Deck 7: Continuous Random Variables
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/150
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Continuous Random Variables
1
The normal probability distribution is a discrete probability distribution.
False
2
If the random variable, x, is normally distributed, 68.26 percent of all possible observed values of x will be within two standard deviations of the mean.
False
3
A continuous random variable may assume only integer values in a given interval.
False
4
The mean and median are the same for a normal distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The z value tells us the number of standard deviations that a value, x, is from the mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The mean of a standard normal distribution is always equal to 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A uniform distribution f(x) is a continuous probability distribution, which says the probability that x is in any two intervals of equal length is the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The number of defective pencils in a total lot of 1000 is an example of a continuous random variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The exponential probability distribution is based on a continuous random variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The standard deviation of a standard normal distribution is always equal to 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If the distances between the ordered data values are proportional to the distances between the actual values, then the normal probability plot will be a straight line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A continuous probability distribution that has a rectangular shape, where the probability is evenly distributed over an interval of numbers, is called a uniform probability distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The actual weight of hamburger patties is an example of a continuous random variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
For a binomial probability experiment, with n = 150 and p = .2, it is appropriate to use the normal approximation to the binomial distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The mean and the median are the same for an exponential distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In a statistical study, the random variable X = 1 if the house is colonial, and X = 0 if the house is not colonial. The random variable X is continuous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
For a continuous distribution, the exact probability of a particular value is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
All continuous random variables are normally distributed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
For a continuous random variable x, the height of the probability curve f(x) at a particular point indicates the value of the probability for that value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
For a continuous distribution, P(X ≤ 100) = P(X < 100).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The standardized normal quantile value Oi is the z value that gives an area of i/(n − 1) to its right under the normal curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If the random variable, X, is normally distributed and has a mean of µ and a standard deviation σ, then the mean and standard deviation, respectively, of (X − µ)/σ are
A) μ and σ.
B)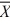 and s.
and s.
C) 1 and 0.
D) 0 and 1.
A) μ and σ.
B)
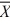 and s.
and s.C) 1 and 0.
D) 0 and 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The first step to constructing a normal probability plot is to
A) calculate Oi.
B) compute area i/(n + 1).
C) construct a box-and-whiskers plot.
D) order the values in the data.
A) calculate Oi.
B) compute area i/(n + 1).
C) construct a box-and-whiskers plot.
D) order the values in the data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The random variable x has a uniform distribution when x lies between the values of 4 and 10. When x = 10, what is the value of f(x)?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 1/6
D) 1/14
A) 0
B) 1
C) 1/6
D) 1/14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The grade a student received on an examination was transformed to a z value, which was negative. Therefore, we know that the student scored
A) higher than 16 percent of the class.
B) higher than 45 percent of the class.
C) above the first quartile.
D) below the mean.
E) lower than 16 percent of the class.
A) higher than 16 percent of the class.
B) higher than 45 percent of the class.
C) above the first quartile.
D) below the mean.
E) lower than 16 percent of the class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The price-to-earnings ratio for firms in a given industry is distributed according to the normal distribution. In this industry, a firm with a standard normal variable value of z = 1
A) has an above average price-to-earnings ratio.
B) has a below average price-to-earnings ratio.
C) has an average price-to-earnings ratio.
D) may have an above average or below average price-to-earnings ratio depending on the value of the mean.
A) has an above average price-to-earnings ratio.
B) has a below average price-to-earnings ratio.
C) has an average price-to-earnings ratio.
D) may have an above average or below average price-to-earnings ratio depending on the value of the mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If the wages of workers for a given company are normally distributed with a mean of $15 per hour, then the proportion of the workers earning more than $13 per hour
A) is greater than the proportion earning less than $13 per hour.
B) is greater than the proportion earning less than $18 per hour.
C) is less than 50 percent.
D) is less than the proportion earning more than the mean wage.
A) is greater than the proportion earning less than $13 per hour.
B) is greater than the proportion earning less than $18 per hour.
C) is less than 50 percent.
D) is less than the proportion earning more than the mean wage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The normal approximation of the binomial distribution is appropriate when
A) np ≥ 5.
B) n(1 − p) ≥ 5.
C) np ≤ 5.
D) n(1 − p) ≤ 5 and np ≤ 5.
E) np ≥ 5 and n(1 − p) ≥ 5.
A) np ≥ 5.
B) n(1 − p) ≥ 5.
C) np ≤ 5.
D) n(1 − p) ≤ 5 and np ≤ 5.
E) np ≥ 5 and n(1 − p) ≥ 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is a continuous distribution?
A) Poisson
B) hypergeometric
C) exponential
D) binomial
A) Poisson
B) hypergeometric
C) exponential
D) binomial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Values of the standard normal random variable are measured
A) with reference to specific units.
B) in the units in which the mean is measured.
C) in the number of standard deviations from the mean.
D) in squared units in which the mean is measured.
E) None of these answers are correct.
A) with reference to specific units.
B) in the units in which the mean is measured.
C) in the number of standard deviations from the mean.
D) in squared units in which the mean is measured.
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The area under the normal curve between z = 0 and z = 1 is ________ the area under the normal curve between z = 1 and z = 2.
A) less than
B) greater than
C) equal to
D) less than, greater than, or equal to, depending on the value of the mean,
E) less than, greater than, or equal to, depending on the value of the standard deviation,
A) less than
B) greater than
C) equal to
D) less than, greater than, or equal to, depending on the value of the mean,
E) less than, greater than, or equal to, depending on the value of the standard deviation,

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A study shows that employees who begin their workday at 9:00 a.m. vary their times of arrival uniformly from 8:40 a.m. to 9:30 a.m. The probability that a randomly chosen employee reports to work between 9:00 and 9:10 is
A) 40 percent.
B) 20 percent.
C) 10 percent.
D) 30 percent.
E) 16.7 percent.
A) 40 percent.
B) 20 percent.
C) 10 percent.
D) 30 percent.
E) 16.7 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A property of continuous distributions is that
A) as with discrete random variables, the probability distribution can be approximated by a smooth curve.
B) probabilities for continuous variables can be approximated using discrete random variables.
C) unlike discrete random variables, probabilities can be found using tables.
D) unlike discrete random variables, the probability that a continuous random variable equals a specific value is zero [P(X = x) = 0].
A) as with discrete random variables, the probability distribution can be approximated by a smooth curve.
B) probabilities for continuous variables can be approximated using discrete random variables.
C) unlike discrete random variables, probabilities can be found using tables.
D) unlike discrete random variables, the probability that a continuous random variable equals a specific value is zero [P(X = x) = 0].

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
It is appropriate to use the uniform distribution to describe a continuous random variable x when
A) the area under the probability curve = 1.
B) the probability curve f(x) > 0.
C) the shape of the histogram of all possible values of x is nonsymmetrical.
D) relative frequencies of all possible values of x are about the same.
A) the area under the probability curve = 1.
B) the probability curve f(x) > 0.
C) the shape of the histogram of all possible values of x is nonsymmetrical.
D) relative frequencies of all possible values of x are about the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In order to approximate the binomial distribution using the normal distribution, the following condition(s) must be met if p is near 1.
A) np > 5 only
B) n must be larger than just meeting the condition of np > 5.
C) n can be as small as np > 5.
D) n > 5
A) np > 5 only
B) n must be larger than just meeting the condition of np > 5.
C) n can be as small as np > 5.
D) n > 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The relationship between the standard normal random variable, z, and normal random variable, X, is that
A) only the normal random variable X is continuous.
B) only the standard normal variable z is continuous.
C) the standard normal variable z counts the number of standard deviations that the value of the normal random variable X is away from its mean.
D) the values of the standard normal random variable z cannot be negative.
E) the values of the normal random variable X cannot be negative.
A) only the normal random variable X is continuous.
B) only the standard normal variable z is continuous.
C) the standard normal variable z counts the number of standard deviations that the value of the normal random variable X is away from its mean.
D) the values of the standard normal random variable z cannot be negative.
E) the values of the normal random variable X cannot be negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The ________ is a graphic that is used to visually check whether data come from a normal population.
A) exponential plot
B) normal probability plot
C) box-and-whiskers plot
D) normal distribution graph
A) exponential plot
B) normal probability plot
C) box-and-whiskers plot
D) normal distribution graph

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The mean life of a pair of shoes is 40 months with a standard deviation of 8 months. If the life of the shoes is normally distributed, how many pairs of shoes out of one million will need replacement before 36 months?
A) 500,073
B) 808,573
C) 191,537
D) 308,537
A) 500,073
B) 808,573
C) 191,537
D) 308,537

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A standard normal distribution has a mean of ________ and standard deviation of ________.
A) zero, zero
B) zero, one
C) one, one
D) one, zero
A) zero, zero
B) zero, one
C) one, one
D) one, zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The ________ distribution would most likely be used to describe the distribution of time between arrivals of customers at the grocery store.
A) normal
B) exponential
C) Poisson
D) binomial
E) uniform
A) normal
B) exponential
C) Poisson
D) binomial
E) uniform

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If the random variable x is normally distributed, ________ percent of all possible observed values of x will be within three standard deviations of the mean.
A) 68.26
B) 95.44
C) 99.73
D) 100
E) None of these answers are correct.
A) 68.26
B) 95.44
C) 99.73
D) 100
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The number of standard deviations that a value, x, is from the mean is a(n) ________.
A) variance
B) exponential value
C) z score
D) area
A) variance
B) exponential value
C) z score
D) area

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The area under the curve of a valid continuous probability distribution must ________.
A) equal 1
B) be between 0 and 1
C) be infinite
D) be less than 1
A) equal 1
B) be between 0 and 1
C) be infinite
D) be less than 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A probability distribution that describes the time or space between successive occurrences of an event is a(n) ________ probability distribution.
A) binomial
B) uniform
C) exponential
D) normal
A) binomial
B) uniform
C) exponential
D) normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A normal distribution with mean equal to zero and a standard deviation equal to one is called the ________ normal distribution.
A) continuous
B) uniform
C) exponential
D) standard
A) continuous
B) uniform
C) exponential
D) standard

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The specific shape of each normal distribution is determined by its ________ and ________.
A) mean, standard deviation
B) median, standard deviation
C) mean, variance
D) median, variance
A) mean, standard deviation
B) median, standard deviation
C) mean, variance
D) median, variance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The standard deviation of a standard normal distribution is always equal to ________.
A) 1
B) .5
C) 0
D) −1
A) 1
B) .5
C) 0
D) −1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Given that X is a normal random variable, the probability that a given value of X is below its mean is ________.
A) 1
B) equal to .5
C) less than .5
D) greater than .5
A) 1
B) equal to .5
C) less than .5
D) greater than .5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A continuous probability distribution that is useful in describing the time or space between successive occurrences of an event is a(n)
A) uniform probability distribution.
B) normal probability distribution.
C) Poisson probability distribution.
D) exponential probability distribution.
A) uniform probability distribution.
B) normal probability distribution.
C) Poisson probability distribution.
D) exponential probability distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When a ________ probability distribution is used to approximate a ________ probability distribution, we must make a ________ correction.
A) continuous, discrete, continuity
B) discrete, continuous, continuity
C) continuous, discrete, finite population
D) None of these answers are correct.
A) continuous, discrete, continuity
B) discrete, continuous, continuity
C) continuous, discrete, finite population
D) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The thickness of a randomly selected metal piece is a ________ random variable.
A) Poisson
B) continuous
C) discrete
D) binomial
A) Poisson
B) continuous
C) discrete
D) binomial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
________ values of the standard deviation result in a normal curve that is wider and flatter.
A) Smaller
B) Equal
C) Larger
D) Uniform
A) Smaller
B) Equal
C) Larger
D) Uniform

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The z value tells us the number of ________ that a value of x is from the mean.
A) variances
B) standard deviations
C) medians
D) standard means
A) variances
B) standard deviations
C) medians
D) standard means

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
________ values of the standard deviation result in a normal curve that is narrower and more peaked.
A) Smaller
B) Equal
C) Larger
D) Uniform
A) Smaller
B) Equal
C) Larger
D) Uniform

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A continuous probability distribution having a rectangular shape, where the probability is evenly distributed over an interval of numbers is a(n) ________ distribution.
A) exponential
B) binomial
C) normal
D) uniform
A) exponential
B) binomial
C) normal
D) uniform

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If the random variable of x is normally distributed, ________ percent of all possible observed values of x will be within two standard deviations of the mean.
A) 99.73
B) 68.26
C) 95.00
D) 95.44
A) 99.73
B) 68.26
C) 95.00
D) 95.44

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The fill weight of a certain brand of adult cereal is normally distributed with a mean of 910 grams and a standard deviation of 5 grams. We calculated the value of z for a specific box of this brand of cereal, and the z value was negative. This negative z value indicates that
A) we made a mistake in our calculations, as z must always be a nonnegative number.
B) the fill weight is more than 910 grams.
C) the fill weight is less than 910 grams.
D) the fill weight is equal to 910 grams.
E) the fill weight may be more or less than 910 grams depending on the value of the standard deviation.
A) we made a mistake in our calculations, as z must always be a nonnegative number.
B) the fill weight is more than 910 grams.
C) the fill weight is less than 910 grams.
D) the fill weight is equal to 910 grams.
E) the fill weight may be more or less than 910 grams depending on the value of the standard deviation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
________ theory is a methodology that attempts to determine the number of servers that strikes an optimum balance between the time customers wait for service and the cost of providing service.
A) Exponential
B) Binomial
C) Uniform distribution
D) Queuing
A) Exponential
B) Binomial
C) Uniform distribution
D) Queuing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following statements is not a property of the normal probability distribution?
A) The normal distribution is symmetric.
B) 95.44 percent of all possible observed values of the random variable x are within plus or minus three standard deviations of the population mean.
C) The mean, median, and mode are equal.
D) The area under the normal curve to the right of the mean is equal to the area under the normal curve to the left of the mean.
E) All of these answers are properties of the normal distribution.
A) The normal distribution is symmetric.
B) 95.44 percent of all possible observed values of the random variable x are within plus or minus three standard deviations of the population mean.
C) The mean, median, and mode are equal.
D) The area under the normal curve to the right of the mean is equal to the area under the normal curve to the left of the mean.
E) All of these answers are properties of the normal distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The mean of a standard normal distribution is always equal to ________.
A) 1
B) .5
C) 0
D) −1
A) 1
B) .5
C) 0
D) −1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The time it takes a woman to travel from her apartment to the bus station follows a uniform distribution over the interval from 20 to 30 minutes. If she leaves home at 9:05 a.m., what is the probability that she will get to the station between 9:25 and 9:30 a.m.?
A) 1.0
B) 0
C) .5
D) .25
A) 1.0
B) 0
C) .5
D) .25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Consider a normal population with a mean of 10 and a variance of 4. Find P(X < 6).
A) .0228
B) .1587
C) .8413
D) .9772
A) .0228
B) .1587
C) .8413
D) .9772

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The lifetime of a stereo component is exponentially distributed with mean 1,000 days. What is the probability that the lifetime of the stereo component exceeds 1,000 days?
A) .6321
B) .5000
C) .3679
D) 1.000
A) .6321
B) .5000
C) .3679
D) 1.000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The flying time of a drone airplane has a normal distribution with mean 4.76 hours and standard deviation of .04 hours. What is the probability that the drone will fly between 4.70 and 4.82 hours?
A) .1336
B) .8664
C) .9332
D) .4332
A) .1336
B) .8664
C) .9332
D) .4332

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Suppose the daily change in price of a stock is normally distributed with mean = .20 and standard deviation = .30. What price change is associated with the 25th percentile?
A) .1925
B) .2075
C) .401
D) −.002
A) .1925
B) .2075
C) .401
D) −.002

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
An aptitude test has a mean score of 80 and a standard deviation of 5. The population of scores is normally distributed. What proportion of tests has scores over 90?
A) .9772
B) .0228
C) .9544
D) .0456
A) .9772
B) .0228
C) .9544
D) .0456

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The flying time of a drone airplane has a normal distribution with mean 4.76 hours and standard deviation of .04 hours. What is the probability that the drone will fly more than 4.80 hours?
A) .1587
B) .8413
C) .6587
D) .3413
A) .1587
B) .8413
C) .6587
D) .3413

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The probability that an appliance is currently being repaired is .5. If an apartment complex has 100 such appliances, what is the probability that at least 60 are currently being repaired? Use the normal approximation to the binomial.
A) .5000
B) .0287
C) .6000
D) .9713
A) .5000
B) .0287
C) .6000
D) .9713

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If the mileage per gallon for a car is normally distributed, 32 mpg has a z score of 1.2, and 24 mpg has a z score of −.4, what is the mean mpg of the distribution?
A) 28
B) 26
C) 30
D) 38
A) 28
B) 26
C) 30
D) 38

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If x is a binomial random variable where n = 100 and p = .1, find the probability that x is less than or equal to 10, using the normal approximation to the binomial.
A) .9544
B) .0446
C) .5662
D) .4325
A) .9544
B) .0446
C) .5662
D) .4325

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The life of a light bulb is exponentially distributed with a mean of 1,000 hours. What is the probability that the bulb will last more than 1,200 hours?
A) .3012
B) .3679
C) .4345
D) .6988
A) .3012
B) .3679
C) .4345
D) .6988

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The flying time of a drone airplane has a normal distribution with mean 4.76 hours and standard deviation of .04 hours. What is the probability that the drone will fly less than 4.66 hours?
A) −.0062
B) .5062
C) .0062
D) .9938
A) −.0062
B) .5062
C) .0062
D) .9938

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The time between breakdowns of an alarm system is exponentially distributed with mean 10 days. What is the probability that there is less than 1 breakdown on a given day?
A) .9048
B) .3679
C) .0952
D) .000
A) .9048
B) .3679
C) .0952
D) .000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Given that the length an athlete throws a hammer is a normal random variable with mean 50 feet and standard deviation 5 feet, what is the probability he throws it no less than 55 feet?
A) .8413
B) .1587
C) .6826
D) .3174
A) .8413
B) .1587
C) .6826
D) .3174

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The lifetime of a stereo component is exponentially distributed with mean 1,000 days. What is the probability that the lifetime of the stereo component is greater than or equal to 700 days?
A) .7603
B) .5034
C) .2397
D) .4966
A) .7603
B) .5034
C) .2397
D) .4966

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
An aptitude test has a mean score of 80 and a standard deviation of 5. The population of scores is normally distributed. What raw score corresponds to the 70th percentile?
A) 77.4
B) 83.5
C) 82.6
D) 76.5
A) 77.4
B) 83.5
C) 82.6
D) 76.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The life of a light bulb is exponentially distributed with a mean of 1,000 hours. What is the probability that the bulb will last less than 800 hours?
A) .6321
B) .5507
C) .7135
D) .4493
A) .6321
B) .5507
C) .7135
D) .4493

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What is the probability that a standard normal random variable will be between −2 and 2?
A) .4772
B) .0228
C) .9772
D) .9544
A) .4772
B) .0228
C) .9772
D) .9544

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Given that the length an athlete throws a hammer is a normal random variable with mean 50 feet and standard deviation 5 feet, what is the probability he throws it between 50 feet and 60 feet?
A) .9972
B) .5000
C) .9544
D) .4772
A) .9972
B) .5000
C) .9544
D) .4772

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
What is the probability that a standard normal random variable will be between .3 and 3.2?
A) .6179
B) .3814
C) .3808
D) .9993
A) .6179
B) .3814
C) .3808
D) .9993

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



