of each will he/she purchase to maximize utility?
A)2 toffee bars and 5 bags of cashews
B)3 toffee bars and 4 bags of cashews
C)6 toffee bars and 1 bag of cashews
D)5 toffee bars and 2 bags of cashews
E)4 toffee bars and 3 bags of cashews
-Refer to Table 6- 1.If the prices of toffee bars and bags of cashews are both $1 and this consumer has $7 per week to spend on these two snacks,how many of each will he/she purchase to maximize utility?
A)2 toffee bars and 5 bags of cashews
B)3 toffee bars and 4 bags of cashews
C)6 toffee bars and 1 bag of cashews
D)5 toffee bars and 2 bags of cashews
E)4 toffee bars and 3 bags of cashews

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
FIGURE 6- 2 
Refer to Figure 6- 2.Suppose the price of X is $2,the price of Y is $1,and the consumer's income is $10.The consumer is currently buying 4 units of good X and 2 units of good Y.In order to maximize his utility,he should
A)buy the same amount of X but less Y.
B)make no changes-he is already maximizing his total utility.
C)buy less of X and more Y.
D)buy more of X but the same amount Y.
E)buy more of X and less Y.

Refer to Figure 6- 2.Suppose the price of X is $2,the price of Y is $1,and the consumer's income is $10.The consumer is currently buying 4 units of good X and 2 units of good Y.In order to maximize his utility,he should
A)buy the same amount of X but less Y.
B)make no changes-he is already maximizing his total utility.
C)buy less of X and more Y.
D)buy more of X but the same amount Y.
E)buy more of X and less Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The figures below show Chris's consumption of specialty coffee per week.
 FIGURE 6- 10
FIGURE 6- 10
Marginal utility analysis predicts a downward- sloping demand curve for good X because
A)as PX rises,the consumer increases purchases of X such that MUX/PX is equal to MU/P for all other products.
B)all demand curves are downward sloping,regardless of the behaviour of consumers.
C)utility- maximizing consumers equate marginal utility received for each product consumed.
D)as PX falls,the consumer increases purchases of X until MUX/PX is equal to MU/P for all other products.
E)as PX falls,the ratio MUX/PX becomes smaller,causing the consumer to purchase more of good X.
 FIGURE 6- 10
FIGURE 6- 10Marginal utility analysis predicts a downward- sloping demand curve for good X because
A)as PX rises,the consumer increases purchases of X such that MUX/PX is equal to MU/P for all other products.
B)all demand curves are downward sloping,regardless of the behaviour of consumers.
C)utility- maximizing consumers equate marginal utility received for each product consumed.
D)as PX falls,the consumer increases purchases of X until MUX/PX is equal to MU/P for all other products.
E)as PX falls,the ratio MUX/PX becomes smaller,causing the consumer to purchase more of good X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The table below shows the total value (in dollars)that Andrew gets from playing 9- hole rounds of golf. TABLE 6- 3
-If money income is reduced by half,and the prices of all goods consumed by the household are reduced by half,the household's budget line will
A)shift inward.
B)not change.
C)become steeper.
D)shift outward.
E)become flatter.
-If money income is reduced by half,and the prices of all goods consumed by the household are reduced by half,the household's budget line will
A)shift inward.
B)not change.
C)become steeper.
D)shift outward.
E)become flatter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If consumption of an extra unit of a product delivers a positive marginal utility,then consumption of that additional unit would mean
A)that total utility would be decreasing.
B)that the consumer would no longer receive any satisfaction from any consumption of this good.
C)that total utility would be increasing.
D)that total utility would not change.
E)that total utility is also zero.
A)that total utility would be decreasing.
B)that the consumer would no longer receive any satisfaction from any consumption of this good.
C)that total utility would be increasing.
D)that total utility would not change.
E)that total utility is also zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The idea that the utility a consumer derives from successive units of a good diminishes as total consumption of the good increases is known as
A)the utility theory of demand.
B)utility maximization.
C)diminishing marginal utility.
D)the paradox of value.
E)diminishing total utility.
A)the utility theory of demand.
B)utility maximization.
C)diminishing marginal utility.
D)the paradox of value.
E)diminishing total utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Economists usually assume that consumers
A)are poor judges of what is best for them.
B)are motivated to maximize their utility.
C)spend all of their current income.
D)usually save as much as possible of their income.
E)are motivated to maximize their profit.
A)are poor judges of what is best for them.
B)are motivated to maximize their utility.
C)spend all of their current income.
D)usually save as much as possible of their income.
E)are motivated to maximize their profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Any consumption point that is on the budget line
A)implies the household is paying above- market prices for the goods in question.
B)implies the household is paying below- market prices for the goods in question.
C)implies that the household is not spending all of its income on the goods in question.
D)indicates consumption spending beyond current income.
E)implies that the household is spending all of its income on the goods in question.
A)implies the household is paying above- market prices for the goods in question.
B)implies the household is paying below- market prices for the goods in question.
C)implies that the household is not spending all of its income on the goods in question.
D)indicates consumption spending beyond current income.
E)implies that the household is spending all of its income on the goods in question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If John consumes only two goods,A and B,and he is maximizing his utility subject to his budget constraint,
A)MUA/MUB equals 1.
B)MUA/MUB equals the ratio of the price of A to the price of B.
C)MUA/MUB is at a maximum.
D)MUA/MUB equals the ratio of the total utility of A to the total utility of B.
E)MUA/MUB equals zero.
A)MUA/MUB equals 1.
B)MUA/MUB equals the ratio of the price of A to the price of B.
C)MUA/MUB is at a maximum.
D)MUA/MUB equals the ratio of the total utility of A to the total utility of B.
E)MUA/MUB equals zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
FIGURE 6- 9 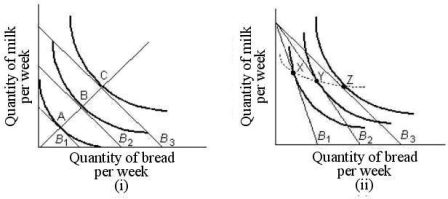
Refer to Figure 6- 9.In part (i),the line joining points A,B,and C is known as ,which shows how .
A)an income- consumption line; consumption changes with changing relative prices and constant income
B)a price- consumption line; consumption changes as relative prices change,with money income constant
C)a price- consumption line; consumption changes as money income and relative prices change
D)an income- consumption line; consumption changes as income changes,with relative prices held constant
E)an indifference map; the value of various combinations of two goods changes

Refer to Figure 6- 9.In part (i),the line joining points A,B,and C is known as ,which shows how .
A)an income- consumption line; consumption changes with changing relative prices and constant income
B)a price- consumption line; consumption changes as relative prices change,with money income constant
C)a price- consumption line; consumption changes as money income and relative prices change
D)an income- consumption line; consumption changes as income changes,with relative prices held constant
E)an indifference map; the value of various combinations of two goods changes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Assume the quantity of good X is measured on the horizontal axis and the quantity of good Y on the vertical axis.Initial prices are PX = $5 and PY = $10.The consumer's income is $100.If PY increases to $20,then
A)the entire budget line shifts parallel to the left.
B)the budget line will rotate to the left with the slope changing from 1/2 to 1/4 (in absolute values).
C)the budget line will rotate to the left,slope remaining constant.
D)the budget line will rotate to the right with the slope changing from 1/4 to 1/2 (in absolute values).
E)the entire budget line shifts parallel to the right.
A)the entire budget line shifts parallel to the left.
B)the budget line will rotate to the left with the slope changing from 1/2 to 1/4 (in absolute values).
C)the budget line will rotate to the left,slope remaining constant.
D)the budget line will rotate to the right with the slope changing from 1/4 to 1/2 (in absolute values).
E)the entire budget line shifts parallel to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The substitution effect of a price change leads consumers to _ their demand for goods whose prices have risen.The income effect leads consumers to buy less of all goods whose prices have risen.
A)reduce; normal
B)reduce; Giffen
C)increase; normal
D)increase; inferior
E)reduce; complement
A)reduce; normal
B)reduce; Giffen
C)increase; normal
D)increase; inferior
E)reduce; complement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The table below shows the total value (in dollars)that Andrew gets from playing 9- hole rounds of golf. TABLE 6- 3
-Refer to Table 6- 3.If the price of a 9- hole round of golf is $19,then Andrew will play rounds per month.
A)6 or more
B)5
C)2
D)3
E)4
-Refer to Table 6- 3.If the price of a 9- hole round of golf is $19,then Andrew will play rounds per month.
A)6 or more
B)5
C)2
D)3
E)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Assume you are consuming two goods,X and Y.X and Y are both normal goods but they are not close complements.The price of good X increases but the price of Y remains unchanged.However,you are given enough additional income to ensure that your utility remains unchanged.What happens to your consumption of good X?
A)it increases or decreases
B)it increases over the long run
C)it stays the same
D)it decreases
E)it increases
A)it increases or decreases
B)it increases over the long run
C)it stays the same
D)it decreases
E)it increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The demand curve for a good with an income elasticity of less than one
A)must be upward sloping.
B)must be downward sloping.
C)indicates a normal good.
D)will be upward sloping only if the substitution effect outweighs the income effect.
E)will be upward sloping only if the income effect outweighs the substitution effect.
A)must be upward sloping.
B)must be downward sloping.
C)indicates a normal good.
D)will be upward sloping only if the substitution effect outweighs the income effect.
E)will be upward sloping only if the income effect outweighs the substitution effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Consider a consumer who divides his income between spending on good X and good Y.The opportunity cost of good X in terms of good Y is reflected by the
A)absolute price of good Y.
B)price of good X relative to the prices of all other goods.
C)ratio of the price of X to the price of Y.
D)absolute price of good X.
E)ratio of the price of Y to the price of X.
A)absolute price of good Y.
B)price of good X relative to the prices of all other goods.
C)ratio of the price of X to the price of Y.
D)absolute price of good X.
E)ratio of the price of Y to the price of X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



