Deck 9: Hypothesis Testing
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Hypothesis Testing
1
The burden of proof is traditionally on the null hypothesis.
False
2
The significance level 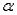 also determines the rejection region.
also determines the rejection region.
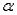 also determines the rejection region.
also determines the rejection region.True
3
A Type II error is committed when we incorrectly accept an alternative hypothesis that is false.
False
4
If a null hypothesis is rejected at the 0.025 level of significance,then it must also be rejected at the 0.01 level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A Type I error probability is represented by 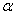 ; it is the probability of incorrectly rejecting a null hypothesis that is true.
; it is the probability of incorrectly rejecting a null hypothesis that is true.
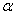 ; it is the probability of incorrectly rejecting a null hypothesis that is true.
; it is the probability of incorrectly rejecting a null hypothesis that is true.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Sample evidence is statistically significant at the 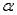 level only if the p-value is larger than
level only if the p-value is larger than 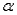 .
.
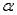 level only if the p-value is larger than
level only if the p-value is larger than 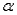 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The p-value of a test is the probability of observing a test statistic at least as extreme as the one computed given that the null hypothesis is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The probability of making a Type I error and the level of significance 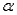 are the same.
are the same.
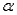 are the same.
are the same.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A one-tailed alternative is one that is supported by evidence in either direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The rejection region is the set of sample data that leads to the rejection of the alternative hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The alternative hypothesis always contains a statement of inequality,such as "less than","greater than",or "not equal to".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The alternative hypothesis,or research hypothesis,is the hypothesis that the analyst is attempting to prove.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The null hypothesis always contains a statement of equality,like "equal to","less than or equal to",or "greater than or equal to".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A professor of statistics doubts the claim that the proportion of Republican voters in Michigan is at most 45%.To test the claim,the hypotheses: 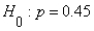 ,
, 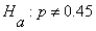 ,should be used.
,should be used.
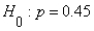 ,
, 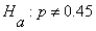 ,should be used.
,should be used.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The p-value of a test is the smallest level of significance 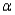 at which the null hypothesis can be rejected.
at which the null hypothesis can be rejected.
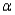 at which the null hypothesis can be rejected.
at which the null hypothesis can be rejected.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If a null hypothesis is rejected at the 0.01 level of significance,then it will also be rejected at the 0.025 level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A low p-value provides evidence for accepting the null hypothesis and rejecting the alternative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Type I errors are usually considered more "costly" which can lead to conservative decision making.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The analyst gets to choose the significance level 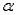 .It is typically chosen to be 0.50,but it is occasionally chosen to be 0.01.
.It is typically chosen to be 0.50,but it is occasionally chosen to be 0.01.
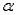 .It is typically chosen to be 0.50,but it is occasionally chosen to be 0.01.
.It is typically chosen to be 0.50,but it is occasionally chosen to be 0.01.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A null hypothesis is a statement about the value of a population parameter.It is usually the current thinking,or "status quo".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A Q-Q plot can be used to test for normality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An example of a paired sample is the number of defective computer chips of a particular type from two different manufacturers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In conducting hypothesis testing for difference between two means when samples are dependent (paired samples),the variable under consideration is 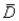 ; the sample mean difference between the pairs.
; the sample mean difference between the pairs.
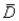 ; the sample mean difference between the pairs.
; the sample mean difference between the pairs.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In statistical analysis,the burden of proof lies traditionally with the
A)alternative hypothesis.
B)null hypothesis.
C)analyst.
D)p-value.
A)alternative hypothesis.
B)null hypothesis.
C)analyst.
D)p-value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The test statistic employed to test 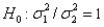 is
is 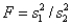 ,which is F distributed with
,which is F distributed with 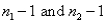 degrees of freedom.
degrees of freedom.
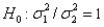 is
is 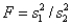 ,which is F distributed with
,which is F distributed with 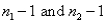 degrees of freedom.
degrees of freedom.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A test for independence is applied to a contingency table with 4 rows and 4 columns.The degrees of freedom for this chi-square test is 9.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A test with a 0.05 significance level has a larger rejection region than a test with a 0.01 significance level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A test with a 0.10 significance level has a larger rejection region than a test with a 0.05 significance level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The null hypothesis usually represents the
A)theory the researcher would like to prove.
B)preconceived ideas of the researcher.
C)perceptions of the sample population.
D)status quo of the situation being studied.
A)theory the researcher would like to prove.
B)preconceived ideas of the researcher.
C)perceptions of the sample population.
D)status quo of the situation being studied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The test statistic for a hypothesis test of a population proportion is the z-value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Side-by-side box plots are typically a good way to begin the analysis when comparing two populations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A chi-square goodness-of-fit test can be used to test for normality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When testing the equality of two population variances,the test statistic is the ratio of the population variances; namely 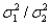 .
.
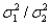 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Lilliefors test for normality compare two cumulative distribution functions (cdf's): the cdf from a normal distribution and the cdf corresponding to the given data (called the empirical cdf).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The F distribution is a skewed distribution useful for testing equality of variances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The power of a test is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when the alternative hypothesis is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The Lilliefors test is used to test for normality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Tests in which samples are not independent are referred to as matched pairs or paired samples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The chi-square test for normality makes a comparison between the observed histogram and a histogram based on normality with the same mean and standard deviation of that of the sample data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The hypothesis that an analyst is trying to prove is called the _____ hypothesis.
A)elective
B)alternative
C)optional
D)null
A)elective
B)alternative
C)optional
D)null

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The form of the alternative hypothesis can be
A)one-tailed only.
B)two-tailed only.
C)neither one nor two-tailed.
D)one-tailed or two-tailed.
A)one-tailed only.
B)two-tailed only.
C)neither one nor two-tailed.
D)one-tailed or two-tailed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The null and alternative hypotheses divide all possibilities into
A)two sets that overlap.
B)two non-overlapping sets.
C)two sets that may or may not overlap.
D)as many sets as necessary to cover all possibilities.
A)two sets that overlap.
B)two non-overlapping sets.
C)two sets that may or may not overlap.
D)as many sets as necessary to cover all possibilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The p-value of a sample is the probability of seeing a sample with at _____ hypothesis as the sample actually observed.
A)most as much evidence in favor of the null
B)most as much evidence in favor of the alternative
C)least as much evidence in favor of the null
D)least as much evidence in favor of the alternative
A)most as much evidence in favor of the null
B)most as much evidence in favor of the alternative
C)least as much evidence in favor of the null
D)least as much evidence in favor of the alternative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A 95% confidence interval can be used to reject the null hypothesis of a two-sided test at the 5% significance level if and only if
A)a 95% confidence interval includes the hypothesized value of the parameter.
B)a 95% confidence interval does not include the hypothesized value of the parameter.
C)the null hypothesis is less than 0.05.
D)the null hypotheses falls in the rejection region.
A)a 95% confidence interval includes the hypothesized value of the parameter.
B)a 95% confidence interval does not include the hypothesized value of the parameter.
C)the null hypothesis is less than 0.05.
D)the null hypotheses falls in the rejection region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which sign is possible in an alternative hypothesis?
A)>
B)<
C)≠
D)All of these signs are possible
A)>
B)<
C)≠
D)All of these signs are possible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A type I error occurs when the
A)null hypothesis is incorrectly accepted when it is false.
B)null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected when it is true.
C)sample mean differs from the population mean.
D)test procedure is fundamentally biased.
A)null hypothesis is incorrectly accepted when it is false.
B)null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected when it is true.
C)sample mean differs from the population mean.
D)test procedure is fundamentally biased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A type II error occurs when the
A)null hypothesis is incorrectly accepted when it is false.
B)null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected when it is true.
C)sample mean differs from the population mean.
D)test procedure itself is fundamentally biased.
A)null hypothesis is incorrectly accepted when it is false.
B)null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected when it is true.
C)sample mean differs from the population mean.
D)test procedure itself is fundamentally biased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The alternative hypothesis is also known as the _____ hypothesis.
A)elective
B)optional
C)research
D)null
A)elective
B)optional
C)research
D)null

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
One-tailed alternative hypotheses use the _____ symbol.
A)≠
B)< or >
C)=
D)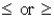
A)≠
B)< or >
C)=
D)
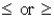

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Smaller p-values indicate more evidence in support of
A)the null hypothesis.
B)the alternative hypothesis.
C)the quality of the researcher.
D)none of these choices.
A)the null hypothesis.
B)the alternative hypothesis.
C)the quality of the researcher.
D)none of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A teacher who is trying to determine if the evidence supports the fact that a new method of teaching economics is more effective than a traditional one will conduct a _____ test.
A)one-tailed
B)two-tailed
C)multi-tailed
D)paired
A)one-tailed
B)two-tailed
C)multi-tailed
D)paired

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following values is not typically used for 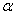 ?
?
A)0.01
B)0.05
C)0.10
D)0.50
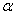 ?
?A)0.01
B)0.05
C)0.10
D)0.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Of type I and type II error,which is more serious?
A)Type I is considered to be more serious.
B)Type II is considered to be more serious.
C)Type I and Type II are equally serious.
D)The situation determines which error is more serious.Sometimes type I errors are more serious and sometimes type II errors are more serious.
A)Type I is considered to be more serious.
B)Type II is considered to be more serious.
C)Type I and Type II are equally serious.
D)The situation determines which error is more serious.Sometimes type I errors are more serious and sometimes type II errors are more serious.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Larger p-values indicate more evidence in support of the
A)null hypothesis.
B)alternative hypothesis.
C)type II error.
D)type I error.
A)null hypothesis.
B)alternative hypothesis.
C)type II error.
D)type I error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The power of a test is the probability that we _____ the null hypothesis when the alternative hypothesis is _____.
A)reject.false
B)reject.true
C)accept,false
D)accept,true
A)reject.false
B)reject.true
C)accept,false
D)accept,true

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A two-tailed test is one where _____ lead to rejection of the null hypothesis.
A)results in only one direction can
B)negative sample means
C)results in either of two directions can
D)no results
A)results in only one direction can
B)negative sample means
C)results in either of two directions can
D)no results

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The value set for 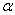 is known as the
is known as the
A)rejection level.
B)acceptance level.
C)significance level.
D)type II error in the hypothesis test.
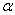 is known as the
is known as theA)rejection level.
B)acceptance level.
C)significance level.
D)type II error in the hypothesis test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following values is a common significance level?
A)0.50
B)0.40
C)0.30
D)0.05
A)0.50
B)0.40
C)0.30
D)0.05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following statements are true of the null and alternative hypotheses?
A)Exactly one hypothesis must be true.
B)Both hypotheses must be true.
C)It is possible for both hypotheses to be true.
D)It is possible for neither hypothesis to be true.
A)Exactly one hypothesis must be true.
B)Both hypotheses must be true.
C)It is possible for both hypotheses to be true.
D)It is possible for neither hypothesis to be true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A sample result is considered "convincing" if the p-value is
A)less than 0.01.
B)between 0.01 and 0.05.
C)between 0.05 and 0.10.
D)greater than 0.10.
A)less than 0.01.
B)between 0.01 and 0.05.
C)between 0.05 and 0.10.
D)greater than 0.10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following statements is true regarding the chi-square goodness-of-fit test for normality?
A)The test does depend on which and how many categories we use for the histogram.
B)The test is not very effective unless the sample size is large,say,at least 80 or 100.
C)The test tends to be too sensitive if the sample size is really large.
D)None of these choices is true.
E)Choices a,b,and c are all true.
A)The test does depend on which and how many categories we use for the histogram.
B)The test is not very effective unless the sample size is large,say,at least 80 or 100.
C)The test tends to be too sensitive if the sample size is really large.
D)None of these choices is true.
E)Choices a,b,and c are all true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is the idea behind the chi-square test for independence?
A)To compare the quantile-quantile (Q-Q)plot with what would be expected under independence
B)To compare the actual counts in a contingency table with what would be expected under independence
C)To compare the cumulative distribution with what would be expected under independence
D)To compare the normal distribution with a chi-squared distribution
A)To compare the quantile-quantile (Q-Q)plot with what would be expected under independence
B)To compare the actual counts in a contingency table with what would be expected under independence
C)To compare the cumulative distribution with what would be expected under independence
D)To compare the normal distribution with a chi-squared distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A 90% confidence interval can be used to reject the null hypothesis of a two-sided test at the 10% significance level if and only if
A)a 90% confidence interval includes the hypothesized value of the parameter.
B)a 90% confidence interval does not include the hypothesized value of the parameter.
C)the null hypothesis is less than 0.05.
D)the null hypotheses includes sampling error is greater than 0.05.
A)a 90% confidence interval includes the hypothesized value of the parameter.
B)a 90% confidence interval does not include the hypothesized value of the parameter.
C)the null hypothesis is less than 0.05.
D)the null hypotheses includes sampling error is greater than 0.05.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The chi-square goodness-of-fit test can be used to test for
A)significance of sample statistics.
B)difference between population means.
C)normality.
D)difference between population variances.
A)significance of sample statistics.
B)difference between population means.
C)normality.
D)difference between population variances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A restaurant manager claims that food servers at this restaurant make at least $15 per hour in tips.A random sample of 50 hours shows the mean amount of tips to be $12 per hour with standard deviation $0.75 per hour.What is the value of the test statistic that can be used to determine if there is convincing evidence that the mean amount of tips made per hour is less than the manager claimed?
A)t = -7.165
B)t = -0.566
C)t = 9.172
D)t = -0.08
A)t = -7.165
B)t = -0.566
C)t = 9.172
D)t = -0.08

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A test for a population mean has _____ degrees of freedom.
A)n + 1
B)n - 1
C)n
D)n - 2
A)n + 1
B)n - 1
C)n
D)n - 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which pair of tests is used to test for normality?
A)A t-test and an ANOVA test
B)An empirical cumulative distribution function test and an F-test
C)A chi-square test and a Lilliefors test
D)A quantile-quantile plot and a p-value test
A)A t-test and an ANOVA test
B)An empirical cumulative distribution function test and an F-test
C)A chi-square test and a Lilliefors test
D)A quantile-quantile plot and a p-value test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
An informal test for normality that utilizes a scatterplot and looks for clustering around a 45° line is known as a(n)
A)Lilliefors test.
B)empirical cumulative distribution function.
C)p-test.
D)quantile-quantile plot.
A)Lilliefors test.
B)empirical cumulative distribution function.
C)p-test.
D)quantile-quantile plot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The test statistic in a hypothesis test for a population proportion is the
A)t-value calculated from the sample.
B)z-value calculated from the sample.
C)F-value calculated from the sample.
D)the sample proportion.
A)t-value calculated from the sample.
B)z-value calculated from the sample.
C)F-value calculated from the sample.
D)the sample proportion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What type of test is used to determine if the population mean is equal to a hypothesized value?
A)t test
B)z test
C)F test
D)Chi-squared test
A)t test
B)z test
C)F test
D)Chi-squared test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



