Deck 2: A: - The Market System and the Circular Flow
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/42
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: A: - The Market System and the Circular Flow
1
What are the economic advantages of the division of labour?
Specialization enables individuals to take advantage of existing differences in their abilities and skills.Other advantages come from increased productivity or output per worker as specialized workers gain skills in performing one task and avoid loss of time in switching from one task to another.Therefore, more is produced with the same amount of resources as before specialization.
2
Explain the term "laissez-faire capitalism.
Pure capitalism is sometimes called "laissez faire" capitalism which is a French term for "let it be." In pure capitalism the government's role is limited to protecting private property and establishing the legal framework for free enterprise and free markets to function.
3
Why does specialization require a convenient means of exchanging goods?
As consumers, individuals prefer to have a wide range of products to satisfy their desires.However, when individuals specialize in production, they focus their efforts on producing one or a few goods.This limited range of production does not match their preferences in consumption.Therefore, individuals must be able to exchange the goods that they specialize in for other goods that they desire to consume.Without a convenient means of exchanging goods, individuals could only consume what they produce.Instead, individuals would be jacks-of-all-trades producing a wide variety of products for their own consumption.There would be little incentive to specialize and to take advantage of the resulting increase in productivity.
4
Describe two types of specialization in production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Describe all the advantages a money economy has over a barter economy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Explain why the market system is an organizing mechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
How does the use of money differ from the use of barter in the exchange of goods and services?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What roles do freedom of enterprise and freedom of choice play in capitalism? How important are they to the operation of a competitive market economy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Explain what is meant by a command economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
One of the characteristics of a modern market economy is an "active, but limited, government." How can the government "help" the economy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Explain the importance of self-interest in the operation of a market system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the importance of competition in relation to self-interest in a market system?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Explain the most important consequence of legally enforceable property rights?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose Tom, Dick, and Harry live in a barter economy.Tom produces wine, Dick bakes bread, and Harry makes cheese.Tom wants some bread to go with his wine and is willing to trade 1 litre of wine for two loaves of bread.Dick wants some cheese to go with his bread and is willing to trade one loaf of bread for one-half kilogram of cheese.Harry doesn't want bread, but wants some wine to go with his cheese and is willing to trade cheese for one litre of wine.It is not possible for all three of them to meet together at one time.(a) Explain how this situation illustrates the difficulty with a barter economy.(b) Devise a money system using rubies where four rubies are equivalent in value to one litre of wine.In other words tell how much bread and cheese would be worth in terms of rubies in this economy.In this system, how much cheese must Harry sell in order to buy one litre of wine?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Respond to the following question: "Producing capital goods takes time, so how can that be a more efficient form of production of consumer goods?"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Describe three ways that the division of labour contributes to society's output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Why is the right of private property an essential characteristic of a market system?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is money and what important function does it perform? Explain how it overcomes the disadvantages associated with barter.What conditions are necessary for people to accept paper currency in exchange for the goods and services, which they sell?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What conditions are necessary for economic competition to exist?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
List nine characteristics of the market system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What factors determine who will get the output?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What are the so-called Five Fundamental Questions that every economy must answer?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is meant by the guiding function of prices?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Explain this quote from Adam Smith: "It is not from the benevolence of the butcher, the brewer, or the baker that we expect our dinner but from their regard to their own interest."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Describe the basic features of the circular flow model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
List and describe the three main categories of businesses?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Assume that a firm finds that its profits will be maximized (or losses minimized) when it produces $50 worth of product X.Each of these techniques shown in the following table will produce exactly $50 worth of X. 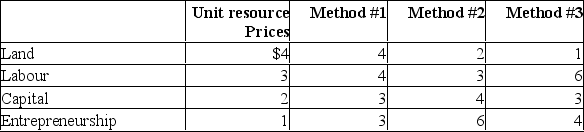 (a) Which method is most efficient? Why?
(a) Which method is most efficient? Why?
(b) Given the above prices, will the firm adopt a new method, which involves 2 units of land, 2 of labour, 4 of capital, and 8 of entrepreneurial ability?
(c) Suppose the price of labour falls to $1 without any other prices changing.Which of the methods will the firm now choose? Why?
 (a) Which method is most efficient? Why?
(a) Which method is most efficient? Why?(b) Given the above prices, will the firm adopt a new method, which involves 2 units of land, 2 of labour, 4 of capital, and 8 of entrepreneurial ability?
(c) Suppose the price of labour falls to $1 without any other prices changing.Which of the methods will the firm now choose? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How does the market system accommodate change in consumer's preferences?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Explain the two different motives that firms have for choosing the lowest-cost production methods to produce goods and services?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Assume that a firm finds that its profits will be maximized (or losses minimized) when it produces $30 worth of product X.Each of these techniques shown in the following table will produce exactly $30 worth of X. 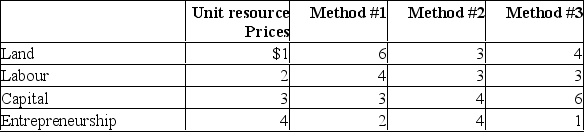 (a) Which method is most efficient? Why?
(a) Which method is most efficient? Why?
(b) Given the above prices, will the firm adopt a new method, which involves 10 units of land, 3 of labour, 2 of capital, and 2 of entrepreneurial ability?
(c) Suppose the price of capital falls to $1 without any other prices changing.Which of the methods will the firm now choose? Why?
 (a) Which method is most efficient? Why?
(a) Which method is most efficient? Why?(b) Given the above prices, will the firm adopt a new method, which involves 10 units of land, 3 of labour, 2 of capital, and 2 of entrepreneurial ability?
(c) Suppose the price of capital falls to $1 without any other prices changing.Which of the methods will the firm now choose? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Assume that a firm can produce product A, product B, or product C with the resources it currently employs.These resources cost the firm a total of $100 per week, this cost is per resource.Assume, for the purposes of this problem, that the firm's costs cannot be changed.The market prices and the quantities of A, B, and C these resources can produce are given below. 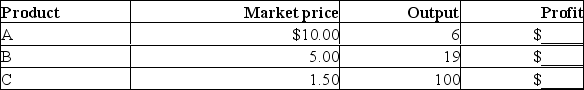 (a) Compute the firm's profit when it produces A, B, or C and enter these data in the table.
(a) Compute the firm's profit when it produces A, B, or C and enter these data in the table.
(b) Which product will the firm produce?
(c) Suppose the quantity of product B the firm was able to produce with the same amount of inputs now rose to 25.Which product will the firm now produce?
(d) As a result of the rise in quantity of product B to 25 that each firm can produce, what will happen to the number of firms producing product B?
 (a) Compute the firm's profit when it produces A, B, or C and enter these data in the table.
(a) Compute the firm's profit when it produces A, B, or C and enter these data in the table.(b) Which product will the firm produce?
(c) Suppose the quantity of product B the firm was able to produce with the same amount of inputs now rose to 25.Which product will the firm now produce?
(d) As a result of the rise in quantity of product B to 25 that each firm can produce, what will happen to the number of firms producing product B?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Describe the three major virtues of a market system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Assume that a firm can produce product A, product B, or product C with the resources it currently employs.These resources cost the firm a total of $100 per week, this cost is per resource.Assume, for the purposes of this problem, that the firm's costs cannot be changed.The market prices and the quantities of A, B, and C these resources can produce are given as follows. 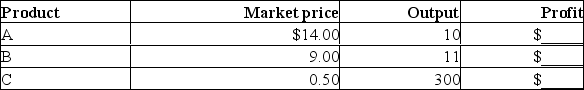
(a) Compute the firm's profit when it produces A, B, or C and enter these data in the table.
(b) Which product will the firm produce?
(c) If the price of A rose to $16, which product will the firm produce?
(d) If the firm produces A at a price of $16, what would tend to happen to the number of firms producing product A?

(a) Compute the firm's profit when it produces A, B, or C and enter these data in the table.
(b) Which product will the firm produce?
(c) If the price of A rose to $16, which product will the firm produce?
(d) If the firm produces A at a price of $16, what would tend to happen to the number of firms producing product A?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
"Competition is the mechanism that brings order out of potential chaos in a price-directed economy." Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Why is the consumer the king (or queen) in a market system?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
List two problems that have contributed to the decline of command systems on a national scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
How can technological advance result in creative destruction?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
"Every economy is based on 'planning' of one sort or another." Interpret and explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
How does consumer choice differ from consumer sovereignty in a market system?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the relationship between businesses and households in the circular flow model?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Provide examples of prominent Canadian corporations and describe the unique implications that arise due to the fact that such corporations are independent legal entities?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In the below circular flow diagram, the household and business sectors are labelled with arrows representing the flows of income and output labelled (a) through (f) and the two appropriate markets labelled (g) and (h).Supply the correct descriptive titles for each of these labels (a) through (h). 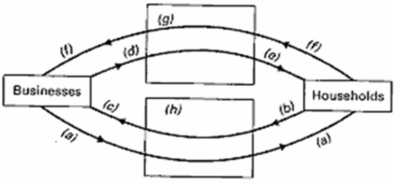


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



