Deck 3: Part A: Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/51
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Part A: Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium
1
What is the difference between a change in supply and a change in quantity supplied?
A change in supply is a shift in the entire supply curve either to the left (a decrease in supply) or to the right (an increase in supply).A change in supply, therefore, is a change in the entire supply schedule or curve.In contrast, a change in quantity supplied is a movement along an existing supply curve or schedule from one price-quantity combination to another.A change in product price causes the change in quantity supplied.
2
List five basic determinants of market demand that could cause demand to decrease.
(a) Consumers' tastes become less favourable toward the item.
(b) The number of buyers decreases.
(c) Incomes fall and the item is a normal good or incomes rise and the item is an inferior good.
(d) A decrease in the price of a substitute product or an increase in the price of a complementary product.
(e) Consumers expect lower prices in the future.
(b) The number of buyers decreases.
(c) Incomes fall and the item is a normal good or incomes rise and the item is an inferior good.
(d) A decrease in the price of a substitute product or an increase in the price of a complementary product.
(e) Consumers expect lower prices in the future.
3
Explain how the prices of related goods also affect demand.
Substitute goods are those that can be used in place of each other.The price of the substitute and demand for the other good are directly related.If the price of Coke rises, demand for Pepsi should increase.Complementary goods are those that are used together like tennis balls and rackets.When goods are complements, there is an inverse relationship between the price of one and the demand for the other.Some goods are not related to each other and are independent goods.In these cases, a change in price of one will not affect the demand for the other.
4
State the law of demand and explain why the other-things-equal assumption is critical to it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Suppose a producer sells 1,000 units of a product at $5 per unit one year, 2,000 units at $8 the next year, and 3,000 units at $10 the third year.Is this evidence that the law of demand is violated? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The Federal government is considering passing an excise tax that would increase the price of a pack of cigarettes by $1.00.What would be the likely effect of this change on the demand and supply of cigarettes? What is likely to happen to cigarette prices and the quantity consumed if the tax bill is enacted?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Define "demand."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What are some of the characteristics of a market that can be described by a demand and supply model?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Give two explanations for the law of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Describe and give a reason for the law of supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What effect will each of the following have upon the supply of television sets? Explain your reasoning in each case.(a) an increase in the price of electronic equipment used in producing television sets
(b) a decline in the number of firms producing television sets
(c) a large new tariff on imported Japanese TV sets
(d) new inexpensive satellite dishes which make televisions more popular among consumers
(b) a decline in the number of firms producing television sets
(c) a large new tariff on imported Japanese TV sets
(d) new inexpensive satellite dishes which make televisions more popular among consumers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Give examples of two substitute goods and two complementary goods.In each case explain why the goods are substitutes or complements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Define "supply."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Differentiate between a normal (superior) and an inferior good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
List six basic determinants of market supply that could cause supply to increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Newspaper item: "Due to lower grain prices, consumers can expect retail prices of choice beef to begin dropping slightly this spring with pork becoming cheaper after midsummer," the Agriculture Department predicted."This reflects increasing supply," the department said.Is the term "supply" used correctly? What effects might this announcement have on consumer demand? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the difference between a change in demand and a change in quantity demanded?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Suppose that a decrease in the price of feed grain leads to a dramatic decrease in the price of beef.Use the income effect and the substitution effect to explain why there was an increase in the quantity of beef purchased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What effect should each of the following have upon the demand for MP3 players? Explain your reasoning in each case.(a) the development of reasonably-priced smart phones that compete with MP3 players
(b) an increase in population and incomes
(c) a substantial increase in the number and quality free downloadable MP3s
(d) consumer expectations of substantial price increases in MP3 players
(e) a decrease in the price of MP3 players
(b) an increase in population and incomes
(c) a substantial increase in the number and quality free downloadable MP3s
(d) consumer expectations of substantial price increases in MP3 players
(e) a decrease in the price of MP3 players

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The demand schedules of three individuals (Tom, Dick, and Harry) are shown.If they are the only three buyers of CDs, complete the market demand schedule for CDs.Graphically, is the market demand for a product the horizontal or vertical sum of the individual demand schedules?
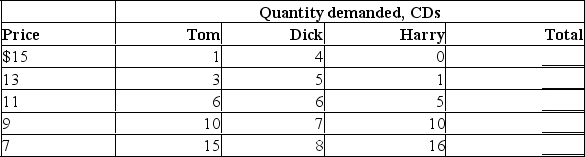


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Evaluate.An increase in demand causes price to rise which, in turn, causes demand to fall.Therefore, an increase in demand will not have lasting effects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Use the data in the following table to explain the economic effects of a price floor at $6. 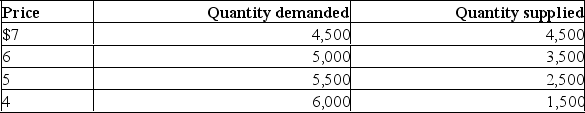


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Describe in words how one can recognize the market equilibrium point in a graph of a demand schedule and a supply schedule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Given the products below and the events that affect them, indicate what happens to demand, supply, equilibrium quantity, and equilibrium price.Identify the determinant of demand and supply that causes the shifts.(a) Calculators.More schools require students to buy and use calculators; improved productivity shortens the time it takes to make calculators.(b) Gasoline.Oil production declines due to a crisis in the Middle East; people take more car vacations and drive more.(c) New homes.The average incomes fall as the economy moves into recession; the productivity of home construction workers and builders increases.(d) Tobacco.The government cut its subsidy to tobacco farmers; more people quit smoking.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Evaluate.A decrease in supply causes price to rise which, in turn, causes supply to rise.Therefore, a decrease in supply will not have lasting effects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Use the data in the following table to explain the economic effects of a price ceiling at $6, at $5, and at $4. 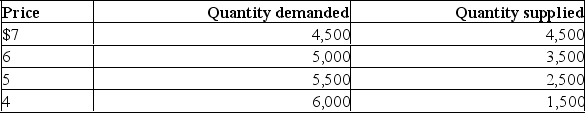


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the space below each of the following, indicate the effect [increase (+), decrease (-)] on equilibrium price (P) and equilibrium quantity (Q) of each of these changes in demand and/or supply. ![In the space below each of the following, indicate the effect [increase (+), decrease (-)] on equilibrium price (P) and equilibrium quantity (Q) of each of these changes in demand and/or supply.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6686/11eacf28_1fde_86f4_b554_0d4fd72679bf_TB6686_00.jpg)
![In the space below each of the following, indicate the effect [increase (+), decrease (-)] on equilibrium price (P) and equilibrium quantity (Q) of each of these changes in demand and/or supply.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6686/11eacf28_1fde_86f4_b554_0d4fd72679bf_TB6686_00.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
"Government-set prices undermine the rationing function of competitive prices." Explain carefully in terms of both price ceilings and price floors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The price of gold is lower today than several decades ago.Yet, the production of gold is greater than in the past.How is this possible without violating the law of supply?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Given the products below and the events that affect them, indicate what happens to demand or supply, and the equilibrium price and quantity.Identify the determinant of demand or supply that causes the shift.(a) Blue jeans.The wearing of blue jeans becomes less fashionable among consumers.(b) Computers.Parts for making computers fall in price because of improvements in technology.(c) Lettuce.El Nino produces heavy rains that destroy a significant portion of the lettuce crop.(d) Chicken.Beef prices rise because severe winter weather reduces cattle herds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In the spaces below each of the following, indicate the [increase (+), decrease (-), or indeterminate (ind)] on equilibrium price (P) and equilibrium quantity (Q) of each of these changes in demand and/or supply. ![In the spaces below each of the following, indicate the [increase (+), decrease (-), or indeterminate (ind)] on equilibrium price (P) and equilibrium quantity (Q) of each of these changes in demand and/or supply.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6686/11eacf28_1fde_ae05_b554_5f12aeef9925_TB6686_00.jpg)
![In the spaces below each of the following, indicate the [increase (+), decrease (-), or indeterminate (ind)] on equilibrium price (P) and equilibrium quantity (Q) of each of these changes in demand and/or supply.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6686/11eacf28_1fde_ae05_b554_5f12aeef9925_TB6686_00.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Using the schedules given, plot the demand curve and the supply curve on the below graph.Label the axes and indicate for each axis the units being used to measure price and quantity.Then answer the questions. 
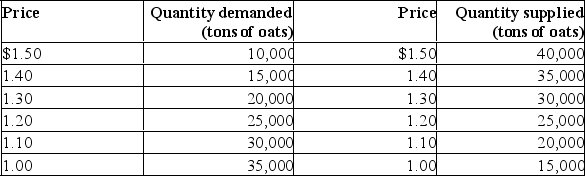 (a) Give the equilibrium price and quantity for oats.(b) Indicate the equilibrium price and quantity on the graph by drawing lines from the intersection of the supply and demand curves to the price and quantity axes.(c) If the Federal government decided to support the price of oats at $1.40 per ton, tell whether there would be a surplus or shortage and how much it would be.(d) Demonstrate your answer to part (c) on your graph being sure to label the quantity you designated as the shortage or surplus.
(a) Give the equilibrium price and quantity for oats.(b) Indicate the equilibrium price and quantity on the graph by drawing lines from the intersection of the supply and demand curves to the price and quantity axes.(c) If the Federal government decided to support the price of oats at $1.40 per ton, tell whether there would be a surplus or shortage and how much it would be.(d) Demonstrate your answer to part (c) on your graph being sure to label the quantity you designated as the shortage or surplus.

 (a) Give the equilibrium price and quantity for oats.(b) Indicate the equilibrium price and quantity on the graph by drawing lines from the intersection of the supply and demand curves to the price and quantity axes.(c) If the Federal government decided to support the price of oats at $1.40 per ton, tell whether there would be a surplus or shortage and how much it would be.(d) Demonstrate your answer to part (c) on your graph being sure to label the quantity you designated as the shortage or surplus.
(a) Give the equilibrium price and quantity for oats.(b) Indicate the equilibrium price and quantity on the graph by drawing lines from the intersection of the supply and demand curves to the price and quantity axes.(c) If the Federal government decided to support the price of oats at $1.40 per ton, tell whether there would be a surplus or shortage and how much it would be.(d) Demonstrate your answer to part (c) on your graph being sure to label the quantity you designated as the shortage or surplus.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Despite a lower price for its product, the widget industry is selling fewer units.How is this possible if the law of demand has not been violated? Give and explain two distinct reasons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Economist Jones defines an increase in supply as a decrease in the prices needed to ensure various amounts of a good being offered for sale.Economist Brown defines an increase in supply as an increase in the amounts that producers will offer at various possible prices.Economist Cole defines an increase in supply as an increase in the amount firms will offer in the market which is caused by an increase in the price of the product.Which, if any, of these is defining an increase in supply correctly? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Use the data in the following table to explain the economic effects of a price floor at $8, at $9, and at $10.Explain the economic effects. 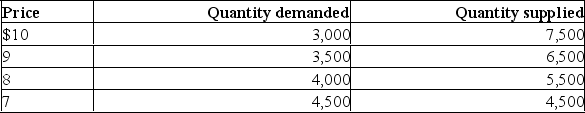


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Using the schedules given, plot the demand curve and the supply curve on the below graph.Label the axes and indicate for each axis the units being used to measure price and quantity.Then answer the questions. 
 (a) Give the equilibrium price and quantity for wheat.(b) Indicate the equilibrium price and quantity on the graph by drawing lines from the intersection of the supply and demand curves to the price and quantity axes.(c) If the Federal government decided to support the price of wheat at $4.00 per ton, tell whether there would be a surplus or shortage and how much it would be.(d) Demonstrate your answer to part (c) on your graph being sure to label the quantity you designated as the shortage or surplus.
(a) Give the equilibrium price and quantity for wheat.(b) Indicate the equilibrium price and quantity on the graph by drawing lines from the intersection of the supply and demand curves to the price and quantity axes.(c) If the Federal government decided to support the price of wheat at $4.00 per ton, tell whether there would be a surplus or shortage and how much it would be.(d) Demonstrate your answer to part (c) on your graph being sure to label the quantity you designated as the shortage or surplus.

 (a) Give the equilibrium price and quantity for wheat.(b) Indicate the equilibrium price and quantity on the graph by drawing lines from the intersection of the supply and demand curves to the price and quantity axes.(c) If the Federal government decided to support the price of wheat at $4.00 per ton, tell whether there would be a surplus or shortage and how much it would be.(d) Demonstrate your answer to part (c) on your graph being sure to label the quantity you designated as the shortage or surplus.
(a) Give the equilibrium price and quantity for wheat.(b) Indicate the equilibrium price and quantity on the graph by drawing lines from the intersection of the supply and demand curves to the price and quantity axes.(c) If the Federal government decided to support the price of wheat at $4.00 per ton, tell whether there would be a surplus or shortage and how much it would be.(d) Demonstrate your answer to part (c) on your graph being sure to label the quantity you designated as the shortage or surplus.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Use the data in the following table to explain the economic effects of a price ceiling at $9. 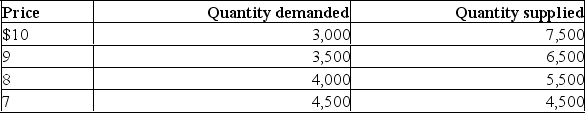


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Assuming no government intervention, describe the market behaviour that should result if the price of a product is below its equilibrium price; then describe the behaviour that should occur if the price is above its equilibrium price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is a price floor and what are its economic effects?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is a price ceiling and what are its economic effects?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Demand is represented by the equation, P = 80 - 0.3QD and supply by the equation P = 30 + 0.2QS.(a) Determine the equilibrium price and quantity.(b) What are the economic effects of a price ceiling at $41?
(c) What are the economic effects of a price ceiling at $72?
(d) What are the economic effects of a price floor at $62?
(e) What are the economic effects of a price floor at $37?
(c) What are the economic effects of a price ceiling at $72?
(d) What are the economic effects of a price floor at $62?
(e) What are the economic effects of a price floor at $37?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What are the consequences of reduced supply of lettuce for equilibrium price and quantity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What are the consequences for equilibrium price and quantity if there is an equal increase in the supply and demand for sushi?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
(a) Determine the equilibrium price and quantity if demand is represented by the equation, P = 40 - .2QD and supply by the equation P = 10 + .4QS.(b) Suppose demand changes and is now represented by the equation P = 52 - .2QD.Has demand increased or decreased? What is the new equilibrium price and quantity?
(c) Suppose instead supply changes and is now represented by the equation P = 16 + .4QS.Has supply increased or decreased? What is the new equilibrium price and quantity?
(c) Suppose instead supply changes and is now represented by the equation P = 16 + .4QS.Has supply increased or decreased? What is the new equilibrium price and quantity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Explain the consequences on the primary and secondary markets for pre-setting below equilibrium prices for the popular women's figure skating event at the Olympic games?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Determine the equilibrium price and quantity in each of the following.(a) Demand is represented by the equation, P = 28 - .2QD and supply by the equation P = 8 + .3QS.(b) Demand is represented by the equation, P = 30 - .5QD and supply by the equation P = 5 + .5QS.(c) Demand is represented by the equation, P = 20 - .3QD and supply by the equation P = 4 + .2QS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What are the consequences for equilibrium price and quantity if the supply of gasoline has decreased and the demand for gasoline has increased? Assume that the increase in demand outweighs the decrease in supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Despite a higher price for widgets, buyers are purchasing more units.How is this possible if the law of demand has not been violated? Give and explain two distinct reasons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
(a) Using the schedules given, determine the demand equation and the supply equation. 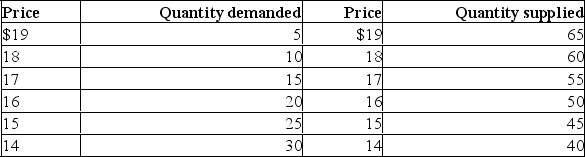 (b) What is the intercept of the demand equation? What is the slope of the demand equation?
(b) What is the intercept of the demand equation? What is the slope of the demand equation?
(c) What is the intercept of the supply equation? What is the slope of the supply equation?
(d) What is the equilibrium price and quantity?
 (b) What is the intercept of the demand equation? What is the slope of the demand equation?
(b) What is the intercept of the demand equation? What is the slope of the demand equation?(c) What is the intercept of the supply equation? What is the slope of the supply equation?
(d) What is the equilibrium price and quantity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What are the consequences of an increase in the demand for Euros on the equilibrium price and quantity of Euros? Does the Canadian dollar appreciate or depreciate as a result? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What are the consequences for equilibrium price and quantity if the supply of pink salmon has increased and the demand for pink salmon has decreased? Assume that supply has increased more than demand has decreased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



