Deck 1: Part A: Limits, Alternatives, and Choices
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Part A: Limits, Alternatives, and Choices
1
"Economic models are somewhat like different types of maps".Evaluate.
Economic models are necessarily a simplification of the real world.The validity of a particular economic model should be based upon a comparison of the model's predictions to observable fact.A world atlas is not the best map to use to find out how to get to Vancouver from Charlottetown, but it will tell you where South Africa is in relation to Luxembourg.If you wanted to get to Vancouver from Charlottetown, you'd need a road map of Canada.But a road map would not sufficiently describe the elevations if you were riding your bike and would not likely tell you how to find Main Street in Golden, B.C.The map you use should be judged based not on its complete accuracy and detail, but on its ability to get you where you are going.
2
Use marginal analysis to explain why it is possible to "have too much of a good thing".Use education as an example.
This explanation is based on an evaluation of the marginal costs and marginal benefit of providing a good or service.We may want more education for our society, but at some point the marginal cost of providing additional education is greater than the marginal benefit of the additional education.We would have to give up too many other things to obtain the additional education.For example, would it make sense to provide additional education resources for everyone so that they can earn a Ph.D.degree? The answer is no.In this case, the marginal cost of these additional educational resources (for example, lost labour time or inefficient use of people's abilities) would not be worth the marginal benefit to society of having everyone earn a Ph.D.degree.
3
The distinguished economist Kenneth Boulding stated: "Theories without facts may be barren, but facts without theories are meaningless".Explain what he meant.
Economic theories are generalizations about the economic behaviour of individuals and institutions.As generalizations or principles, they are abstractions and may not offer specific information about a particular issue that can be obtained from facts.Economic theories are barren in the sense that they offer a framework for thinking about the economic issue without a lot of the details about it.Having a lot of facts about an economic issue, however, is not very meaningful.Facts need to be arranged and organized if they are to have meaning and give insight into the issue.Economic theory offers that framework for organizing the factual information.
4
Explain the importance of the ceteris paribus or "other-things-equal" assumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What are the three interrelated features of the economic perspective?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is utility and what is its relevance to rational behaviour?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
"Bad theories are abstract and therefore unrealistic; good theories are fully realistic and fit all the facts".Evaluate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What are the key economic concepts that pertain to the individual?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Why have the last few years been an exciting time to study macroeconomics?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What do economists mean when they say that "there is no free lunch"? Give another example to which this statement applies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Below are six statements.Indicate whether each one pertains to microeconomics (MIC) or macroeconomics (MAC).(a) "The inflation rate in Canada hit its lowest level in the last twenty years".(b) "The profits of BCE rose 20 percent during the past quarter".(c) "A drought has occurred in the Prairies.The prices for barley are expected to rise sharply".(d) "The nation's economy grew at an annual rate of 3.7 percent in the final quarter of the year".(e) "The trade surplus in Canada was $4 billion last month".(f) "General Motors plans to spend $800 million on a new automobile plant".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What are the key economic concepts that pertain to interactions among individuals?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What does it mean to say that theories, principles, and models are "purposeful simplifications"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Give one example of a positive economic statement and one example of a normative economic statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What are the key economic concepts that pertain to the economy as a whole?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Identify whether each of the following is a positive or normative statement.(a) Should tuition fees increase, fewer students would obtain a post-secondary education.(b) The Prime Minister announced that Canada is the best place in the world to live.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is a brief definition of economics? What are the conditions that give rise to this definition?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Below are six statements.Identify whether each is a positive or normative statement.(a) The minimum wage should be increased so low-income workers can earn a living wage.(b) The unemployment rate is too high and should be reduced through government actions.(c) The rate of inflation was about 2 percent last year, an all time low for the past decade.(d) The government should take action to break up the monopoly power of Air Canada.(e) Interest rates should be lower in Canada so that people can afford to build a home.(f) The Federal government achieved a budget surplus for the first time in thirty years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
"Economists are scientists and therefore should not become involved in making value judgments which policy formulation necessarily entails".Do you agree?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Describe the Greek Debt Crisis, and explain its relation to the Economic Problem?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
"Economics cannot be scientific because it is based upon the value judgment that 'more (output) is better'".Do you agree?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What were the approximate average incomes of Canadians and Pakistanis in 2015?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is meant by the "the individual's economic problem"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
List the four resource categories and give a brief description of each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Explain the relationship between full employment of resources and full production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is the economic rationale for the law of increasing costs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What four basic functions does the entrepreneur perform for the economy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What variables are used to determine the individual's budget line?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Explain and evaluate: "If resources were infinitely abundant in relation to the demand for them, the economic problem would dissolve in a sea of affluence".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The production possibilities table below shows the hypothetical relationship between the production of food and clothing in an economy.(a) What is the marginal opportunity cost of producing the second unit of clothing?
(b) What is the total opportunity cost of producing two units of clothing?
(c) What is the marginal opportunity cost of producing the third unit of clothing?
(d) What is the total opportunity cost of producing three units of clothing?
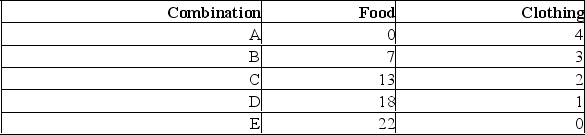
(b) What is the total opportunity cost of producing two units of clothing?
(c) What is the marginal opportunity cost of producing the third unit of clothing?
(d) What is the total opportunity cost of producing three units of clothing?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A production possibilities table for two products, grain and airplanes, is found below.Usual assumptions regarding production possibilities are implied.Grain is measured in tons and airplanes are measured in units of 1,000.(a) Using the below graph construct a production possibilities curve from this information placing grain on the vertical axis and airplanes on the horizontal axis.  (b) What is the opportunity cost of producing the first unit of airplanes? The marginal opportunity cost of producing the fourth unit of airplanes?
(b) What is the opportunity cost of producing the first unit of airplanes? The marginal opportunity cost of producing the fourth unit of airplanes?
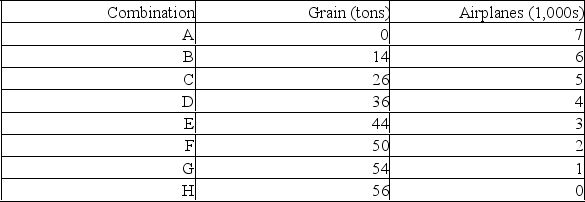
 (b) What is the opportunity cost of producing the first unit of airplanes? The marginal opportunity cost of producing the fourth unit of airplanes?
(b) What is the opportunity cost of producing the first unit of airplanes? The marginal opportunity cost of producing the fourth unit of airplanes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is meant by "society's economic problem"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What were the approximate average incomes of Canadians and Pakistanis in 2015?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What do economists mean when they say that economic resources or factors of production are scarce or limited in supply?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Explain how increasing opportunity costs are reflected graphically in the production possibilities curve.How would the curve appear if opportunity costs were constant?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
"The relative scarcity of resources makes the operation of any economy a matter of choosing between alternatives".Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A production possibilities table for two products, corn and paper, is found below.Usual assumptions regarding production possibilities are implied.Corn is measured in tons, and paper is measured per unit. 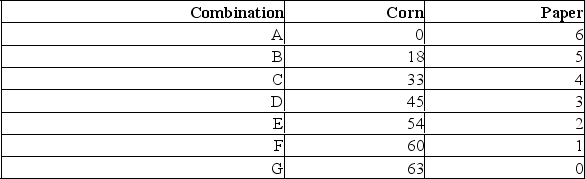 (a) Using the following graph construct a production possibilities curve from this information placing corn on the vertical axis and paper on the horizontal axis.
(a) Using the following graph construct a production possibilities curve from this information placing corn on the vertical axis and paper on the horizontal axis.  (b) What is the marginal opportunity cost of producing the first unit of paper? The marginal opportunity cost of producing the fourth unit of paper?
(b) What is the marginal opportunity cost of producing the first unit of paper? The marginal opportunity cost of producing the fourth unit of paper?
 (a) Using the following graph construct a production possibilities curve from this information placing corn on the vertical axis and paper on the horizontal axis.
(a) Using the following graph construct a production possibilities curve from this information placing corn on the vertical axis and paper on the horizontal axis.  (b) What is the marginal opportunity cost of producing the first unit of paper? The marginal opportunity cost of producing the fourth unit of paper?
(b) What is the marginal opportunity cost of producing the first unit of paper? The marginal opportunity cost of producing the fourth unit of paper?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
"The two cornerstones of economics are the scarcity of resources and the multiplicity of wants.True economy consists of deriving maximum want satisfaction from available resources".Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
How do income changes affect the position of the budget line?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Show graphically on the below graph the expected relationship between investment spending and interest rates.Put investment expenditures on the horizontal axis and the rate of interest on the vertical axis; connect the points and label the curve "Investment demand".Describe this relationship between the rate of interest and investment expenditures.Describe the slope of the investment curve. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
One application of the production possibilities concept has been to explain the difference in growth patterns of a nation with a high level of investment (Alta) and an equivalent nation with a low level of investment (Zorn).Use the concept to explain why Alta's economic growth would be greater than that of Zorn over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Explain how each event affects production possibilities.(a) The population becomes more educated over time as the number of high school dropouts falls and the number of college graduates rises.(b) The unemployment rate declines from 8 to 6 percent of the labour force.(c) Businesses and government are unable to solve a major computer problem, thus reducing economic efficiency and national output.(d) Advances in telecommunications and new technology significantly contribute to economic growth over time.(e) The Federal government decides to allocate more resources to national defence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Describe the adjustments in the production possibilities curves in each of the following situations for the Canadian economy.(a) the economy moves from full employment into a deep recession
(b) the economy makes great strides in eliminating discrimination
(c) the end of the Cold War leads to cuts in military spending
(d) the government significantly increases spending for health and education
(b) the economy makes great strides in eliminating discrimination
(c) the end of the Cold War leads to cuts in military spending
(d) the government significantly increases spending for health and education

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An economy consists of five workers, who can produce either fish or fruit.The following table shows the daily output of each worker. 
 (a) Suppose one worker catches fish and four workers pick fruit.For the economy to achieve productive efficiency, which of the five workers must fish?
(a) Suppose one worker catches fish and four workers pick fruit.For the economy to achieve productive efficiency, which of the five workers must fish?
(b) Does the economy achieve full employment and productive efficiency by producing 26 fish and 20 fruit?

 (a) Suppose one worker catches fish and four workers pick fruit.For the economy to achieve productive efficiency, which of the five workers must fish?
(a) Suppose one worker catches fish and four workers pick fruit.For the economy to achieve productive efficiency, which of the five workers must fish?(b) Does the economy achieve full employment and productive efficiency by producing 26 fish and 20 fruit?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
How do you determine the slope of a nonlinear curve? Will the slope be the same along the curve? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An economy consists of five workers, who can produce either fish or fruit.The following table shows the daily output of each worker. 
 (a) Suppose one worker catches fish and four workers pick fruit.For the economy to achieve productive efficiency, which of the five workers must fish?
(a) Suppose one worker catches fish and four workers pick fruit.For the economy to achieve productive efficiency, which of the five workers must fish?
(b) Does the economy achieve full employment and productive efficiency by producing 12 fish and 4 fruit?

 (a) Suppose one worker catches fish and four workers pick fruit.For the economy to achieve productive efficiency, which of the five workers must fish?
(a) Suppose one worker catches fish and four workers pick fruit.For the economy to achieve productive efficiency, which of the five workers must fish?(b) Does the economy achieve full employment and productive efficiency by producing 12 fish and 4 fruit?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Describe the slope of a direct and an inverse relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What changes must occur for the potential total output of the economy to grow?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Define what is meant by a positive or direct relationship between two variables and describe the line graph depicting such a relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Evaluate.Since the production possibilities curve can shift outward over time, it is possible for an economy to get more of a product without incurring an opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Look at the following production possibilities curve illustrating the possibilities in Sluggerville for producing bats and/or peanuts with the existing level of resources and technology. 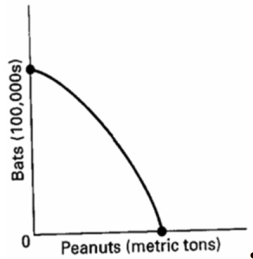


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
There are two sets of x, y points on a straight line in a two-variable graph with y on the vertical axis and x on the horizontal axis.What would be the linear equation for the line if one set of points was (0, 12) and the other set was (12, 36)?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Define what is meant by an inverse relationship between two variables and describe the line graph depicting such a relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In a two-dimensional graph showing the relationship between income and consumption in the economy, what is shown on the vertical axis and what is shown on the horizontal axis?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The value of the vertical intercept is $100 and the slope is 0.8 in a linear equation for consumption (measured on the vertical axis) and disposable income (measured on the horizontal axis).If disposable income is $1000, what is consumption? State the linear equation and show how you found the answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Why do economists use graphs in their work?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The production possibilities curve suggests that a nation cannot live beyond its means or production potential.Explain why international trade would cause this statement to be modified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Differentiate between the independent and dependent variables in an economic relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Show graphically the relationships that you would expect to find between (a) student IQs and grade point averages (GPAs); (b) the price of a product and the amount consumers will purchase; (c) the temperature and the number of people at the swimming pool.Which of these are direct relationships and which are inverse? What considerations might change the expected relationships?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



