Deck 14: Business Decisions Under Uncertainty
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/200
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Business Decisions Under Uncertainty
1
 The above table provides the possible prices for a bushel of corn next year along with the associated probabilities (in percent).
The above table provides the possible prices for a bushel of corn next year along with the associated probabilities (in percent).Refer to the table above. If these are the only three price options for a bushel of corn, what is the expected value of the price of a bushel of corn?
A)$2.50
B)$2.78
C)$3.00
D)$2.25
B
2
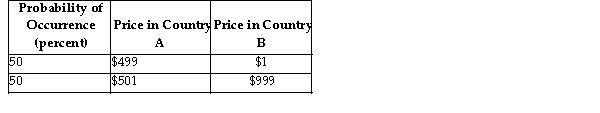 The above table provides the probability distribution of price of an input next year in Country A and Country B.
The above table provides the probability distribution of price of an input next year in Country A and Country B.Refer to the table above. The expected value of the price of the input in Country A is the expected value of the input in Country B.
A)greater than
B)the same as
C)less than
D)twice
B
3
 The above table provides the probability distribution of price of an input next year in Country A and Country B.
The above table provides the probability distribution of price of an input next year in Country A and Country B.Refer to the table above. What is the expected price of the input in Country A?
A)$500
B)$501
C)$499
D)$999
A
4
If an event has three possible outcomes, A, B, and C, and the probability of event A occurring is 0.20, the probability of event B occurring is 0.20, the probability of event C occurring is .
A)0.20
B)1.00
C)0.60
D)0.30
A)0.20
B)1.00
C)0.60
D)0.30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a coin is flipped two times, what is the probability of a tail appearing on both tosses?
A)0.25
B)0.75
C)1.0
D)0.50
A)0.25
B)0.75
C)1.0
D)0.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A standard deck of playing cards has 52 cards with 13 cards in each of the four suits; hearts, diamonds, spades, and clubs. Each of the four suits has a king card. If a single card is drawn from a standard deck, what is the probability that the card will be the king of spades?
A)0.077
B)0.25
C)0.019
D)0.05
A)0.077
B)0.25
C)0.019
D)0.05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
 The above table provides the probability distribution of price of an input next year in Country A and Country B.
The above table provides the probability distribution of price of an input next year in Country A and Country B.Refer to the table above. The expected value of the price of the input in Country A is the expected value of the input in Country B and the extent of the variation in price in Country A is than the extent of variation in price in Country B.
A)greater than; greater
B)the same as; greater
C)less than; less
D)the same as; less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The price of a bushel of corn next year is a variable because the price _ known with certainty.
A)random; is not
B)known; is
C)random; is
D)known; is not
A)random; is not
B)known; is
C)random; is
D)known; is not

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Uncertainty is the result of information that is often associated with events.
A)incomplete; known
B)incomplete; random
C)complete; known
D)complete; random
A)incomplete; known
B)incomplete; random
C)complete; known
D)complete; random

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
 The above table provides the possible prices for a bushel of corn next year along with the associated probabilities (in percent).
The above table provides the possible prices for a bushel of corn next year along with the associated probabilities (in percent).Refer to the table above. If these are the only three price options for a bushel of corn, what is the value of A?
A)0.30
B)0.45
C)0.25
D)0.55

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
 The above table provides the possible prices for a pound of sugar next year along with the associated probabilities (in percent
The above table provides the possible prices for a pound of sugar next year along with the associated probabilities (in percentRefer to the table above. If these are the only four price options for a pound of sugar, what is the value of A?
A)0.45
B)0.25
C)1.00
D)0.10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If an event has two possible outcomes, A and B, and the probability of event A occurring is 0.30, the probability of event B occurring is _.
A)0.30
B)0.20
C)0.70
D)1.00
A)0.30
B)0.20
C)0.70
D)1.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a six- sided die is rolled 90,000 times and a number one appears 15,000 times, the relative frequency of the number one appearing is .
A)0.167
B)15,000
C)0.667
D)90,000
A)0.167
B)15,000
C)0.667
D)90,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
 The above table provides the probability distribution of price of an input next year in Country A and Country B.
The above table provides the probability distribution of price of an input next year in Country A and Country B.Refer to the table above. Because the extent of variation in the price of the input is in Country B compared to Country A, it is less risky to plan to purchase the input in Country .
A)greater; B
B)greater; A
C)lower; B
D)lower; A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If a coin is flipped two times, what is the probability of a tail appearing on the first toss and then a head appearing on the second toss?
A)1.0
B)0.50
C)0.75
D)0.25
A)1.0
B)0.50
C)0.75
D)0.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A standard deck of playing cards has 52 cards with 13 cards in each of the four suits; hearts, diamonds, spades, and clubs. Each of the four suits has a king card. If a single card is drawn from a standard deck, what is the probability that the card will be a king?
A)0.33
B)0.25
C)0.019
D)0.077
A)0.33
B)0.25
C)0.019
D)0.077

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
 The above table provides the probability distribution of price of an input next year in Country A and Country B.
The above table provides the probability distribution of price of an input next year in Country A and Country B.Refer to the table above. What is the expected price of the input in Country B?
A)$1
B)$999
C)$500
D)$501

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Objective probabilities are based on _ and _ frequencies.
A)data; relative
B)data; popular
C)educated guesses; relative
D)educated guesses; popular
A)data; relative
B)data; popular
C)educated guesses; relative
D)educated guesses; popular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If a six- sided die is rolled 90,000 times and a number five appears 15,000 times, the relative frequency of the number five appearing is .
A)15,000
B)0.167
C)90,000
D)5
A)15,000
B)0.167
C)90,000
D)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A standard deck of playing cards has 52 cards with 13 cards in each of the four suits; hearts, diamonds, spades, and clubs. If a single card is drawn from a standard deck, what is the probability that the card will be a spade?
A)0.25
B)0.52
C)0.13
D)0.75
A)0.25
B)0.52
C)0.13
D)0.75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
 The above table summarizes the marginal cost of production at various quantity levels for a perfectly competitive firm.
The above table summarizes the marginal cost of production at various quantity levels for a perfectly competitive firm.Refer to the table above. The perfectly competitive firm has a random demand with a 50 percent chance of being $6 and a 50 percent chance of being $8. What quantity should the firm produce to maximize its expected profit?
A)110
B)120
C)140
D)130

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A perfectly competitive firm has a random demand with a 20 percent chance of being $18 and an 80 percent chance of being $26. What is the firm's expected marginal revenue?
A)$26.00
B)$24.40
C)$25.60
D)$18.50
A)$26.00
B)$24.40
C)$25.60
D)$18.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A perfectly competitive firm with a random demand has an expected demand curve that is its expected marginal revenue curve.
A)equal to
B)greater than
C)less than
D)exactly double
A)equal to
B)greater than
C)less than
D)exactly double

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A perfectly competitive firm with a random demand has an expected marginal revenue that is its expected price.
A)equal to
B)exactly double
C)less than
D)greater than
A)equal to
B)exactly double
C)less than
D)greater than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A perfectly competitive firm with a random demand has an expected demand curve that is its expected price.
A)equal to
B)less than
C)exactly double
D)greater than
A)equal to
B)less than
C)exactly double
D)greater than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A perfectly competitive firm has a random demand with a 30 percent chance of being $15 and a 70 percent chance of being $20. What is the firm's expected marginal revenue?
A)$15.00
B)$18.50
C)$19.00
D)$20.00
A)$15.00
B)$18.50
C)$19.00
D)$20.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When a random demand and marginal cost are linear, producing the quantity at which the marginal cost equals the maximizes _ _.
A)expected marginal revenue; expected profit
B)expected marginal revenue; profit
C)marginal revenue; profit
D)marginal revenue; expected profit
A)expected marginal revenue; expected profit
B)expected marginal revenue; profit
C)marginal revenue; profit
D)marginal revenue; expected profit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A perfectly competitive firm with a random demand has a demand curve and _ marginal revenue curve.
A)horizontal; vertical
B)horizontal; horizontal
C)vertical; vertical
D)vertical; horizontal
A)horizontal; vertical
B)horizontal; horizontal
C)vertical; vertical
D)vertical; horizontal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A perfectly competitive firm with a random demand has a expected demand curve and expected marginal revenue curve.
A)vertical; horizontal
B)horizontal; vertical
C)vertical; vertical
D)horizontal; horizontal
A)vertical; horizontal
B)horizontal; vertical
C)vertical; vertical
D)horizontal; horizontal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The larger the extent of variation, the smaller the risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Managers will use probabilities to estimate the likelihood of a profitable entry into a foreign market.
A)subjective
B)relative
C)objective
D)known
A)subjective
B)relative
C)objective
D)known

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A perfectly competitive firm has a random demand with a 90 percent chance of being $100, a 5 percent chance of $90, and a 5 percent chance of being $80. What is the firm's expected marginal revenue?
A)$96.40
B)$92.75
C)$98.50
D)$90.50
A)$96.40
B)$92.75
C)$98.50
D)$90.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Subjective probabilities are based on and data.
A)relative frequencies; on
B)best estimates; not on
C)best estimates; on
D)relative frequencies; not on
A)relative frequencies; on
B)best estimates; not on
C)best estimates; on
D)relative frequencies; not on

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A perfectly competitive firm has a random demand with a 20 percent chance of being $10, a 20 percent chance of $16, and a 60 percent chance of being $20. What is the firm's expected marginal revenue?
A)$16.00
B)$15.20
C)$17.20
D)$16.40
A)$16.00
B)$15.20
C)$17.20
D)$16.40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Probability is the chance that an event occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A probability distribution of a random variable is a listing of all of the possible outcomes of the random variable and the associated probabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Suppose the local government will determine if a contracting firm will be given a job based on rolling a fair die. If a four or above appears after the die has been rolled, the contracting firm will be given the job. The managers of the contracting firm will use _ probabilities to estimate the likelihood that their firm will be given the job.
A)unknown
B)relative
C)objective
D)subjective
A)unknown
B)relative
C)objective
D)subjective

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Uncertainty is the result of incomplete information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Managers will use probabilities to estimate the likelihood of a successful launch of a new brand of peanut butter.
A)subjective
B)known
C)relative
D)objective
A)subjective
B)known
C)relative
D)objective

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
It is possible for the probability of an event to be 1.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
 The above table summarizes the marginal cost of production at various quantity levels for a perfectly competitive firm.
The above table summarizes the marginal cost of production at various quantity levels for a perfectly competitive firm.Refer to the table above. The perfectly competitive firm has a random demand with a 25 percent chance of being $5 and a 75 percent chance of being $9. What quantity should the firm produce to maximize its expected profit?
A)110
B)120
C)130
D)100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
To maximize expected profit, a perfectly competitive firm with a random marginal cost and random demand should produce at the level that sets _ equal to _.
A)expected marginal revenue; expected marginal cost
B)marginal revenue; marginal cost
C)expected marginal revenue; marginal cost
D)marginal revenue; expected marginal cost
A)expected marginal revenue; expected marginal cost
B)marginal revenue; marginal cost
C)expected marginal revenue; marginal cost
D)marginal revenue; expected marginal cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
For a perfectly competitive firm with a known marginal cost and random demand, as the expected marginal revenue decreases, the profit- maximizing quantity _ .
A)decreases
B)increases exponentially
C)does not change
D)increases
A)decreases
B)increases exponentially
C)does not change
D)increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When both demand and cost are random, firms cannot maximize expected profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
For a perfectly competitive firm with a known marginal cost and random demand, as the expected marginal revenue increases, the profit- maximizing quantity _ .
A)increases
B)does not change
C)decreases
D)approaches zero
A)increases
B)does not change
C)decreases
D)approaches zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If a perfectly competitive firm has a random demand and known marginal cost, producing at a level that sets expected price equal to marginal cost minimizes the reduction in expected profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
To maximize expected profit, a perfectly competitive firm with a random marginal cost and known demand should produce at the level that sets equal to _.
A)marginal cost; expected marginal revenue
B)expected marginal cost; marginal revenue
C)marginal cost; marginal revenue
D)expected marginal cost; expected marginal revenue
A)marginal cost; expected marginal revenue
B)expected marginal cost; marginal revenue
C)marginal cost; marginal revenue
D)expected marginal cost; expected marginal revenue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A perfectly competitive firm has a random marginal cost with a 20 percent chance of a high marginal cost of $20 and an 80 percent chance of a low marginal cost of $5. What is the firm's expected marginal cost?
A)$12
B)$10
C)$8
D)$7
A)$12
B)$10
C)$8
D)$7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
 The above table summarizes the marginal cost of production at various quantity levels for a perfectly competitive firm.
The above table summarizes the marginal cost of production at various quantity levels for a perfectly competitive firm.Refer to the table above. The perfectly competitive firm has a random demand with a 50 percent chance of being $7 and a 50 percent chance of being $9. What quantity should the firm produce to maximize its expected profit?
A)130
B)120
C)110
D)140

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When a firm's demand fluctuates randomly,
A)the profit- maximizing inventory is found where the expected marginal benefit exceeds the expected marginal cost.
B)managers cannot use marginal analysis to determine the optimal inventory.
C)no profit can be earned on the inventory.
D)the optimal inventory maximizes the profit of the inventory.
A)the profit- maximizing inventory is found where the expected marginal benefit exceeds the expected marginal cost.
B)managers cannot use marginal analysis to determine the optimal inventory.
C)no profit can be earned on the inventory.
D)the optimal inventory maximizes the profit of the inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
 The above table summarizes the marginal cost of production at various quantity levels for a perfectly competitive firm.
The above table summarizes the marginal cost of production at various quantity levels for a perfectly competitive firm.Refer to the table above. The perfectly competitive firm has a random demand with a 75 percent chance of being $5 and a 25 percent chance of being $9. What quantity should the firm produce to maximize its expected profit?
A)120
B)110
C)100
D)130

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If a perfectly competitive firm with a known demand and random marginal cost is producing at a level in which the marginal cost is less than the expected marginal cost and the marginal revenue, which of the following is true?
A)To maximize expected profit, the firm should decrease production by one- half.
B)The firm is maximizing expected profit.
C)To maximize expected profit, the firm should increase production.
D)To maximize expected profit, the firm should decrease production.
A)To maximize expected profit, the firm should decrease production by one- half.
B)The firm is maximizing expected profit.
C)To maximize expected profit, the firm should increase production.
D)To maximize expected profit, the firm should decrease production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If a firm's demand is known, but has random costs, it cannot maximize its actual profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A perfectly competitive firm has a random marginal cost with a 30 percent chance of a high marginal cost of $50 and a 70 percent chance of a low marginal cost of $40. What is the firm's expected marginal cost?
A)$45
B)$48
C)$46
D)$43
A)$45
B)$48
C)$46
D)$43

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
To maximize expected profit, a perfectly competitive firm with a random marginal cost and random demand should produce at the level that sets _ equal to _.
A)expected price; expected marginal cost
B)expected price; marginal cost
C)price; expected marginal cost
D)price; marginal cost
A)expected price; expected marginal cost
B)expected price; marginal cost
C)price; expected marginal cost
D)price; marginal cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A perfectly competitive firm has a random marginal cost with a 60 percent chance of a high marginal cost of $100 and a 40 percent chance of a low marginal cost of $90. What is the firm's expected marginal cost?
A)$96
B)$92
C)$94
D)$98
A)$96
B)$92
C)$94
D)$98

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If your firm has a random demand, producing at the level that maximizes your expected profit will earn the same profit as the profit- maximizing production level with a known demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A perfectly competitive firm has a random marginal cost with a 50 percent chance of a high marginal cost of $10, a 30 percent chance of a marginal cost of $8, and a 20 percent chance of a low marginal cost of $5. What is the firm's expected marginal cost?
A)$7.80
B)$9.20
C)$8.40
D)$8.00
A)$7.80
B)$9.20
C)$8.40
D)$8.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
 The above table summarizes the marginal cost of production at various quantity levels for a perfectly competitive firm.
The above table summarizes the marginal cost of production at various quantity levels for a perfectly competitive firm.Refer to the table above. The perfectly competitive firm has a random demand with a 50 percent chance of being $5 and a 50 percent chance of being $7. What quantity should the firm produce to maximize its expected profit?
A)120
B)110
C)130
D)100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If a firm's demand is random, the firm's price and profit are also random.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
 The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.
The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.Refer to the table above. What is the probability of selling exactly 24 cakes?
A)0.20
B)0.00
C)0.10
D)0.90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
 The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.
The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.Refer to the table above. Busy Betty sells her cakes for $20 each and her constant marginal cost to produce each cake is $12, which is equal to her (constant)average total cost. If she does not sell a cake the day she makes it, she sells it as day- old cake for $10. What is her expected marginal cost of holding the 22nd cake in inventory?
A)$1.20
B)$2.00
C)$0.80
D)$0.40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
 The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.
The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.Refer to the table above. What is the probability of selling 23 or more cakes?
A)0.40
B)0.70
C)0.60
D)0.30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
 The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.
The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.Refer to the table above. What is the probability of selling less than 22 cakes?
A)0.20
B)0.10
C)0.60
D)0.40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The price of a firm's product is $6 and the firm faces a constant marginal cost of $4 that is equal to its (constant)average total cost. If the firm does not sell a unit of its product on the day it was produced, it is sold in a secondary market for a price of $3. If the firm does not sell a unit of its product on the day it was produced, there is a _ of per unit not sold.
A)profit; $1
B)profit; $2
C)loss; $2
D)loss; $1
A)profit; $1
B)profit; $2
C)loss; $2
D)loss; $1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
 The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.
The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.Refer to the table above. Busy Betty sells her cakes for $20 each and her constant marginal cost to produce each cake is $12, which is equal to her (constant)average total cost. What is her expected marginal benefit from holding the 20th cake in inventory?
A)$8.00
B)$7.80
C)$7.20
D)$12.80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Happy Bagels sells its bagels for $6 each and the firm has a constant marginal cost of $4 per bagel, which is equal to its (constant)average total cost. If Happy Bagels does not sell a bagel the day it is produced, the bagel is sold as day- old for $2. If Happy Bagels is currently holding 50 bagels in inventory and the probability that Happy Bagels will sell 50 bagels or more is 0.40, which of the following statements is true?
A)To obtain the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory, Happy Bagels needs to double its inventory.
B)To obtain the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory, Happy Bagels needs to decrease its inventory.
C)To obtain the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory, Happy Bagels needs to increase its inventory.
D)Happy Bagels is holding the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory.
A)To obtain the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory, Happy Bagels needs to double its inventory.
B)To obtain the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory, Happy Bagels needs to decrease its inventory.
C)To obtain the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory, Happy Bagels needs to increase its inventory.
D)Happy Bagels is holding the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Happy Bagels sells its bagels for $6 each and the firm has a constant marginal cost of $4 per bagel, which is equal to its (constant)average total cost. If Happy Bagels does not sell a bagel the day it is produced, the bagel is sold as day- old for $2. If Happy Bagels is currently holding 50 bagels in inventory and the probability that Happy Bagels will sell 50 bagels or more is 0.60, which of the following statements is true?
A)To obtain the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory, Happy Bagels needs to increase its inventory.
B)Happy Bagels is holding the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory.
C)To obtain the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory, Happy Bagels needs to decrease its inventory.
D)To obtain the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory, Happy Bagels needs to decrease its inventory by exactly one- half.
A)To obtain the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory, Happy Bagels needs to increase its inventory.
B)Happy Bagels is holding the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory.
C)To obtain the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory, Happy Bagels needs to decrease its inventory.
D)To obtain the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory, Happy Bagels needs to decrease its inventory by exactly one- half.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
 The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.
The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.Refer to the table above. Busy Betty sells her cakes for $20 each and her constant marginal cost to produce each cake is $12, which is equal to her (constant)average total cost. What is her expected marginal benefit from holding the 23rd cake in inventory?
A)$8.00
B)$4.80
C)$3.20
D)$8.20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
 The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.
The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.Refer to the table above. What is the probability of selling 22 or more cakes?
A)0.40
B)0.20
C)0.60
D)0.10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The optimal inventory to hold maximizes the profit of the inventory, which is the profit from the units sold _ the from the units that remain unsold.
A)plus; profit
B)minus; profit
C)plus; loss
D)minus; loss
A)plus; profit
B)minus; profit
C)plus; loss
D)minus; loss

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
 The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.
The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.Refer to the table above. What is the probability of selling exactly 23 cakes?
A)0.00
B)0.30
C)0.10
D)0.20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If the price of a firm's product is $12 and the firm faces a constant marginal cost of $5 that is equal to its (constant)average total cost, the profit from selling a unit of the firm's product from its inventory is equal to _ .
A)$15
B)$5
C)$7
D)$8
A)$15
B)$5
C)$7
D)$8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The price of a firm's product is $8 and the firm faces a constant marginal cost of $5 that is equal to its (constant)average total cost. If the firm does not sell a unit of its product on the day it was produced, it is sold in a secondary market for a price of $2. If the firm does not sell a unit of its product on the day it was produced, there is a _ of per unit not sold.
A)loss; $3
B)loss; $2
C)profit; $5
D)profit; $3
A)loss; $3
B)loss; $2
C)profit; $5
D)profit; $3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
 The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.
The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.Refer to the table above. What is the probability of selling less than 24 cakes?
A)0.10
B)0.00
C)0.80
D)0.90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If the price of a firm's product is $10 and the firm faces a constant marginal cost of $4 that is equal to its (constant)average total cost, the profit from selling a unit of the firm's product from its inventory is equal to _ .
A)$10
B)$4
C)$6
D)$14
A)$10
B)$4
C)$6
D)$14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Happy Bagels sells its bagels for $6 each and the firm has a constant marginal cost of $4 per bagel, which is equal to its (constant)average total cost. If Happy Bagels does not sell a bagel the day it is produced, the bagel is sold as day- old for $2. If Happy Bagels is currently holding 50 bagels in inventory and the probability that Happy Bagels will sell 50 bagels or more is 0.50, which of the following statements is true?
A)To obtain the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory, Happy Bagels needs to increase its inventory.
B)To obtain the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory, Happy Bagels needs to double its inventory.
C)To obtain the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory, Happy Bagels needs to decrease its inventory.
D)Happy Bagels is holding the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory.
A)To obtain the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory, Happy Bagels needs to increase its inventory.
B)To obtain the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory, Happy Bagels needs to double its inventory.
C)To obtain the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory, Happy Bagels needs to decrease its inventory.
D)Happy Bagels is holding the profit- maximizing, optimal level of inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
 The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.
The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.Refer to the table above. Busy Betty sells her cakes for $20 each and her constant marginal cost to produce each cake is $12, which is equal to her (constant)average total cost. What is her expected marginal benefit from holding the 21st cake in inventory?
A)$6.10
B)$6.40
C)$8.00
D)$7.20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
 The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.
The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.Refer to the table above. Busy Betty sells her cakes for $20 each and her constant marginal cost to produce each cake is $12, which is equal to her (constant)average total cost. If she does not sell a cake the day she makes it, she sells it as day- old cake for $10. What is her expected marginal cost of holding the 23rd cake in inventory?
A)$1.20
B)$6.60
C)$0.40
D)$2.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
 The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.
The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.Refer to the table above. Busy Betty sells her cakes for $20 each and her constant marginal cost to produce each cake is $12, which is equal to her (constant)average total cost. If she does not sell a cake the day she makes it, she sells it as day- old cake for $10. What is her expected marginal cost of holding the 20th cake in inventory?
A)$0.20
B)$0.40
C)$10.00
D)$2.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



