Deck 7: Portfolio Theory
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/34
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Portfolio Theory
1
An investor buys shares for £10 and sells them after two years for £15. At the end of each of the two years the dividends paid are 10p and 20p respectively. What is the rate of return?
A) 15%
B) 34%
C) 6%
D) 24%
A) 15%
B) 34%
C) 6%
D) 24%
D
2
What are the possible values of covariance?
A) -œ to 0
B) - 1 to + 1
C) 0 to + œ
D) -œ to + œ
A) -œ to 0
B) - 1 to + 1
C) 0 to + œ
D) -œ to + œ
D
3
What can you conclude if the standard deviation of returns from Project X is smaller than the standard deviation of returns from Project Y?
A) The expected returns from Project X are less predictable.
B) Past returns from Project X are smaller.
C) Returns from Project X are larger.
D) The expected returns from Project X are easier to estimate.
A) The expected returns from Project X are less predictable.
B) Past returns from Project X are smaller.
C) Returns from Project X are larger.
D) The expected returns from Project X are easier to estimate.
D
4
What is R, when calculated using the formula R = Σ Ripi ?
I=1
A) Mean return
B) Standard deviation
C) Market rate return
D) Expected return
I=1
A) Mean return
B) Standard deviation
C) Market rate return
D) Expected return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is R, as calculated by the formula R = D1 + P1 - P0 , when P0 is the purchase price, P1 the 
 0
0
Security's
Value at the end of the one- year holding period, and D1 the dividend paid during the period?
A) The multi- period return
B) The discount rate
C) The one- year holding period return
D) The internal rate of return

 0
0Security's
Value at the end of the one- year holding period, and D1 the dividend paid during the period?
A) The multi- period return
B) The discount rate
C) The one- year holding period return
D) The internal rate of return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Two constituents of a portfolio show perfectly positive correlation. What is the correlation coefficient?
A) +1
B) 0
C) - 1
D) + infinity
A) +1
B) 0
C) - 1
D) + infinity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the return if a share is bought for £8, a dividend is paid of 80p, and the share is sold for £9.20 after one year?
A) 20%
B) 10%
C) 30%
D) 25%
A) 20%
B) 10%
C) 30%
D) 25%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A two- asset portfolio is made up of 60 per cent of funds with expected return 13 per cent, and 40 per cent of funds with expected return 15 per cent. What is the total return expected from the portfolio?
A) 13.8%
B) 12.8%
C) 18.8%
D) 14.8%
A) 13.8%
B) 12.8%
C) 18.8%
D) 14.8%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is represented by Rp in the formula Rp = aRA + (1 - a) RB ?
A) Portfolio expected returns
B) Internal rate of return
C) Predicted rate of return
D) Present rate of return
A) Portfolio expected returns
B) Internal rate of return
C) Predicted rate of return
D) Present rate of return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An investor decides to invest in shares in two companies, rather than in just one. The expected returns of each company are RA and RB (where RB > RA). Which statement best describes RP, the expected return from the portfolio?
A) RB < RP < RA
B) RP < RA < RB
C) RP = RA + RB
D) RA < RP < RB
A) RB < RP < RA
B) RP < RA < RB
C) RP = RA + RB

D) RA < RP < RB

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is the standard deviation of the return of the following project? 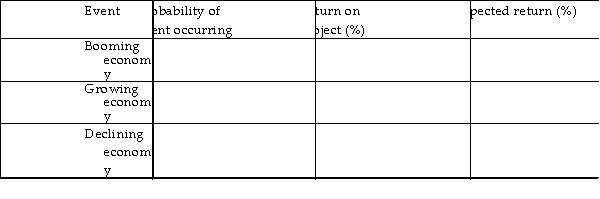
A) 5.22%
B) 25.10%
C) 15.34%
D) 10.68%

A) 5.22%
B) 25.10%
C) 15.34%
D) 10.68%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which three of the following statements are correct?
A) For a portfolio to be described as efficient there must be no other combinations of proportions of the underlying investments which provide a higher return for the same risk.
B) Portfolio returns are a weighted average of the expected returns on the individual investments but portfolio standard deviation is more than the weighted average risk of the individual investments.
C) Both covariance and the correlation coefficient measure the degree to which returns move together.
D) The degree of risk reduction from diversification depends on the extent of statistical interdependence between the returns of the different investments.
A) For a portfolio to be described as efficient there must be no other combinations of proportions of the underlying investments which provide a higher return for the same risk.
B) Portfolio returns are a weighted average of the expected returns on the individual investments but portfolio standard deviation is more than the weighted average risk of the individual investments.
C) Both covariance and the correlation coefficient measure the degree to which returns move together.
D) The degree of risk reduction from diversification depends on the extent of statistical interdependence between the returns of the different investments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is X in the formula X = n
Σ [(RA - RA )(RB - RB) pi ] ?
I=1
A) Covariance between A and B
B) Probability of positive covariance
C) Correlation between A and B
D) Deviation of the mean of A and B
Σ [(RA - RA )(RB - RB) pi ] ?
I=1
A) Covariance between A and B
B) Probability of positive covariance
C) Correlation between A and B
D) Deviation of the mean of A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What term is used for the weighted average of the expected returns on the constituent investments?
A) Mean return
B) Sum of the expected returns
C) Portfolio expected return
D) Market expected return
A) Mean return
B) Sum of the expected returns
C) Portfolio expected return
D) Market expected return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which two of the following options correctly give rules for portfolio management according to mean- variance portfolio theory?
A) Portfolio standard deviation is less than the weighted average risk of the individual investments, except for perfectly positively correlated investments.
B) Portfolio returns are a weighted average of the expected returns on the individual investments.
C) Portfolio standard deviation is greater than the weighted average risk of the individual investments, except for perfectly negatively correlated investments.
D) Expected returns are a weighted average of the portfolio return on the group of investments.
A) Portfolio standard deviation is less than the weighted average risk of the individual investments, except for perfectly positively correlated investments.
B) Portfolio returns are a weighted average of the expected returns on the individual investments.
C) Portfolio standard deviation is greater than the weighted average risk of the individual investments, except for perfectly negatively correlated investments.
D) Expected returns are a weighted average of the portfolio return on the group of investments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Two companies operate in the same industry and tend to follow practically identical patterns of performance. Which statement describes the relationship between the returns of the two companies?
A) They show imperfect correlation.
B) They are uncorrelated.
C) They show perfect negative correlation.
D) They show perfect positive correlation.
A) They show imperfect correlation.
B) They are uncorrelated.
C) They show perfect negative correlation.
D) They show perfect positive correlation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which one of the following approaches will increase the level of risk, provided the constituents of a portfolio are not perfectly positively correlated?
A) Make the statistical interdependence between the securities more negative
B) Decreasing the number of securities
C) Reduce diversification
D) Identify high profit investments
A) Make the statistical interdependence between the securities more negative
B) Decreasing the number of securities
C) Reduce diversification
D) Identify high profit investments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the effect on outcomes if a portfolio has statistically independent shares from two companies, and the expected returns are the same for both?
A) The expected return is halved but the standard deviation remains constant.
B) The expected return is the same but the standard deviation increases.
C) The expected return doubles but the standard deviation remains constant.
D) The expected return is the same but the standard deviation is reduced.
A) The expected return is halved but the standard deviation remains constant.
B) The expected return is the same but the standard deviation increases.
C) The expected return doubles but the standard deviation remains constant.
D) The expected return is the same but the standard deviation is reduced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) To achieve maximum attainable utility, always select a portfolio on a person's highest indifference curve.
B) To achieve maximum utility, select the portfolio with the lowest risk.
C) To achieve the highest utility, first choose the best efficiency frontier and then select the highest returns portfolio.
D) To achieve the highest utility, select the portfolio where the highest attainable indifference curve is tangential to the efficiency frontier.
A) To achieve maximum attainable utility, always select a portfolio on a person's highest indifference curve.
B) To achieve maximum utility, select the portfolio with the lowest risk.
C) To achieve the highest utility, first choose the best efficiency frontier and then select the highest returns portfolio.
D) To achieve the highest utility, select the portfolio where the highest attainable indifference curve is tangential to the efficiency frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A two- asset portfolio is made up of 80 per cent of Share A, for which the variance is 50%, and 20 per cent of Share B, with variance 60%. The covariance between the two shares is 25%. What is the standard deviation of the two- asset portfolio?
A) 87.54%
B) 65.12%
C) 73.23%
D) 91.63%
A) 87.54%
B) 65.12%
C) 73.23%
D) 91.63%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Companies A and B show perfect negative correlation. What are the risks associated with investing in the two companies?
A) Infinite
B) A minimum
C) A maximum
D) Zero, if weights are appropriately chosen
A) Infinite
B) A minimum
C) A maximum
D) Zero, if weights are appropriately chosen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following equations correctly shows the relation between the semi- annual rate (s) and the annual rate (R)?
A) 1 + s = 2(1 + R)
B) (1 + s)2 = 1 + R
C) (1 + s)2 = 1 + R
D) 2(1 + s) = 1 - R
A) 1 + s = 2(1 + R)
B) (1 + s)2 = 1 + R
C) (1 + s)2 = 1 + R
D) 2(1 + s) = 1 - R

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which two factors have the greatest effect on the degree of risk reduction?
A) The extent of statistical interdependency between the returns on different investments
B) The number of securities in the portfolio
C) The expected return on the constituent investments
D) The total return on the investments
A) The extent of statistical interdependency between the returns on different investments
B) The number of securities in the portfolio
C) The expected return on the constituent investments
D) The total return on the investments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which two of the statements are correct?
A) For perfectly positive correlated investments portfolio standard deviation is equal to the weighted average of the standard deviation of the constituent investment.
B) For perfectly negatively correlated investments portfolio standard deviation is equal to the weighted average of the standard deviation of the constituent investment.
C) Portfolio standard deviation is usually greater than the weighted average of the standard deviation of the constituent investments.
D) Portfolio standard deviation is usually less than the weighted average of the standard deviation of the constituent investments.
A) For perfectly positive correlated investments portfolio standard deviation is equal to the weighted average of the standard deviation of the constituent investment.
B) For perfectly negatively correlated investments portfolio standard deviation is equal to the weighted average of the standard deviation of the constituent investment.
C) Portfolio standard deviation is usually greater than the weighted average of the standard deviation of the constituent investments.
D) Portfolio standard deviation is usually less than the weighted average of the standard deviation of the constituent investments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following could reduce the risk on a portfolio to zero?
A) Appropriate allocation of funds where there is perfectly negative correlation
B) Any allocation of funds provided there is perfectly negative correlation.
C) Appropriate allocation of funds where there is perfectly positive correlation
D) Appropriate allocation of funds provided there is negative correlation.
A) Appropriate allocation of funds where there is perfectly negative correlation
B) Any allocation of funds provided there is perfectly negative correlation.
C) Appropriate allocation of funds where there is perfectly positive correlation
D) Appropriate allocation of funds provided there is negative correlation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What does X represent in the formula X = Σ (Ri - Ri )2 pi ? i=1
A) Standard deviation
B) Sum of the expected returns
C) Variance
D) Expected return
A) Standard deviation
B) Sum of the expected returns
C) Variance
D) Expected return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What term is used for the extent to which the returns on two investments move together?
A) Covariance
B) Correlativity
C) Correspondence
D) Coefficient
A) Covariance
B) Correlativity
C) Correspondence
D) Coefficient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How can you reduce the level of risk, provided the constituents of a portfolio are not perfectly positively correlated?
A) Decrease the number of securities
B) Make the statistical interdependence between the securities more positive
C) Identify high profit investments
D) Increase the number of securities
A) Decrease the number of securities
B) Make the statistical interdependence between the securities more positive
C) Identify high profit investments
D) Increase the number of securities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What does P0 represent in the formula for the one- year holding period return, R = D1 + P1 - P0 ?
P0

A) Price after year one
B) Issue price
C) Purchase price
D) Sale price
P0

A) Price after year one
B) Issue price
C) Purchase price
D) Sale price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What does the symbol Ri represent in the formula used to calculate standard deviation?
A) Mean return
B) Expected return for event i
C) Probability of event i occurring
D) Expected mean return
A) Mean return
B) Expected return for event i
C) Probability of event i occurring
D) Expected mean return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the range of possible values of the correlation coefficient?
A) 0 to +1
B) 0 to + infinity
C) - 1 to +1
D) - infinity to + infinity
A) 0 to +1
B) 0 to + infinity
C) - 1 to +1
D) - infinity to + infinity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
How would you assess the risks associated with a portfolio of two companies that show perfect positive correlation?
A) Assume that they were zero
B) Calculate the difference between the two risks
C) Calculate the sum of the two risks
D) Calculate the average of the two risks
A) Assume that they were zero
B) Calculate the difference between the two risks
C) Calculate the sum of the two risks
D) Calculate the average of the two risks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The table shows share prices for two shares. What type of covariance do the figures suggest? 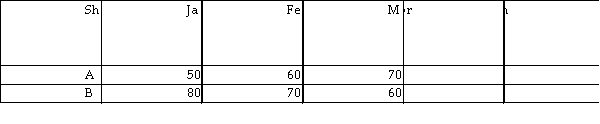
A) Perfectly positive
B) Perfectly negative
C) Zero
D) Infinite

A) Perfectly positive
B) Perfectly negative
C) Zero
D) Infinite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which two of the following provide useful rules to assess the degree of risk reduction (provided there is not perfectly positive correlation)?
A) The smaller the number of securities, the lower the risk.
B) The more negative the correlation the better.
C) The more positive the correlation the better.
D) The greater the number of securities, the lower the risk.
A) The smaller the number of securities, the lower the risk.
B) The more negative the correlation the better.
C) The more positive the correlation the better.
D) The greater the number of securities, the lower the risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



