Deck 1: The Central Idea
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: The Central Idea
1
The concept of scarcity refers to
A) a situation in which an item is very expensive.
B) a situation in which an item is available only in very small quantities.
C) a situation in which a resource is nonrenewable.
D) a situation in which people face a shortage in a particular market.
E) a situation in which the available resources are not enough to satisfy the wants of the people.
A) a situation in which an item is very expensive.
B) a situation in which an item is available only in very small quantities.
C) a situation in which a resource is nonrenewable.
D) a situation in which people face a shortage in a particular market.
E) a situation in which the available resources are not enough to satisfy the wants of the people.
E
2
Economics deals with how
A) individuals make decisions to use scarce resources in order to satisfy their unlimited wants.
B) to run a business successfully.
C) individuals become rich.
D) society can eliminate scarcity.
E) society creates more resources in order to raise its standard of living.
A) individuals make decisions to use scarce resources in order to satisfy their unlimited wants.
B) to run a business successfully.
C) individuals become rich.
D) society can eliminate scarcity.
E) society creates more resources in order to raise its standard of living.
A
3
Economic interactions occur only in the presence of government.
False
4
Buyers and sellers interact in a
A) government.
B) face-to-face forum.
C) family.
D) market.
E) classroom.
A) government.
B) face-to-face forum.
C) family.
D) market.
E) classroom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Economics is the study of how people deal with
A) unlimited resources.
B) too much money.
C) scarcity.
D) limited human wants.
E) a lack of choices.
A) unlimited resources.
B) too much money.
C) scarcity.
D) limited human wants.
E) a lack of choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Scarcity applies to everyone regardless of income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
People make decisions when doing something involves
A) no benefits.
B) only benefits.
C) giving up nothing else.
D) an opportunity cost.
E) different types of resources.
A) no benefits.
B) only benefits.
C) giving up nothing else.
D) an opportunity cost.
E) different types of resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
An example of opportunity cost is the
A) income that a person does not earn because she has retired and decided not to work at all.
B) pleasure that an economics student derives from studying economics.
C) Chinese food that you gave up when you chose to eat Italian food.
D) tuition you pay to attend college.
E) price paid for a concert ticket when you go to that concert.
A) income that a person does not earn because she has retired and decided not to work at all.
B) pleasure that an economics student derives from studying economics.
C) Chinese food that you gave up when you chose to eat Italian food.
D) tuition you pay to attend college.
E) price paid for a concert ticket when you go to that concert.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The opportunity cost of a choice is the
A) benefit associated with making that choice.
B) value of the next best activity not chosen.
C) fair market price of whatever is chosen.
D) dollar amount paid to purchase what is chosen.
E) consequence associated with failure.
A) benefit associated with making that choice.
B) value of the next best activity not chosen.
C) fair market price of whatever is chosen.
D) dollar amount paid to purchase what is chosen.
E) consequence associated with failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
From an economic perspective, people make decisions because of
A) social custom.
B) genetics.
C) scarcity.
D) their own habit.
E) religion.
A) social custom.
B) genetics.
C) scarcity.
D) their own habit.
E) religion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The basic economic problem is
A) a lack of money.
B) a lack of jobs.
C) poverty.
D) scarcity.
E) a rising standard of living.
A) a lack of money.
B) a lack of jobs.
C) poverty.
D) scarcity.
E) a rising standard of living.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following statements is false?
A) There is an opportunity cost associated with any choice made.
B) If there is a budget constraint, there will be scarcity.
C) A person without a budget constraint does not face opportunity costs.
D) Opportunity costs occur because of scarce resources.
E) Because of scarcity, choices have to be made.
A) There is an opportunity cost associated with any choice made.
B) If there is a budget constraint, there will be scarcity.
C) A person without a budget constraint does not face opportunity costs.
D) Opportunity costs occur because of scarce resources.
E) Because of scarcity, choices have to be made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements about economic interaction is not true?
A) It is a fact of economic life.
B) It requires a market.
C) It can occur within a family.
D) It makes our lives better.
E) It requires people to make sacrifices by giving up what they may have otherwise.
A) It is a fact of economic life.
B) It requires a market.
C) It can occur within a family.
D) It makes our lives better.
E) It requires people to make sacrifices by giving up what they may have otherwise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Economics is a study of
a.
choices and interactions among people when resources are scarce.
b.
how to eliminate scarcity.
c.
how to make choices and interact in order to avoid scarcity.
d.
how to avoid scarcity by making choices.
e.
how to make money in stock markets.
a Moderate
a.
choices and interactions among people when resources are scarce.
b.
how to eliminate scarcity.
c.
how to make choices and interact in order to avoid scarcity.
d.
how to avoid scarcity by making choices.
e.
how to make money in stock markets.
a Moderate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Scarcity is a problem
A) only for poor countries.
B) only for economies under complete government control.
C) faced by all economies.
D) that can be eliminated as the economy grows.
E) not faced by free market economies.
A) only for poor countries.
B) only for economies under complete government control.
C) faced by all economies.
D) that can be eliminated as the economy grows.
E) not faced by free market economies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A budget constraint
A) does not occur if there is scarcity.
B) is faced only by poor people.
C) is a way to overcome scarcity.
D) forces people to make choices.
E) prohibits consumers from spending.
A) does not occur if there is scarcity.
B) is faced only by poor people.
C) is a way to overcome scarcity.
D) forces people to make choices.
E) prohibits consumers from spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Choices are made in order to avoid scarcity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A market is
A) a place where firms meet to set prices.
B) an arrangement by which economic exchanges take place.
C) an organization controlled by a government.
D) a place where goods are produced.
E) anywhere people come close to each other.
A) a place where firms meet to set prices.
B) an arrangement by which economic exchanges take place.
C) an organization controlled by a government.
D) a place where goods are produced.
E) anywhere people come close to each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Economics is the study of how individuals become wealthy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Stephanie has only one hour to study for an exam in math or to complete an assignment in economics. For Stephanie, the opportunity cost of spending the hour completing the economics assignment is
A) a lower grade in the math exam.
B) a higher grade in the math exam.
C) a lower grade in both the math exam and the economics assignment.
D) a higher grade in both the math exam and the economics assignment.
E) none because history and economics are unrelated.
A) a lower grade in the math exam.
B) a higher grade in the math exam.
C) a lower grade in both the math exam and the economics assignment.
D) a higher grade in both the math exam and the economics assignment.
E) none because history and economics are unrelated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If an individual is able to produce a good with a lower opportunity cost than someone else, then that individual has
A) avoided opportunity costs.
B) an interaction advantage.
C) the advantage of producing all goods.
D) removed scarcity.
E) a comparative advantage.
A) avoided opportunity costs.
B) an interaction advantage.
C) the advantage of producing all goods.
D) removed scarcity.
E) a comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When the economy is in recession, jobs are generally harder to find and more people go to college. We can conclude that the opportunity cost of
A) going to college decreases when the economy is in recession.
B) going to college increases when the economy is in recession.
C) working increases when the economy is in recession.
D) working is zero when the economy is in recession.
E) going to college is always higher than the opportunity cost of working.
A) going to college decreases when the economy is in recession.
B) going to college increases when the economy is in recession.
C) working increases when the economy is in recession.
D) working is zero when the economy is in recession.
E) going to college is always higher than the opportunity cost of working.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The opportunity cost of an activity is the total value of all activities that a person cannot do.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The division of labor enables
A) people not to work at all.
B) the elimination of scarcity.
C) opportunity costs.
D) self-sufficiency.
E) specialization.
A) people not to work at all.
B) the elimination of scarcity.
C) opportunity costs.
D) self-sufficiency.
E) specialization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Of the following individuals, who bears the highest opportunity cost of going to college?
A) A pro-football player earning $2 million a year
B) A high school graduate without a job
C) A high school dropout earning the minimum wage in a fast-food restaurant
D) A teenager who attends college and also works on campus
E) A retiree
A) A pro-football player earning $2 million a year
B) A high school graduate without a job
C) A high school dropout earning the minimum wage in a fast-food restaurant
D) A teenager who attends college and also works on campus
E) A retiree

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
According to the textbook, the main reason for Mark Zuckerberg to leave college and to start a new company, Facebook, is that
A) he had failed many courses in college.
B) the opportunity cost is higher for him to stay in college than to run Facebook.
C) the opportunity cost is lower for him to stay in college than to run Facebook.
D) the opportunity cost is zero for him to stay in college.
E) the opportunity cost is zero for him to run Facebook.
A) he had failed many courses in college.
B) the opportunity cost is higher for him to stay in college than to run Facebook.
C) the opportunity cost is lower for him to stay in college than to run Facebook.
D) the opportunity cost is zero for him to stay in college.
E) the opportunity cost is zero for him to run Facebook.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The opportunity cost of attending college
A) is zero because the return is always positive.
B) includes the skills earned from attending college.
C) is the living expenses, which are the same whether the students attend college or not.
D) includes the lost incomes that would have been earned if the student had not attended college.
E) includes the scholarships for attending college.
A) is zero because the return is always positive.
B) includes the skills earned from attending college.
C) is the living expenses, which are the same whether the students attend college or not.
D) includes the lost incomes that would have been earned if the student had not attended college.
E) includes the scholarships for attending college.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Gains from voluntary trade arise because
A) it reallocates goods between individuals.
B) it occurs in a household.
C) it reallocates goods between individuals in a way they both prefer.
D) it occurs in a market.
E) of the power involved.
A) it reallocates goods between individuals.
B) it occurs in a household.
C) it reallocates goods between individuals in a way they both prefer.
D) it occurs in a market.
E) of the power involved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Exhibit 1-3 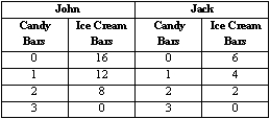
When people specialize in the activity in which they have a comparative advantage,
A) there cannot be a division of labor, though production will increase.
B) there will likely be a division of labor as well as an increase in output.
C) there will be a gain from trade, but production will not be increased.
D) there will likely be a division of labor, and output will stay the same.
E) there will likely be a division of labor, and output will decline.

When people specialize in the activity in which they have a comparative advantage,
A) there cannot be a division of labor, though production will increase.
B) there will likely be a division of labor as well as an increase in output.
C) there will be a gain from trade, but production will not be increased.
D) there will likely be a division of labor, and output will stay the same.
E) there will likely be a division of labor, and output will decline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A college student faces no opportunity cost if her parents pay her college tuition and her living expenses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Production can be increased whenever people
A) engage in activities with a high opportunity cost.
B) specialize in whichever field they have a comparative advantage in.
C) specialize in whatever interests them.
D) do not allocate goods through trade.
E) make decisions according to societal needs.
A) engage in activities with a high opportunity cost.
B) specialize in whichever field they have a comparative advantage in.
C) specialize in whatever interests them.
D) do not allocate goods through trade.
E) make decisions according to societal needs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
As a result of economic interaction,
A) the number of available choices is reduced.
B) scarcity is increased.
C) opportunity costs increase.
D) people are able to specialize.
E) scarcity is eliminated.
A) the number of available choices is reduced.
B) scarcity is increased.
C) opportunity costs increase.
D) people are able to specialize.
E) scarcity is eliminated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Exhibit 1-3 
Refer to Exhibit 1-3. Suppose John and Jack can produce the above combinations of candy bars and ice cream bars in one hour. John and Jack can maximize their total production if
A) both produce candy bars.
B) both produce ice cream bars.
C) John produces both candy bars and ice cream bars, while Jack produces nothing.
D) Jack produces both candy bars and ice cream bars, while John produces nothing.
E) each of them produces what he has a comparative advantage in producing.

Refer to Exhibit 1-3. Suppose John and Jack can produce the above combinations of candy bars and ice cream bars in one hour. John and Jack can maximize their total production if
A) both produce candy bars.
B) both produce ice cream bars.
C) John produces both candy bars and ice cream bars, while Jack produces nothing.
D) Jack produces both candy bars and ice cream bars, while John produces nothing.
E) each of them produces what he has a comparative advantage in producing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The goods that individual producers specialize in are determined solely by the amounts of time and resources they need to produce those goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The opportunity cost for a student to attend college is zero if the student receives a scholarship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Maria has two options to spend her school break in the summer: get a summer job that pays $3,000 or travel in Mexico. The opportunity cost of the summer job is that Maria
A) can earn more than $3,000.
B) can also travel in Mexico.
C) has to give up traveling in Mexico.
D) can save the money for traveling in Mexico.
E) has to work and travel at the same time.
A) can earn more than $3,000.
B) can also travel in Mexico.
C) has to give up traveling in Mexico.
D) can save the money for traveling in Mexico.
E) has to work and travel at the same time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Trade benefits people only when they together produce more goods or services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Gains from trade occur when there are differences in opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
____ must exist in order for gains from trade to be realized.
A) Governments
B) Markets
C) An increase in production
D) Economic interaction
E) Firms
A) Governments
B) Markets
C) An increase in production
D) Economic interaction
E) Firms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Trade enables people to specialize in activities in which they have a comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A country trades with other countries because
A) it can gain in production and consumption.
B) it wants to improve foreign relations.
C) its government can earn taxes on imported goods.
D) it has an excess production capacity.
E) its residents always prefer imported goods to domestic goods.
A) it can gain in production and consumption.
B) it wants to improve foreign relations.
C) its government can earn taxes on imported goods.
D) it has an excess production capacity.
E) its residents always prefer imported goods to domestic goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Economic growth in the future can be encouraged by tradeoffs made today.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Explain how trade between two different countries is similar to trade occurring between two individuals within a country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A division of labor occurs when some workers do all tasks while others do nothing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What explains the occurrence of increasing opportunity costs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In general, what is economics the study of?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following statements is true?
A) There are no gains from trade between people in different countries because, with international trade, it's the countries that trade, and not its people, that realize the gains.
B) Trade between people in different countries cannot occur.
C) Trade between people in different countries can occur, but it will not result in an increase in consumer satisfaction.
D) Trade between people in different countries can occur, but it will not lead them to better utilize their comparative advantage.
E) Trade between people in different countries can occur, and the gains that occur are the same as the gains from trade within a country.
A) There are no gains from trade between people in different countries because, with international trade, it's the countries that trade, and not its people, that realize the gains.
B) Trade between people in different countries cannot occur.
C) Trade between people in different countries can occur, but it will not result in an increase in consumer satisfaction.
D) Trade between people in different countries can occur, but it will not lead them to better utilize their comparative advantage.
E) Trade between people in different countries can occur, and the gains that occur are the same as the gains from trade within a country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
International trade exists only when a country can gain a trade advantage over another country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Trade always results in a gain for one or both participants in the trade

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The movement from a point inside a production possibilities curve to a point outside the curve is likely to result in no change in an economy's total production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The table below depicts the choices George and Sarah face when deciding whether to cook, wait on tables, or both. 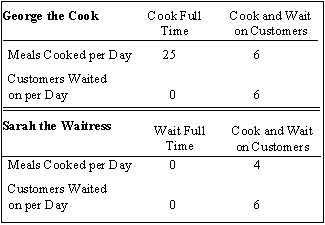


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
After purchasing a can of soda from a convenience store, David complained that the store had charged too much for the soda. Comment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What is division of labor, and why is this a reason for economic interaction?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the relationship among economic interaction, specialization, comparative advantage, and gains from trade?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Why is it reasonable to assume that when trade is voluntary, those involved in the trade will gain?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Any point on the production possibilities curve represents the fact that resources are efficiently allocated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The production possibilities curve is immovable, meaning that it is fixed regardless of the availability of resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What is the meaning of comparative advantage?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Moving from a point on the production possibilities curve to another point on the same curve implies a gain in production efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
It is impossible for two people to increase their total production if one has a comparative advantage in the production of one particular good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
There is no legitimate role for government in a market economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Transaction costs are the costs of
A) bribing government officials.
B) buying and selling in a market.
C) doing something within an organization.
D) avoiding any economic interactions.
E) producing a product instead of buying it from someone else.
A) bribing government officials.
B) buying and selling in a market.
C) doing something within an organization.
D) avoiding any economic interactions.
E) producing a product instead of buying it from someone else.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In a market economy, prices are
A) mainly transfer prices.
B) affordable by all consumers.
C) determined by the government.
D) freely determined.
E) determined solely by firms and not by consumers.
A) mainly transfer prices.
B) affordable by all consumers.
C) determined by the government.
D) freely determined.
E) determined solely by firms and not by consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following statements is false?
A) In a centrally planned economy, decisions concerning the three essential questions are made by those who control the government.
B) In a market economy, firms do not interact with consumers.
C) The two alternative approaches to the three essential questions are market economies and command economies.
D) In a market economy, decisions concerning the three essential questions result from interactions taking place in markets.
E) In both centrally planned and market economies, the three essential economic questions are what, how, and for whom.
A) In a centrally planned economy, decisions concerning the three essential questions are made by those who control the government.
B) In a market economy, firms do not interact with consumers.
C) The two alternative approaches to the three essential questions are market economies and command economies.
D) In a market economy, decisions concerning the three essential questions result from interactions taking place in markets.
E) In both centrally planned and market economies, the three essential economic questions are what, how, and for whom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Without property rights,
A) people would have more of an incentive to specialize, and the economy would become more efficient.
B) there would be more inventions.
C) people would not have an incentive to specialize.
D) a market economy would become more efficient.
E) people would have more of an incentive to specialize.
A) people would have more of an incentive to specialize, and the economy would become more efficient.
B) there would be more inventions.
C) people would not have an incentive to specialize.
D) a market economy would become more efficient.
E) people would have more of an incentive to specialize.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Economic interaction with other countries
A) benefits only small countries that cannot produce everything.
B) benefits only large countries that have a comparative advantage in producing everything.
C) can benefit no country.
D) can benefit small or large countries.
E) benefits only small countries that have a comparative disadvantage.
A) benefits only small countries that cannot produce everything.
B) benefits only large countries that have a comparative advantage in producing everything.
C) can benefit no country.
D) can benefit small or large countries.
E) benefits only small countries that have a comparative disadvantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Is it possible for an economy to make tradeoffs in the present in order to attain what is currently unattainable? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The key elements of a market economy include all of the following except
A) freely determined prices.
B) property rights.
C) freedom to trade at home.
D) freedom to trade with another country.
E) strong government intervention.
A) freely determined prices.
B) property rights.
C) freedom to trade at home.
D) freedom to trade with another country.
E) strong government intervention.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The government can improve market conditions in case of a market failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When a country like North Korea is characterized as a command economy, it's because most prices are
A) determined in the market, and they usually lead to market failures.
B) set by the government, which usually leads to inefficiencies.
C) determined in the market, and they result in efficient outcomes.
D) set by the government, and they result in efficient outcomes.
E) determined in the market, and they usually lead to inefficiencies.
A) determined in the market, and they usually lead to market failures.
B) set by the government, which usually leads to inefficiencies.
C) determined in the market, and they result in efficient outcomes.
D) set by the government, and they result in efficient outcomes.
E) determined in the market, and they usually lead to inefficiencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The role of government in a market system
A) includes encouraging market failures.
B) does not exist.
C) is restricted to establishing property rights.
D) includes improving situations that would otherwise result in a government failure.
E) includes improving situations that would otherwise result in a market failure.
A) includes encouraging market failures.
B) does not exist.
C) is restricted to establishing property rights.
D) includes improving situations that would otherwise result in a government failure.
E) includes improving situations that would otherwise result in a market failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose an economy can produce either smartphones or trucks. The production possibilities for this economy are shown in the table below. Show that this production possibilities schedule depicts increasing opportunity costs.
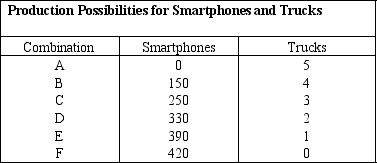


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Economic interaction occurs in firms as opposed to markets
A) because markets are too competitive.
B) because this is what the government wants.
C) in order to lower transaction costs.
D) in order to increase transaction costs.
E) if workers want to increase wages but not product prices.
A) because markets are too competitive.
B) because this is what the government wants.
C) in order to lower transaction costs.
D) in order to increase transaction costs.
E) if workers want to increase wages but not product prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A government failure results when
A) the government allows a market failure to occur.
B) the government establishes property rights.
C) the market economy does not provide good answers to the three questions.
D) government intervention is unable to correct a market failure.
E) the government intervenes in a market economy.
A) the government allows a market failure to occur.
B) the government establishes property rights.
C) the market economy does not provide good answers to the three questions.
D) government intervention is unable to correct a market failure.
E) the government intervenes in a market economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In a pure market economy, the what, how, and for whom problems are determined by
A) consumers only.
B) firms only.
C) the government.
D) both consumers and firms.
E) no one.
A) consumers only.
B) firms only.
C) the government.
D) both consumers and firms.
E) no one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In a command economy, the what, how, and for whom problems are determined by
A) consumers.
B) firms.
C) the government.
D) both consumers and firms.
E) markets.
A) consumers.
B) firms.
C) the government.
D) both consumers and firms.
E) markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Market failure
A) caused the collapse of centrally planned economies in Eastern Europe.
B) is the consequence of government involvement in the economy.
C) is something that never happens in a market economy.
D) occurs when the market is unable to allocate resources correctly.
E) occurs only when supply exceeds demand.
A) caused the collapse of centrally planned economies in Eastern Europe.
B) is the consequence of government involvement in the economy.
C) is something that never happens in a market economy.
D) occurs when the market is unable to allocate resources correctly.
E) occurs only when supply exceeds demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Property rights to inventions discourage people and firms to produce inventions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Does the production possibilities curve represent the economy in which some people win only if others lose? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Establishing property rights
A) is a characteristic of most centrally planned economies.
B) provides incentives.
C) is the most important feature of a centrally planned economy.
D) is not necessary for a market economy to function.
E) is a key obstacle for the economy to grow over time.
A) is a characteristic of most centrally planned economies.
B) provides incentives.
C) is the most important feature of a centrally planned economy.
D) is not necessary for a market economy to function.
E) is a key obstacle for the economy to grow over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



