Deck 12: Middle Childhood: Cognitive Development
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/189
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Middle Childhood: Cognitive Development
1
Describe Vygotsky's beliefs about learning, especially with respect to the zone of proximal development.
Vygotsky believed that 1) education occurs everywhere and often and that 2) every experience, from birth onward, teaches individuals something. Vygotsky believed that 3) peers, family members, and teachers use guided participation and scaffolding to provide the bridge between a child's developmental potential and needed skills in the zone of proximal development. 4) Peers, family members, and teachers can all provide the necessary instruction in the zone of proximal development. 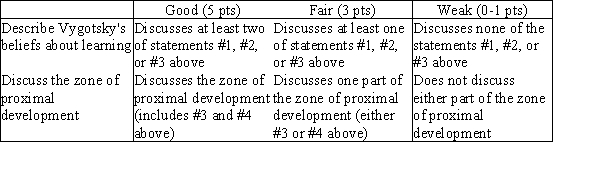

2
A body of knowledge in a particular area that makes it easier to master new information in that area is referred to as a knowledge _____.
base
3
In the United States, there are four types of educational environments for children: public schools, charter schools, private schools, and home schooling. Define each of these alternatives and identify which type of school the majority of children in the United States attend.
A public school is one that is free to all children because it is funded by taxpayers; it must educate all students. A charter school is a public school with its own set of standards that is funded and licensed by the state or local district in which it is located; it has control over admissions and expulsions. A private school is one funded by tuition, endowments, and often religious or other nonprofit sponsors. Home schooling is education in which children are taught at home, usually by a parent. The majority of children in the United States attend public schools. 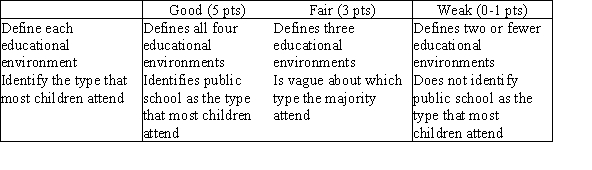

4
Explain what is meant by metacognition. Then describe how 9-year-old Bolgen can use metacognition to help him prepare for a spelling test. Bolgen gets 10 spelling words on Monday and is tested on Friday.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Identify the three ways in which children from low-SES families differ in language compared to children from high-SES families. Then identify and explain the most important factor proven to affect language learning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Kirby is sorting through his mother's cup of change. As he makes piles of pennies, nickels, and dimes, he utilizes the cognitive skill called _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Using concepts from the information-processing view of learning, list and explain the three major steps in the memory process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Explain how the information-processing approach compares human information processing to that of a computer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The capacity of a person's _____ memory is huge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Explain what Piaget meant by concrete operational thought.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Vygotsky regarded _____ as crucial in human cognitive development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Piaget's concrete operational thought is characterized by concepts that enable children to use _____ regarding tangible things.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The two crucial components of long-term memory are storage and _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The cognition of middle childhood that was described by Piaget as the ability to reason logically about tangible things is called _____ operational thought.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Explain the process of switching codes in speech. Identify the two codes and offer a real-life example of each, including the circumstances under which each code typically would be used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Define classification and seriation and provide an example of each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The cognitive theory that most closely approximates the operation of a computer is _____ theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When Sharona recalls plans that she has made for this weekend, she retrieves them from her long-term memory and brings them into her _____ memory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Briefly describe the immersion and bilingual schooling approaches to teaching a second language in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Current, conscious mental activity occurs in _____ memory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The unspoken and often unrecognized lessons that children learn in school, which have unofficial, unstated, or implicit influences on the academic curriculum and every other aspect of learning in school, are called the _____ curriculum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Sian would like to share her ideas in class, but she knows that her teacher wants students to raise their hands and wait to be called on before speaking. Her teacher's values about class discipline are part of the _____ curriculum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Traditionally in the United States, most _____ schools were operated by the Catholic Church.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Internationally, girls tend to outscore boys on the _____ test of reading ability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The practical use of language is called _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Nine-year-old Devon writes, "My dad is as big a star." This statement demonstrates his understanding of a figure of speech called a _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Control processes include emotional regulation, selective attention, and _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Based on results from the international test known as the _____, children in East Asian nations are the most advanced in math and science.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An approach to learning a new language in which instruction occurs exclusively in the new language is called _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
_____ is one's ability to evaluate a task to determine what to do and in what order and also to monitor one's progress while working on the task.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
As of 2014, the United States' public schools have become "majority _____."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
_____ schools are licensed and funded by states or local districts. They may also receive private money from sponsors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The analysis and flow of information within the information-processing system are both regulated by _____ processes in the brain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In _____ schooling, teachers instruct children in their native language as well as in English.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Mastery of language pragmatics allows children to change _____ depending on the audience.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In the United States, experts from all 50 states developed high national standards known as the _____ to replace the various state standards and tests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The main test used to assess reading internationally is the _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A public subsidy for tuition payment at a nonpublic school is referred to as a(n) _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Approximately 4 percent of children in the United States are _____ by parents who avoid public and private schools.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The majority of children in the United States go to _____ schools.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which statement about the difference between a 4-year-old and a 9-year-old is accurate?
A) The 4-year-old can separate the relevant from the irrelevant, but the 9-year-old is unable to do so.
B) The 9-year-old can apply abstract thought to the classification process, whereas the 4-year-old is unable to do so.
C) The 4-year-old will be able to think logically about concrete situations, whereas the 9-year-old is unable to do so.
D) The 9-year-old can use mental categories flexibly, inductively, and simultaneously, whereas the 4-year-old is unable to do so.
A) The 4-year-old can separate the relevant from the irrelevant, but the 9-year-old is unable to do so.
B) The 9-year-old can apply abstract thought to the classification process, whereas the 4-year-old is unable to do so.
C) The 4-year-old will be able to think logically about concrete situations, whereas the 9-year-old is unable to do so.
D) The 9-year-old can use mental categories flexibly, inductively, and simultaneously, whereas the 4-year-old is unable to do so.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Vygotsky argued that playing with peers, watching television, and eating with one's family all provide _____ to a 6-year-old child.
A) annoyances
B) joy
C) instruction
D) negativity
A) annoyances
B) joy
C) instruction
D) negativity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Dr. Holiday is doing a study to determine how 9-year-olds think. Based on theory, he believes that 9-year-olds should be able to reason logically about concrete situations-situations that are real, tangible, and visible. Dr. Holiday's belief is based on _____.
A) the information-processing perspective
B) Piaget's theory of cognitive development
C) Vygotsky's theory of cognitive development
D) Erikson's theory of psychosocial development
A) the information-processing perspective
B) Piaget's theory of cognitive development
C) Vygotsky's theory of cognitive development
D) Erikson's theory of psychosocial development

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The knowledge that things can be arranged in a logical sequence is the logical principle of _____.
A) conservation
B) seriation
C) classification
D) reversibility
A) conservation
B) seriation
C) classification
D) reversibility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When capable of concrete operational thought, children _____.
A) are limited to intuitive, perceptual focusing
B) can apply logical reasoning to real, tangible situations
C) can reason about abstractions
D) are likely to be misled by appearances
A) are limited to intuitive, perceptual focusing
B) can apply logical reasoning to real, tangible situations
C) can reason about abstractions
D) are likely to be misled by appearances

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
According to Piaget, which ability do children gain during middle childhood?
A) static reasoning
B) abstract reasoning
C) logic
D) egocentrism
A) static reasoning
B) abstract reasoning
C) logic
D) egocentrism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Seven-year-old Hannah can arrange 10 buttons in order from smallest to largest. Her understanding of _____ allows her to accomplish this.
A) conservation
B) transitive inference
C) seriation
D) abstract reasoning
A) conservation
B) transitive inference
C) seriation
D) abstract reasoning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In one international study of the effects of early formal instruction, it was found that children who started school at age 4 or 5 instead of age 6 or 7 tended to _____.
A) resist attending college
B) drop out of school before graduation
C) be behind peers in academic achievement
D) be ahead of peers in academic achievement
A) resist attending college
B) drop out of school before graduation
C) be behind peers in academic achievement
D) be ahead of peers in academic achievement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
According to Vygotsky's sociocultural framework, every experience after _____ teaches individuals something.
A) birth
B) childhood
C) adolescence
D) adulthood
A) birth
B) childhood
C) adolescence
D) adulthood

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A child is shown a large box and a small box. The large box contains a 5-pound weight, and the small box contains a 10-pound weight. The child picks up the boxes and looks at them closely and then is asked which one weighs more. The child is no longer focused only on appearances, so he answers that the small box weighs more. Piaget would say that this child is in the _____ stage of cognitive development.
A) sensorimotor
B) preoperational
C) metacognitive
D) concrete operational
A) sensorimotor
B) preoperational
C) metacognitive
D) concrete operational

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Dr. Smith is conducting a study to determine what 9-year-olds know. Based on theory, he believes that 9-year-olds will advance in knowledge as a result of direct instruction. Dr. Smith's belief is based on _____.
A) the information-processing perspective
B) Piaget's theory of cognitive development
C) Vygotsky's theory of cognitive development
D) Erikson's theory of psychosocial development
A) the information-processing perspective
B) Piaget's theory of cognitive development
C) Vygotsky's theory of cognitive development
D) Erikson's theory of psychosocial development

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
With respect to sociocultural context, children from the Varanasi region in India learn what specific ability from their culture?
A) observational learning
B) fractions
C) spatial orientation
D) individual discovery
A) observational learning
B) fractions
C) spatial orientation
D) individual discovery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
With concrete operational thought, children can _____.
A) think logically about visible, tangible things
B) think logically about abstract ideas
C) consistently make good decisions
D) solve most problems on their own
A) think logically about visible, tangible things
B) think logically about abstract ideas
C) consistently make good decisions
D) solve most problems on their own

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Nine-year-old Pete sorted screws, bolts, and nails into three piles by type. He is able to correctly sort the objects into separate piles because of the logical principle of _____.
A) conservation
B) seriation
C) classification
D) reversibility
A) conservation
B) seriation
C) classification
D) reversibility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The logical principle that allows objects to be grouped according to some characteristic that they share is called _____.
A) concrete thought
B) transitive inference
C) classification
D) reversibility
A) concrete thought
B) transitive inference
C) classification
D) reversibility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
According to Piaget, a child between the ages of 6 and 11 can apply logical principles to _____.
A) abstractions, such as truth and liberty
B) chemistry and physics
C) concrete situations (real, tangible, visible)
D) questions of social justice and equality
A) abstractions, such as truth and liberty
B) chemistry and physics
C) concrete situations (real, tangible, visible)
D) questions of social justice and equality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following statements is true?
A) School-age children are able to understand complex, abstract concepts.
B) School-age children are as rigid in their thinking as preschoolers.
C) School-age children are slightly less advanced thinkers than preschoolers.
D) There is no sudden shift between preoperational and concrete operational thought.
A) School-age children are able to understand complex, abstract concepts.
B) School-age children are as rigid in their thinking as preschoolers.
C) School-age children are slightly less advanced thinkers than preschoolers.
D) There is no sudden shift between preoperational and concrete operational thought.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Vygotsky viewed _____ as being crucial to children's development of skills and knowledge.
A) instruction
B) independence
C) exploration
D) passive learning
A) instruction
B) independence
C) exploration
D) passive learning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Piaget believed that in middle childhood, children are in the cognitive period of _____ thought.
A) formal operational
B) preoperational
C) metacognitive
D) concrete operational
A) formal operational
B) preoperational
C) metacognitive
D) concrete operational

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The information-processing theory was inspired by the knowledge of how _____ function.
A) animals' brains
B) high-level businesses
C) computers
D) athletic teams
A) animals' brains
B) high-level businesses
C) computers
D) athletic teams

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
_____ is one of the leading theorists of the information-processing perspective.
A) Vygotsky
B) Piaget
C) Siegler
D) Silva
A) Vygotsky
B) Piaget
C) Siegler
D) Silva

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
From an information-processing approach, the memory process has three major steps. What is the correct order of this process, beginning with the first component?
A) sensory memory, working memory, long-term memory
B) long-term memory, working memory, sensory memory
C) sensory memory, long-term memory, working memory
D) working memory, sensory memory, long-term memory
A) sensory memory, working memory, long-term memory
B) long-term memory, working memory, sensory memory
C) sensory memory, long-term memory, working memory
D) working memory, sensory memory, long-term memory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which information is most likely to be in your current working memory?
A) everything that is on this page
B) your understanding of this question
C) the location of the term working memory in the text
D) the definitions of the words working and memory
A) everything that is on this page
B) your understanding of this question
C) the location of the term working memory in the text
D) the definitions of the words working and memory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Siegler has studied the day-by-day details of children's cognition in math. He has found that children _____.
A) suddenly grasp the logic of the number system
B) gradually acquire math knowledge and strategies
C) already understand all they need to know about math by 3 years of age
D) do not understand math knowledge and strategies until they are in adolescence
A) suddenly grasp the logic of the number system
B) gradually acquire math knowledge and strategies
C) already understand all they need to know about math by 3 years of age
D) do not understand math knowledge and strategies until they are in adolescence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Strategies for processing information within working memory _____.
A) are universal across cultures
B) can be culturally specific
C) are not impacted by culture
D) are culture-free
A) are universal across cultures
B) can be culturally specific
C) are not impacted by culture
D) are culture-free

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Important to long-term memory is _____.
A) storage only
B) retrieval only
C) storage and retrieval
D) neither storage nor retrieval
A) storage only
B) retrieval only
C) storage and retrieval
D) neither storage nor retrieval

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The component of the information-processing system in which current conscious mental activity occurs is the _____.
A) working memory
B) long-term memory
C) sensory memory
D) icon memory
A) working memory
B) long-term memory
C) sensory memory
D) icon memory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
By the end of middle childhood, the capacity of long-term memory is _____.
A) limited to facts and knowledge gained through repetition
B) limited to highly emotional experiences and objective information
C) unlimited regarding information but limited about emotional experiences
D) huge
A) limited to facts and knowledge gained through repetition
B) limited to highly emotional experiences and objective information
C) unlimited regarding information but limited about emotional experiences
D) huge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Within an information-processing perspective, the three major steps of the memory process are affected by _____.
A) maturation only
B) experience only
C) maturation and experience
D) maturation for girls and experience for boys
A) maturation only
B) experience only
C) maturation and experience
D) maturation for girls and experience for boys

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Tony came to walk to school with José. When José saw Tony's notebook in his backpack, José rushed back into his house to retrieve his own notebook, which contained his homework. Seeing Tony's notebook triggered José to retrieve from his _____ the fact that he needed his notebook.
A) sensory memory
B) working memory
C) long-term memory
D) knowledge base
A) sensory memory
B) working memory
C) long-term memory
D) knowledge base

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
How readily past learning can be brought into working memory from long-term memory is referred to as _____.
A) storage
B) retrieval
C) input
D) short-term memory
A) storage
B) retrieval
C) input
D) short-term memory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
To retain information in working memory, individuals must _____.
A) merely be exposed to the information
B) process the information
C) unconsciously be aware of the information
D) do nothing, as the information will be passively absorbed into working memory
A) merely be exposed to the information
B) process the information
C) unconsciously be aware of the information
D) do nothing, as the information will be passively absorbed into working memory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The memory system in which incoming stimuli are held for a split second is called _____ memory.
A) short-term
B) working
C) sensory
D) holding
A) short-term
B) working
C) sensory
D) holding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Emma studied for the spelling test all week and spelled each of the tested words correctly. Emma's ability to do well on her spelling test was based on her ability to _____.
A) store the spelling words in long-term memory
B) retrieve the correct spelling of words from long-term memory
C) classify each word in long-term memory
D) conserve the list of words in long-term memory
A) store the spelling words in long-term memory
B) retrieve the correct spelling of words from long-term memory
C) classify each word in long-term memory
D) conserve the list of words in long-term memory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Professor Schuyler believes that people's brains work very much like a computer in terms of input, processing, and output. The professor believes in _____.
A) the information-processing perspective
B) Piaget's theory of cognitive development
C) Vygotsky's theory of cognitive development
D) Erikson's theory of psychosocial development
A) the information-processing perspective
B) Piaget's theory of cognitive development
C) Vygotsky's theory of cognitive development
D) Erikson's theory of psychosocial development

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following is the best predictor of later science understanding?
A) placing the number 53 on a number line from 0 to 100
B) score on a math achievement test
C) memorization of multiplication tables
D) an advanced theory of mind
A) placing the number 53 on a number line from 0 to 100
B) score on a math achievement test
C) memorization of multiplication tables
D) an advanced theory of mind

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following is the best predictor of later math achievement?
A) placing the number 53 on a number line from 0 to 100
B) score on a math achievement test
C) memorization of multiplication tables
D) an advanced theory of mind
A) placing the number 53 on a number line from 0 to 100
B) score on a math achievement test
C) memorization of multiplication tables
D) an advanced theory of mind

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The component of the information-processing system in which huge amounts of information can be stored indefinitely is _____.
A) working memory
B) long-term memory
C) sensory memory
D) iconic memory
A) working memory
B) long-term memory
C) sensory memory
D) iconic memory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Sensory memory improves until about age _____ and then remains adequate until late adulthood.
A) 4
B) 7
C) 10
D) 13
A) 4
B) 7
C) 10
D) 13

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Jill has just heard her teacher say something. The sounds produced by the teacher are first stored briefly in Jill's _____.
A) working memory
B) long-term memory
C) sensory memory
D) short-term memory
A) working memory
B) long-term memory
C) sensory memory
D) short-term memory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



