Deck 11: A: The Aggregate Expenditures Model
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/47
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: A: The Aggregate Expenditures Model
1
What is the effect of net exports, either positive or negative, on equilibrium GDP?
Positive net exports increase aggregate expenditures beyond what they would be in a closed economy and thus have an expansionary effect.The multiplier effect also is at work.Positive net exports will lead to a positive change that is greater than the amount of the initial change.Negative net exports decrease aggregate expenditures beyond what they would be in a closed economy and thus have a contractionary effect.The multiplier effect also is at work here.Negative net exports lead to a negative change in equilibrium GDP that is greater than the initial change.
2
Other things being constant, what will be the effect of each of the following upon the equilibrium level of GDP?
(a) An increase in the amount of liquid assets consumers are holding;
(b) A sharp rise in stock prices;
(c) A rapid upsurge in the rate of technological advance; and
(d) A sharp increase in the interest rate.
(a) An increase in the amount of liquid assets consumers are holding;
(b) A sharp rise in stock prices;
(c) A rapid upsurge in the rate of technological advance; and
(d) A sharp increase in the interest rate.
(a) This should increase GDP because an increase in consumer wealth would lead to an increase in consumer spending which would shift the aggregate expenditures curve upward to a higher equilibrium output level.
(b) The probable effect of a sharp rise in stock prices would be to increase in consumption by shareholders who have seen an increase in wealth, thus shifting the aggregate expenditures curve upward and increasing the equilibrium level of GDP.It also could encourage business investment with funds gained by issuing new shares of stock at the now higher prices.This would also tend to increase GDP.
(c) This should increase GDP because of the impact on new investment spending and possible increased consumer purchases of goods having the new technology.The aggregate expenditures curve will shift upward and real output will rise.
(d) A sharp increase in the interest rate would limit consumer durable purchases and also limit investment spending.Both of these events would cause a downward shift in aggregate expenditures causing a decrease in GDP.
(b) The probable effect of a sharp rise in stock prices would be to increase in consumption by shareholders who have seen an increase in wealth, thus shifting the aggregate expenditures curve upward and increasing the equilibrium level of GDP.It also could encourage business investment with funds gained by issuing new shares of stock at the now higher prices.This would also tend to increase GDP.
(c) This should increase GDP because of the impact on new investment spending and possible increased consumer purchases of goods having the new technology.The aggregate expenditures curve will shift upward and real output will rise.
(d) A sharp increase in the interest rate would limit consumer durable purchases and also limit investment spending.Both of these events would cause a downward shift in aggregate expenditures causing a decrease in GDP.
3
If prices are stuck, how can firms receive feedback from the market to tell them how much to produce?
When underlying conditions change, but the price cannot change, firms take their signals from unplanned changes in their inventories.
4
The aggregate expenditures model has one over-arching assumption.What is this assumption?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the difference between the investment-demand curve and the investment schedule for the economy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Define the equilibrium level of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In addition to stuck prices, what are the two simplifying assumptions of the initial model in this chapter? What are two implications from these simplifications?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Whenever there is an upshift or downshift in aggregate expenditures due to a change in one of its non-income determinants, the equilibrium GDP changes by a multiple of the initial change in spending.Explain this multiplier effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Explain the difference between an equilibrium level of GDP and a level of GDP that is in disequilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Evaluate the statement that "for an open economy the equilibrium GDP always corresponds with an equality of exports and imports."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In a graph relating private spending (C + Ig) to real gross domestic product (GDP), what does the 45-degree line represent?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Explain why saving equals planned investment at equilibrium GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
How does the fact that imports vary directly with GDP affect the stability of the domestic economy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Explain why exports are added to, and imports are subtracted from, aggregate expenditures in moving from a closed to an open economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Use the graph below to explain the determination of equilibrium GDP by the aggregate expenditures-domestic output approach.At equilibrium C + Ig = Real GDP ($550 + $50 = $600).Why does the intersection of the aggregate expenditures schedule and the 45-degree line determine the equilibrium GDP? 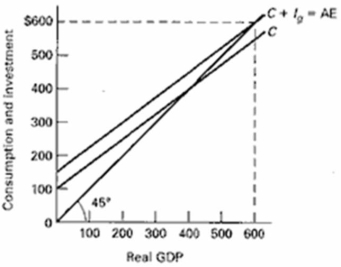


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Explain the difference between planned and actual investment in the economy.Why is the distinction important?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What are two components of aggregate expenditures in a closed private economy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Whenever there is a shift in the investment schedule and/or the consumption-saving schedules, there will be a new equilibrium level of GDP.Explain why this is so.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What differentiates the planned equilibrium level of investment from disequilibrium levels of investment? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the relationship between actual investment, planned investment, and saving in an economy? What conditions among these concepts produce equilibrium?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Explain the effect of a cut in lump-sum taxes of $40 billion on the economy.Assume that investment, net exports, government expenditures, and taxes do not change with changes in real GDP and the MPC is .75.How does the impact of this change differ from that of a $40 billion increase in government spending?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Explain why are nations are tempted to use policies of imposing tariffs on imported goods, and devaluating their national currency? Further explain why implementing such policies are huge mistakes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The data in the first two columns below are for a closed economy without government.Use this table to answer the following questions. 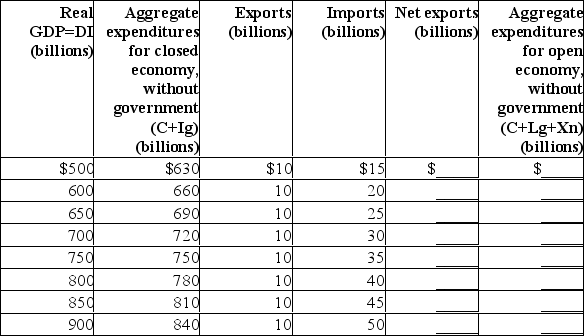 (a) What is the equilibrium GDP for the closed economy?
(a) What is the equilibrium GDP for the closed economy?
(b) What is the size of the multiplier in the closed economy?
(c) Including the international trade figures for exports and imports, calculate net exports and determine the equilibrium GDP for an open economy.(d) What will happen to equilibrium GDP if exports were $25 billion larger at each level of GDP?
(e) What is the size of the multiplier in the open economy?
 (a) What is the equilibrium GDP for the closed economy?
(a) What is the equilibrium GDP for the closed economy?(b) What is the size of the multiplier in the closed economy?
(c) Including the international trade figures for exports and imports, calculate net exports and determine the equilibrium GDP for an open economy.(d) What will happen to equilibrium GDP if exports were $25 billion larger at each level of GDP?
(e) What is the size of the multiplier in the open economy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Describe the impact of an increase in government spending assuming no change in taxes and less than full-employment output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Explain how the recession resulting from the financial crisis in the United States in late-2008 was transmitted to Canada.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Why does the inclusion of a lump-sum tax cause domestic consumption to fall initially by an amount less than the tax?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If there is a recessionary gap of $100 billion and the MPC is 0.8, by how much must taxes be reduced to eliminate the recessionary gap? Assume that prices are stuck and that investment, net exports, government expenditures, and taxes do not change with changes in real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the difference between the multiplier in a closed private economy and the multiplier in a mixed open economy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
At the current level of real GDP,
Sa = $160
Ig = $180
X = $320
M = $280
G = $270
T = $240
(a) What is the size of injections? Leakages?
(b) Is GDP at its equilibrium level? Explain.(c) What is the unplanned change in inventories? Explain.
Sa = $160
Ig = $180
X = $320
M = $280
G = $270
T = $240
(a) What is the size of injections? Leakages?
(b) Is GDP at its equilibrium level? Explain.(c) What is the unplanned change in inventories? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Compare and contrast the recessionary gap and the inflationary gap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
At the current level of real GDP,
Sa = $180
Ig = $160
X = $300
M = $280
G = $250
T = $270
(a) What is the size of injections? Leakages?
(b) Is GDP at its equilibrium level? Explain.(c) What is the unplanned change in inventories? Explain.
Sa = $180
Ig = $160
X = $300
M = $280
G = $250
T = $270
(a) What is the size of injections? Leakages?
(b) Is GDP at its equilibrium level? Explain.(c) What is the unplanned change in inventories? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Explain the relationship between net exports and the following factors: prosperity abroad, tariffs on Canadian exports abroad, depreciation of the Canadian dollar on foreign exchange markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Some critics of the Chinese government accuse it of "manipulating" its currency, the Chinese yuan.Explain the nature of and the effects of this "manipulation".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Assume the level of investment is $8 billion and independent of the level of total output.Complete the following table and answer the following questions about this private closed economy. 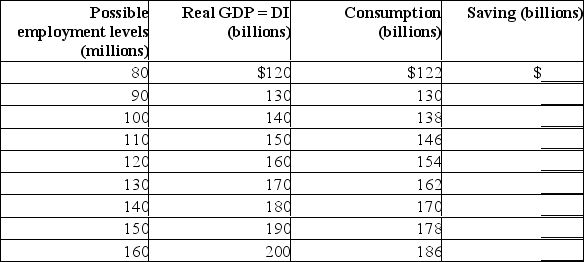 (a) What are the sizes of the MPC, MPS, and multiplier in this economy?
(a) What are the sizes of the MPC, MPS, and multiplier in this economy?
(b) If full employment in this economy is 140 million, will there be a recessionary or inflationary gap? Explain the consequences of this gap.(c) Using the multiplier concept, determine what change in investment is needed to eliminate the output gap.(d) If full employment in this economy is 110 million, will there be an inflationary or recessionary gap? Explain the consequences of this gap.(e) Using the multiplier concept, determine what change in investment is needed to eliminate the output gap from part (d).
 (a) What are the sizes of the MPC, MPS, and multiplier in this economy?
(a) What are the sizes of the MPC, MPS, and multiplier in this economy?(b) If full employment in this economy is 140 million, will there be a recessionary or inflationary gap? Explain the consequences of this gap.(c) Using the multiplier concept, determine what change in investment is needed to eliminate the output gap.(d) If full employment in this economy is 110 million, will there be an inflationary or recessionary gap? Explain the consequences of this gap.(e) Using the multiplier concept, determine what change in investment is needed to eliminate the output gap from part (d).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
"If taxes and government spending are increased by the same amount, there will still be a positive effect on equilibrium GDP." Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Explain the effect of an increase in government spending of $50 billion on the economy.Assume that investment, net exports, government expenditures, and taxes do not change with changes in real GDP and the MPC is .75.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Assume that investment, net exports, government expenditures, and taxes do not change with changes in real GDP and the MPC is .75.(a) Suppose government spending increases by $20 billion.What is the impact on real GDP?
(b) Suppose that instead lump-sum taxes increase by $20 billion.What is the impact on real GDP?
(c) How would the results in (a) and (b) be different if imports and taxes increase as real GDP increases?
(b) Suppose that instead lump-sum taxes increase by $20 billion.What is the impact on real GDP?
(c) How would the results in (a) and (b) be different if imports and taxes increase as real GDP increases?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Keynes developed his theory during the height of the Great Depression (a severe recessionary gap) in the 1930s.What two policy tools did he recommend to close this gap?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The data in the first two columns below are for a closed economy without government.Use this table to answer the following questions. 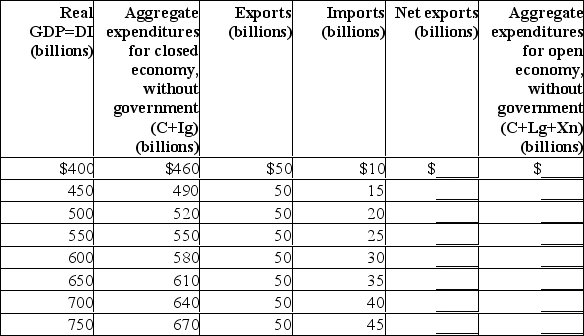 (a) What is the equilibrium GDP for the closed economy?
(a) What is the equilibrium GDP for the closed economy?
(b) What is the size of the multiplier in the closed economy?
(c) Including the international trade figures for exports and imports, calculate net exports and determine the equilibrium GDP for an open economy.(d) What will happen to equilibrium GDP if exports were $25 billion larger at each level of GDP?
(e) What is the size of the multiplier in the open economy?
 (a) What is the equilibrium GDP for the closed economy?
(a) What is the equilibrium GDP for the closed economy?(b) What is the size of the multiplier in the closed economy?
(c) Including the international trade figures for exports and imports, calculate net exports and determine the equilibrium GDP for an open economy.(d) What will happen to equilibrium GDP if exports were $25 billion larger at each level of GDP?
(e) What is the size of the multiplier in the open economy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When international trade is considered, explain how net exports could be either positive or negative additions to aggregate expenditures.In which case would the impact of net exports be expansionary? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Assume the level of investment is $12 billion and independent of the level of total output.Complete the following table and answer the following questions about this private closed economy. 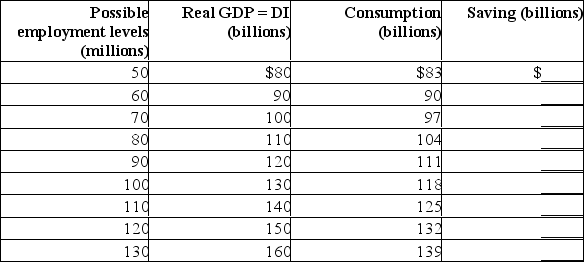 (a) What are the sizes of the MPC, MPS, and multiplier in this economy?
(a) What are the sizes of the MPC, MPS, and multiplier in this economy?
(b) If full employment in this economy is 110 million, will there be a recessionary or inflationary gap? Explain the consequences of this gap.(c) Using the multiplier concept, determine what change in investment is needed to eliminate the output gap.(d) If full employment in this economy is 80 million, will there be an inflationary or recessionary gap? Explain the consequences of this gap.(e) Using the multiplier concept, determine what change in investment is needed to eliminate the output gap from part (d).
 (a) What are the sizes of the MPC, MPS, and multiplier in this economy?
(a) What are the sizes of the MPC, MPS, and multiplier in this economy?(b) If full employment in this economy is 110 million, will there be a recessionary or inflationary gap? Explain the consequences of this gap.(c) Using the multiplier concept, determine what change in investment is needed to eliminate the output gap.(d) If full employment in this economy is 80 million, will there be an inflationary or recessionary gap? Explain the consequences of this gap.(e) Using the multiplier concept, determine what change in investment is needed to eliminate the output gap from part (d).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Answer the following questions using the aggregate expenditures model of the economy described below.C = 90 + .7Yd
T = 50 + .2Y
Ia = 36
Ga = 45
Xa = 62
M = .16Y
(a) What are the marginal propensity to consume, the marginal tax rate, and the marginal propensity to import?
(b) What is the saving function? What is the marginal propensity to save?
(c) What is the aggregate expenditure function? What is autonomous expenditure? What is the marginal propensity to withdraw?
(d) What is the equilibrium level of real GDP?
(e) What is the size of the multiplier?
(f) Suppose the full employment level of real GDP is $350.Does a recessionary gap or an inflationary gap exist? How can the government eliminate the gap by altering government expenditures?
T = 50 + .2Y
Ia = 36
Ga = 45
Xa = 62
M = .16Y
(a) What are the marginal propensity to consume, the marginal tax rate, and the marginal propensity to import?
(b) What is the saving function? What is the marginal propensity to save?
(c) What is the aggregate expenditure function? What is autonomous expenditure? What is the marginal propensity to withdraw?
(d) What is the equilibrium level of real GDP?
(e) What is the size of the multiplier?
(f) Suppose the full employment level of real GDP is $350.Does a recessionary gap or an inflationary gap exist? How can the government eliminate the gap by altering government expenditures?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Answer the following questions using the aggregate expenditures model of the economy described below.C = 100 + .8Yd
T = 60 + .25Y
Ia = 28
Ga = 48
Xa = 54
M = .1Y
(a) What are the marginal propensity to consume, the marginal tax rate, and the marginal propensity to import?
(b) What is the saving function? What is the marginal propensity to save?
(c) What is the aggregate expenditure function? What is autonomous expenditure? What is the marginal propensity to withdraw?
(d) What is the equilibrium level of real GDP?
(e) What is the size of the multiplier?
(f) Suppose the full employment level of real GDP is $380.Does a recessionary gap or an inflationary gap exist? How can the government eliminate the gap by altering government expenditures?
T = 60 + .25Y
Ia = 28
Ga = 48
Xa = 54
M = .1Y
(a) What are the marginal propensity to consume, the marginal tax rate, and the marginal propensity to import?
(b) What is the saving function? What is the marginal propensity to save?
(c) What is the aggregate expenditure function? What is autonomous expenditure? What is the marginal propensity to withdraw?
(d) What is the equilibrium level of real GDP?
(e) What is the size of the multiplier?
(f) Suppose the full employment level of real GDP is $380.Does a recessionary gap or an inflationary gap exist? How can the government eliminate the gap by altering government expenditures?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Refer to the following table to answer the questions. 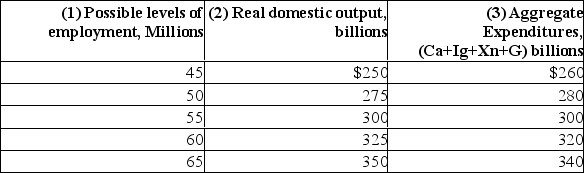 (a) Assuming that investment, net exports, government expenditures, and taxes do not change with changes in real GDP, what are the sizes of the MPC, the MPS, and the multiplier?
(a) Assuming that investment, net exports, government expenditures, and taxes do not change with changes in real GDP, what are the sizes of the MPC, the MPS, and the multiplier?
(b) If full employment in this economy is 65 million, will there be an inflationary or recessionary gap? What will be the consequence of this gap? By how much would aggregate expenditures in column 3 have to change at each level of GDP to eliminate the inflationary or recessionary gap? Explain.(c) Will there be an inflationary or recessionary gap if the full-employment level of output is $250 billion? Explain the consequences.By how much would aggregate expenditures in column 3 have to change at each level of GDP to eliminate the inflationary or recessionary gap? Explain.
 (a) Assuming that investment, net exports, government expenditures, and taxes do not change with changes in real GDP, what are the sizes of the MPC, the MPS, and the multiplier?
(a) Assuming that investment, net exports, government expenditures, and taxes do not change with changes in real GDP, what are the sizes of the MPC, the MPS, and the multiplier?(b) If full employment in this economy is 65 million, will there be an inflationary or recessionary gap? What will be the consequence of this gap? By how much would aggregate expenditures in column 3 have to change at each level of GDP to eliminate the inflationary or recessionary gap? Explain.(c) Will there be an inflationary or recessionary gap if the full-employment level of output is $250 billion? Explain the consequences.By how much would aggregate expenditures in column 3 have to change at each level of GDP to eliminate the inflationary or recessionary gap? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Use the table below to answer the following questions.Assume that investment, net exports, government expenditures, and taxes do not change with changes in real GDP. 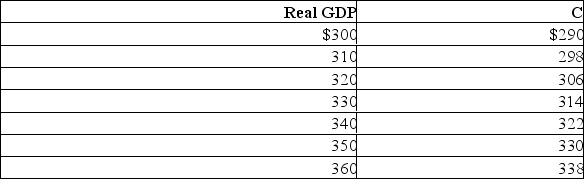 (a) What is the size of the multiplier in this economy?
(a) What is the size of the multiplier in this economy?
(b) If taxes are zero, government expenditures are $10, investment is $6, and net exports are zero, what is the equilibrium GDP?
(c) If taxes are $5, government expenditures are $10, investment is $6, and net exports are zero, what is the equilibrium GDP?
(d) Assume investment is $50, taxes are $50, net exports and government expenditures are each zero.The full-employment level of real GDP is $340.How much of a reduction in taxes is needed to eliminate the recessionary gap?
(e) Assume that investment, net exports, and taxes are zero.Government expenditures are $20 and the full-employment level of real GDP is $330.By how much must government spending be reduced to eliminate the inflationary gap?
 (a) What is the size of the multiplier in this economy?
(a) What is the size of the multiplier in this economy?(b) If taxes are zero, government expenditures are $10, investment is $6, and net exports are zero, what is the equilibrium GDP?
(c) If taxes are $5, government expenditures are $10, investment is $6, and net exports are zero, what is the equilibrium GDP?
(d) Assume investment is $50, taxes are $50, net exports and government expenditures are each zero.The full-employment level of real GDP is $340.How much of a reduction in taxes is needed to eliminate the recessionary gap?
(e) Assume that investment, net exports, and taxes are zero.Government expenditures are $20 and the full-employment level of real GDP is $330.By how much must government spending be reduced to eliminate the inflationary gap?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Use the table below to answer the following questions.Assume that investment, net exports, government expenditures, and taxes do not change with changes in real GDP. 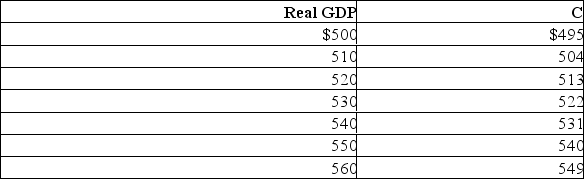 (a) What is the size of the multiplier in this economy?
(a) What is the size of the multiplier in this economy?
(b) If taxes are zero, government expenditures are $5, investment is $3, and net exports are zero, what is the equilibrium GDP?
(c) If taxes are $10, government expenditures are $10, investment is $6, and net exports are zero, what is the equilibrium GDP?
(d) Assume investment is $50, taxes are $50, and net exports and government expenditures are each zero.The full-employment level of real GDP is $540.How much of a reduction in taxes is needed to eliminate the recessionary gap?
(e) Assume that investment, net exports, and taxes are zero.Government expenditures are $10 and the full-employment level of real GDP is $530.By how much must government spending be reduced to eliminate the inflationary gap?
 (a) What is the size of the multiplier in this economy?
(a) What is the size of the multiplier in this economy?(b) If taxes are zero, government expenditures are $5, investment is $3, and net exports are zero, what is the equilibrium GDP?
(c) If taxes are $10, government expenditures are $10, investment is $6, and net exports are zero, what is the equilibrium GDP?
(d) Assume investment is $50, taxes are $50, and net exports and government expenditures are each zero.The full-employment level of real GDP is $540.How much of a reduction in taxes is needed to eliminate the recessionary gap?
(e) Assume that investment, net exports, and taxes are zero.Government expenditures are $10 and the full-employment level of real GDP is $530.By how much must government spending be reduced to eliminate the inflationary gap?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Answer the following questions using the aggregate expenditures model of the economy described below.C = 80 + .6Yd
T = 40 + .2Y
Ia = 28
Ga = 64
Xa = 76
M = .18Y
(a) What are the marginal propensity to consume, the marginal tax rate, and the marginal propensity to import?
(b) What is the saving function? What is the marginal propensity to save?
(c) What is the aggregate expenditure function? What is autonomous expenditure? What is the marginal propensity to withdraw?
(d) What is the equilibrium level of real GDP?
(e) What is the size of the multiplier?
(f) Suppose the full employment level of real GDP is $340.Does a recessionary gap or an inflationary gap exist? How can the government eliminate the gap by altering government expenditures?
T = 40 + .2Y
Ia = 28
Ga = 64
Xa = 76
M = .18Y
(a) What are the marginal propensity to consume, the marginal tax rate, and the marginal propensity to import?
(b) What is the saving function? What is the marginal propensity to save?
(c) What is the aggregate expenditure function? What is autonomous expenditure? What is the marginal propensity to withdraw?
(d) What is the equilibrium level of real GDP?
(e) What is the size of the multiplier?
(f) Suppose the full employment level of real GDP is $340.Does a recessionary gap or an inflationary gap exist? How can the government eliminate the gap by altering government expenditures?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



