Deck 14: Solutions and Their Behavior
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/80
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Solutions and Their Behavior
1
What is the molality of ethanol (C2H5OH) in an aqueous solution that is 39.8% ethanol by mass?
A) 1 m..
B) 0 m
C) 14 m
D) 1 m
E) 84.0 m
A) 1 m..
B) 0 m
C) 14 m
D) 1 m
E) 84.0 m
14 m
2
What is the mass percent of an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution in which the mole fraction of NaOH is 0.0736?
A) 15.0%
B) 16%
C) 69%
D) 9%
E) 3%
A) 15.0%
B) 16%
C) 69%
D) 9%
E) 3%
15.0%
3
What is the mass of H2SO4 in a 38.2-mL sample of concentrated sulfuric acid that has a density of 1.84 g/mL and consists of 98.3% H2SO4?
A) 37.6 g
B) 69.1 g
C) 4.73 g
D) 1.81 g
E) 20.4 g
A) 37.6 g
B) 69.1 g
C) 4.73 g
D) 1.81 g
E) 20.4 g
69.1 g
4
What is the definition of molality?
A) moles of solute per kg of solvent
B) grams of solute per kg of solution
C) grams of solute per liter of solution
D) moles of solute per liter of solvent
E) moles of solute per liter of solution
A) moles of solute per kg of solvent
B) grams of solute per kg of solution
C) grams of solute per liter of solution
D) moles of solute per liter of solvent
E) moles of solute per liter of solution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A concentrated nitric acid solution has a density of 1.41 g/mL at 25°C and is 15.8 M. What is the percent by mass of HNO3 in the solution?
A) 70.6% HNO3 by mass
B) 1.12% HNO3 by mass
C) 0.895% HNO3 by mass
D) 1.77% HNO3 by mass
E) 44.7% HNO3 by mass
A) 70.6% HNO3 by mass
B) 1.12% HNO3 by mass
C) 0.895% HNO3 by mass
D) 1.77% HNO3 by mass
E) 44.7% HNO3 by mass

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What mass of an aqueous 18.8% glucose solution contains 85.5 g of water?
A) 105 g
B) 19.8 g
C) 14.5 g
D) 16.1 g
E) 85.5 g
A) 105 g
B) 19.8 g
C) 14.5 g
D) 16.1 g
E) 85.5 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What volume of a 0.758 M solution of CaCl2 contains 1.28 g of solute?
A) 65.7 mL
B) 15.2 mL
C) 1.69 mL
D) 8.74 mL
E) 84.8 mL
A) 65.7 mL
B) 15.2 mL
C) 1.69 mL
D) 8.74 mL
E) 84.8 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Calculate the molarity of a solution of magnesium chloride with a concentration of 27.0 mg/mL.
A) 0.142 M
B) 3.53 M
C) 0.567 M
D) 0.452 M
E) 0.284 M
A) 0.142 M
B) 3.53 M
C) 0.567 M
D) 0.452 M
E) 0.284 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the mole fraction of calcium chloride in 3.35 m CaCl2(aq)? The molar mass of CaCl2 is 111.0 g/mol and the molar mass of water is 18.02 g/mol.
A) 0.000866
B) 0.0569
C) 0.271
D) 37.2
E) 59.2
A) 0.000866
B) 0.0569
C) 0.271
D) 37.2
E) 59.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the mass percent of an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution in which the molality of NaOH is 10.7 m?
A) 0%
B) 69%
C) 2%
D) 30.0%
E) 0%..
A) 0%
B) 69%
C) 2%
D) 30.0%
E) 0%..

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If 11.7 g of naphthalene, C10H8, is dissolved in 104.2 g of chloroform, CHCl3, what is the molality of the solution?
A) 0.0914 m
B) 13.4 m
C) 0.877 m
D) 0.101 m
E) 0.105 m
A) 0.0914 m
B) 13.4 m
C) 0.877 m
D) 0.101 m
E) 0.105 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A concentrated hydrochloric acid solution is 37.2% HCl by mass and has a density of 1.19 g/mL at 25°C. What is the molarity of HCl?
A) 12.1 M
B) 0.0434 M
C) 8.57 M
D) 11.7 M
E) 0.0857 M
A) 12.1 M
B) 0.0434 M
C) 8.57 M
D) 11.7 M
E) 0.0857 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the mole fraction of urea, CH4N2O, in an aqueous solution that is 49% urea by mass?
A) 0.22
B) 0.78
C) 0.49
D) 0.42
E) 0.76
A) 0.22
B) 0.78
C) 0.49
D) 0.42
E) 0.76

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the mole fraction of urea, CO(NH2)2, in a solution prepared by dissolving 4.8 g of urea in 30.3 g of methanol, CH3OH?
A) 0.86
B) 0.14
C) 0.078
D) 0.92
E) 0.23
A) 0.86
B) 0.14
C) 0.078
D) 0.92
E) 0.23

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The volume of a 32.4% (by mass) solution is 179.1 mL. The density of the solution is 1.296 g/mL. What is the mass of solute in this solution?
A) 232 g
B) 75.2 g
C) 716 g
D) 44.8 g
E) 157 g
A) 232 g
B) 75.2 g
C) 716 g
D) 44.8 g
E) 157 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How many milliliters of 11.7 M H2SO4 are needed to prepare 600.0 mL of 0.10 M H2SO4?
A) 0.19 mL
B) 70 mL
C) 5.1 mL
D) 2.6 mL
E) 6.1 mL
A) 0.19 mL
B) 70 mL
C) 5.1 mL
D) 2.6 mL
E) 6.1 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If the concentration of sodium carbonate in water is 12.8 ppm, what is the molarity of Na2CO3(aq)? The molar mass of Na2CO3 is 106.0 g/mol. Assume the density of the solution is 1.00 g/mL.
A) 8.28 × 10-6 M
B) 1.21 × 10-4 M
C) 1.36 × 10-3 M
D) 0.136 M
E) 0.121 M
A) 8.28 × 10-6 M
B) 1.21 × 10-4 M
C) 1.36 × 10-3 M
D) 0.136 M
E) 0.121 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the molality of a 19.4 M sodium hydroxide solution that has a density of 1.54 g/mL?
A) 12.6 m
B) 19.8 m
C) 25.4 m
D) 29.9 m
E) 50.4 m
A) 12.6 m
B) 19.8 m
C) 25.4 m
D) 29.9 m
E) 50.4 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A 12.0% sucrose solution by mass has a density of 1.05 g/cm3. What mass of sucrose is present in a 53.0-mL sample of this solution?
A) 6.68 g
B) 6.06 g
C) 0.126 g
D) 464 g
E) 6.36 g
A) 6.68 g
B) 6.06 g
C) 0.126 g
D) 464 g
E) 6.36 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If 27.9 g LiCl is dissolved in 175 g H2O, what is the weight percent of LiCl in the solution?
A) 0.376%
B) 6.78%
C) 13.8%
D) 15.9%
E) 19.0%
A) 0.376%
B) 6.78%
C) 13.8%
D) 15.9%
E) 19.0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What partial pressure of oxygen gas is required in order for 0.00284 g of the gas to dissolve in 15.9 mL of pure water? The Henry's law constant for oxygen gas is 1.3 × 10-3 M atm-1.
A) 2.3 × 10-7 atm
B) 4.3 × 100 atm
C) 1.2 × 10-7 atm
D) 2.3 × 10-1 atm
E) 4.2 × 10-2 atm
A) 2.3 × 10-7 atm
B) 4.3 × 100 atm
C) 1.2 × 10-7 atm
D) 2.3 × 10-1 atm
E) 4.2 × 10-2 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Henry's Law constant is 0.0013 mol/kg?bar and 0.034 mol/kg?bar for O2 and CO2 respectively at 25°C. What pressure of CO2 is required to achieve the same solubility as 0.711 bar of O2?
A) 0.0 bar
B) 19.0 bar
C) bar
D) bar
E) 37.0 bar
A) 0.0 bar
B) 19.0 bar
C) bar
D) bar
E) 37.0 bar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
According to the National Institute of Standards webbook, the Henry's Law constant for O2 gas is 0.0013 mol/kg?bar at 25°C What is the Henry's law constant in units of mol/kg?mmHg? (1 bar = 0.9869 atm; 1 atm = 760 mmHg)
A) mol/kg?mmHg
B) mol/kg?mmHg
C) mol/kg?mmHg
D) mol/kg?mmHg
E) mol/kg?mmHg
A) mol/kg?mmHg
B) mol/kg?mmHg
C) mol/kg?mmHg
D) mol/kg?mmHg
E) mol/kg?mmHg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The Henry's law constant for N2 in water at 25 °C is 6.0 × 10-4 mol/kg⋅bar. What is the equilibrium concentration of N2 in water when the partial pressure of N2 is 586 mm Hg? (760 mm Hg = 1 atm = 0.9869 bar)
A) 1.4 × 10-9 M
B) 1.8 × 10-5 M
C) 4.6 × 10-4 M
D) 7.7 × 10-4 M
E) 7.9 × 10-4 M
A) 1.4 × 10-9 M
B) 1.8 × 10-5 M
C) 4.6 × 10-4 M
D) 7.7 × 10-4 M
E) 7.9 × 10-4 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following liquids are miscible with water in any proportion?
A) Ethanol (CH3CH2OH) and carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)
B) Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and hexane (C6H14)
C) Ethanol (CH3CH2OH) and formic acid (HCO2H)
D) Ethanol (CH3CH2OH), carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), and hexane (C6H14)
E) Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and formic acid (HCO2H)
A) Ethanol (CH3CH2OH) and carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)
B) Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and hexane (C6H14)
C) Ethanol (CH3CH2OH) and formic acid (HCO2H)
D) Ethanol (CH3CH2OH), carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), and hexane (C6H14)
E) Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and formic acid (HCO2H)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following equations illustrates the formation of an aqueous solution of KF from its elements in their standard states?
A) K+(g) + F?(g) ? K+(aq) + F?(aq)
B) KF(s) ? KF(aq, 1 m)
C) K+(g) + F?(g) ? KF(s)
D) K(s) + F2(g) ? KF(s)
E) K(s) + F2(g) ? KF(aq, 1 m)
A) K+(g) + F?(g) ? K+(aq) + F?(aq)
B) KF(s) ? KF(aq, 1 m)
C) K+(g) + F?(g) ? KF(s)
D) K(s) + F2(g) ? KF(s)
E) K(s) + F2(g) ? KF(aq, 1 m)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The change in energy accompanying the equation below is the _____ of MX. MX(s) → M+(aq) + X−(aq)
A) enthalpy of hydration
B) enthalpy of solution
C) lattice energy
D) enthalpy of formation
E) electron attachment enthalpy
A) enthalpy of hydration
B) enthalpy of solution
C) lattice energy
D) enthalpy of formation
E) electron attachment enthalpy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The lattice enthalpy of LiCl is −834 kJ/mol and the enthalpy of solution of LiCl is -37 kJ/mol. Calculate the enthalpy of hydration of LiCl(s).
A) -797.0 kJ/mol
B) -74.0 kJ/mol
C) -871.0 kJ/mol
D) 797.0 kJ/mol
E) 871.0 kJ/mol
A) -797.0 kJ/mol
B) -74.0 kJ/mol
C) -871.0 kJ/mol
D) 797.0 kJ/mol
E) 871.0 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the Henry's law constant for O2 if the solubility of O2 in water is 0.590 g/L at a pressure of 15.5 atm?
A) 3.81 × 10-2 L·atm/mol
B) 8.41 × 102 L·atm/mol
C) 2.86 × 10-1 L·atm/mol
D) 1.19 × 10-3 L·atm/mol
E) None of these
A) 3.81 × 10-2 L·atm/mol
B) 8.41 × 102 L·atm/mol
C) 2.86 × 10-1 L·atm/mol
D) 1.19 × 10-3 L·atm/mol
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The Henry's law constant for O2 in water at 25 °C is 1.3 × 10-3 mol/kg⋅bar. What partial pressure of O2 (in atm) is necessary to achieve an equilibrium concentration of 2.9 × 10-3 mol/kg O2? (1 atm = 0.9869 bar)
A) 0.44 atm
B) 0.45 atm
C) 2.1 atm
D) 2.3 atm
E) 3.8 atm
A) 0.44 atm
B) 0.45 atm
C) 2.1 atm
D) 2.3 atm
E) 3.8 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The solubility of 1-pentanol in water is 2.7 g per 100 g of water at 25°C. What is the maximum amount of 1-pentanol that will dissolve in 2.1 g of water at 25°C?
A) 0.057 g
B) 1.3 g
C) 2.7 g
D) 5.7 g
E) 0.013 g
A) 0.057 g
B) 1.3 g
C) 2.7 g
D) 5.7 g
E) 0.013 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If the solubility of O2 at 0.300 bar and 25°C is 12.5 g/100 g H2O, what is the solubility of O2 at a pressure of 1.64 bar and 25°C?
A) 68 g/100 g H2O
B) 25.4 g/100 g H2O
C) 0.4 g/100 g H2O
D) 0.0 g/100 g H2O
E) 2.3 g/100 g H2O
A) 68 g/100 g H2O
B) 25.4 g/100 g H2O
C) 0.4 g/100 g H2O
D) 0.0 g/100 g H2O
E) 2.3 g/100 g H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What mass of Zn(NO3)2 must be diluted to a mass of 1.00 kg with H2O to prepare 97 ppm Zn2+(aq)?
A) 7.8 × 10-6 g
B) 7.8 × 10-3 g
C) 3.3 × 10-2 g
D) 1.3 × 10-1 g
E) 2.8 × 10-1 g
A) 7.8 × 10-6 g
B) 7.8 × 10-3 g
C) 3.3 × 10-2 g
D) 1.3 × 10-1 g
E) 2.8 × 10-1 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT?
A) The solubility of a gas in water decreases with increasing temperature.
B) The solubility of a gas in water is proportional to the partial pressure of the gas above the water.
C) The dissolution of a gas in water is usually an exothermic process.
D) The relationship between the solubility of a gas and its partial pressure is known as Henry's law.
E) The solubility of a gas in water is inversely proportional to the molar mass of the gas.
A) The solubility of a gas in water decreases with increasing temperature.
B) The solubility of a gas in water is proportional to the partial pressure of the gas above the water.
C) The dissolution of a gas in water is usually an exothermic process.
D) The relationship between the solubility of a gas and its partial pressure is known as Henry's law.
E) The solubility of a gas in water is inversely proportional to the molar mass of the gas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What concentration of silver nitrate (in ppm) is present in 7.1 × 10-7 M AgNO3(aq)? For very dilute aqueous solutions, you can assume the solution's density is 1.0 g/mL. The molar mass of AgNO3 is 169.9 g/mol.
A) 0.0071 ppm
B) 0.12 ppm
C) 0.71 ppm
D) 1.7 ppm
E) 8.3 ppm
A) 0.0071 ppm
B) 0.12 ppm
C) 0.71 ppm
D) 1.7 ppm
E) 8.3 ppm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Two nonpolar solvents, such as hexane and carbon tetrachloride, may be miscible even though the enthalpy of mixing of these liquids might be small. A reason that mixing occurs is that mixtures have a greater dispersal of energy relative to pure solvents. The tendency toward greater dispersal of energy is a thermodynamic function called ____.
A) entropy
B) enthalpy
C) saturation
D) adhesion
E) cohesion
A) entropy
B) enthalpy
C) saturation
D) adhesion
E) cohesion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following favor(s) the solubility of an ionic solid in a liquid solvent?
A) a small magnitude of the lattice energy of the solute
B) a large magnitude of the solvation energy of the ions
C) a large polarity of the solvent
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) a small magnitude of the lattice energy of the solute
B) a large magnitude of the solvation energy of the ions
C) a large polarity of the solvent
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A 15 meter by 12 meter pool of water has a depth of 2.2 meters. What mass of silver ion is present in the reservoir if the concentration of silver ion is 0.14 ppm? (1 m3 = 1000 L; assume the density of the solution is 1.00 g/mL)
A) 5.5 × 10-4 g
B) 5.5 × 10-2 g
C) 0.55 g
D) 5.5 g
E) 55 g
A) 5.5 × 10-4 g
B) 5.5 × 10-2 g
C) 0.55 g
D) 5.5 g
E) 55 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The standard enthalpy of formation of RbF(s) is -557.7kJ/mol and the standard enthalpy of formation of RbF(aq, 1 m) is -583.8 kJ/mol. Determine the enthalpy of solution of RbF and indicate whether the solution temperature will increase or decrease when RbF is dissolved in water.
A) -26.1 kJ/mol; increase
B) 26.1 kJ/mol; increase
C) -26.1 kJ/mol; decrease
D) +1141.5 kJ/mol; increase
E) -1141.5 kJ/mol; decrease
A) -26.1 kJ/mol; increase
B) 26.1 kJ/mol; increase
C) -26.1 kJ/mol; decrease
D) +1141.5 kJ/mol; increase
E) -1141.5 kJ/mol; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following compounds is not miscible with water?
A) CH3NH2
B) CH3COOH
C) CCl4
D) CH3CN
E) HOCH2CH2OH
A) CH3NH2
B) CH3COOH
C) CCl4
D) CH3CN
E) HOCH2CH2OH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is the equilibrium partial pressure of water vapor above a mixture of 37.5 g H2O and 62.5 g HOCH2CH2OH at 55 °C. The partial pressure of pure water at 55.0 °C is 118.0 mm Hg. Assume ideal behavior for the solution.
A) 3.54 mm Hg
B) 31.7 mm Hg
C) 38.5 mm Hg
D) 79.5 mm Hg
E) 175 mm Hg
A) 3.54 mm Hg
B) 31.7 mm Hg
C) 38.5 mm Hg
D) 79.5 mm Hg
E) 175 mm Hg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Assuming ideal behavior, which of the following aqueous solutions would be expected to exhibit the smallest freezing-point lowering?
A) 0.1 m NaCl
B) 0.05 m CH3COOH
C) 0.05 m Al2(SO4)3
D) 0.1 m BaCl2
E) 0.25 m C6H12O6
A) 0.1 m NaCl
B) 0.05 m CH3COOH
C) 0.05 m Al2(SO4)3
D) 0.1 m BaCl2
E) 0.25 m C6H12O6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is the freezing point of an aqueous 1.38 m NaCl solution? (Kfp for water is 1.858°C/m.) Assume no ion pairing occurs.
A) 5.1 °C
B) 2.6 °C
C) -5.1 °C
D) 0.0 °C
E) -2.6 °C
A) 5.1 °C
B) 2.6 °C
C) -5.1 °C
D) 0.0 °C
E) -2.6 °C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the freezing point of a 0.29 m solution of glucose (C6H12O6) in water? (Kfp for water is 1.858 °C/m.)
A) 0.27 °C
B) 0.54 °C
C) -0.54 °C
D) -0.27 °C
E) -1.08 °C
A) 0.27 °C
B) 0.54 °C
C) -0.54 °C
D) -0.27 °C
E) -1.08 °C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A 0.20 M solution of MgSO4 has an observed osmotic pressure of 7.7 atm at 25°C. Determine the observed van't Hoff factor for this experiment.
A) 2.0
B) 1.6
C) 0.31
D) 19
E) 1.8
A) 2.0
B) 1.6
C) 0.31
D) 19
E) 1.8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
For the following gas-aqueous liquid equilibrium for a closed system at a constant temperature, N2(g)
D
N2(aq)
What is the effect on the equilibrium composition of the liquid when the partial pressure of N2 gas above the liquid is decreased?
A) The amount of N2 dissolved in the liquid decreases.
B) The amount of N2 dissolved in the liquid increases.
C) The amount of N2 dissolved in the liquid does not change.
D) Not enough information is provided to answer the question.
E) Either A or B is possible.
D
N2(aq)
What is the effect on the equilibrium composition of the liquid when the partial pressure of N2 gas above the liquid is decreased?
A) The amount of N2 dissolved in the liquid decreases.
B) The amount of N2 dissolved in the liquid increases.
C) The amount of N2 dissolved in the liquid does not change.
D) Not enough information is provided to answer the question.
E) Either A or B is possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If a 15.6-g sample of a nonelectrolyte is dissolved in 100.0 g of water, the resulting solution will freeze at -0.93°C. What is the molar mass of the nonelectrolyte? (Kfp for water is 1.858°C/m.)
A) 81 g/mol
B) 0.31 g/mol
C) 430 g/mol
D) 270 g/mol
E) 310 g/mol
A) 81 g/mol
B) 0.31 g/mol
C) 430 g/mol
D) 270 g/mol
E) 310 g/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Ideally, colligative properties depend only on the:
A) relative number of solute and solvent particles in a solution.
B) molar masses of the solute particles in a solution.
C) density of a solution.
D) hydrated radii of the molecules or ions dissolved in a solution.
E) partial pressure of the gases above the surface of a solution.
A) relative number of solute and solvent particles in a solution.
B) molar masses of the solute particles in a solution.
C) density of a solution.
D) hydrated radii of the molecules or ions dissolved in a solution.
E) partial pressure of the gases above the surface of a solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following solutions would have the highest osmotic pressure?
A) 0.2 M C6H12O6, glucose
B) 0.15 M MgCl2, magnesium chloride
C) 0.15 M KCl, potassium chloride
D) 0.2 M CH3OH, methanol
E) 0.2 M C12H22O11, sucrose
A) 0.2 M C6H12O6, glucose
B) 0.15 M MgCl2, magnesium chloride
C) 0.15 M KCl, potassium chloride
D) 0.2 M CH3OH, methanol
E) 0.2 M C12H22O11, sucrose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What mass of ethylene glycol, when mixed with 225 g H2O, will reduce the equilibrium vapor pressure of H2O from 1.00 atm to 0.800 atm at 100 °C? The molar masses of water and ethylene glycol are 18.02 g/mol and 62.07 g/mol, respectively. Assume ideal behavior for the solution.
A) 15.6 g
B) 49.9 g
C) 194 g
D) 969 g
E) 3.10 × 103 g
A) 15.6 g
B) 49.9 g
C) 194 g
D) 969 g
E) 3.10 × 103 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Assuming ideal behavior, which of the following aqueous solutions should have the highest boiling point?
A) 1.00 m LiBr
B) 0.75 m K2SO4
C) 0.50 m Ca(NO3)2
D) 0.75 m NaCl
E) 1.25 m C6H12O6
A) 1.00 m LiBr
B) 0.75 m K2SO4
C) 0.50 m Ca(NO3)2
D) 0.75 m NaCl
E) 1.25 m C6H12O6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
For the following gas-liquid equilibrium for an aqueous system at a constant partial pressure of CO2, CO2(g) D CO2(aq)
What is the effect on the equilibrium composition of the liquid when the temperature of the liquid is increased?
A) The amount of CO2 dissolved in the liquid increases.
B) The amount of CO2 dissolved in the liquid decreases.
C) The amount of CO2 dissolved in the liquid does not change.
D) Not enough information is provided to answer the question.
E) Either A or B could occur.
What is the effect on the equilibrium composition of the liquid when the temperature of the liquid is increased?
A) The amount of CO2 dissolved in the liquid increases.
B) The amount of CO2 dissolved in the liquid decreases.
C) The amount of CO2 dissolved in the liquid does not change.
D) Not enough information is provided to answer the question.
E) Either A or B could occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What is the boiling-point change for a solution containing 0.251 mol of naphthalene (a nonvolatile, nonionizing compound) in 250. g of liquid benzene? (Kbp = 2.53°C/m for benzene)
A) 2.54 °C
B) 10.08 °C
C) 0.159 °C
D) 2.52 °C
E) 0.635 °C
A) 2.54 °C
B) 10.08 °C
C) 0.159 °C
D) 2.52 °C
E) 0.635 °C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the vapor pressure at 20°C of an ideal solution prepared by the addition of 4.50 g of the nonvolatile solute urea, CO(NH2)2, to 22.7 g of methanol, CH3OH? The vapor pressure of pure methanol at 20°C is 89.0 mmHg.
A) 8.51 mmHg
B) 64.9 mmHg
C) 74.3 mmHg
D) 80.5 mmHg
E) 24.1 mmHg
A) 8.51 mmHg
B) 64.9 mmHg
C) 74.3 mmHg
D) 80.5 mmHg
E) 24.1 mmHg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What is the freezing point of a solution containing 2.80 grams benzene (molar mass = 78.11 g/mol) dissolved in 43.0 grams paradichlorobenzene (molar mass = 147.0 g/mol)? The freezing point of pure paradichlorobenzene is 53.0 °C and the freezing point depression constant, Kfp, is -7.10 °C/m.
A) 46.7 °C
B) 47.1 °C
C) 58.9 °C
D) 52.6 °C
E) 58.9 °C..
A) 46.7 °C
B) 47.1 °C
C) 58.9 °C
D) 52.6 °C
E) 58.9 °C..

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The vapor pressure of pure water at 15 °C is 12.8 mm Hg. What is the equilibrium vapor pressure of water above a mixture of 72.0 g ethanol (CH3CH2OH, molar mass = 46.07 g/mol) and 22.0 g water?
A) 2.84 mm Hg
B) 5.61 mm Hg
C) 7.19 mm Hg
D) 10.0 mm Hg
E) 12.8 mm Hg
A) 2.84 mm Hg
B) 5.61 mm Hg
C) 7.19 mm Hg
D) 10.0 mm Hg
E) 12.8 mm Hg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The vapor pressure of water at 90°C is 0.692 atm. What is the vapor pressure (in atm) of a solution made by dissolving 2.91 mole(s) of CsF(s) in 1.00 kg of water? Assume that Raoult's law applies.
A) 0.626 atm
B) 0.658 atm
C) 0.692 atm
D) 0.765 atm
E) none of these
A) 0.626 atm
B) 0.658 atm
C) 0.692 atm
D) 0.765 atm
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What mass of Na2SO4 must be dissolved in 100.0 grams of water to lower the freezing point by 2.50 °C? The freezing point depression constant, Kfp, of water is -1.86 °C/m. Assume the van't Hoff factor for Na2SO4 is 2.85.
A) 3.77 g
B) 6.36 g
C) 6.70 g
D) 11.3 g
E) 19.1 g
A) 3.77 g
B) 6.36 g
C) 6.70 g
D) 11.3 g
E) 19.1 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A solution consisting of 0.278 mol of methylbenzene, C6H5CH3, in 244 g of nitrobenzene, C6H5NO2, freezes at -2.0°C. Pure nitrobenzene freezes at 6.0°C. What is the freezing-point depression constant of nitrobenzene?
A) 7.1°C/m
B) 29°C/m
C) 14.0°C/m
D) 3.5°C/m
E) 7.0°C/m
A) 7.1°C/m
B) 29°C/m
C) 14.0°C/m
D) 3.5°C/m
E) 7.0°C/m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
For a dilute solution of (NH4)2SO4, the van't Hoff factor (i) would be approximately ___.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Aqueous colloidal solutions can be classified as ________ (water-fearing), or hydrophilic (water-loving).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If an egg's shell is carefully dissolved using an acid, the egg white and yolk will remain intact inside a membrane. If the egg is then placed in distilled water, it will slowly expand until it bursts. Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Colloids are described by all of the following except:
A) The particles in a colloid are so small that settling is negligible.
B) The mixture appears cloudy.
C) Only combinations of liquids and gases can form colloids.
D) Colloids are not suspensions or homogeneous mixtures.
E) Mayonnaise, whipped cream and fog are all examples of colloids.
A) The particles in a colloid are so small that settling is negligible.
B) The mixture appears cloudy.
C) Only combinations of liquids and gases can form colloids.
D) Colloids are not suspensions or homogeneous mixtures.
E) Mayonnaise, whipped cream and fog are all examples of colloids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Because ________ particles are relatively large (say, 1000 nm in diameter) they scatter visible light, making the mixtures containing these particles appear cloudy. This scattering is known as the Tyndall effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A solution is prepared by dissolving 5.88 g of an unknown nonelectrolyte in enough water to make 0.355 L of solution. The osmotic pressure of the solution is 1.21 atm at 27 °C. What is the molar mass of the solute? (R = 0.08206 L⋅atm/mol⋅K)
A) 0.00297 g/mol
B) 30.3 g/mol
C) 42.5 g/mol
D) 175 g/mol
E) 337 g/mol
A) 0.00297 g/mol
B) 30.3 g/mol
C) 42.5 g/mol
D) 175 g/mol
E) 337 g/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What is the osmotic pressure of an aqueous solution that is 0.46% NaCl by weight at 36°C. Assume the density of the solution is 1.0 g/mL. Assume no ion pairing. (R = 0.0821 L · atm/K·mol)
A) 0.20 atm
B) 2.0 atm
C) 2.3 × 102 atm
D) 4.0 atm
E) 0.47 atm
A) 0.20 atm
B) 2.0 atm
C) 2.3 × 102 atm
D) 4.0 atm
E) 0.47 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
_____ are colloidal dispersions of one liquid in another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A solution in which there is more dissolved solute than in a saturated solution is known as a(n) ________ solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A surfactant used for cleaning is called a(n) ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What type of colloid is formed when a liquid is dispersed in a gas?
A) Aerosol
B) Foam
C) Gel
D) Sol
E) Emulsion
A) Aerosol
B) Foam
C) Gel
D) Sol
E) Emulsion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The osmotic pressure of blood is 7.65 atm at 37 °C. What mass of glucose (C6H12O6, molar mass = 180.2 g/mol) is needed to prepare 2.25 L of solution for intravenous injection? The osmotic pressure of the glucose solution must equal the osmotic pressure of blood. (R = 0.08206 L⋅atm/mol⋅K)
A) 0.676 g
B) 0.698 g
C) 5.67 g
D) 122 g
E) 1.02 × 103 g
A) 0.676 g
B) 0.698 g
C) 5.67 g
D) 122 g
E) 1.02 × 103 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
All of the following are colloidal dispersions EXCEPT ____.
A) marshmallow
B) white wine
C) milk
D) whipped cream
E) cheese
A) marshmallow
B) white wine
C) milk
D) whipped cream
E) cheese

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following solutions has the lowest osmotic pressure?
A) 0.10 M Al(NO3)3
B) 0.20 M C6.0H12O6
C) 0.15 M Ba(NO3)2
D) 0.10 M CaBr2
E) 0.15 M Na2Cl
A) 0.10 M Al(NO3)3
B) 0.20 M C6.0H12O6
C) 0.15 M Ba(NO3)2
D) 0.10 M CaBr2
E) 0.15 M Na2Cl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Henry's law states that the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to its pressure above the liquid. This law holds Right for gases such as nitrogen and oxygen. However, Henry's law does not hold Right for hydrogen chloride gas. Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What is the concentration unit used in the calculation of osmotic pressure of a dilute solution?
A) Molality
B) Weight percent
C) Mass fraction
D) Mole fraction
E) Molarity
A) Molality
B) Weight percent
C) Mass fraction
D) Mole fraction
E) Molarity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following is a colligative property?
A) Vapor pressure addition
B) Boiling point depression
C) Freezing point depression
D) Osmotic pressure
E) Melting point elevation
A) Vapor pressure addition
B) Boiling point depression
C) Freezing point depression
D) Osmotic pressure
E) Melting point elevation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The following equation is known as ________ law: 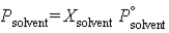 .
.
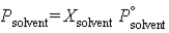 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A 3.0 g sample of a small protein having a molecular weight of 42,000 g/mol is dissolved in 52.8 mL of water at 21°C. What is the osmotic pressure of the solution? (R = 0.0821 L · atm/K·mol, 1 atm = 760 mmHg)
A) 25 mmHg
B) 1900 mmHg
C) 1.8 mmHg
D) 23,000 mmHg
E) 0.033 mmHg
A) 25 mmHg
B) 1900 mmHg
C) 1.8 mmHg
D) 23,000 mmHg
E) 0.033 mmHg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following statements about soaps and detergents is false?
A) The polar end is attracted to grease and oil.
B) They have a polar and a nonpolar end.
C) They are emulsifiers for grease and oil.
D) Phosphate detergents can produce pollution.
E) They can be described as surfactants.
A) The polar end is attracted to grease and oil.
B) They have a polar and a nonpolar end.
C) They are emulsifiers for grease and oil.
D) Phosphate detergents can produce pollution.
E) They can be described as surfactants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If one of the factors determining the equilibrium of a system is changed, the system adjusts to counteract that change. This is known as ________ principle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



