Deck 1: Part B: Limits, Alternatives, and Choices
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/265
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Part B: Limits, Alternatives, and Choices
1
An economy will always operate at some point on its production possibilities curve.
False
2
Choices entail marginal costs because resources are scarce.
True
3
Macroeconomics explains the behaviour of individual households and business firms; microeconomics is concerned with the behaviour of aggregates or the economy as a whole.
False
4
The production possibilities curve shows various combinations of two products which an economy can produce when achieving full employment and productive efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Certain inherently desirable products such as education and health care should be produced so long as resources are available.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
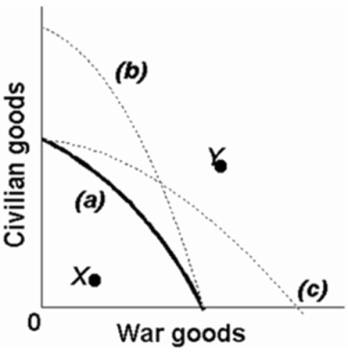 Refer to the above production possibilities curves.Given production possibilities curve (a), point Y indicates that society is failing to use available resources efficiently.
Refer to the above production possibilities curves.Given production possibilities curve (a), point Y indicates that society is failing to use available resources efficiently.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Products and services are scarce because resources are scarce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The entrepreneur's sole function is to combine other resources (land, labour, and capital) in the production of some good or service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Normative statements are expressions of facts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Individuals face an economic problem but society does not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Rational individuals may make different choices because their information and circumstances differ.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The process by which capital goods are accumulated is known as investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Marginal analysis means that decision-makers compare the extra benefits with the extra costs of a specific choice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Positive statements are expressions of value judgments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If economic theories are solidly based on relevant facts, then there can be no question as to the character of appropriate economic policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
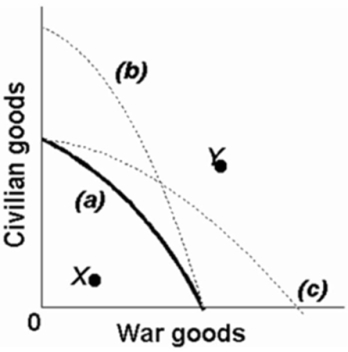 Refer to the above production possibilities curves.The movement from curve (a) to curve (b) implies an increase in the quantity and/or quality of society's productive resources.
Refer to the above production possibilities curves.The movement from curve (a) to curve (b) implies an increase in the quantity and/or quality of society's productive resources.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An economy cannot produce at a point outside of its production possibilities curve because human material wants are insatiable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Although sleeping in on a work day or school day has an opportunity cost, sleeping late on the weekend does not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The fact that economic generalizations are abstract renders them impractical and useless.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
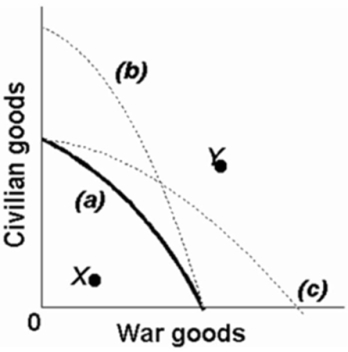 Refer to the above production possibilities curves.Given production possibilities curve (a), the combination of civilian and war goods indicated by point X is unattainable to this economy.
Refer to the above production possibilities curves.Given production possibilities curve (a), the combination of civilian and war goods indicated by point X is unattainable to this economy.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Specialization and trade are beneficial to society because:
A)the output of economic goods may be increased with no increase in resources.
B)scarce resources are utilized more efficiently.
C)a division of labour lowers prices for products.
D)all of the above are correct.
A)the output of economic goods may be increased with no increase in resources.
B)scarce resources are utilized more efficiently.
C)a division of labour lowers prices for products.
D)all of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Tammie makes $150 a day as a bank clerk.She takes off two days of work without pay to fly to another city to attend the concert of her favourite music group.The cost of transportation for the trip is $250.The cost of the concert ticket is $50.The opportunity cost of Tammie's trip to the concert is:
A)$300
B)$450
C)$500
D)$600
A)$300
B)$450
C)$500
D)$600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A major argument for economic growth is that it:
A)creates an equal distribution of income.
B)protects common property resources.
C)leads to a higher standard of living.
D)reduces the amount of taxation.
A)creates an equal distribution of income.
B)protects common property resources.
C)leads to a higher standard of living.
D)reduces the amount of taxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The study of economics exists because:
A)government interferes with the efficient allocation of scarce resources.
B)resources are scarce in relation to human material wants.
C)the market system is an obstacle to the efficient use of plentiful resources to satisfy constrained wants.
D)resources are overly abundant as compared to wants; thus, an allocation problem exists.
A)government interferes with the efficient allocation of scarce resources.
B)resources are scarce in relation to human material wants.
C)the market system is an obstacle to the efficient use of plentiful resources to satisfy constrained wants.
D)resources are overly abundant as compared to wants; thus, an allocation problem exists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Refer to the production possibilities curves.The movement from curve (a) to curve (c) indicates an improvement in civilian goods technology but not in war goods technology. 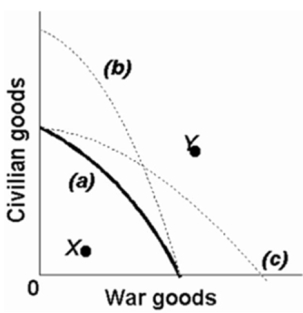


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The economic concept that serves as the basis for the study of economics is:
A)inflation.
B)unemployment.
C)money.
D)scarcity.
A)inflation.
B)unemployment.
C)money.
D)scarcity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
One of the basic economic defences of economic growth rests on the conclusion that:
A)growth makes workers less obsolete and more secure in employment.
B)growth reduces the cost of "common property" resources to society.
C)growth makes the gap between unlimited wants and scarce resources less acute.
D)a growth-oriented society has a relatively equitable income distribution.
A)growth makes workers less obsolete and more secure in employment.
B)growth reduces the cost of "common property" resources to society.
C)growth makes the gap between unlimited wants and scarce resources less acute.
D)a growth-oriented society has a relatively equitable income distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Concern about the general level of prices in an economy is primarily a concern about the economic goal of:
A)economic efficiency.
B)economic security.
C)price-level stability.
D)equity.
A)economic efficiency.
B)economic security.
C)price-level stability.
D)equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Recessions are characterised by points that are not attainable on the production possibilities curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The study of economics is primarily concerned with:
A)keeping private businesses from losing money.
B)demonstrating that capitalistic economies are superior to socialistic economies.
C)choices which are made in seeking to use scarce resources efficiently.
D)determining the most equitable distribution of society's output.
A)keeping private businesses from losing money.
B)demonstrating that capitalistic economies are superior to socialistic economies.
C)choices which are made in seeking to use scarce resources efficiently.
D)determining the most equitable distribution of society's output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Opportunity cost is best defined as:
A)marginal cost minus marginal benefit.
B)the time spent on an economic activity.
C)the value of the best foregone alternative.
D)the money cost of an economic decision.
A)marginal cost minus marginal benefit.
B)the time spent on an economic activity.
C)the value of the best foregone alternative.
D)the money cost of an economic decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In every economic system, choices must be made because resources are:
A)infinite, but economic wants are finite.
B)finite, but economic wants are insatiable.
C)unlimited, but economic wants are limited.
D)limited, and so are economic wants.
A)infinite, but economic wants are finite.
B)finite, but economic wants are insatiable.
C)unlimited, but economic wants are limited.
D)limited, and so are economic wants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Economics may best be defined as:
A)the interaction between macro and micro considerations.
B)the study of the behaviour of people and institutions in the production, distribution, and consumption of scarce goods.
C)the empirical testing of value judgments through the use of induction and deduction.
D)the use of policy to refute facts and hypotheses.
A)the interaction between macro and micro considerations.
B)the study of the behaviour of people and institutions in the production, distribution, and consumption of scarce goods.
C)the empirical testing of value judgments through the use of induction and deduction.
D)the use of policy to refute facts and hypotheses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When a provincial government chooses to build more roads, the required resources are no longer available for spending on public education.This dilemma illustrates the concept of:
A)marginal analysis.
B)full employment.
C)full production.
D)opportunity cost.
A)marginal analysis.
B)full employment.
C)full production.
D)opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The institution that coordinates actions of consumers and producers to establish prices for goods and services is known as:
A)a market.
B)a monopoly.
C)a production possibilities curve.
D)consumer sovereignty.
A)a market.
B)a monopoly.
C)a production possibilities curve.
D)consumer sovereignty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When economists describe "a market," they mean:
A)a place where stocks and bonds are traded.
B)information networks that allow individuals to keep in touch with each other.
C)a hypothetical place where the production of goods and services takes place.
D)a mechanism which coordinates actions of consumers and producers to establish equilibrium prices and quantities.
A)a place where stocks and bonds are traded.
B)information networks that allow individuals to keep in touch with each other.
C)a hypothetical place where the production of goods and services takes place.
D)a mechanism which coordinates actions of consumers and producers to establish equilibrium prices and quantities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The assertion that "There is no free lunch" means:
A)there are always tradeoffs between economic goals.
B)all production involves the use of scarce resources and thus the sacrifice of alternative goods.
C)marginal analysis is not used in economic reasoning.
D)choices do not need be made if behaviour is rational.
A)there are always tradeoffs between economic goals.
B)all production involves the use of scarce resources and thus the sacrifice of alternative goods.
C)marginal analysis is not used in economic reasoning.
D)choices do not need be made if behaviour is rational.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Assume that a tradeoff exists in the short run between inflation and unemployment.This relationship means that:
A)a low rate of unemployment causes a low rate of inflation.
B)the unemployment rate always equals the inflation rate.
C)less unemployment can be achieved with more inflation.
D)less unemployment can be achieved with less inflation.
A)a low rate of unemployment causes a low rate of inflation.
B)the unemployment rate always equals the inflation rate.
C)less unemployment can be achieved with more inflation.
D)less unemployment can be achieved with less inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
As a consequence of the condition of scarcity:
A)there is always enough of everything.
B)production has to be centrally planned.
C)things which are plentiful have relatively high prices.
D)individuals and communities have to make choices among alternatives.
A)there is always enough of everything.
B)production has to be centrally planned.
C)things which are plentiful have relatively high prices.
D)individuals and communities have to make choices among alternatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The present choice of position on the production possibilities curve will not influence the future location of the curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Consumers spend their incomes to get the maximum benefit or satisfaction from the goods and services they purchase.This is a reflection of:
A)resource scarcity and the necessity of choice.
B)purposeful behaviour.
C)marginal costs which exceed marginal benefits.
D)the tradeoff problem which exists between competing goals.
A)resource scarcity and the necessity of choice.
B)purposeful behaviour.
C)marginal costs which exceed marginal benefits.
D)the tradeoff problem which exists between competing goals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
You should decide to go to a movie:
A)if the marginal cost of the movie exceeds its marginal benefit.
B)if the marginal benefit of the movie exceeds its marginal cost.
C)if your income will allow you to buy a ticket
D)because movies are inherently good products.
A)if the marginal cost of the movie exceeds its marginal benefit.
B)if the marginal benefit of the movie exceeds its marginal cost.
C)if your income will allow you to buy a ticket
D)because movies are inherently good products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How is the economic perspective reflected in lines for fast food?
A)Customers select the shortest line because they have perfect information.
B)Customers select the shortest line because they believe it will reduce their time cost of obtaining food.
C)Lines will typically be of unequal length because of the inefficiencies in counter service.
D)The set of food choices is often too complex for most customers and thus creates long lines.
A)Customers select the shortest line because they have perfect information.
B)Customers select the shortest line because they believe it will reduce their time cost of obtaining food.
C)Lines will typically be of unequal length because of the inefficiencies in counter service.
D)The set of food choices is often too complex for most customers and thus creates long lines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
From the perspective of economists, which term provides the highest degree of confidence for explaining economic behaviour?
A)an economic principle or a law
B)a fact
C)a hypothesis
D)an assumption
A)an economic principle or a law
B)a fact
C)a hypothesis
D)an assumption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
At fast-food restaurants:
A)consumers enjoy complete and accurate information.
B)decisions are usually made by trial and error.
C)decisions entail comparisons of marginal costs and marginal benefits.
D)benefits always exceed costs.
A)consumers enjoy complete and accurate information.
B)decisions are usually made by trial and error.
C)decisions entail comparisons of marginal costs and marginal benefits.
D)benefits always exceed costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The "economic perspective" refers to:
A)macroeconomic phenomena, but not microeconomic phenomena.
B)microeconomic phenomena, but not macroeconomic phenomena.
C)the making of rational decisions in a context of marginal costs and marginal benefits.
D)unlimited resources in a context of limited material wants.
A)macroeconomic phenomena, but not microeconomic phenomena.
B)microeconomic phenomena, but not macroeconomic phenomena.
C)the making of rational decisions in a context of marginal costs and marginal benefits.
D)unlimited resources in a context of limited material wants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The "economic perspective" entails:
A)rational behaviour by individuals and institutions.
B)a comparison of marginal benefits and marginal costs in decision making.
C)the altering of behaviour when marginal benefits and marginal costs change.
D)all of the above.
A)rational behaviour by individuals and institutions.
B)a comparison of marginal benefits and marginal costs in decision making.
C)the altering of behaviour when marginal benefits and marginal costs change.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
An economic model is:
A)a value judgment.
B)a fact.
C)built using theory.
D)built on correlations.
A)a value judgment.
B)a fact.
C)built using theory.
D)built on correlations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The process of developing hypotheses, testing them against facts, and using the results to construct theories is called:
A)opportunity cost calculation.
B)the scientific method.
C)marginal analysis.
D)microeconomics.
A)opportunity cost calculation.
B)the scientific method.
C)marginal analysis.
D)microeconomics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Suppose an economist says that "Other things equal, the lower the price of bananas, the greater the amount of bananas purchased." This statement indicates that:
A)the quantity of bananas purchased determines the price of bananas.
B)all factors other than the price of bananas (for example, consumer tastes and incomes) are assumed to be constant.
C)economists can conduct controlled laboratory experiments.
D)one cannot generalize about the relationship between the price of bananas and the quantity purchased.
A)the quantity of bananas purchased determines the price of bananas.
B)all factors other than the price of bananas (for example, consumer tastes and incomes) are assumed to be constant.
C)economists can conduct controlled laboratory experiments.
D)one cannot generalize about the relationship between the price of bananas and the quantity purchased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The economic perspective used in customer decision making at fast-food restaurants is reflected in:
A)customers selecting the shortest line.
B)customers leaving rather than waiting if all lines are long.
C)all customer lines tending to be of equal length.
D)all of the above.
A)customers selecting the shortest line.
B)customers leaving rather than waiting if all lines are long.
C)all customer lines tending to be of equal length.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Economic models:
A)are of limited use because they cannot be tested empirically.
B)are limited to variables which are directly related to one another.
C)emphasize basic economic relationships by abstracting from the complexities of the real world.
D)are unrealistic and therefore of no practical consequence.
A)are of limited use because they cannot be tested empirically.
B)are limited to variables which are directly related to one another.
C)emphasize basic economic relationships by abstracting from the complexities of the real world.
D)are unrealistic and therefore of no practical consequence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Consumers might leave a fast-food restaurant without being served because:
A)they are misinformed about the marginal cost and marginal benefits of the food being served.
B)they conclude that the marginal cost (monetary plus time costs) exceeds the marginal benefit.
C)the environment is not conducive to a rational choice.
D)the lines waiting for service are not of equal length.
A)they are misinformed about the marginal cost and marginal benefits of the food being served.
B)they conclude that the marginal cost (monetary plus time costs) exceeds the marginal benefit.
C)the environment is not conducive to a rational choice.
D)the lines waiting for service are not of equal length.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A "hypothesis" is:
A)a fundamental truth which all economists accept.
B)a tentative, untested principle.
C)the same as a normative statement.
D)always the result of induction.
A)a fundamental truth which all economists accept.
B)a tentative, untested principle.
C)the same as a normative statement.
D)always the result of induction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Purposeful behaviour suggests that:
A)everyone will make identical choices.
B)resource availability exceeds material wants.
C)individuals make decisions with some desired outcome in mind.
D)an individual's economic goals cannot involve tradeoffs.
A)everyone will make identical choices.
B)resource availability exceeds material wants.
C)individuals make decisions with some desired outcome in mind.
D)an individual's economic goals cannot involve tradeoffs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
From an economic perspective, when consumers leave a fast-food restaurant because the lines to be served are too long, they have concluded that the:
A)marginal cost of waiting is less than the marginal benefit of being served.
B)marginal cost of waiting is greater than the marginal benefit of being served.
C)management is exhibiting irrational behaviour by not maximizing profits.
D)management is making an assumption that other things are equal.
A)marginal cost of waiting is less than the marginal benefit of being served.
B)marginal cost of waiting is greater than the marginal benefit of being served.
C)management is exhibiting irrational behaviour by not maximizing profits.
D)management is making an assumption that other things are equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Marginal costs exist because:
A)the decision to produce more of some product means the sacrifice of other products.
B)wants are scarce relative to resources.
C)households and businesses make rational decisions.
D)most decisions do not involve sacrifices or tradeoffs.
A)the decision to produce more of some product means the sacrifice of other products.
B)wants are scarce relative to resources.
C)households and businesses make rational decisions.
D)most decisions do not involve sacrifices or tradeoffs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Even though local newspapers are very inexpensive, people rarely buy more than one of them each day.This fact:
A)is an example of irrational behaviour.
B)implies that reading should be taught through phonics rather than the whole language method.
C)contradicts the economic perspective.
D)implies that, for most people, the marginal benefit of reading a second newspaper is less than the marginal cost.
A)is an example of irrational behaviour.
B)implies that reading should be taught through phonics rather than the whole language method.
C)contradicts the economic perspective.
D)implies that, for most people, the marginal benefit of reading a second newspaper is less than the marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In constructing models, economists:
A)make simplifying assumptions.
B)include all available information.
C)must use mathematical equations.
D)attempt to duplicate the real world.
A)make simplifying assumptions.
B)include all available information.
C)must use mathematical equations.
D)attempt to duplicate the real world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Economics involves "marginal analysis" because:
A)most decisions involve changes in the status quo.
B)marginal benefits always exceed marginal costs.
C)marginal costs always exceed marginal benefits.
D)much economic behaviour is irrational.
A)most decisions involve changes in the status quo.
B)marginal benefits always exceed marginal costs.
C)marginal costs always exceed marginal benefits.
D)much economic behaviour is irrational.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following statements pertains to macroeconomics?
A)Because the minimum wage was raised, Mrs.Beepath decided to enter the labour force.
B)A decline in the price of soybeans caused farmer Wanek to plant more land in wheat.
C)The national productivity rate grew by 1.4 percent last year.
D)The Pumpkin Center Chartered Bank increased its interest rate on consumer loans by 1 percent.
A)Because the minimum wage was raised, Mrs.Beepath decided to enter the labour force.
B)A decline in the price of soybeans caused farmer Wanek to plant more land in wheat.
C)The national productivity rate grew by 1.4 percent last year.
D)The Pumpkin Center Chartered Bank increased its interest rate on consumer loans by 1 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Economics is concerned with using scarce productive resources efficiently in attempting to satisfy society's material wants.This statement is:
A)positive, but incorrect.
B)positive and correct.
C)normative, but incorrect.
D)normative and correct.
A)positive, but incorrect.
B)positive and correct.
C)normative, but incorrect.
D)normative and correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following is associated with macroeconomics?
A)an examination of the incomes of the University of Toronto Business School graduates
B)an empirical investigation of the general price level and unemployment rates in the 2000s
C)a study of the trend of pecan prices since World War II
D)a case study of pricing and production in the textbook industry
A)an examination of the incomes of the University of Toronto Business School graduates
B)an empirical investigation of the general price level and unemployment rates in the 2000s
C)a study of the trend of pecan prices since World War II
D)a case study of pricing and production in the textbook industry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A positive statement is one which is:
A)derived by an abstract generalization.
B)suggestive of what should be done.
C)subjective and is based on a value judgment.
D)objective and is also based on facts.
A)derived by an abstract generalization.
B)suggestive of what should be done.
C)subjective and is based on a value judgment.
D)objective and is also based on facts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following is a macroeconomic statement?
A)The gross profits of all Canadian businesses were $70 billion last year.
B)The price of beef declined by 3 percent last year.
C)General Motors' profits increased in 2012.
D)The productivity of steelworkers increased by 1 percent in 2012.
A)The gross profits of all Canadian businesses were $70 billion last year.
B)The price of beef declined by 3 percent last year.
C)General Motors' profits increased in 2012.
D)The productivity of steelworkers increased by 1 percent in 2012.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Most of the disagreement among economists involves:
A)facts.
B)theories.
C)positive statements.
D)normative statements.
A)facts.
B)theories.
C)positive statements.
D)normative statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A positive statement is concerned with:
A)some goal which is desirable to society.
B)what should be.
C)what is.
D)the formulation of economic policy.
A)some goal which is desirable to society.
B)what should be.
C)what is.
D)the formulation of economic policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A normative statement is one which:
A)is based on the law of averages.
B)pertains only to microeconomics.
C)pertains only to macroeconomics.
D)is based upon value judgments.
A)is based on the law of averages.
B)pertains only to microeconomics.
C)pertains only to macroeconomics.
D)is based upon value judgments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is a microeconomic statement?
A)The real domestic output increased by 2.5 percent last year.
B)Unemployment was 8.3 percent of the labour force last year.
C)The price of personal computers declined last year.
D)The general price level increased by 4 percent last year.
A)The real domestic output increased by 2.5 percent last year.
B)Unemployment was 8.3 percent of the labour force last year.
C)The price of personal computers declined last year.
D)The general price level increased by 4 percent last year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Microeconomics is concerned with:
A)the aggregate or total levels of income, employment, and output.
B)a detailed examination of specific economic units which comprise the economic system.
C)the concealing of detailed information about specific segments of the economy.
D)the establishing of an overall view of the operation of the economic system.
A)the aggregate or total levels of income, employment, and output.
B)a detailed examination of specific economic units which comprise the economic system.
C)the concealing of detailed information about specific segments of the economy.
D)the establishing of an overall view of the operation of the economic system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following is a normative statement?
A)The temperature is high today.
B)The humidity is high today.
C)It is too hot to play tennis today.
D)It will cool off later this evening.
A)The temperature is high today.
B)The humidity is high today.
C)It is too hot to play tennis today.
D)It will cool off later this evening.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The term "other things equal" means that:
A)the associated statement is normative.
B)many variables affect the variable under consideration.
C)the assumption that factors other than those being considered do not change.
D)when variable X increases so does related variable Y.
A)the associated statement is normative.
B)many variables affect the variable under consideration.
C)the assumption that factors other than those being considered do not change.
D)when variable X increases so does related variable Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following is a positive statement?
A)The humidity is too high today.
B)It is too hot to jog today.
C)The temperature is 30 degrees today.
D)I enjoy summer evenings when it cools off.
A)The humidity is too high today.
B)It is too hot to jog today.
C)The temperature is 30 degrees today.
D)I enjoy summer evenings when it cools off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The basic purpose of the "other things equal" assumption is to:
A)allow one to reason about the relationship between variables X and Y without the intrusion of variable Z.
B)allow one to focus upon micro variables by ignoring macro variables.
C)allow one to focus upon macro variables by ignoring micro variables.
D)determine whether X causes Y or vice versa.
A)allow one to reason about the relationship between variables X and Y without the intrusion of variable Z.
B)allow one to focus upon micro variables by ignoring macro variables.
C)allow one to focus upon macro variables by ignoring micro variables.
D)determine whether X causes Y or vice versa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The problems of aggregate inflation and unemployment are:
A)major topics of macroeconomics.
B)not relevant to the Canadian economy.
C)major topics of microeconomics.
D)peculiar to socialistic economies.
A)major topics of macroeconomics.
B)not relevant to the Canadian economy.
C)major topics of microeconomics.
D)peculiar to socialistic economies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Ben says that "An increase in the tax on beer will raise its price." Holly argues that "Taxes should be increased on beer because college students drink too much." We can conclude that:
A)Ben's statement is normative, but Holly's is positive.
B)Holly's statement is normative, but Ben's is positive.
C)Both statements are normative.
D)Both statements are positive.
A)Ben's statement is normative, but Holly's is positive.
B)Holly's statement is normative, but Ben's is positive.
C)Both statements are normative.
D)Both statements are positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Macroeconomics approaches the study of economics from the viewpoint of:
A)the entire economy.
B)governmental units.
C)the operation of specific product and resource markets.
D)individual firms.
A)the entire economy.
B)governmental units.
C)the operation of specific product and resource markets.
D)individual firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Macroeconomics can best be described as the:
A)analysis of how a consumer tries to spend income.
B)study of the large aggregates of the economy or the economy as a whole.
C)analysis of how firms attempt to maximize their profits.
D)study of how supply and demand determine prices in individual markets.
A)analysis of how a consumer tries to spend income.
B)study of the large aggregates of the economy or the economy as a whole.
C)analysis of how firms attempt to maximize their profits.
D)study of how supply and demand determine prices in individual markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Microeconomics:
A)is concerned with the aggregate or total levels of income, employment, and output.
B)is not concerned with details, but only with the overall "big picture" of the economy.
C)is concerned with individual economic units and specific markets.
D)describes the aggregate flows of output and income.
A)is concerned with the aggregate or total levels of income, employment, and output.
B)is not concerned with details, but only with the overall "big picture" of the economy.
C)is concerned with individual economic units and specific markets.
D)describes the aggregate flows of output and income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Normative statements are concerned with:
A)facts and theories.
B)what ought to be.
C)what is.
D)rational choice involving costs and benefits.
A)facts and theories.
B)what ought to be.
C)what is.
D)rational choice involving costs and benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



