Deck 2: The Cardiovascular System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/80
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: The Cardiovascular System
1
The innermost layer of the heart is the:
A)endocardium.
B)myocardium.
C)epicardium.
D)pericardium.
A)endocardium.
B)myocardium.
C)epicardium.
D)pericardium.
endocardium.
2
The valve located between the right atrium and right ventricle is the:
A)mitral (bicuspid)valve.
B)tricuspid valve.
C)aortic valve.
D)pulmonary valve.
A)mitral (bicuspid)valve.
B)tricuspid valve.
C)aortic valve.
D)pulmonary valve.
tricuspid valve.
3
The valves located in the heart are important because they:
A)regulate the speed of blood flow.
B)prevent blood from flowing backwards.
C)form electrical conduction through the heart.
D)allow for good blood flow to the body.
A)regulate the speed of blood flow.
B)prevent blood from flowing backwards.
C)form electrical conduction through the heart.
D)allow for good blood flow to the body.
prevent blood from flowing backwards.
4
The purpose of the pericardium is to:
A)protect the heart from infection and trauma.
B)contract the heart.
C)circulate blood through the coronary arteries.
D)keep blood flow headed in the right direction.
A)protect the heart from infection and trauma.
B)contract the heart.
C)circulate blood through the coronary arteries.
D)keep blood flow headed in the right direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The two semilunar valves are the:
A)pulmonary and mitral valves.
B)aortic and tricuspid valves.
C)tricuspid and mitral valves.
D)aortic and pulmonary valves.
A)pulmonary and mitral valves.
B)aortic and tricuspid valves.
C)tricuspid and mitral valves.
D)aortic and pulmonary valves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The heart is divided into four chambers. The top chambers are the:
A)right atrium and right ventricle.
B)left atrium and left ventricle.
C)right atrium and left atrium.
D)right ventricle and left ventricle.
A)right atrium and right ventricle.
B)left atrium and left ventricle.
C)right atrium and left atrium.
D)right ventricle and left ventricle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Blood returns to the heart via the veins. The largest vein is the:
A)vena cava.
B)cava vena.
C)jugular vein.
D)subclavian vein.
A)vena cava.
B)cava vena.
C)jugular vein.
D)subclavian vein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What are the first vessels to branch off the aorta?
A)Coronary arteries
B)Capillaries
C)Venae cavae
D)Pulmonary arteries
A)Coronary arteries
B)Capillaries
C)Venae cavae
D)Pulmonary arteries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Blood that leaves the right ventricle is considered:
A)deoxygenated.
B)systemic.
C)peripheral venous return.
D)visceral.
A)deoxygenated.
B)systemic.
C)peripheral venous return.
D)visceral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The sac of tissue that encloses the entire heart is the:
A)atrium.
B)ventricle.
C)myocardium.
D)pericardium.
A)atrium.
B)ventricle.
C)myocardium.
D)pericardium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The middle layer of the heart is the:
A)endocardium.
B)myocardium.
C)epicardium.
D)pericardium.
A)endocardium.
B)myocardium.
C)epicardium.
D)pericardium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is recorded on the ECG strip?
A)The electrical activity of the heart
B)The muscle contractions of the heart
C)The circulation of blood in the heart
D)The size of the heart
A)The electrical activity of the heart
B)The muscle contractions of the heart
C)The circulation of blood in the heart
D)The size of the heart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The tricuspid and mitral (bicuspid)valves are known as ________ because they separate the atria from the ventricles.
A)semilunar valves
B)pulmonary valves
C)atrioventricular (AV)valves
D)aortic valves
A)semilunar valves
B)pulmonary valves
C)atrioventricular (AV)valves
D)aortic valves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The average heart is approximately what size?
A)The size of a baseball
B)The size of your fist
C)The size of a cantaloupe
D)The size of your foot
A)The size of a baseball
B)The size of your fist
C)The size of a cantaloupe
D)The size of your foot

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The time from the beginning of atrial depolarization to the beginning of ventricular depolarization is shown on the ECG waveform as the:
A)QRS complex.
B)PR interval.
C)QT interval.
D)ST segment.
A)QRS complex.
B)PR interval.
C)QT interval.
D)ST segment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The heart is divided into four chambers. The bottom chambers are the:
A)right atrium and right ventricle.
B)left atrium and left ventricle.
C)right atrium and left atrium.
D)right ventricle and left ventricle.
A)right atrium and right ventricle.
B)left atrium and left ventricle.
C)right atrium and left atrium.
D)right ventricle and left ventricle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The valve located between the left atrium and left ventricle is the:
A)mitral (bicuspid)valve.
B)tricuspid valve.
C)aortic valve.
D)pulmonary valve.
A)mitral (bicuspid)valve.
B)tricuspid valve.
C)aortic valve.
D)pulmonary valve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The outermost layer of the heart is the:
A)endocardium.
B)myocardium.
C)epicardium.
D)pericardium.
A)endocardium.
B)myocardium.
C)epicardium.
D)pericardium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Oxygenated blood travels through the heart via the
A)pulmonary arteries.
B)peripheral venous system.
C)coronary arteries.
D)pulmonary veins.
A)pulmonary arteries.
B)peripheral venous system.
C)coronary arteries.
D)pulmonary veins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The ________ valves separate the ventricles from the arteries leading to the lungs and body.
A)tricuspid
B)semilunar
C)mitral (bicuspid)
D)atrioventricular (AV)
A)tricuspid
B)semilunar
C)mitral (bicuspid)
D)atrioventricular (AV)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Depolarization of the cells causes the heart muscle to:
A)relax.
B)refill the chambers of the heart.
C)conduct electrical impulses.
D)contract.
A)relax.
B)refill the chambers of the heart.
C)conduct electrical impulses.
D)contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The AV node has several important functions that help the heart work effectively. Which of the following is not a function of the AV node?
A)It causes the delay of electrical impulses, which limits the number of impulses traveling to the ventricles.
B)It allows for a delay to provide time for the blood to travel from the atria to the ventricles before they contract.
C)It causes a loss of atrial kick.
D)It serves as a backup pacemaker if the SA node fails.
A)It causes the delay of electrical impulses, which limits the number of impulses traveling to the ventricles.
B)It allows for a delay to provide time for the blood to travel from the atria to the ventricles before they contract.
C)It causes a loss of atrial kick.
D)It serves as a backup pacemaker if the SA node fails.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The volume of blood ejected with each contraction is referred to as the:
A)cardiac cycle.
B)cardiac output.
C)stroke volume.
D)systole.
A)cardiac cycle.
B)cardiac output.
C)stroke volume.
D)systole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The T wave represents:
A)atrial contraction.
B)atrial relaxation.
C)ventricular contraction.
D)ventricular relaxation.
A)atrial contraction.
B)atrial relaxation.
C)ventricular contraction.
D)ventricular relaxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The P wave represents:
A)atrial contraction.
B)atrial relaxation.
C)ventricular contraction.
D)ventricular relaxation.
A)atrial contraction.
B)atrial relaxation.
C)ventricular contraction.
D)ventricular relaxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the heart's response to stimulation of the vagus nerve?
A)It beats more regularly.
B)It contracts with greater force.
C)It speeds up.
D)It slows down.
A)It beats more regularly.
B)It contracts with greater force.
C)It speeds up.
D)It slows down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When the sympathetic branch of the ANS (automatic nervous system)is stimulated, the heart responds by:
A)speeding up.
B)slowing down.
C)beating more regularly.
D)contracting with greater force.
A)speeding up.
B)slowing down.
C)beating more regularly.
D)contracting with greater force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The primary pacemaker of a normal heart, where the electrical impulse for the heartbeat originates, is the:
A)SA node.
B)AV node.
C)bundle of His.
D)Purkinje network.
A)SA node.
B)AV node.
C)bundle of His.
D)Purkinje network.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The function of the bundle branches is to:
A)delay the electrical impulse to allow for the atrial kick to occur.
B)conduct electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles.
C)conduct electrical impulses from the AV node to the left and right ventricles.
D)distribute the electrical impulse through the myocardium.
A)delay the electrical impulse to allow for the atrial kick to occur.
B)conduct electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles.
C)conduct electrical impulses from the AV node to the left and right ventricles.
D)distribute the electrical impulse through the myocardium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The ability of the heart muscle cells to shorten in response to an electrical impulse is known as:
A)contractility.
B)excitability.
C)conductivity.
D)automaticity.
A)contractility.
B)excitability.
C)conductivity.
D)automaticity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The "lubb" and "dupp" sounds you hear are made by the:
A)opening and closing of the heart valves.
B)atria contracting.
C)ventricles contracting.
D)blood flow through the heart.
A)opening and closing of the heart valves.
B)atria contracting.
C)ventricles contracting.
D)blood flow through the heart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The volume of blood pumped each minute is referred to as the:
A)cardiac cycle.
B)cardiac output.
C)stroke volume.
D)systole.
A)cardiac cycle.
B)cardiac output.
C)stroke volume.
D)systole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The phase of the cardiac cycle when the heart is pumping blood out to the body, also known as the contraction phase, is:
A)systole.
B)diastole.
C)automaticity.
D)conductivity.
A)systole.
B)diastole.
C)automaticity.
D)conductivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The heart's own ability to initiate an electrical impulse without being stimulated by another source is known as:
A)contractility.
B)excitability.
C)conductivity.
D)automaticity.
A)contractility.
B)excitability.
C)conductivity.
D)automaticity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The ability of the heart cells to receive and transmit an electrical impulse is known as:
A)contractility.
B)excitability.
C)conductivity.
D)automaticity.
A)contractility.
B)excitability.
C)conductivity.
D)automaticity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The ability of the heart muscle cells to respond to an impulse or stimulus is known as:
A)contractility.
B)excitability.
C)conductivity.
D)automaticity.
A)contractility.
B)excitability.
C)conductivity.
D)automaticity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Together, the contraction and relaxation of the heart make up:
A)systole.
B)diastole.
C)the cardiac cycle.
D)coronary circulation.
A)systole.
B)diastole.
C)the cardiac cycle.
D)coronary circulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The phase of the cardiac cycle when the heart is expanding and refilling, also known as the relaxation phase, is:
A)systole.
B)diastole.
C)automaticity.
D)conductivity.
A)systole.
B)diastole.
C)automaticity.
D)conductivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Circulation is the process of;
A)electricity flowing through the heart.
B)blood flowing through the ventricles.
C)transporting blood to and from body tissues.
D)systole and diastole.
A)electricity flowing through the heart.
B)blood flowing through the ventricles.
C)transporting blood to and from body tissues.
D)systole and diastole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The SA node sends electrical impulses at a rate of:
A)72 to 100 bpm.
B)40 to 60 bpm.
C)20 to 40 bpm.
D)60 to 100 bpm.
A)72 to 100 bpm.
B)40 to 60 bpm.
C)20 to 40 bpm.
D)60 to 100 bpm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The structure that transfers an electrical impulse from the atria to the ventricles is the:
A)AV node.
B)bundle of His.
C)Purkinje network.
D)Bachmann's bundle.
A)AV node.
B)bundle of His.
C)Purkinje network.
D)Bachmann's bundle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Electrical impulses are spread throughout the ventricles by the:
A)AV node.
B)bundle of His.
C)Purkinje network.
D)Bachmann's bundle.
A)AV node.
B)bundle of His.
C)Purkinje network.
D)Bachmann's bundle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The rapid change in polarization that occurs when the electrical charge is reversed across the cell membrane so that the inside of each cell is positively charged is referred to as:
A)repolarization.
B)polarization.
C)action potential.
D)excitability.
A)repolarization.
B)polarization.
C)action potential.
D)excitability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The part of the autonomic nervous system that helps slow the heart rate is the:
A)sympathetic branch.
B)parasympathetic branch.
C)somatic nervous system.
D)peripheral nervous system.
A)sympathetic branch.
B)parasympathetic branch.
C)somatic nervous system.
D)peripheral nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Coronary circulation is the movement of blood:
A)between the heart and lungs.
B)between the heart and kidneys.
C)to and from the heart muscle.
D)throughout the body tissues.
A)between the heart and lungs.
B)between the heart and kidneys.
C)to and from the heart muscle.
D)throughout the body tissues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Your employer requires you to check patient vital signs before performing an ECG. Today, you find that a patient's blood pressure is 90/40. The patient looks pale and complains of dizziness. Based on these signs and symptoms, you might suspect that the patient:
A)has hypertension.
B)has a low cardiac output.
C)has cardiac ischemia.
D)is having a myocardial infarction.
A)has hypertension.
B)has a low cardiac output.
C)has cardiac ischemia.
D)is having a myocardial infarction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following actions occurs during diastole?
A)Blood from the vena cava fills the right atrium.
B)Blood from the left ventricle is pushed through the aorta.
C)Blood from the right ventricle is pushed to the lungs.
D)Blood from the right atrium moves to the left ventricle.
A)Blood from the vena cava fills the right atrium.
B)Blood from the left ventricle is pushed through the aorta.
C)Blood from the right ventricle is pushed to the lungs.
D)Blood from the right atrium moves to the left ventricle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In pulmonary circulation, blood is transported from the right ventricle to the:
A)body tissues.
B)lungs.
C)left atrium.
D)coronary arteries.
A)body tissues.
B)lungs.
C)left atrium.
D)coronary arteries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following electrolytes plays a large role in the control of the heart rate?
A)Iron
B)Copper
C)Potassium
D)Manganese
A)Iron
B)Copper
C)Potassium
D)Manganese

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following statements best describes the function of the heart?
A)It transports nutrients and oxygen to the body tissues.
B)It pumps blood to and from the body tissues.
C)It oxygenates blood to be sent to the body tissues.
D)It removes waste gases from the body tissues.
A)It transports nutrients and oxygen to the body tissues.
B)It pumps blood to and from the body tissues.
C)It oxygenates blood to be sent to the body tissues.
D)It removes waste gases from the body tissues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following statements is true about heart rates?
A)In adults, the average heart beats approximately 40 to 60 times per minute.
B)Children's heart rates are usually slower than an adult's heart rate.
C)Children's heart rates depend on the age and size of the child.
D)Women generally have a slower heart rate than men.
A)In adults, the average heart beats approximately 40 to 60 times per minute.
B)Children's heart rates are usually slower than an adult's heart rate.
C)Children's heart rates depend on the age and size of the child.
D)Women generally have a slower heart rate than men.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The state of cellular stimulation that precedes cardiac contraction is:
A)repolarization.
B)polarization.
C)action potential.
D)depolarization.
A)repolarization.
B)polarization.
C)action potential.
D)depolarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following statements best describes the right side of the heart?
A)It is a low-pressure pump that moves blood with a low oxygen concentration.
B)It is a low-pressure pump that moves blood with a high oxygen concentration.
C)It is a high-pressure pump that moves blood with a low oxygen concentration.
D)It is a high-pressure pump that moves blood with a high oxygen concentration.
A)It is a low-pressure pump that moves blood with a low oxygen concentration.
B)It is a low-pressure pump that moves blood with a high oxygen concentration.
C)It is a high-pressure pump that moves blood with a low oxygen concentration.
D)It is a high-pressure pump that moves blood with a high oxygen concentration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The state in which the inside of each heart cell is negatively charged and the outside is positively charged is:
A)polarization.
B)depolarization.
C)excitability.
D)action potential.
A)polarization.
B)depolarization.
C)excitability.
D)action potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The average volume of blood pumped each minute in a normal heart is:
A)1 liter per minute.
B)3 liters per minute.
C)5 liters per minute.
D)7 liters per minute.
A)1 liter per minute.
B)3 liters per minute.
C)5 liters per minute.
D)7 liters per minute.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Systemic circulation is the movement of blood:
A)between the heart and lungs.
B)between the heart and kidneys.
C)to and from the heart muscle.
D)throughout the body tissues.
A)between the heart and lungs.
B)between the heart and kidneys.
C)to and from the heart muscle.
D)throughout the body tissues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The structure that relays an electrical impulse from the SA node to the left atrium in a normal heart is the:
A)AV node.
B)bundle of His.
C)Purkinje network.
D)Bachmann's bundle.
A)AV node.
B)bundle of His.
C)Purkinje network.
D)Bachmann's bundle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
To estimate a person's cardiac output, you can:
A)count the patient's heart rate for 15 seconds and multiply by 4.
B)multiply the respiratory rate by the heart rate.
C)multiply the stroke volume by the respiratory rate.
D)multiply the heart rate by the stroke volume.
A)count the patient's heart rate for 15 seconds and multiply by 4.
B)multiply the respiratory rate by the heart rate.
C)multiply the stroke volume by the respiratory rate.
D)multiply the heart rate by the stroke volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The straight, horizontal line on an electrocardiogram that occurs when the tracing is at zero and no deflections are occurring is called the:
A)interval.
B)isoelectric line.
C)complex.
D)action potential.
A)interval.
B)isoelectric line.
C)complex.
D)action potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following actions occurs during systole?
A)Blood from the vena cava fills the right atrium.
B)The heart muscle relaxes.
C)The tricuspid and mitral valves open.
D)The pulmonary and aortic valves open.
A)Blood from the vena cava fills the right atrium.
B)The heart muscle relaxes.
C)The tricuspid and mitral valves open.
D)The pulmonary and aortic valves open.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following is a sign of ischemia?
A)absence of R waves.
B)ST segment located on the isoelectric line.
C)ST segment depression.
D)P wave inversion.
A)absence of R waves.
B)ST segment located on the isoelectric line.
C)ST segment depression.
D)P wave inversion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The rapid change in polarization is known as ________.
A)repolarization
B)cardiac cycle
C)action potential
D)contraction
A)repolarization
B)cardiac cycle
C)action potential
D)contraction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The U wave, which follows the T wave in an ECG tracing, represents:
A)repolarization of the ventricles.
B)the time required for ventricular depolarization and repolarization.
C)the end of ventricular depolarization and the beginning of ventricular repolarization.
D)repolarization of the Purkinje fibers and the bundle of His.
A)repolarization of the ventricles.
B)the time required for ventricular depolarization and repolarization.
C)the end of ventricular depolarization and the beginning of ventricular repolarization.
D)repolarization of the Purkinje fibers and the bundle of His.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
You are working in an outpatient facility that performs ECGs by appointment. You go to the lobby to call your next patient. The patient gets up and comes with you, but you notice that he is out of breath. When you ask, he tells you that he works only two blocks away, but he was held up at the office and had to run in order to make his appointment time. Which of the following is your best course of action?
A)Compliment the patient on making his appointment time and perform the ECG.
B)Ask the patient to make another appointment and come back when he is not out of breath.
C)Explain that you need to wait for his vital signs to return to normal before running the ECG.
D)Perform the ECG and place a note in the patient's file that his vital signs were abnormal.
A)Compliment the patient on making his appointment time and perform the ECG.
B)Ask the patient to make another appointment and come back when he is not out of breath.
C)Explain that you need to wait for his vital signs to return to normal before running the ECG.
D)Perform the ECG and place a note in the patient's file that his vital signs were abnormal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Where is the PR interval measured?
A)From the beginning of the P wave to the beginning of the QRS complex.
B)From the beginning of the Q wave to the end of the T waves.
C)From the end of the P wave to the beginning of the QRS complex.
D)From the end of the P wave to the end of the QRS complex.
A)From the beginning of the P wave to the beginning of the QRS complex.
B)From the beginning of the Q wave to the end of the T waves.
C)From the end of the P wave to the beginning of the QRS complex.
D)From the end of the P wave to the end of the QRS complex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The QRS complex represents:
A)atrial depolarization.
B)ventricular repolarization.
C)ventricular depolarization.
D)atrial repolarization.
A)atrial depolarization.
B)ventricular repolarization.
C)ventricular depolarization.
D)atrial repolarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The ST segment represents
A)the time between atrial depolarization and atrial repolarization.
B)the time it takes the Purkinje fibers to repolarize.
C)the time from the beginning of atrial depolarization to the beginning of ventricular depolarization.
D)the time between ventricular depolarization and the beginning of ventricular repolarization.
A)the time between atrial depolarization and atrial repolarization.
B)the time it takes the Purkinje fibers to repolarize.
C)the time from the beginning of atrial depolarization to the beginning of ventricular depolarization.
D)the time between ventricular depolarization and the beginning of ventricular repolarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The J point is the
A)junction of the QRS interval and the ST interval.
B)highest peak of the R wave.
C)point at which the bundle of His divides into branches.
D)attachment point for the papillary muscles.
A)junction of the QRS interval and the ST interval.
B)highest peak of the R wave.
C)point at which the bundle of His divides into branches.
D)attachment point for the papillary muscles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
On an ECG tracing, the period of time from the start of ventricular depolarization to the end of ventricular repolarization is the:
A)U wave.
B)QT interval.
C)ST segment.
D)PR interval.
A)U wave.
B)QT interval.
C)ST segment.
D)PR interval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A sudden loss of blood supply and oxygen to a region of heart tissue is known as:
A)ischemia.
B)pericarditis.
C)myocardial infarction.
D)atherosclerosis.
A)ischemia.
B)pericarditis.
C)myocardial infarction.
D)atherosclerosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The QRS complex on an ECG tracing represents:
A)atrial depolarization and contraction.
B)ventricular depolarization and contraction.
C)repolarization of the bundle of His.
D)ventricular repolarization.
A)atrial depolarization and contraction.
B)ventricular depolarization and contraction.
C)repolarization of the bundle of His.
D)ventricular repolarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The first positive wave in a normal QRS complex is the R wave, which represents conduction of the electrical impulse:
A)through the right ventricle.
B)through the left atrium.
C)to the left ventricle.
D)to the right atrium.
A)through the right ventricle.
B)through the left atrium.
C)to the left ventricle.
D)to the right atrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A complete ECG waveform is called a(n):
A)interval.
B)segment.
C)action potential.
D)complex.
A)interval.
B)segment.
C)action potential.
D)complex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Match the numbers from the figure to the correct structure located on the chest.
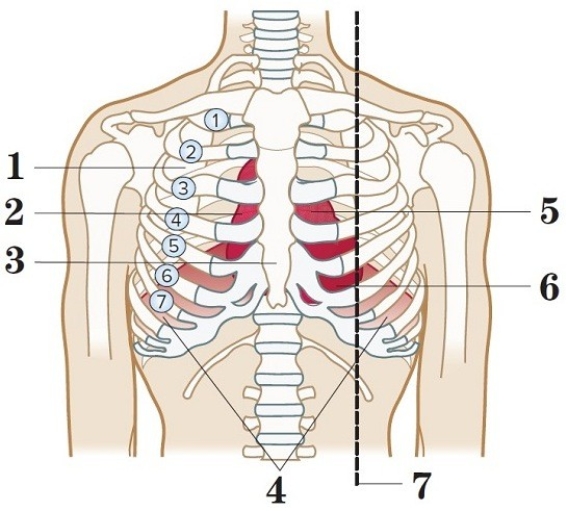
A. Diaphragm ________
B. Apex of heart ________
C. Intercostal space ________
D. Sternum ________
E. Base of heart ________
F. Midclavicular line ________
G. Heart ________

A. Diaphragm ________
B. Apex of heart ________
C. Intercostal space ________
D. Sternum ________
E. Base of heart ________
F. Midclavicular line ________
G. Heart ________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following is not included in the QT interval?
A)R wave
B)P wave
C)T wave
D)ST segment
A)R wave
B)P wave
C)T wave
D)ST segment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
You are preparing to perform an ECG on a young woman when she tells you that she just had her blood tested and her blood potassium level is very low. What might you expect to see on the ECG tracing as a result of this?
A)The heart rate will be slow.
B)The rhythm will be irregular.
C)The heart rate will be fast.
D)The heart contractions will be longer than normal.
A)The heart rate will be slow.
B)The rhythm will be irregular.
C)The heart rate will be fast.
D)The heart contractions will be longer than normal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
An interval on an ECG tracing is:
A)the period of time between two activities within the heart.
B)any portion of the electrical tracing that is produced by the heart.
C)a complete ECG waveform.
D)the result of atrial depolarization.
A)the period of time between two activities within the heart.
B)any portion of the electrical tracing that is produced by the heart.
C)a complete ECG waveform.
D)the result of atrial depolarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The conduction of the electrical impulse through both ventricles appears on an ECG tracing as the:
A)P wave.
B)S wave.
C)Q wave.
D)U wave.
A)P wave.
B)S wave.
C)Q wave.
D)U wave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Repolarization of the cells causes the heart muscle to:
A)return to their resting phase.
B)eject the chambers of the heart.
C)infarct.
D)contract.
A)return to their resting phase.
B)eject the chambers of the heart.
C)infarct.
D)contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Ventricular repolarization is represented on the ECG tracing by the:
A)R wave.
B)Q wave.
C)S wave.
D)T wave.
A)R wave.
B)Q wave.
C)S wave.
D)T wave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



