Deck 14: The Federal Reserve and Monetary Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/203
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: The Federal Reserve and Monetary Policy
1
Which of the following is a tool used by the Fed to control the money supply?
A) the reserve requirement
B) open market operations
C) the discount rate
D) All of the above are correct.
A) the reserve requirement
B) open market operations
C) the discount rate
D) All of the above are correct.
All of the above are correct.
2
If a bond has a promised value next year of $440 and the interest rate is 10 percent, then the price of a bond today is:
A) $484.
B) $400.
C) $44.
D) $444.4.
A) $484.
B) $400.
C) $44.
D) $444.4.
$400.
3
All else equal, when the Fed purchases government bonds, the money supply curve shifts to the _______ and the equilibrium interest rate _______.
A) right; falls
B) left; rises
C) right; rises
D) left; falls
A) right; falls
B) left; rises
C) right; rises
D) left; falls
right; falls
4
Fed actions that increase the money supply:
A) tends to lead to a depreciation of a nation's currency.
B) tends to lead to an appreciation of a nation's currency.
C) tends to lead to a depreciation of the currencies of other nations.
D) usually has no effect on a currency's exchange value.
A) tends to lead to a depreciation of a nation's currency.
B) tends to lead to an appreciation of a nation's currency.
C) tends to lead to a depreciation of the currencies of other nations.
D) usually has no effect on a currency's exchange value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The Fed's efforts to stimulate and make the economy grow require that the Fed:
A) sell bonds to lower the interest rates.
B) buy bonds to raise the interest rates.
C) sell bonds to raise the interest rates.
D) buy bonds to lower the interest rates.
A) sell bonds to lower the interest rates.
B) buy bonds to raise the interest rates.
C) sell bonds to raise the interest rates.
D) buy bonds to lower the interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The interest rate that the banks pay to borrow money from the Fed is the:
A) prime lending rate.
B) discount rate.
C) reserve rate.
D) federal funds rate.
A) prime lending rate.
B) discount rate.
C) reserve rate.
D) federal funds rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
MAKING THE FEDERAL RESERVE MORE TRANSPARENT
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the Federal Reserve becoming more transparent about its actions and
decisions and disclosing more information to the public?
In recent years, the Fed has gradually become more open in its deliberations. For many years, the Fed would not even say if it
had changed interest rates. These policies began to change slowly in the 1990s. Starting in 2000, after each FOMC meeting the
Fed announces its target for the federal funds rate and makes a brief statement
explaining its actions. But should the Fed go further in describing its intended future policies?
There was enough interest on this very topic for the FOMC to hold a special meeting—the first since 1979—to discuss the
issue. Some members of the FOMC, including the current chairman Ben Bernanke, believed that the financial markets
needed more information so that they would have a clearer idea of what future Fed
policy—and short-term interest rates—were likely to be. Other members, including William Poole, the president of the St.
Louis Federal Reserve Bank, disagreed. Poole felt that the financial markets understood the implicit rules that the Fed
followed and that issuing a more complex public statement would just confuse
matters.
The special meeting did not lead to any dramatic change in the Fed’s communication policies. But now the members of the
FOMC participate in drafting statements. The Fed clearly recognizes that its statements
may be just as important as its actions.
According to the application, the Federal Reserve started announcing its targeted federal funds rate only after:
A) 1990.
B) 2000.
C) 1970.
D) 1980.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the Federal Reserve becoming more transparent about its actions and
decisions and disclosing more information to the public?
In recent years, the Fed has gradually become more open in its deliberations. For many years, the Fed would not even say if it
had changed interest rates. These policies began to change slowly in the 1990s. Starting in 2000, after each FOMC meeting the
Fed announces its target for the federal funds rate and makes a brief statement
explaining its actions. But should the Fed go further in describing its intended future policies?
There was enough interest on this very topic for the FOMC to hold a special meeting—the first since 1979—to discuss the
issue. Some members of the FOMC, including the current chairman Ben Bernanke, believed that the financial markets
needed more information so that they would have a clearer idea of what future Fed
policy—and short-term interest rates—were likely to be. Other members, including William Poole, the president of the St.
Louis Federal Reserve Bank, disagreed. Poole felt that the financial markets understood the implicit rules that the Fed
followed and that issuing a more complex public statement would just confuse
matters.
The special meeting did not lead to any dramatic change in the Fed’s communication policies. But now the members of the
FOMC participate in drafting statements. The Fed clearly recognizes that its statements
may be just as important as its actions.
According to the application, the Federal Reserve started announcing its targeted federal funds rate only after:
A) 1990.
B) 2000.
C) 1970.
D) 1980.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If a bond promises a payment of $200 and the interest rate is 3%, then the price of the bond is:
A) $197.
B) $206.2.
C) $206.
D) $194.2.
A) $197.
B) $206.2.
C) $206.
D) $194.2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is not a motive for holding money?
A) the transaction motive
B) the liquidity motive
C) the inflation motive
D) the speculative motive
A) the transaction motive
B) the liquidity motive
C) the inflation motive
D) the speculative motive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is true when the US dollar depreciates against the euro?
A) It takes fewer euros to buy the dollar.
B) It takes more dollars to buy the euro.
C) It becomes more expensive for Americans to buy goods from Germany.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) It takes fewer euros to buy the dollar.
B) It takes more dollars to buy the euro.
C) It becomes more expensive for Americans to buy goods from Germany.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Recall Application 3, "The Effectiveness of Committees," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, research by Alan Blinder showed that the actual process of having meetings and discussions appears to have:
A) improved the performance individuals in the committee.
B) improved the overall performance of the leader in the committee.
C) worsened the overall performance of the committee.
D) improved the overall performance of the committee.
According to the application, research by Alan Blinder showed that the actual process of having meetings and discussions appears to have:
A) improved the performance individuals in the committee.
B) improved the overall performance of the leader in the committee.
C) worsened the overall performance of the committee.
D) improved the overall performance of the committee.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
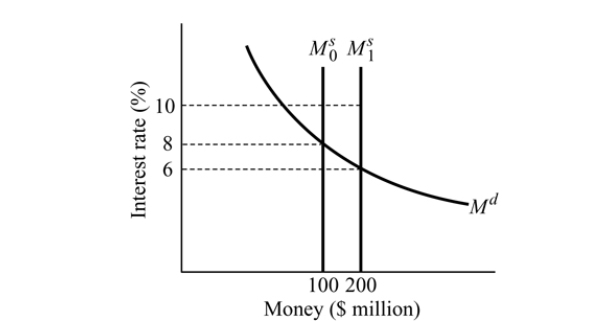 Figure 14.6
Figure 14.6Refer to Figure 14.6. The money supply curve will shift from
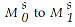 , if:
, if:A) the Fed sells U.S. government bonds in the open market.
B) the Fed decreases the discount rate.
C) the equilibrium level of output decreases.
D) the price level increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
MAKING THE FEDERAL RESERVE MORE TRANSPARENT
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the Federal Reserve becoming more transparent about its actions and
decisions and disclosing more information to the public?
In recent years, the Fed has gradually become more open in its deliberations. For many years, the Fed would not even say if it
had changed interest rates. These policies began to change slowly in the 1990s. Starting in 2000, after each FOMC meeting the
Fed announces its target for the federal funds rate and makes a brief statement
explaining its actions. But should the Fed go further in describing its intended future policies?
There was enough interest on this very topic for the FOMC to hold a special meeting—the first since 1979—to discuss the
issue. Some members of the FOMC, including the current chairman Ben Bernanke, believed that the financial markets
needed more information so that they would have a clearer idea of what future Fed
policy—and short-term interest rates—were likely to be. Other members, including William Poole, the president of the St.
Louis Federal Reserve Bank, disagreed. Poole felt that the financial markets understood the implicit rules that the Fed
followed and that issuing a more complex public statement would just confuse
matters.
The special meeting did not lead to any dramatic change in the Fed’s communication policies. But now the members of the
FOMC participate in drafting statements. The Fed clearly recognizes that its statements
may be just as important as its actions.
According to the application, some members of the FOMC are against making its intended policies more explicit because:
A) making a more complex public statement would confuse the financial market.
B) making a more complex public statement would make the Fed useless.
C) making a more complex public statement could cause a recession.
D) making a more complex public statement would allow the possibility for increased bank profits.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the Federal Reserve becoming more transparent about its actions and
decisions and disclosing more information to the public?
In recent years, the Fed has gradually become more open in its deliberations. For many years, the Fed would not even say if it
had changed interest rates. These policies began to change slowly in the 1990s. Starting in 2000, after each FOMC meeting the
Fed announces its target for the federal funds rate and makes a brief statement
explaining its actions. But should the Fed go further in describing its intended future policies?
There was enough interest on this very topic for the FOMC to hold a special meeting—the first since 1979—to discuss the
issue. Some members of the FOMC, including the current chairman Ben Bernanke, believed that the financial markets
needed more information so that they would have a clearer idea of what future Fed
policy—and short-term interest rates—were likely to be. Other members, including William Poole, the president of the St.
Louis Federal Reserve Bank, disagreed. Poole felt that the financial markets understood the implicit rules that the Fed
followed and that issuing a more complex public statement would just confuse
matters.
The special meeting did not lead to any dramatic change in the Fed’s communication policies. But now the members of the
FOMC participate in drafting statements. The Fed clearly recognizes that its statements
may be just as important as its actions.
According to the application, some members of the FOMC are against making its intended policies more explicit because:
A) making a more complex public statement would confuse the financial market.
B) making a more complex public statement would make the Fed useless.
C) making a more complex public statement could cause a recession.
D) making a more complex public statement would allow the possibility for increased bank profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following would cause an increase in GDP?
A) a higher discount rate
B) an open market purchase
C) an open market sale
D) a higher required reserve ratio
A) a higher discount rate
B) an open market purchase
C) an open market sale
D) a higher required reserve ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When the Fed conducts open market sales, the:
A) commercial banks sell bonds to the private sector.
B) Fed buys bonds from the private sector.
C) Fed sells bonds to the private sector.
D) commercial banks sell bonds to the Fed.
A) commercial banks sell bonds to the private sector.
B) Fed buys bonds from the private sector.
C) Fed sells bonds to the private sector.
D) commercial banks sell bonds to the Fed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Assume that the required reserve ratio is 25%. If the Fed buys $5 million worth of government bonds from the public, the maximum change in the money supply is:
A) 1.25 million.
B) more than 5 million.
C) less than 5 million.
D) $125 million.
A) 1.25 million.
B) more than 5 million.
C) less than 5 million.
D) $125 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the money market, the demand and supply of money determine the equilibrium:
A) nominal interest rate.
B) mortgage interest rate.
C) real interest rate.
D) inflation rate.
A) nominal interest rate.
B) mortgage interest rate.
C) real interest rate.
D) inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Recall Application 1, "Beyond Purchasing Treasury Securities," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, how did the Fed conduct monetary policy prior to 2008?
A) The Fed's asset holdings were less than $1 trillion.
B) The Fed only held U.S. Treasury securities as its assets.
C) The Fed never intervened in a specific credit or security market.
D) All of the above are correct.
According to the application, how did the Fed conduct monetary policy prior to 2008?
A) The Fed's asset holdings were less than $1 trillion.
B) The Fed only held U.S. Treasury securities as its assets.
C) The Fed never intervened in a specific credit or security market.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which basic principle of economics best explains why the demand for money is negatively related to the nominal interest rate?
A) the principle of diminishing returns
B) the principle of voluntary exchange
C) the principle of opportunity cost
D) the marginal principle
A) the principle of diminishing returns
B) the principle of voluntary exchange
C) the principle of opportunity cost
D) the marginal principle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A reduction in the British interest rate relative to the U.S. interest rate will cause a(n):
A) depreciation of the dollar and an appreciation of the British pound.
B) appreciation of the dollar and an appreciation of the British pound.
C) appreciation of the dollar and a depreciation of the British pound.
D) depreciation of the dollar and a depreciation of the British pound.
A) depreciation of the dollar and an appreciation of the British pound.
B) appreciation of the dollar and an appreciation of the British pound.
C) appreciation of the dollar and a depreciation of the British pound.
D) depreciation of the dollar and a depreciation of the British pound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The price of one country's currency in terms of another country's currency is called the:
A) exchange rate.
B) balance of trade.
C) currency valuation.
D) terms of trade.
A) exchange rate.
B) balance of trade.
C) currency valuation.
D) terms of trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is true about inside and outside lags in monetary policy?
A) Inside lags are equally as long as outside lags.
B) Outside lags are shorter than inside lags.
C) Inside lags are shorter than outside lags.
D) There are no inside lags or outside lags in monetary policy.
A) Inside lags are equally as long as outside lags.
B) Outside lags are shorter than inside lags.
C) Inside lags are shorter than outside lags.
D) There are no inside lags or outside lags in monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
 Figure 14.4
Figure 14.4Refer to Figure 14.4. If the Fed wants to reduce the economy's market interest rate from 6 percent to 4 percent, and the reserve ratio is 10 percent, then it needs to _______.
A) buy $20 in government bonds
B) buy $200 in government bonds
C) sell $200 in government bonds
D) sell $20 in government bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is not a tool used by the Fed to control the money supply?
A) the reserve requirement
B) the fed funds rate
C) open market operations
D) the discount rate
A) the reserve requirement
B) the fed funds rate
C) open market operations
D) the discount rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following sequence of events follows an expansionary monetary policy?
A)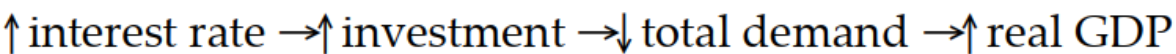
B)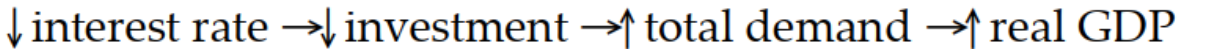
C)
D)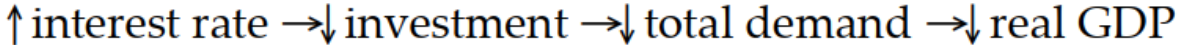
A)
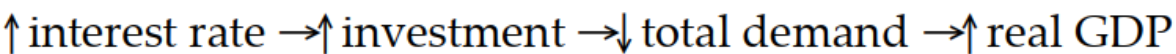
B)
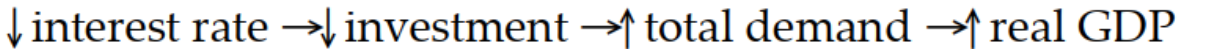
C)

D)
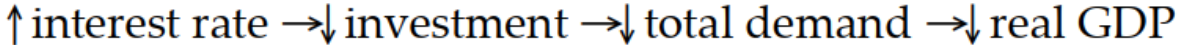

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
An example of a Federal Reserve action that decreases the money supply is:
A) a reduction in the taxes banks pay on their profits.
B) a decrease in the discount rate.
C) the Fed buying government bonds in the open market.
D) an increase in the required reserve ratio.
A) a reduction in the taxes banks pay on their profits.
B) a decrease in the discount rate.
C) the Fed buying government bonds in the open market.
D) an increase in the required reserve ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
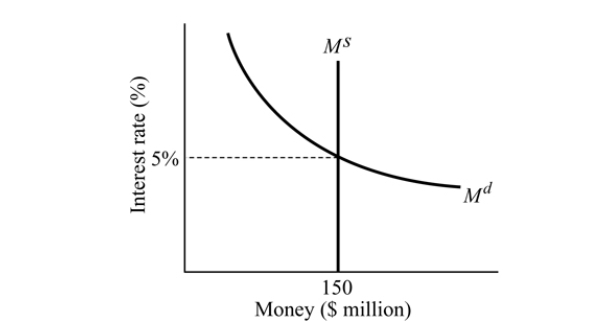 Figure 14.2
Figure 14.2Refer to Figure 14.2. At an interest rate of 8%, there is:
A) excess supply of money and the interest rate will decline.
B) excess demand for money and the interest rate will rise.
C) excess demand for money and the interest rate will decline.
D) excess supply of money and the interest rate will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Recall Application 1, "Beyond Purchasing Treasury Securities," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, which of the following is an example of the sharp change in the Fed's conduct of monetary policy in 2008?
A) The Fed increased total asset holdings by $1 trillion.
B) The Fed intervened in the credit and the mortgage markets.
C) The Fed held mortgage backed securities.
D) All of the above are correct.
According to the application, which of the following is an example of the sharp change in the Fed's conduct of monetary policy in 2008?
A) The Fed increased total asset holdings by $1 trillion.
B) The Fed intervened in the credit and the mortgage markets.
C) The Fed held mortgage backed securities.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When the interest rate rises, bond prices:
A) rise.
B) fall.
C) are unchanged because the interest rate paid on a bond is fixed.
D) will either increase or decrease depending on the type of bond.
A) rise.
B) fall.
C) are unchanged because the interest rate paid on a bond is fixed.
D) will either increase or decrease depending on the type of bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If the quantity of money demanded is greater than the quantity of money supplied, then the interest rate will:
A) fall.
B) remain constant.
C) equal zero.
D) rise.
A) fall.
B) remain constant.
C) equal zero.
D) rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Recall Application 2, "Rising Interest Rates During an Economic Recovery," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, an economy that is experiencing a recession (and hence, a lower income) is usually associated with lower interest rates because:
A) lower incomes cause a higher supply of money.
B) lower incomes cause a lower demand for money.
C) lower incomes cause a lower supply of money.
D) lower incomes cause a higher demand for money.
According to the application, an economy that is experiencing a recession (and hence, a lower income) is usually associated with lower interest rates because:
A) lower incomes cause a higher supply of money.
B) lower incomes cause a lower demand for money.
C) lower incomes cause a lower supply of money.
D) lower incomes cause a higher demand for money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Recall Application 3, "The Effectiveness of Committees," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, later research by Alan Blinder showed that:
A) the wisdom of the leader magnifies the superiority of the decisions of the committee.
B) the wisdom of the leader magnifies the inferiority of the decisions of the committee.
C) the wisdom of the whole group contributes to the superiority of committee decisions than the wisdom of the leader alone.
D) the wisdom of the leader contributes to superiority of committee decisions than the average wisdom of the group.
According to the application, later research by Alan Blinder showed that:
A) the wisdom of the leader magnifies the superiority of the decisions of the committee.
B) the wisdom of the leader magnifies the inferiority of the decisions of the committee.
C) the wisdom of the whole group contributes to the superiority of committee decisions than the wisdom of the leader alone.
D) the wisdom of the leader contributes to superiority of committee decisions than the average wisdom of the group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Excess demand in the money market causes:
A) a decrease in the equilibrium interest rate.
B) an increase in the quantity demanded of money.
C) a decrease in the money supply.
D) an increase in the equilibrium interest rate.
A) a decrease in the equilibrium interest rate.
B) an increase in the quantity demanded of money.
C) a decrease in the money supply.
D) an increase in the equilibrium interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A country's currency depreciates relative to a foreign currency if:
A) it takes more of the home currency to buy the foreign currency.
B) it takes less foreign currency to buy the home currency.
C) the prices of goods in the home country increases faster than in the foreign country.
D) A and B are correct.
A) it takes more of the home currency to buy the foreign currency.
B) it takes less foreign currency to buy the home currency.
C) the prices of goods in the home country increases faster than in the foreign country.
D) A and B are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Suppose the exchange rate between the United States and France changed from $1 = 5 euros to $1 = 4 euros, which of the following statements is true?
A) The euro appreciated.
B) The price of euros in dollars increased.
C) The dollar depreciated.
D) all of the above
A) The euro appreciated.
B) The price of euros in dollars increased.
C) The dollar depreciated.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When the economy is in a recession and the stock market plunges, the interest rates _______ and the bond prices _______ .
A) increase; increase
B) decrease; increase
C) decrease; decrease
D) increase; decrease
A) increase; increase
B) decrease; increase
C) decrease; decrease
D) increase; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The price of a bond is equal to:
A) future payment / (1 - interest rate).
B) future payment / (1 + interest rate).
C) past value / (1 - interest rate).
D) past value / (1 + interest rate).
A) future payment / (1 - interest rate).
B) future payment / (1 + interest rate).
C) past value / (1 - interest rate).
D) past value / (1 + interest rate).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Recall Application 2, "Rising Interest Rates During an Economic Recovery," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, a recovering economy (and hence, a higher income) is usually associated with higher interest rates because:
A) higher incomes cause a lower supply of money.
B) higher incomes cause a higher demand for money.
C) higher incomes cause a lower demand for money.
D) higher incomes cause a higher supply of money.
According to the application, a recovering economy (and hence, a higher income) is usually associated with higher interest rates because:
A) higher incomes cause a lower supply of money.
B) higher incomes cause a higher demand for money.
C) higher incomes cause a lower demand for money.
D) higher incomes cause a higher supply of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following sequence of events would follow an open market purchase of bonds?
A)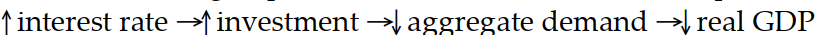
B)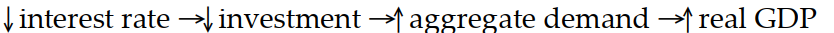
C)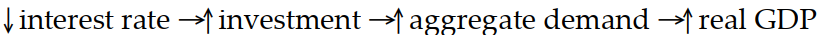
D)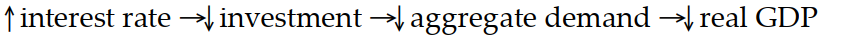
A)
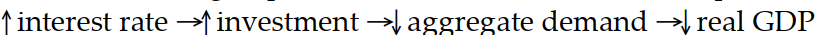
B)
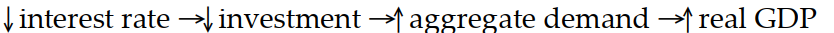
C)
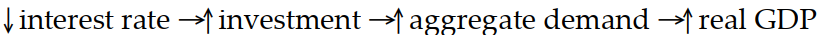
D)
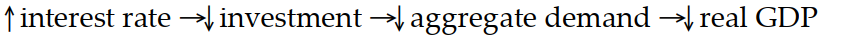

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Suppose Bob converted his portfolio into cash in 2008 as a result of the bad return he has received in the stock market. In this scenario, the reason Bob holds on to money is the:
A) speculative demand for money.
B) liquidity demand for money.
C) transactions demand for money.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) speculative demand for money.
B) liquidity demand for money.
C) transactions demand for money.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
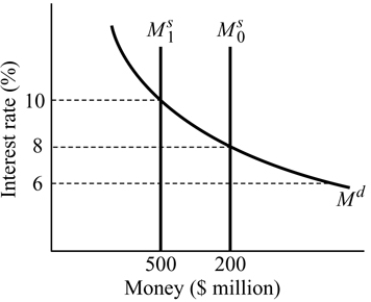 Figure 14.5
Figure 14.5Refer to Figure 14.5. Assume the interest rate equals 8% and the money supply decreases from
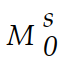 to
to  If the interest rate remains at 8% :
If the interest rate remains at 8% :A) there will be an excess demand for money.
B) money demand will decrease.
C) money demand will increase.
D) there will be an excess supply of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is the tool most used by the Fed to control the money supply in the US?
A) open market operations
B) the discount rate
C) the reserve requirement
D) All of these are used equally often.
A) open market operations
B) the discount rate
C) the reserve requirement
D) All of these are used equally often.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The speculative demand for money is:
A) positively related to income.
B) negatively related to the interest rate.
C) negatively related to income.
D) positively related to the interest rate.
A) positively related to income.
B) negatively related to the interest rate.
C) negatively related to income.
D) positively related to the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
All else constant, if the GDP in an economy decreases then:
A) demand for money increases.
B) the quantity demanded for money increases.
C) demand for money decreases.
D) the quantity demanded for money decreases.
A) demand for money increases.
B) the quantity demanded for money increases.
C) demand for money decreases.
D) the quantity demanded for money decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A reduction in the U.S. interest rate relative to the British interest rate will cause a(an):
A) appreciation of the dollar and an appreciation of the British pound.
B) depreciation of the dollar and an appreciation of the British pound.
C) depreciation of the dollar and a depreciation of the British pound.
D) appreciation of the dollar and a depreciation of the British pound.
A) appreciation of the dollar and an appreciation of the British pound.
B) depreciation of the dollar and an appreciation of the British pound.
C) depreciation of the dollar and a depreciation of the British pound.
D) appreciation of the dollar and a depreciation of the British pound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
All else constant, if the economy in experiences a deflation, then:
A) the quantity demanded for money increases.
B) the quantity demanded for money decreases.
C) demand for money increases.
D) demand for money decreases.
A) the quantity demanded for money increases.
B) the quantity demanded for money decreases.
C) demand for money increases.
D) demand for money decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following pairs of events will definitely lead to an increase in the equilibrium interest rate?
A) a decrease in the required reserve ratio and an increase in the level of real GDP
B) an increase in the discount rate and an increase in the price level
C) the purchase of government bonds by the Federal Reserve and a decrease in the level of real GDP
D) the sale of government bonds by the Federal Reserve and a decrease in the price level
A) a decrease in the required reserve ratio and an increase in the level of real GDP
B) an increase in the discount rate and an increase in the price level
C) the purchase of government bonds by the Federal Reserve and a decrease in the level of real GDP
D) the sale of government bonds by the Federal Reserve and a decrease in the price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The amount of time it takes a given policy action to bring about a change in the state of the economy is called the:
A) outside lag.
B) inside lag.
C) stabilization lag.
D) external lag.
A) outside lag.
B) inside lag.
C) stabilization lag.
D) external lag.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which choice is true?
A) A higher interest rate causes lower investment, higher demand, and higher real GDP.
B) A higher interest rate causes lower investment, lower demand, and lower real GDP.
C) A higher interest rate causes higher investment, lower demand, and lower real GDP.
D) A lower interest rate causes lower investment, higher demand, and higher real GDP.
A) A higher interest rate causes lower investment, higher demand, and higher real GDP.
B) A higher interest rate causes lower investment, lower demand, and lower real GDP.
C) A higher interest rate causes higher investment, lower demand, and lower real GDP.
D) A lower interest rate causes lower investment, higher demand, and higher real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following sequence of events follows a rise in the discount rate?
A)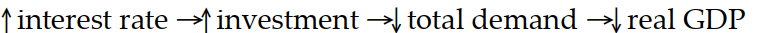
B)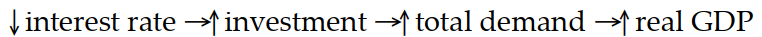
C)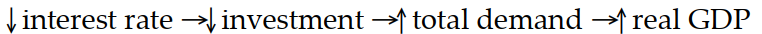
D)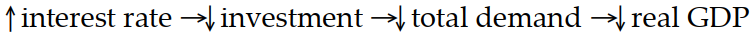
A)
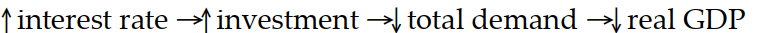
B)
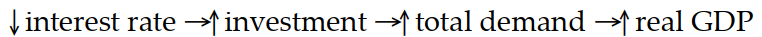
C)
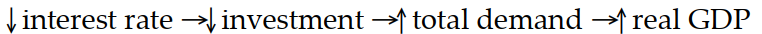
D)
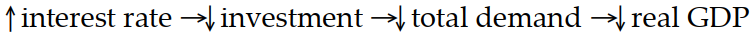

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A depreciation of the U.S. dollar will likely cause U.S. net exports to _______ and U.S. real GDP to _______.
A) decrease; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) increase; increase
D) decrease; decrease
A) decrease; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) increase; increase
D) decrease; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Though a powerful tool, the reserve requirement is seldomly used by the Fed to control the money supply because:
A) it causes significant disruptions in the banking system.
B) using the reserve requirement can be inflationary.
C) it is very difficult for the Fed to monitor the reserve requirement.
D) it takes a long time for the policy to be implemented.
A) it causes significant disruptions in the banking system.
B) using the reserve requirement can be inflationary.
C) it is very difficult for the Fed to monitor the reserve requirement.
D) it takes a long time for the policy to be implemented.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In terms of the demand for money, the interest rate is:
A) the rate at which current consumption can be exchanged for future consumption.
B) the opportunity cost of holding money.
C) the price of borrowing money.
D) the return on money that is saved for the future.
A) the rate at which current consumption can be exchanged for future consumption.
B) the opportunity cost of holding money.
C) the price of borrowing money.
D) the return on money that is saved for the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If the Fed reduces the money supply to reduce inflation:
A) the interest rate will increase, and the price of U.S. exports will rise and the price of U.S. imports will fall.
B) the interest rate will increase, and the price of U.S. exports and U.S. imports will fall.
C) the interest rate will increase, and the price of both U.S. exports and U.S. imports will rise.
D) the interest rate will increase, and the price of U.S. exports will fall and the price of U.S. imports will rise.
A) the interest rate will increase, and the price of U.S. exports will rise and the price of U.S. imports will fall.
B) the interest rate will increase, and the price of U.S. exports and U.S. imports will fall.
C) the interest rate will increase, and the price of both U.S. exports and U.S. imports will rise.
D) the interest rate will increase, and the price of U.S. exports will fall and the price of U.S. imports will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In a graph where the interest rate is on the y- axis and the quantity of money is on the x- axis, a money supply curve that is drawn as a vertical line implies that:
A) the interest rate is independent of the quantity of money.
B) the money market is in equilibrium.
C) the demand for money is independent of the interest rate.
D) the money supply is independent of the interest rate.
A) the interest rate is independent of the quantity of money.
B) the money market is in equilibrium.
C) the demand for money is independent of the interest rate.
D) the money supply is independent of the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
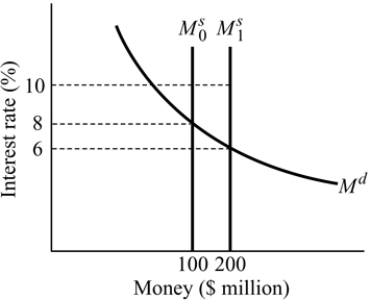 Figure 14.6
Figure 14.6Refer to Figure 14.6. The money supply curve will shift from
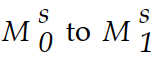 ,if:
,if:A) the Fed buys U.S. government bonds in the open market.
B) the price level increases.
C) the equilibrium level of output decreases.
D) the Fed increases the reserve requirement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
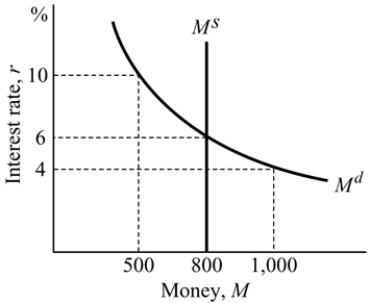 Figure 14.3
Figure 14.3Refer to Figure 14.3. At an interest rate of 4%, there is:
A) an excess demand for money of $200.
B) an excess demand for money of $600.
C) an excess supply of money of $600.
D) an excess supply of money of $200.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
When the Fed conducts open market operations, the Fed buys and sells government securities to:
A) the US. Treasury.
B) foreign countries only.
C) state and local government agencies only.
D) the private sector.
A) the US. Treasury.
B) foreign countries only.
C) state and local government agencies only.
D) the private sector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following represents an action by the Federal Reserve that is designed to increase the money supply?
A) buying government bonds in the open market
B) an increase in the discount rate
C) an increase in the required reserve ratio
D) a decrease in federal spending
A) buying government bonds in the open market
B) an increase in the discount rate
C) an increase in the required reserve ratio
D) a decrease in federal spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If the quantity of money demanded is less than the quantity of money supplied, then the interest rate will:
A) remain constant.
B) fall.
C) change in an uncertain direction.
D) rise.
A) remain constant.
B) fall.
C) change in an uncertain direction.
D) rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Because the Fed can meet anytime in addition to the 8 scheduled meetings every year, and because the Fed can implement policy changes during any of these meetings, it follows that:
A) the Fed's inside lag is very short.
B) the Fed's outside lag is shorter than the inside lag.
C) the Fed's inside lag is equally as long as the outside lag.
D) the Fed's outside lag is very short.
A) the Fed's inside lag is very short.
B) the Fed's outside lag is shorter than the inside lag.
C) the Fed's inside lag is equally as long as the outside lag.
D) the Fed's outside lag is very short.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following is true when the US dollar appreciates against the euro?
A) It takes fewer euros to buy the dollar.
B) It becomes more expensive for Americans to buy goods from Germany.
C) It takes fewer dollars to buy the euro.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) It takes fewer euros to buy the dollar.
B) It becomes more expensive for Americans to buy goods from Germany.
C) It takes fewer dollars to buy the euro.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The outside lag associated with economic policy represents:
A) the time needed for the Federal Reserve Board to meet.
B) the time that it takes for a newly implemented policy to take effect.
C) the time that is necessary to recognize and implement policy.
D) the time it takes for the policy makers to admit that a policy is not working.
A) the time needed for the Federal Reserve Board to meet.
B) the time that it takes for a newly implemented policy to take effect.
C) the time that is necessary to recognize and implement policy.
D) the time it takes for the policy makers to admit that a policy is not working.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following represents an action by the Federal Reserve that is designed to increase the money supply?
A) a decrease in the required reserve ratio
B) selling government bonds in the open market
C) an increase in the discount rate
D) a decrease in federal tax rates
A) a decrease in the required reserve ratio
B) selling government bonds in the open market
C) an increase in the discount rate
D) a decrease in federal tax rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following policies tends to cause the dollar to appreciate?
A) an increase in the U.S. money supply
B) a decrease in U.S. interest rates
C) a decrease in the money supply
D) none of the above
A) an increase in the U.S. money supply
B) a decrease in U.S. interest rates
C) a decrease in the money supply
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When inflation increases, the
A) the demand for money decreases.
B) demand for money increases.
C) the quantity demanded for money increases.
D) the quantity demanded for money decreases.
A) the demand for money decreases.
B) demand for money increases.
C) the quantity demanded for money increases.
D) the quantity demanded for money decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
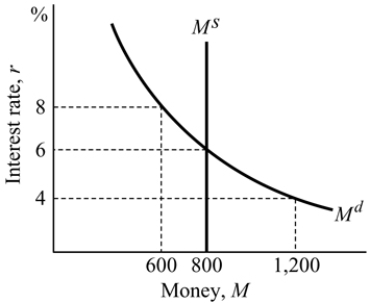 Figure 14.4
Figure 14.4Refer to Figure 14.4. If the Fed wants to reduce the economy's market interest rate from 6 percent to 4 percent, it needs to _______.
A) buy government bonds
B) sell government bonds
C) increase Md D) keep Ms constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
An open- market purchase of government bonds by the Fed results in _______ in bank reserves and _______ in the supply of money.
A) an increase; an increase
B) an increase; a decrease
C) a decrease; an increase
D) a decrease; a decrease
A) an increase; an increase
B) an increase; a decrease
C) a decrease; an increase
D) a decrease; a decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Suppose Bob holds cash because he expects to need it in the future and it may be costly for him to convert his assets into money later, then the reason Bob holds on to money is the:
A) speculative demand for money.
B) liquidity demand for money.
C) transactions demand for money.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) speculative demand for money.
B) liquidity demand for money.
C) transactions demand for money.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following is the result of a sale of government bonds by the Fed?
A) an increase in the supply of money
B) a decrease in the discount rate
C) an increase in the required reserve ratio
D) a decrease in banks' reserves
A) an increase in the supply of money
B) a decrease in the discount rate
C) an increase in the required reserve ratio
D) a decrease in banks' reserves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If the quantity of money demanded equals the quantity of money supplied, then the interest rate will:
A) remain constant.
B) fall.
C) equal zero.
D) rise.
A) remain constant.
B) fall.
C) equal zero.
D) rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
An appreciation of the U.S. dollar will likely cause U.S. net exports to _______ and U.S. real GDP to _______.
A) increase; decrease
B) increase; increase
C) decrease; decrease
D) decrease; increase
A) increase; decrease
B) increase; increase
C) decrease; decrease
D) decrease; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
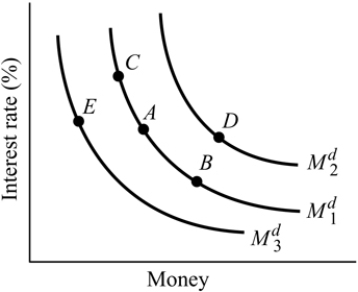 Figure 14.1
Figure 14.1Refer to Figure 14.1. A movement from Point A to Point B can be caused by:
A) an increase in the price of bonds.
B) an increase in the price level.
C) a decrease in the interest rate.
D) a decrease in income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When the economy is in a boom, the interest rates _______ and the bond prices _______.
A) increase; increase
B) decrease; increase
C) increase; decrease
D) decrease; decrease
A) increase; increase
B) decrease; increase
C) increase; decrease
D) decrease; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Increasing the required reserve ratio shifts the money supply curve to the _______ and _______ the equilibrium interest rate.
A) left; decreases
B) left; increases
C) right; decreases
D) right; increases
A) left; decreases
B) left; increases
C) right; decreases
D) right; increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
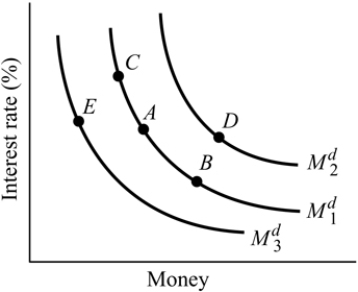 Figure 14.1
Figure 14.1Refer to Figure 14.1. The money demand curve will shift from
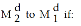
A) income increases.
B) interest rates rise.
C) interest rates fall.
D) the price level decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The Fed indirectly controls long- term interest rates by:
A) reducing outside lags and increasing inside lags.
B) influencing market expectations about future short- term interest rates.
C) setting the Federal Funds rate in advance.
D) determining the interest rate offered by Treasury Bills.
A) reducing outside lags and increasing inside lags.
B) influencing market expectations about future short- term interest rates.
C) setting the Federal Funds rate in advance.
D) determining the interest rate offered by Treasury Bills.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
An example of a tool used by the Fed that decreases the money supply is:
A) a decrease in the prime lending rate.
B) an increase in the required reserve ratio.
C) the Fed buying government bonds in the open market.
D) a decrease in the discount rate.
A) a decrease in the prime lending rate.
B) an increase in the required reserve ratio.
C) the Fed buying government bonds in the open market.
D) a decrease in the discount rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following sequence of events would follow an open market sale of bonds?
A)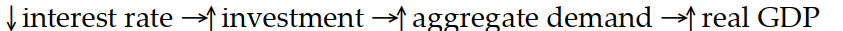
B)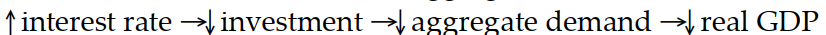
C)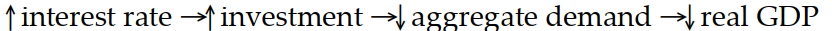
D)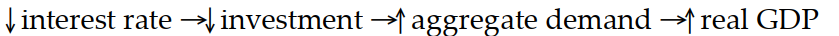
A)
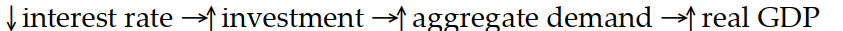
B)
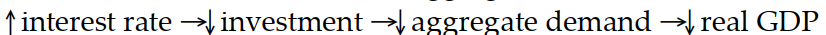
C)
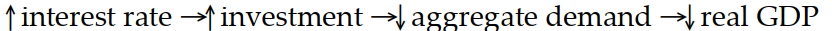
D)
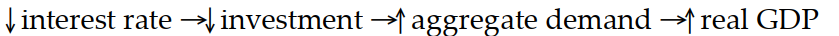

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
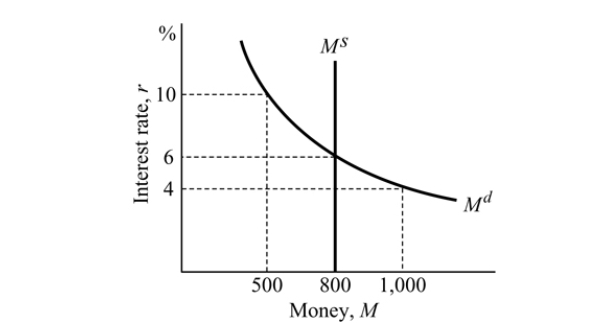 Figure 14.3
Figure 14.3Refer to Figure 14.3. The money market will be in equilibrium at an interest rate of:
A) 6%.
B) 0%.
C) 3%.
D) 8%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 203 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



