Deck 2: Lets Review: the Tools of Quantitative Chemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/73
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Lets Review: the Tools of Quantitative Chemistry
1
Which method is correct for converting kelvin to Celsius?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
2
Which is the largest mass?
A) 10 dg
B) 10 ng
C) 10 mg
D) 10 pg
E) 10 cg
A) 10 dg
B) 10 ng
C) 10 mg
D) 10 pg
E) 10 cg
10 dg
3
Light with a wavelength of 1.5 × 10-8 m is in the X-ray region of the electromagnetic spectrum. What is the wavelength of this light in picometers (pm)?
A) 1.5 × 10-80 pm
B) 1.5 × 10-20 pm
C) 1.5 × 10-1 pm
D) 1.5 × 104 pm
E) 1.5 × 107 pm
A) 1.5 × 10-80 pm
B) 1.5 × 10-20 pm
C) 1.5 × 10-1 pm
D) 1.5 × 104 pm
E) 1.5 × 107 pm
1.5 × 104 pm
4
A particular liquid boils at -374°F. What is its boiling point on the Kelvin scale?
A) 83 K
B) 65 K
C) 47 K
D) 97 K
E) 165 K
A) 83 K
B) 65 K
C) 47 K
D) 97 K
E) 165 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is the smallest mass?
A) 1.5 × 108 pg
B) 1.5 × 106 ng
C) 1.5 × 103 μg
D) 1.5 × 10-1 mg
E) 1.5 × 10-5 g
A) 1.5 × 108 pg
B) 1.5 × 106 ng
C) 1.5 × 103 μg
D) 1.5 × 10-1 mg
E) 1.5 × 10-5 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How many nutritional calories are equivalent to 1150 kJ?
A) 0.10 Cal
B) 1.15 Cal
C) 275 Cal
D) 4.8 × 103 Cal
E) 3.6 × 10-3 Cal
A) 0.10 Cal
B) 1.15 Cal
C) 275 Cal
D) 4.8 × 103 Cal
E) 3.6 × 10-3 Cal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Express the volume 622.8 cm3 in liters.
A) 6.228 L
B) 0.06228 L
C) 0.6228 L
D) 62.28 L
E) 622.8 L
A) 6.228 L
B) 0.06228 L
C) 0.6228 L
D) 62.28 L
E) 622.8 L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the area of nanotechnology, particles defined as nanoparticles range in size from 1 nm to 2500 nm. One nm is equivalent to 1 × 10-9 m. If the size of the particles that make up a particular material is 5.34 × 10-8 cm, what is this size in nanometers?
A) 53,400 nm
B) 5.34 nm
C) 0.534 nm
D) 5340 nm
E) 534 nm
A) 53,400 nm
B) 5.34 nm
C) 0.534 nm
D) 5340 nm
E) 534 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The distance between atoms is sometimes given in picometers, where 1 pm is equivalent to 1 × 10-12 m. If the distance between the layers of atoms in a particular compound is given as 328 pm, what is the distance in cm?
A) 3.28 × 10-6 cm
B) 3.28 × 10-14 cm
C) 3.28 × 10-12 cm
D) 3.28 × 10-8 cm
E) 3.28 × 10-10 cm
A) 3.28 × 10-6 cm
B) 3.28 × 10-14 cm
C) 3.28 × 10-12 cm
D) 3.28 × 10-8 cm
E) 3.28 × 10-10 cm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is the largest volume?
A) 5.0 × 102 cm3
B) 5.0 × 10-4 L
C) 5.0 × 103 mL
D) 5.0 × 10-1 L
E) 5.0 × 105 μL
A) 5.0 × 102 cm3
B) 5.0 × 10-4 L
C) 5.0 × 103 mL
D) 5.0 × 10-1 L
E) 5.0 × 105 μL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following volumes are equivalent to 75 L? 1.75 cm3
2)7.5 × 104 mL
3)0.0075 kL
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2
E) 1, 2, and 3
2)7.5 × 104 mL
3)0.0075 kL
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2
E) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Order the four metric units provided from smallest to largest.
1) liter
2) centiliter
3) microliter
4) milliliter
A) liter < centiliter < milliliter < microliter
B) microliter < milliliter < centiliter < liter
C) milliliter < microliter < centiliter < liter
D) centiliter < microliter < liter < milliliter
E) liter < centiliter < microliter < milliliter
1) liter
2) centiliter
3) microliter
4) milliliter
A) liter < centiliter < milliliter < microliter
B) microliter < milliliter < centiliter < liter
C) milliliter < microliter < centiliter < liter
D) centiliter < microliter < liter < milliliter
E) liter < centiliter < microliter < milliliter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The boiling point of liquid argon is 87.3 K. What is the boiling point in Celsius degrees?
A) 189.1 °C
B) -185.9 °C
C) 87.3 °C
D) 360.5 °C
E) -210.7 °C
A) 189.1 °C
B) -185.9 °C
C) 87.3 °C
D) 360.5 °C
E) -210.7 °C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The melting point of a solid is 39 °F. This corresponds to _____.
A) 295 K
B) 312 K
C) 286 K
D) 277 K
E) 312 K.
A) 295 K
B) 312 K
C) 286 K
D) 277 K
E) 312 K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
7.2 seconds contain this many picoseconds.
A) 7.2 × 109
B) 7.2 × 1012
C) 7.2 × 10-9
D) 7.2 × 10-12
E) 7.2 × 1015
A) 7.2 × 109
B) 7.2 × 1012
C) 7.2 × 10-9
D) 7.2 × 10-12
E) 7.2 × 1015

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How many joules are equivalent to 450 calories?
A) 0.45 J
B) 4.5 × 102 J
C) 9.3 × 10-3 J
D) 1.9 × 103 J
E) 4.5 × 105 J
A) 0.45 J
B) 4.5 × 102 J
C) 9.3 × 10-3 J
D) 1.9 × 103 J
E) 4.5 × 105 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The melting point of a certain solid is -27°C. This corresponds to
A) 9°F.
B) -33°F.
C) -17°F.
D) -106°F.
E) 17°F.
A) 9°F.
B) -33°F.
C) -17°F.
D) -106°F.
E) 17°F.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The figure below depicts a shooting target. The black dots represent the shots fired by a shooter. 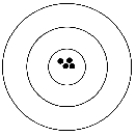 Which of the following best describes the shooter's results?
Which of the following best describes the shooter's results?
A) Accurate and precise.
B) Precise but not accurate.
C) Neither accurate nor precise.
D) Accurate but not precise.
E) None of the these.
 Which of the following best describes the shooter's results?
Which of the following best describes the shooter's results?A) Accurate and precise.
B) Precise but not accurate.
C) Neither accurate nor precise.
D) Accurate but not precise.
E) None of the these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The wavelength of light emitted from a particular red diode laser is 651 nm. What is the wavelength in meters?
A) 6.51 × 1011 m
B) 6.51 × 10-2 m
C) 6.51 × 10-4 m
D) 6.51 × 10-7 m
E) 6.51 × 10-9 m
A) 6.51 × 1011 m
B) 6.51 × 10-2 m
C) 6.51 × 10-4 m
D) 6.51 × 10-7 m
E) 6.51 × 10-9 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The melting point of a particular solid is 2863 K. This corresponds to
A) 4694°F.
B) 3136°C.
C) 2529°C.
D) 4630°F.
E) 1471°F.
A) 4694°F.
B) 3136°C.
C) 2529°C.
D) 4630°F.
E) 1471°F.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the correct answer to the following expression? 8.67 × 10-10 + 6.22 × 10-12
A) 8.7322 × 10-10
B) 8.732 × 10-10
C) 9 × 10-10
D) 8.7 × 10-10
E) 8.73 × 10-10
A) 8.7322 × 10-10
B) 8.732 × 10-10
C) 9 × 10-10
D) 8.7 × 10-10
E) 8.73 × 10-10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Express the result of the following calculation in scientific notation: 437 cm × 885 cm
A) 38.7 × 104 cm2
B) 38.7 × 105 cm2
C) 4 × 104 cm2
D) 4 × 106 cm2
E) 4 × 105 cm2
A) 38.7 × 104 cm2
B) 38.7 × 105 cm2
C) 4 × 104 cm2
D) 4 × 106 cm2
E) 4 × 105 cm2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Assuming a large number of measurements is used to calculate the average of measurements, slightly more than _____ of the values collected are expected to be within two standard deviations
A) 50%
B) 68%
C) 83%
D) 95%
E) 100%
A) 50%
B) 68%
C) 83%
D) 95%
E) 100%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Express the result of the following calculation in scientific notation: 0.0573 cm2 ÷ 81.8 cm
A) 7 × 105 cm
B) 7 × 104 cm
C) 7 × 10-3 cm
D) 7 × 10-4 cm
E) 1 × 103 cm
A) 7 × 105 cm
B) 7 × 104 cm
C) 7 × 10-3 cm
D) 7 × 10-4 cm
E) 1 × 103 cm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Using the rules of significant figures, calculate the following:
A) 4.825
B) 4.8249
C) 4.8
D) 4.82
E) 4.82486
A) 4.825
B) 4.8249
C) 4.8
D) 4.82
E) 4.82486

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
How many significant figures are there in the value 0.0490 g/mL?
A) 4
B) 3
C) 2
D) 5
E) 6
A) 4
B) 3
C) 2
D) 5
E) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Convert 1.400× 10-8 liters to nanoliters and express the answer in fixed notation using the correct number of significant figures.
A) 14 nL
B) 14.0 nL
C) 14.00 nL
D) 1.40 nL
E) 0.1400 nL
A) 14 nL
B) 14.0 nL
C) 14.00 nL
D) 1.40 nL
E) 0.1400 nL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
As the standard deviation of an average of several measurements increases, _____.
A) the accuracy of the measurement increases.
B) the precision of the measurement increases.
C) the accuracy and precision of the measurement decreases.
D) the accuracy of the measurement decreases.
E) the precision of the measurement decreases.
A) the accuracy of the measurement increases.
B) the precision of the measurement increases.
C) the accuracy and precision of the measurement decreases.
D) the accuracy of the measurement decreases.
E) the precision of the measurement decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Calculate the following:
A) 1 × 10-220
B) 1 × 10540
C) 1 × 10-740
D) 1 × 10-940
E) 1 × 10-420
A) 1 × 10-220
B) 1 × 10540
C) 1 × 10-740
D) 1 × 10-940
E) 1 × 10-420

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A student uses a balance to determine the mass of an object as 5.719 grams. The correct mass of the object is 5.586 grams. What is the percent error in the student's mass determination?
A) 2.38%
B) 0.133%
C) 13.3%
D) 74.3%
E) 97.7%
A) 2.38%
B) 0.133%
C) 13.3%
D) 74.3%
E) 97.7%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Using the rules of significant figures, calculate the following: (2.335 + 7.026) ÷ 2.57 = _____
A) 3.642
B) 3.6424
C) 3.6
D) 3.64
E) 3.64241
A) 3.642
B) 3.6424
C) 3.6
D) 3.64
E) 3.64241

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Convert 0.390 ng to milligrams and express the answer in scientific notation using the correct number of significant figures.
A) 3.90 × 10-5 mg
B) 3.90 × 10-7 mg
C) 3.9 × 10-7 mg
D) 0.390 × 10-8 mg
E) 0.390 × 10-7 mg
A) 3.90 × 10-5 mg
B) 3.90 × 10-7 mg
C) 3.9 × 10-7 mg
D) 0.390 × 10-8 mg
E) 0.390 × 10-7 mg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The number of significant figures in 2.1948 × 10-9 nm is _____.
A) 5
B) 6
C) 3
D) 7
E) 4
A) 5
B) 6
C) 3
D) 7
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
How many significant figures are there in the number 4.700?
A) 1
B) 5
C) 3
D) 4
E) 2
A) 1
B) 5
C) 3
D) 4
E) 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Express 0.00580 in exponential notation.
A) 5.80 × 103
B) 5.8 × 10-3
C) 5.80 × 10-3
D) 5.8 × 103
E) 5.800 × 10-3
A) 5.80 × 103
B) 5.8 × 10-3
C) 5.80 × 10-3
D) 5.8 × 103
E) 5.800 × 10-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The volume of a carbon atom is 1.9 × 10-30 m3. What is the approximate radius of the atom in picometers (pm)? The volume of a sphere is (4/3)πr3.
A) 77 pm
B) 520 pm
C) 770 pm
D) 3.0 × 102 pm
E) 52 pm
A) 77 pm
B) 520 pm
C) 770 pm
D) 3.0 × 102 pm
E) 52 pm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Express 2.260 × 101 in fixed notation.
A) 0.2260
B) 2.260
C) 2.260..
D) 22.6
E) 22.60
A) 0.2260
B) 2.260
C) 2.260..
D) 22.6
E) 22.60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Two students independently determine the volume of water delivered by a 10.00-mL pipet. Each student takes 8 measurements, then computes the average volume delivered and the standard deviation. The results are tabulated below.
Which statement best describes the results?
A) A: good precision, good accuracy. B: good precision, good accuracy.
B) A: good precision, poor accuracy. B: poor precision, good accuracy.
C) A: poor precision, good accuracy. B: good precision, poor accuracy.
D) A: poor precision, poor accuracy. B: good precision, good accuracy.
E) A: poor precision, poor accuracy. B: poor precision, poor accuracy.
Which statement best describes the results?
A) A: good precision, good accuracy. B: good precision, good accuracy.
B) A: good precision, poor accuracy. B: poor precision, good accuracy.
C) A: poor precision, good accuracy. B: good precision, poor accuracy.
D) A: poor precision, poor accuracy. B: good precision, good accuracy.
E) A: poor precision, poor accuracy. B: poor precision, poor accuracy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Round 0.00274485 to 1 significant figure.
A) 0.00
B) 0.003
C) 0.0027
D) 0.00274
E) 0.002745
A) 0.00
B) 0.003
C) 0.0027
D) 0.00274
E) 0.002745

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Carry out the following calculation and report your answer to the correct number of sig figs:
A) 1.6
B) 1.57
C) 1.566
D) 1.5662
E) 1.56625
A) 1.6
B) 1.57
C) 1.566
D) 1.5662
E) 1.56625

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A thin sheet of iridium metal that is 2.70 cm by 5.93 cm has a mass of 16.1 g and a thickness of 0.444 mm. What is the density of iridium?
A) 22.600 g/cm3
B) 2.270 g/cm3
C) 1.14 × 102 g/cm3
D) 0.044 g/cm3
E) 0.442 g/cm3
A) 22.600 g/cm3
B) 2.270 g/cm3
C) 1.14 × 102 g/cm3
D) 0.044 g/cm3
E) 0.442 g/cm3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
How many 500-mg aspirin tablets can be made from 50.0 kg of aspirin?
A) 10,000,000
B) 1,000,000
C) 1000
D) 10,000
E) 100,000
A) 10,000,000
B) 1,000,000
C) 1000
D) 10,000
E) 100,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Convert 42.12 cm3 to cubic inches (in3) given that 1 inch = 2.54 cm (exact).
A) 2.570 in3
B) 16.580 in3
C) 107.0 in3
D) 690.200 in3
E) 0.3890 in3
A) 2.570 in3
B) 16.580 in3
C) 107.0 in3
D) 690.200 in3
E) 0.3890 in3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The density of a particular solid is 7.62 g/cm3 at 25°C. What is its density in kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m3)?
A) 7.62 × 1010
B) 7.62 × 101
C) 7.62 × 10-2
D) 7.62 × 103
E) 7.62 × 107
A) 7.62 × 1010
B) 7.62 × 101
C) 7.62 × 10-2
D) 7.62 × 103
E) 7.62 × 107

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is the volume of a cube that has an edge length of 0.011 m?
A) 1.3 × 10-3 m3
B) 1.3 × 10-3 km3
C) 1.3 × 10-3 cm3
D) 1.3 × 10-3 mm3
E) 1.3 cm3
A) 1.3 × 10-3 m3
B) 1.3 × 10-3 km3
C) 1.3 × 10-3 cm3
D) 1.3 × 10-3 mm3
E) 1.3 cm3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The SI unit for the diffusion coefficient is m2/s, but older texts sometimes report diffusion coefficients in units of in2/min. What is the value of a diffusion coefficient of 21.3 in2/min expressed in SI units? (2.54 cm = 1 in exactly)
A) 9.02 × 10-3 m2/s
B) 3.25 × 105 m2/s
C) 14.0 m2/s
D) 5.50 × 102 m2/s
E) 2.29 × 10-4 m2/s
A) 9.02 × 10-3 m2/s
B) 3.25 × 105 m2/s
C) 14.0 m2/s
D) 5.50 × 102 m2/s
E) 2.29 × 10-4 m2/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If a gallon (3.78 L) of latex paint can cover 365 ft2 of the surface of a wall, what is the average thickness of one coat of paint (in millimeters)? (12 in = 1 ft, 2.54 cm = 1 in)
A) 1.11 × 10-1 mm
B) 2.83 × 10-1 mm
C) 4.64 × 10-1 mm
D) 4.89 × 10-1 mm
E) 3.40 mm
A) 1.11 × 10-1 mm
B) 2.83 × 10-1 mm
C) 4.64 × 10-1 mm
D) 4.89 × 10-1 mm
E) 3.40 mm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Silver chloride (AgCl) is relatively insoluble in water. At 25 °C, 1.3 × 103 L of water is needed to dissolve 2.5 g of AgCl. What mass (in milligrams) of AgCl will dissolve in 1.0 L of water?
A) 1.9 × 10-3 mg
B) 1.9 mg
C) 0.52 mg
D) 520 mg
E) 1.9 × 10-6 mg
A) 1.9 × 10-3 mg
B) 1.9 mg
C) 0.52 mg
D) 520 mg
E) 1.9 × 10-6 mg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
You can identify a metal by carefully determining its density. A 29.51 g sample of an unknown metal is 1.50 cm long, 2.50 cm wide, and 1.00 cm thick. What is the possible identity of the element?
A) Nickel; density = 8.90 g/cm3
B) Aluminum; density = 2.70 g/cm3
C) Silver; density = 10.5 g/cm3
D) Iron; density = 7.87 g/cm3
E) Chromium; density = 7.20 g/cm3
A) Nickel; density = 8.90 g/cm3
B) Aluminum; density = 2.70 g/cm3
C) Silver; density = 10.5 g/cm3
D) Iron; density = 7.87 g/cm3
E) Chromium; density = 7.20 g/cm3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What length of a cylindrical piece of tungsten wire having a radius of 2.27 mm has a mass of 10.0 g? The density of tungsten is 19.25 g/cm3 and Volume = πr2h.
A) 3.21 × 10-4 m
B) 3.12 × 101 m
C) 3.21 × 10-2 m
D) 3.12 × 10-1 m
E) 3.12 × 10-3 m
A) 3.21 × 10-4 m
B) 3.12 × 101 m
C) 3.21 × 10-2 m
D) 3.12 × 10-1 m
E) 3.12 × 10-3 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Calculate the mass of silver that occupies the same volume as 22.1 g of cobalt. The density of cobalt is 8.90 g/cm3 and the density of silver is 10.50 g/cm3.
A) 4.23 g
B) 26.1 g
C) 2 × 103 g
D) 0.0534 g
E) 0.236 g
A) 4.23 g
B) 26.1 g
C) 2 × 103 g
D) 0.0534 g
E) 0.236 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
How many feet (ft) make up 0.397 km if 1 mi = 1.609 km and 5280 ft = 1 mi?
A) 1303.10 ft
B) ft
C) ft
D) 3370.000 ft
E) ft
A) 1303.10 ft
B) ft
C) ft
D) 3370.000 ft
E) ft

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
How many cubic millimeters equal one cubic meter?
A) 104
B) 10-9
C) 103
D) 109
E) 10-3
A) 104
B) 10-9
C) 103
D) 109
E) 10-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A car averages 26.5 miles per gallon of gasoline. How many liters of gasoline will be needed for a trip of 621 km? Some conversion factors that may be helpful are the following: 1 qt = 0.946 L 1 mile = 1.609 km 4 qt = 1 gal (exact) 1 ft = 12 in (exact)
A) 6 × 101 L
B) 7 × 103 L
C) 3 × 103 L
D) 1 × 102 L
E) 4 × 104 L
A) 6 × 101 L
B) 7 × 103 L
C) 3 × 103 L
D) 1 × 102 L
E) 4 × 104 L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A cylinder has a radius of 2.38 mm and a height of 175 mm. Calculate the volume of the cylinder in liters. (Volume = πr2h)
A) 3.11 × 10-3 L
B) 3.11 × 10-2 L
C) 0.311 L
D) 3.11 L
E) 3.11 × 103 L
A) 3.11 × 10-3 L
B) 3.11 × 10-2 L
C) 0.311 L
D) 3.11 L
E) 3.11 × 103 L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The volume of space occupied by a beryllium atom is 6.0 × 10-30 m3. What is this volume in units of nm3?
A) 6.0 × 10-57 nm
B) 6.0 × 10-21 nm
C) 6.0 × 10-12 nm
D) 6.0 × 10-3 nm
E) 6.0 × 106 nm
A) 6.0 × 10-57 nm
B) 6.0 × 10-21 nm
C) 6.0 × 10-12 nm
D) 6.0 × 10-3 nm
E) 6.0 × 106 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A 4.75 cm3 sample of solid gallium metal has a density of 5.910 g/cm3. What volume does this sample of gallium occupy in its liquid state? The density of liquid gallium is 6.100 g/cm3.
A) 4.60 cm3
B) 4.90 cm3
C) 0.13 cm3
D) 171.00 cm3
E) 0.20 cm3
A) 4.60 cm3
B) 4.90 cm3
C) 0.13 cm3
D) 171.00 cm3
E) 0.20 cm3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The speed of light in a vacuum is 3.00 × 108 m/s. What is the speed of light in units of kilometers per hour?
A) 1.20 × 10-2 km/hr
B) 8.33 × 101 km/hr
C) 8.33 × 107 km/hr
D) 1.08 × 109 km/hr
E) 1.08 × 1015 km/hr
A) 1.20 × 10-2 km/hr
B) 8.33 × 101 km/hr
C) 8.33 × 107 km/hr
D) 1.08 × 109 km/hr
E) 1.08 × 1015 km/hr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What volume of a pure liquid (density 0.720 g/mL) has a mass of 0.420 kg?
A) 5.83 × 102 mL
B) 1.71 × 10-3 mL
C) 3.02 × 10-1 mL
D) 1.710 × 105 mL
E) 5.83 × 10-1 mL
A) 5.83 × 102 mL
B) 1.71 × 10-3 mL
C) 3.02 × 10-1 mL
D) 1.710 × 105 mL
E) 5.83 × 10-1 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Calcium carbonate, or limestone, is relatively insoluble in water. At 25 °C, only 5.8 mg will dissolve in 1.0 liter of water. What volume of water is needed to dissolve 5.0 g of calcium carbonate?
A) 4.6 × 10-3 L
B) 3.0 × 10-2 L
C) 1.4 × 102 L
D) 3.4 × 102 L
E) 8.6 × 102 L
A) 4.6 × 10-3 L
B) 3.0 × 10-2 L
C) 1.4 × 102 L
D) 3.4 × 102 L
E) 8.6 × 102 L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Assuming the density of water is 1.00 g/cm3, the mass of 1.0 cubic meter (m3) of water is _____
g.
g.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The absolute zero point on the Kelvin scale is equal to _____.
A) -273.15 °C
B) 0 °C
C) 14.5 °C
D) 25 °C
E) -373.15 ⁰C
A) -273.15 °C
B) 0 °C
C) 14.5 °C
D) 25 °C
E) -373.15 ⁰C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Significant figures allow us to estimate uncertainty in calculated values. In some circumstances, following significant figure rules can lead to estimates of uncertainty that are too high or low. This is the case for the mathematical expression below.
99 × 1.02 = 100.98
Following the rules governing significant figures in multiplication, the answer can be rounded to 1.0 × 102. What is wrong with rounding this answer to two significant figures?
99 × 1.02 = 100.98
Following the rules governing significant figures in multiplication, the answer can be rounded to 1.0 × 102. What is wrong with rounding this answer to two significant figures?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A piece of metal (mass = 17.268 g) is placed in 10.50 mL of chloroform (d = 1.498 g/mL) in a 25-mL graduated cylinder. The chloroform level increases to 15.46 mL. The best value for density of this metal from these data is
A) 1.12 g/mL.
B) 2.32 g/mL.
C) 3.481 g/mL.
D) 5.22 g/mL.
E) 3.48 g/mL.
A) 1.12 g/mL.
B) 2.32 g/mL.
C) 3.481 g/mL.
D) 5.22 g/mL.
E) 3.48 g/mL.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which response has the correct number of significant figures and units for the following mathematical operation? ?
A) 2.206 × 10-5 J/cal
B) 2 × 10-5 kcal
C) 2.206 × 10-5 kcal
D) 2.21 × 10-5 kcal
E) 2.2 × 10-5 kcal
A) 2.206 × 10-5 J/cal
B) 2 × 10-5 kcal
C) 2.206 × 10-5 kcal
D) 2.21 × 10-5 kcal
E) 2.2 × 10-5 kcal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Express the number 0.000160 in scientific notation.
A) 0.16 × 10-3
B) 1.6 × 104
C) 1.6 × 102
D) 1.6 × 10-4
E) 160 × 10-6
A) 0.16 × 10-3
B) 1.6 × 104
C) 1.6 × 102
D) 1.6 × 10-4
E) 160 × 10-6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
As part of the calibration of a new laboratory balance, a solid with a mass of 0.200 g is taken as a standard and determined with the following results: Trial Mass
1 0.197 g
2 0.192 g
3 0.212 g
Average mass: 0.200 g
A) The balance is both accurate and precise.
B) The balance is accurate but imprecise.
C) The balance is precise but inaccurate.
D) The balance is both inaccurate and imprecise.
E) None of these
1 0.197 g
2 0.192 g
3 0.212 g
Average mass: 0.200 g
A) The balance is both accurate and precise.
B) The balance is accurate but imprecise.
C) The balance is precise but inaccurate.
D) The balance is both inaccurate and imprecise.
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The average speed of oxygen molecules at 570°C is 1.49 × 105 cm/s. Which of the following calculations would convert this speed to units of miles per hour?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is the difference between the accuracy of measurements and the precision of measurements?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A graph of number of marbles (y-axis) versus the weight of the marbles (x-axis, grams) is shown to be linear with a trendline of y = 2.7x. What is the weight of the marbles when the number of marbles is 11?
A) 29
B) 0
C) 3
D) 10
E) 4
A) 29
B) 0
C) 3
D) 10
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A graph of a certain set of data is shown to be linear with a trendline of y = 32.0x + 8. What is the sign and slope of the trendline obtained from this data?
A) positive, 32.0
B) negative, 32.0
C) positive, 8
D) negative, 8
E) positive, 40.0
A) positive, 32.0
B) negative, 32.0
C) positive, 8
D) negative, 8
E) positive, 40.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The distance from Austin, Texas, to Lincoln, Nebraska, is 822 miles by car. Which of the following series of calculations will yield this distance in units of kilometers? (1 in = 2.54 cm (exact), 1 mi = 5280 ft (exact), 1 ft = 12 in (exact))
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following statements about dimensional analysis is true?
A) It is a general problem-solving approach that uses the dimensions or units of each value to guide us through calculations.
B) It is a problem-solving approach that guides us through calculations without using conversion factors.
C) It is a method of calculation that uses graphs for deriving exact values.
D) It is a method of calculation that does not require the use of a conversion factor.
E) It is a problem-solving approach that takes into consideration the standard deviation values.
A) It is a general problem-solving approach that uses the dimensions or units of each value to guide us through calculations.
B) It is a problem-solving approach that guides us through calculations without using conversion factors.
C) It is a method of calculation that uses graphs for deriving exact values.
D) It is a method of calculation that does not require the use of a conversion factor.
E) It is a problem-solving approach that takes into consideration the standard deviation values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



