Deck 12: Intermolecular Forces and Liquids
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/64
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Intermolecular Forces and Liquids
1
Which of the following bonds can potentially form a hydrogen bond in a solid or liquid phase?
A) Cl-H
B) Si-H
C) N-H
D) I-H
E) Br-H
A) Cl-H
B) Si-H
C) N-H
D) I-H
E) Br-H
N-H
2
Which one of the following statements is false?
A) All ions are hydrated in aqueous solution.
B) All cations are hydrated in aqueous solution.
C) All anions are hydrated in aqueous solution.
D) Hydration is generally highly endothermic for ionic compounds.
E) The heats of hydration of cations increases as their charge-to-radius ratios increase.
A) All ions are hydrated in aqueous solution.
B) All cations are hydrated in aqueous solution.
C) All anions are hydrated in aqueous solution.
D) Hydration is generally highly endothermic for ionic compounds.
E) The heats of hydration of cations increases as their charge-to-radius ratios increase.
Hydration is generally highly endothermic for ionic compounds.
3
Which one of the following molecules will exhibit dipole-dipole intermolecular forces as a pure liquid or solid?
A) CSe2
B) C2H2
C) SiF4
D) O2
E) PF3
A) CSe2
B) C2H2
C) SiF4
D) O2
E) PF3
PF3
4
When a water molecule forms a hydrogen bond with another water molecule, which atoms are involved in the interaction?
A) a hydrogen from one molecule and a hydrogen from the other molecule
B) a hydrogen from one molecule and an oxygen from the other molecule
C) an oxygen from one molecule and an oxygen from the other molecule
D) an oxygen and a hydrogen from the same molecule
E) two hydrogens from one molecule and one hydrogen from the other molecule
A) a hydrogen from one molecule and a hydrogen from the other molecule
B) a hydrogen from one molecule and an oxygen from the other molecule
C) an oxygen from one molecule and an oxygen from the other molecule
D) an oxygen and a hydrogen from the same molecule
E) two hydrogens from one molecule and one hydrogen from the other molecule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
As pure molecular solids, which of the following exhibits dipole-dipole intermolecular forces: HBr, NBr3, SBr2, and CBr4?
A) HBr only
B) CBr4 only
C) HBr and SBr2
D) NBr3 and CBr4
E) HBr, NBr3, and SBr2
A) HBr only
B) CBr4 only
C) HBr and SBr2
D) NBr3 and CBr4
E) HBr, NBr3, and SBr2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Hydrogen bonding is present in all of the following molecular solids EXCEPT ____.
A) H2SO4 (dihydrogen sulfate)
B) CH3OH (methanol)
C) CH3OCH3 (dimethyl ether)
D) HF (hydrogen fluoride)
E) CH3CO2H (acetic acid)
A) H2SO4 (dihydrogen sulfate)
B) CH3OH (methanol)
C) CH3OCH3 (dimethyl ether)
D) HF (hydrogen fluoride)
E) CH3CO2H (acetic acid)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Place the following cations in order from the most negative to the least negative hydration enthalpy: Li+, H+, and K+.
A) K+ < Li+ < H+
B) K+ < H+ < Li+
C) H+ < Li+ < K+
D) H+ < K+ < Li+
E) Li+ < H+ < K+
A) K+ < Li+ < H+
B) K+ < H+ < Li+
C) H+ < Li+ < K+
D) H+ < K+ < Li+
E) Li+ < H+ < K+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following substances will have the strongest intermolecular forces?
A) H2S
B) CO
C) CH3OH
D) HBr
E) Rn
A) H2S
B) CO
C) CH3OH
D) HBr
E) Rn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A molecule will always be polar if it ___.
A) has polar bonds
B) contains both carbon and chlorine
C) consists of more than three atoms
D) is diatomic with different electronegativities
E) contains atoms with different electronegativities
A) has polar bonds
B) contains both carbon and chlorine
C) consists of more than three atoms
D) is diatomic with different electronegativities
E) contains atoms with different electronegativities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following strong electrolytes has the most negative hydration enthalpy?
A) NaCl
B) KCl
C) RbCl
D) CsCl
E) HCl
A) NaCl
B) KCl
C) RbCl
D) CsCl
E) HCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following pure liquids is expected have the highest boiling point?
A) CO
B) NO
C) PH3
D) AsH3
E) ICl
A) CO
B) NO
C) PH3
D) AsH3
E) ICl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which intermolecular force or bond is responsible for the density of
H2O(s) being less than that of H2O( )?
A) London dispersion forces
B) hydrogen bonding
C) ionic bonding
D) covalent bonding
E) dipole/induced dipole forces
H2O(s) being less than that of H2O( )?
A) London dispersion forces
B) hydrogen bonding
C) ionic bonding
D) covalent bonding
E) dipole/induced dipole forces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Arrange HF, HCl, and HBr in increasing order of their boiling point.
A) HF < HCl < HBr
B) HF < HBr < HCl
C) HBr < HF < HCl
D) HBr < HCl < HF
E) HCl < HBr < HF
A) HF < HCl < HBr
B) HF < HBr < HCl
C) HBr < HF < HCl
D) HBr < HCl < HF
E) HCl < HBr < HF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
As pure molecular solids, which of the following exhibits dipole-dipole intermolecular forces: PH3, SO3, HCl, and CO2?
A) PH3 only
B) HCl only
C) SO3 and CO2
D) PH3 and HCl
E) SO3, HCl, and CO2
A) PH3 only
B) HCl only
C) SO3 and CO2
D) PH3 and HCl
E) SO3, HCl, and CO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Arrange the following cations in the increasing order their enthalpy of hydration:
K+, Ca2+, and Mg2+.
A) K+ < Ca2+ < Mg2+
B) Mg2+ < Ca2+ < K+
C) Ca2+ < K+ < Mg2+
D) Ca2+ < Mg2+ < K+
E) Mg2+ < K+ < Ca2+
K+, Ca2+, and Mg2+.
A) K+ < Ca2+ < Mg2+
B) Mg2+ < Ca2+ < K+
C) Ca2+ < K+ < Mg2+
D) Ca2+ < Mg2+ < K+
E) Mg2+ < K+ < Ca2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The elements of group 5A, the nitrogen family, form compounds with hydrogen having the boiling points listed below:
SbH3, -17 °C; AsH3, -55 °C; PH3, -87 °C; and NH3, -33 °C
The first three compounds illustrate a trend where the boiling point decreases as the mass decreases; however, ammonia (NH3) does not follow the trend because of _____.
A) debye forces
B) metallic bonding
C) hydrogen bonding
D) London dispersion forces
E) ionic bonding
SbH3, -17 °C; AsH3, -55 °C; PH3, -87 °C; and NH3, -33 °C
The first three compounds illustrate a trend where the boiling point decreases as the mass decreases; however, ammonia (NH3) does not follow the trend because of _____.
A) debye forces
B) metallic bonding
C) hydrogen bonding
D) London dispersion forces
E) ionic bonding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which one of the following sets of ions are listed in order of lowest to highest hydration energy?
A) H+ < Na+ < Mg2+
B) Mg2+ < Ca2+ < Ba2+
C) Mg2+ < Ba2+ < Ca2+
D) Ca2+ < K+ < Rb+
E) Rb+ < K+ < Ca2+
A) H+ < Na+ < Mg2+
B) Mg2+ < Ca2+ < Ba2+
C) Mg2+ < Ba2+ < Ca2+
D) Ca2+ < K+ < Rb+
E) Rb+ < K+ < Ca2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Arrange H2S, H2Se, and H2Te in order from lowest to highest boiling point.
A) H2Te < H2Se < H2S
B) H2S < H2Se < H2Te
C) H2S < H2Te < H2Se
D) H2Se < H2Te < H2S
E) H2Te < H2S < H2Se
A) H2Te < H2Se < H2S
B) H2S < H2Se < H2Te
C) H2S < H2Te < H2Se
D) H2Se < H2Te < H2S
E) H2Te < H2S < H2Se

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Consider the following molecules: ethanol (CH3CH2OH), acetic acid (CH3CO2H), acetaldehyde (CH3CHO), and dimethyl ether (CH3OCH3). Which of these molecules is/are expected to form hydrogen bonds in the liquid or solid phase?
A) Ethanol only
B) Acetaldehyde only
C) Ethanol and acetic acid
D) Acetaldehyde and dimethyl ether
E) Ethanol and dimethyl ether
A) Ethanol only
B) Acetaldehyde only
C) Ethanol and acetic acid
D) Acetaldehyde and dimethyl ether
E) Ethanol and dimethyl ether

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following statements best describes what happens when a small amount of solid potassium chloride is dissolved in water?
A) The heat from the warm water melts the solid, making it a liquid.
B) Nothing happens, because potassium chloride is insoluble in water.
C) The solid KCl breaks apart into separate K and Cl atoms by interacting with the water molecules.
D) The water molecules surround each ion in the solid KCl, separating the K ions from the Cl ions.
E) The solid undergoes a chemical change by reacting with the water.
A) The heat from the warm water melts the solid, making it a liquid.
B) Nothing happens, because potassium chloride is insoluble in water.
C) The solid KCl breaks apart into separate K and Cl atoms by interacting with the water molecules.
D) The water molecules surround each ion in the solid KCl, separating the K ions from the Cl ions.
E) The solid undergoes a chemical change by reacting with the water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following intermolecular forces or bonds is primarily responsible for the solubility of methanol ( CH3OH) in water?
A) Ion-dipole force
B) Debye force
C) Ionic bonding
D) Covalent bonding
E) Hydrogen bonding
A) Ion-dipole force
B) Debye force
C) Ionic bonding
D) Covalent bonding
E) Hydrogen bonding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following nonpolar molecules has the highest boiling point?
A) N2
B) C2H4
C) F2
D) O2
E) CS2
A) N2
B) C2H4
C) F2
D) O2
E) CS2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following liquids has the lowest enthalpy of vaporization?
A) C4H10
B) C5H12
C) C6H14
D) C7H16
E) C8H18
A) C4H10
B) C5H12
C) C6H14
D) C7H16
E) C8H18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
As pure molecular solids, which of the following exhibit only induced dipole/induced dipole forces: CO2,
CH2Cl2, and SO2?
A) CO2 only
B) CH2Cl2 only
C) SO2 only
D) CO2 and CH2Cl2
E) CO2 and SO2
CH2Cl2, and SO2?
A) CO2 only
B) CH2Cl2 only
C) SO2 only
D) CO2 and CH2Cl2
E) CO2 and SO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
For which of the following pure solids is it necessary to break covalent bonds to make a liquid or gas: C(graphite), CO2(s), C60(s), and C(diamond)?
A) C(graphite) only
B) CO2(s) only
C) CO2(s) and C60(s)
D) C(graphite), C60(s) and C(diamond)
E) C(graphite) and C(diamond)
A) C(graphite) only
B) CO2(s) only
C) CO2(s) and C60(s)
D) C(graphite), C60(s) and C(diamond)
E) C(graphite) and C(diamond)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The vapor pressure of a given liquid will increase if
A) the liquid is moved to a container in which its surface area is very much larger.
B) the volume of the liquid is increased.
C) the temperature is increased.
D) the volume of the vapor phase is increased.
E) a more volatile liquid is added to the given liquid.
A) the liquid is moved to a container in which its surface area is very much larger.
B) the volume of the liquid is increased.
C) the temperature is increased.
D) the volume of the vapor phase is increased.
E) a more volatile liquid is added to the given liquid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
London dispersion forces are the only significant factor affecting boiling point for all the following except?
A) Kr
B) NH3
C) CBr4
D) Cl2
E) CH4
A) Kr
B) NH3
C) CBr4
D) Cl2
E) CH4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following liquids would you expect to have the lowest vapor pressure at room temperature?
A) Ethylene glycol (bp, 198°C)
B) Benzene (bp, 80°C)
C) Ethanol (bp, 78.3°C)
D) Chloroform (bp, 62°C)
E) n-pentane (bp, 36.1°C)
A) Ethylene glycol (bp, 198°C)
B) Benzene (bp, 80°C)
C) Ethanol (bp, 78.3°C)
D) Chloroform (bp, 62°C)
E) n-pentane (bp, 36.1°C)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is the strongest intermolecular force present in NH3?
A) London dispersion
B) Hydrogen-bonding
C) Debye force
D) Ion-dipole
E) None of these
A) London dispersion
B) Hydrogen-bonding
C) Debye force
D) Ion-dipole
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The normal boiling points of some group 7A hydrides are tabulated below.
Which of the following intermolecular forces or bonds is responsible for the high boiling point of HF relative to HCl and HBr?
A) Hydrogen bonding
B) Dipole-induced dipole force
C) Induced dipole-induced dipole force
D) Covalent bonding
E) Ion-induced dipole force
Which of the following intermolecular forces or bonds is responsible for the high boiling point of HF relative to HCl and HBr?
A) Hydrogen bonding
B) Dipole-induced dipole force
C) Induced dipole-induced dipole force
D) Covalent bonding
E) Ion-induced dipole force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following molecules has the lowest boiling point?
A) CH4
B) CHCl3
C) CH2Cl2
D) CH3Cl
E) CCl4
A) CH4
B) CHCl3
C) CH2Cl2
D) CH3Cl
E) CCl4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Ammonia (NH3) is used as a refrigerant. At its boiling point of -33 °C, the standard enthalpy of vaporization of ammonia is 23.3 kJ/mol. How much heat is released when 50.0 g of ammonia is condensed at -33 °C?
A) -0.466 kJ
B) -7.94 kJ
C) -36.6 × 103 kJ
D) -68.4 kJ
E) -1.17 × 103 kJ
A) -0.466 kJ
B) -7.94 kJ
C) -36.6 × 103 kJ
D) -68.4 kJ
E) -1.17 × 103 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Arrange Cl2, ICl, and Br2 in order from lowest to highest boiling point.
A) Cl2 < Br2 < ICl
B) Cl2 < ICl < Br2
C) ICl < Cl2 < Br2
D) Br2 < Cl2 < ICl
E) Br2 < ICl < Cl2
A) Cl2 < Br2 < ICl
B) Cl2 < ICl < Br2
C) ICl < Cl2 < Br2
D) Br2 < Cl2 < ICl
E) Br2 < ICl < Cl2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following molecules has the lowest boiling temperature?
A) C4H10
B) C5H12
C) C6H14
D) C7H16
E) C8H18
A) C4H10
B) C5H12
C) C6H14
D) C7H16
E) C8H18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Equilibrium is established between a liquid and its vapor when
A) the rate of evaporation equals the rate of condensation.
B) equal masses exist in the liquid and gas phases.
C) equal concentrations (in molarity) exist in the liquid and gas phases.
D) all the liquid has evaporated.
E) the liquid ceases to evaporate and the gas ceases to condense.
A) the rate of evaporation equals the rate of condensation.
B) equal masses exist in the liquid and gas phases.
C) equal concentrations (in molarity) exist in the liquid and gas phases.
D) all the liquid has evaporated.
E) the liquid ceases to evaporate and the gas ceases to condense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following compounds has a boiling point closest to that of argon?
A) F2
B) Cl2
C) HCl
D) NaF
E) HF
A) F2
B) Cl2
C) HCl
D) NaF
E) HF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
On a relative basis, the weaker the intermolecular forces in a substance are,
A) the larger is its heat of vaporization.
B) the more it deviates from the ideal gas law.
C) the greater is its vapor pressure at a particular temperature.
D) the larger is its molar heat capacity as a liquid.
E) the higher is its boiling point.
A) the larger is its heat of vaporization.
B) the more it deviates from the ideal gas law.
C) the greater is its vapor pressure at a particular temperature.
D) the larger is its molar heat capacity as a liquid.
E) the higher is its boiling point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
List all the intermolecular forces present in pure acetone. 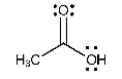
A) hydrogen bonding only
B) dipole-dipole force only
C) dipole-dipole force and London dispersion forces
D) hydrogen bonding and London dispersion forces
E) hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole force, and London dispersion forces

A) hydrogen bonding only
B) dipole-dipole force only
C) dipole-dipole force and London dispersion forces
D) hydrogen bonding and London dispersion forces
E) hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole force, and London dispersion forces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following has the greatest boiling point?
A) Cl2
B) I2
C) O2
D) Ar
E) Xe
A) Cl2
B) I2
C) O2
D) Ar
E) Xe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
At its boiling point of 58.8 °C, 2.82 kJ of heat is required to vaporize 15.0 g of bromine (Br2). What is the molar enthalpy of vaporization of bromine?
A) 0.264 kJ/mol
B) 0.188 kJ/mol
C) 30.0 kJ/mol
D) 5.33 kJ/mol
E) 56.76 kJ/mol
A) 0.264 kJ/mol
B) 0.188 kJ/mol
C) 30.0 kJ/mol
D) 5.33 kJ/mol
E) 56.76 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
At 80.0 °C, water has an equilibrium vapor pressure of 355.1 mm Hg. If 4.22 g H2O is sealed in an evacuated 5.00 L flask and heated to 80.0 °C, what mass of H2O will be found in the gas phase when liquid-vapor equilibrium is established? Assume any liquid remaining in the flask has a negligible volume. (R = 0.08206 L⋅atm/mol⋅K, 1 atm = 760 mm Hg)
A) 0.689 g
B) 1.45 g
C) 1.67 g
D) 2.77 g
E) 4.22 g
A) 0.689 g
B) 1.45 g
C) 1.67 g
D) 2.77 g
E) 4.22 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Ethanol has an enthalpy of vaporization of 42.3 kJ/mol. The compound has a vapor pressure of 1.00 atm at 78.3 °C. At what temperature is the vapor pressure equal to 0.800 atm? (R = 8.314 J/K ⋅ mol)
A) -83.8 °C
B) -24.4 °C
C) 62.6 °C
D) 73.0 °C
E) 78.0 °C
A) -83.8 °C
B) -24.4 °C
C) 62.6 °C
D) 73.0 °C
E) 78.0 °C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
________ is a measure of the degree to which the electron cloud surrounding an atom or molecule can be distorted in an electric field.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A particular compound has an enthalpy of vaporization of 29600 J/mol. At 274 K it has a vapor pressure of 103 mmHg. What is its vapor pressure at 309 K? (R = 8.31 J/K·mol; 1 atm = 760 mmHg)
A) 98.6 mmHg
B) 241 mmHg
C) 23.6 mmHg
D) 449 mmHg
E) 107 mmHg
A) 98.6 mmHg
B) 241 mmHg
C) 23.6 mmHg
D) 449 mmHg
E) 107 mmHg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The heat of vaporization of benzene (C6H6) is 30.7 kJ/mol at its boiling point of 80.1 °C. How much energy in the form of heat is required to vaporize 110 g benzene at its boiling point?
A) 0.279 kJ
B) 3.58 kJ
C) 21.8 kJ
D) 43.2 kJ
E) kJ
A) 0.279 kJ
B) 3.58 kJ
C) 21.8 kJ
D) 43.2 kJ
E) kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Xenon has an enthalpy of vaporization of 12.6 kJ/mol and a vapor pressure of 1.00 atm at -108.0 °C. What is the vapor pressure of xenon at -148.0 °C? (R = 8.314 J/K⋅mol)
A) 0.053 atm
B) 0.73 atm
C) 0.93 atm
D) 0.99 atm
E) 19 atm
A) 0.053 atm
B) 0.73 atm
C) 0.93 atm
D) 0.99 atm
E) 19 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A cup of oil takes longer to pour from a glass than a cup of water. A liquid's resistance to flow is referred to as its ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Freon-113, C2Cl3F3, has an enthalpy of vaporization of 27.0 kJ/mol and a normal boiling point of 48.0 °C. What is the vapor pressure (in atm) of Freon-113 at 22.0 °C? (R = 8.314 J/K⋅mol)
A) 0.21 atm
B) 0.35 atm
C) 0.41 atm
D) 0.46 atm
E) 4.4 atm
A) 0.21 atm
B) 0.35 atm
C) 0.41 atm
D) 0.46 atm
E) 4.4 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Sulfur dioxide has a vapor pressure of 462.7 mm Hg at -21.0 °C and a vapor pressure of 140.5 mm Hg at -44.0 °C. What is the enthalpy of vaporization of sulfur dioxide? (R = 8.314 J/K⋅mol)
A) 0.398 kJ/mol
B) 6.33 kJ/mol
C) 14.0 kJ/mol
D) 24.9 kJ/mol
E) 39.8 kJ/mol
A) 0.398 kJ/mol
B) 6.33 kJ/mol
C) 14.0 kJ/mol
D) 24.9 kJ/mol
E) 39.8 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is the slope of the line that illustrates the relationship between the natural logarithm of the vapor pressure of a gas and the reciprocal of its temperature (in kelvin)?
A)
B)
C) T
D)
E)
A)
B)
C) T
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is not a characteristic of volatile liquids?
A) Volatile liquids are easily vaporized.
B) Volatile liquids have relatively high vapor pressures.
C) Volatile liquids have strong cohesive forces.
D) Volatile liquids have weak intermolecular forces.
E) All of these
A) Volatile liquids are easily vaporized.
B) Volatile liquids have relatively high vapor pressures.
C) Volatile liquids have strong cohesive forces.
D) Volatile liquids have weak intermolecular forces.
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The vapor pressure of nitric acid is 26.6 mmHg at 10.0 °C and 208 mmHg at 50.0 °C. Using this information, calculate the heat of vaporization (ΔvapH) of nitric acid. (R = 8.314 J/K ⋅ mol)
A) 25.6 kJ/mol
B) 39.1 kJ/mol
C) 48.4 kJ/mol
D) 225 kJ/mol
E) 566 kJ/mol
A) 25.6 kJ/mol
B) 39.1 kJ/mol
C) 48.4 kJ/mol
D) 225 kJ/mol
E) 566 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A liquid has an enthalpy of vaporization of 30.3 kJ/mol. At 262 K it has a vapor pressure of 121 mmHg. What is the normal boiling point of this liquid? (R = 8.314 J/(K· mol))
A) 278 K
B) 302 K
C) 262 K
D) 248 K
E) 231 K
A) 278 K
B) 302 K
C) 262 K
D) 248 K
E) 231 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In a certain mountain range, water boils at 93°C. What is the atmospheric pressure under these conditions? The enthalpy of vaporization of water at 100°C is 40.7 kJ/mol. (R = 8.314 J/K·mol; 1 atm = 760 mmHg)
A) 2040 mmHg
B) 278 mmHg
C) 591 mmHg
D) 977 mmHg
E) 283 mmHg
A) 2040 mmHg
B) 278 mmHg
C) 591 mmHg
D) 977 mmHg
E) 283 mmHg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
For a particular liquid, raising its temperature from 331 K to 351 K causes its vapor pressure to double. What is the enthalpy of vaporization of this liquid? (R = 8.314 J/K · mol)
A) 34 kJ/mol
B) 288 kJ/mol
C) 2 kJ/mol
D) 244 kJ/mol
E) 115 kJ/mol
A) 34 kJ/mol
B) 288 kJ/mol
C) 2 kJ/mol
D) 244 kJ/mol
E) 115 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Above its critical temperature and pressure, a substance becomes a(n) ________ fluid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The ________ equation relates the equilibrium vapor pressure of a volatile liquid to the molar enthalpy of vaporization at a given temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
When a glass tube with a small diameter is placed in water, the water rises in the tube. This is known as ________ action.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Mount Everest rises to a height of 8.850 × 103 m above sea level. At this height, the atmospheric pressure is 231 mm Hg. At what temperature (in °C) will water boil at the summit of Mount Everest? The vapor pressure of water at 373 K is 760.0 mm Hg. (ΔvapH° for H2O = 40.7 kJ/mol and R = 8.314 J/K ⋅ mol)
A) 4.07 °C
B) 69.0 °C
C) 72 °C
D) 87 °C
E) 364 °C
A) 4.07 °C
B) 69.0 °C
C) 72 °C
D) 87 °C
E) 364 °C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If 4.61 g of water is sealed in an evacuated 3.35 L flask and heated to the normal boiling point of 373 K, what is the pressure in the flask? (R = 0.08206 L⋅atm/mol⋅K)
A) 0.214 atm
B) 0.428 atm
C) 1.00 atm
D) 2.34 atm
E) 42.1 atm
A) 0.214 atm
B) 0.428 atm
C) 1.00 atm
D) 2.34 atm
E) 42.1 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Make a sketch to show the hydrogen bonding between two acetic acid molecules (HC2H3O2).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which ion, K+ or Ca2+, is expected to have the more negative enthalpy of hydration? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following molecules has the highest enthalpy of vaporization?
A) N2
B) O2
C) I2
D) CH4
E) C6H6
A) N2
B) O2
C) I2
D) CH4
E) C6H6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Two important allotropes of phosphorus are white phosphorus and red phosphorus. White phosphorus, P4, has a melting point of 44.1 °C and spontaneously reacts with oxygen. Red phosphorus, a network solid, melts at 280 °C and is stable in air. Use your knowledge of intermolecular and intramolecular bonding to explain why these two forms of the same element have such different properties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



