Deck 9: The Nucleus, Radioactivity, and Nuclear Medicine
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/82
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: The Nucleus, Radioactivity, and Nuclear Medicine
1
What is the nuclear symbol for the isotope formed when 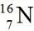 undergoes beta decay?
undergoes beta decay?
A)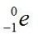
B)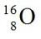
C)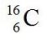
D)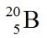
E)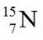
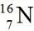 undergoes beta decay?
undergoes beta decay?A)
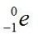
B)
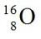
C)
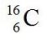
D)
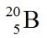
E)
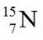
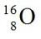
2
Which type of radiation is negatively charged?
A)alpha particle
B)beta particle
C)positron
D)gamma ray
E)All radiation types are negatively charged.
A)alpha particle
B)beta particle
C)positron
D)gamma ray
E)All radiation types are negatively charged.
beta particle
3
What nuclear process is used in commercial nuclear power plants to produce energy?
A)fusion
B)fission
C)metastable induction
D)radiocarbon dating
E)positron emission tomography
A)fusion
B)fission
C)metastable induction
D)radiocarbon dating
E)positron emission tomography
fission
4
What term is used to describe radioactive substances that are used as probes to study internal organs?
A)isotopes
B)tracers
C)metastable nuclides
D)Geiger counter
E)roentgens
A)isotopes
B)tracers
C)metastable nuclides
D)Geiger counter
E)roentgens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What statement concerning the half-life of a radioactive isotope is FALSE?
A)The half-life of a radioactive isotope is the amount of time it takes for one half of the sample to undergo radioactive decay.
B)The stability of a radioactive isotope is indicated by its half-life; isotopes with shorter half-lives are very unstable.
C)A radioactive isotope with a short half-life emits its radiation quickly.
D)The half-life of a particular radioactive isotope decreases as the amount of the radioactive material decreases.
E)Different radioactive isotopes have different decay rates, and therefore have different half-lives.
A)The half-life of a radioactive isotope is the amount of time it takes for one half of the sample to undergo radioactive decay.
B)The stability of a radioactive isotope is indicated by its half-life; isotopes with shorter half-lives are very unstable.
C)A radioactive isotope with a short half-life emits its radiation quickly.
D)The half-life of a particular radioactive isotope decreases as the amount of the radioactive material decreases.
E)Different radioactive isotopes have different decay rates, and therefore have different half-lives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Why are cancer cells more sensitive to radiation than normal cells?
A)The cells most sensitive to radiation are the ones undergoing rapid cellular division; cancer cells are an example of rapidly dividing cells.
B)The cells most sensitive to radiation are the ones undergoing slow cellular division; cancer cells are an example of slowly dividing cells.
C)The cells most sensitive to radiation are the ones that do not undergo cellular division; cancer cells are an example of cells that do not divide.
D)Cancer cells generally form on top of normal cells; they are therefore the cells closest to the applied radiation.
E)Cancer cells are shielded from radiation by their thick cellular membrane; normal cells lack this cellular membrane.
A)The cells most sensitive to radiation are the ones undergoing rapid cellular division; cancer cells are an example of rapidly dividing cells.
B)The cells most sensitive to radiation are the ones undergoing slow cellular division; cancer cells are an example of slowly dividing cells.
C)The cells most sensitive to radiation are the ones that do not undergo cellular division; cancer cells are an example of cells that do not divide.
D)Cancer cells generally form on top of normal cells; they are therefore the cells closest to the applied radiation.
E)Cancer cells are shielded from radiation by their thick cellular membrane; normal cells lack this cellular membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which phrase best describes a metastable isotope?
A)an isotope that is only partially stable
B)an isotope that decays by emitting only a gamma ray
C)an isotope that decays only when prompted by neutron bombardment
D)an isotope that is man-made
E)any isotope of an element that is radioactive
A)an isotope that is only partially stable
B)an isotope that decays by emitting only a gamma ray
C)an isotope that decays only when prompted by neutron bombardment
D)an isotope that is man-made
E)any isotope of an element that is radioactive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which is the most widely used radioactive isotope in nuclear medicine?
A)technetium-99m
B)hydrogen-3
C)uranium-235
D)carbon-14
E)plutonium-244
A)technetium-99m
B)hydrogen-3
C)uranium-235
D)carbon-14
E)plutonium-244

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which type of radiation emitted by radioactive nuclei has no mass and no charge?
A)alpha particle
B)beta particle
C)positron
D)gamma ray
E)All radiation types have a mass and charge.
A)alpha particle
B)beta particle
C)positron
D)gamma ray
E)All radiation types have a mass and charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the correct nuclear symbol for the unknown product "X" in the nuclear equation shown below? 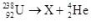
A)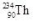
B)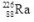
C)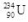
D)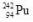
E)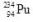
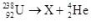
A)
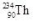
B)
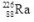
C)
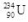
D)
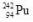
E)
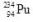

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Unstable nuclei become more stable by spontaneously undergoing a change in their nucleus and emitting radiation.What is the term used to describe this process?
A)stabilization
B)nuclear dissociation
C)radioactive decay
D)nuclear fusion
E)ionization
A)stabilization
B)nuclear dissociation
C)radioactive decay
D)nuclear fusion
E)ionization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The isotope  decays to
decays to 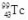 by emitting radiation.What type of radiation is emitted?
by emitting radiation.What type of radiation is emitted?
A)alpha particle
B)beta particle
C)positron
D)gamma ray
E)neutron
 decays to
decays to 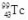 by emitting radiation.What type of radiation is emitted?
by emitting radiation.What type of radiation is emitted?A)alpha particle
B)beta particle
C)positron
D)gamma ray
E)neutron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Control rods made of cadmium or boron moderate the fission reactions in nuclear power plants.Which of the following best describes how control rods function?
A)Control rods absorb the high heat that is produced from the fission reactions, preventing overheating from occurring.
B)Control rods absorb some of the fast moving neutrons that are produced in the fission reactions, preventing their initiation of other fission reactions.
C)Control rods absorb the steam produced when the water is heated to a high temperature, preventing the generation of electricity.
D)Control rods absorb gamma rays that are responsible for initiating a chain reaction.
E)Control rods act as a catalyst for the reverse of the fission reaction, preventing the fission reaction from continuing.
A)Control rods absorb the high heat that is produced from the fission reactions, preventing overheating from occurring.
B)Control rods absorb some of the fast moving neutrons that are produced in the fission reactions, preventing their initiation of other fission reactions.
C)Control rods absorb the steam produced when the water is heated to a high temperature, preventing the generation of electricity.
D)Control rods absorb gamma rays that are responsible for initiating a chain reaction.
E)Control rods act as a catalyst for the reverse of the fission reaction, preventing the fission reaction from continuing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When a molecule is hit by gamma radiation, which of the following is likely to occur?
A)increase in mass
B)decrease in mass
C)ionization
D)swelling
E)replication
A)increase in mass
B)decrease in mass
C)ionization
D)swelling
E)replication

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A high degree of stability is predicted for nuclei with which of the following characteristics?
A)high neutron/proton ratio (>2)
B)more protons than neutrons
C)even number of protons or neutrons
D)odd number of protons
E)large number of protons (84 or more)
A)high neutron/proton ratio (>2)
B)more protons than neutrons
C)even number of protons or neutrons
D)odd number of protons
E)large number of protons (84 or more)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which radioactive isotope is involved in radiocarbon dating?
A)C-6
B)C-12
C)C-13
D)C-14
E)C-6 and C-12.
A)C-6
B)C-12
C)C-13
D)C-14
E)C-6 and C-12.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which type of radiation has the greatest penetrating power?
A)alpha particle
B)beta particle
C)positron
D)gamma ray
E)All radiation types are equally penetrating.
A)alpha particle
B)beta particle
C)positron
D)gamma ray
E)All radiation types are equally penetrating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What product nucleus results from the alpha decay of radium-226?
A)radium-226m
B)thorium-230
C)radon-222
D)radium-230
E)thorium-222
A)radium-226m
B)thorium-230
C)radon-222
D)radium-230
E)thorium-222

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Because iodine tends to concentrate in one particular organ of the body, radioactive iodine is often used as a diagnostic tool to determine how this organ is functioning.In which organ does iodine tend to concentrate?
A)liver
B)kidneys
C)brain
D)pancreas
E)thyroid
A)liver
B)kidneys
C)brain
D)pancreas
E)thyroid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the name given to the energy that is responsible for holding the protons and neutrons together in the nucleus?
A)nuclear energy
B)kinetic energy
C)static energy
D)binding energy
E)activation energy
A)nuclear energy
B)kinetic energy
C)static energy
D)binding energy
E)activation energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which type of radiation emitted by radioactive nuclei is similar in mass to a helium atom?
A)alpha
B)beta
C)gamma
D)delta
E)positron
A)alpha
B)beta
C)gamma
D)delta
E)positron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is the complete nuclear symbol for X in the equation for radioactive decay shown below? 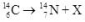
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)None of the choices are correct.
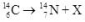
A)
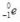
B)
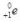
C)
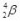
D)
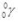
E)None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following isotopes has no neutrons?
A)H-1
B)H-2
C)H-3
D)He-4
E)C-12
A)H-1
B)H-2
C)H-3
D)He-4
E)C-12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which radioactive element is sometimes found in indoor air in such places as basements?
A)polonium
B)thallium
C)uranium
D)radon
E)plutonium
A)polonium
B)thallium
C)uranium
D)radon
E)plutonium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Phosphorus-31 is a non-radioactive isotope of phosphorus, and phosphorus-32 is a radioactive isotope of phosphorus used in nuclear medicine.Which statement concerning these two isotopes is TRUE?
A)Both isotopes emit high energy particles or rays known as radiation.
B)The radioactive isotope has one more proton than the non-radioactive isotope.
C)The non-radioactive isotope has 31 neutrons and the radioactive isotope has 32 neutrons.
D)Both isotopes have the same number of protons and neutrons.
E)The non-radioactive isotope has 16 neutrons and the radioactive isotope has 17 neutrons.
A)Both isotopes emit high energy particles or rays known as radiation.
B)The radioactive isotope has one more proton than the non-radioactive isotope.
C)The non-radioactive isotope has 31 neutrons and the radioactive isotope has 32 neutrons.
D)Both isotopes have the same number of protons and neutrons.
E)The non-radioactive isotope has 16 neutrons and the radioactive isotope has 17 neutrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The half-life of tritium ( 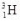 ) is 12 years.How long does it take for 16.0 ng of tritium to decay to the point where 2.0 ng remains?
) is 12 years.How long does it take for 16.0 ng of tritium to decay to the point where 2.0 ng remains?
A)12 years
B)24 years
C)36 years
D)48 years
E)52 years
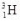 ) is 12 years.How long does it take for 16.0 ng of tritium to decay to the point where 2.0 ng remains?
) is 12 years.How long does it take for 16.0 ng of tritium to decay to the point where 2.0 ng remains?A)12 years
B)24 years
C)36 years
D)48 years
E)52 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What percentage of the initial amount of a radioactive isotope will remain after ten half-lives?
A)0.50%
B)0.78%
C)0.36%
D)0.11%
E)0.098%
A)0.50%
B)0.78%
C)0.36%
D)0.11%
E)0.098%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Why do radiation workers wear a film badge?
A)to measure their cumulative level of exposure to radiation
B)to measure the amount of time they spend in close proximity to radiation
C)to monitor the different types of radiation to which they are being exposed
D)to measure the radioactivity in their blood
E)to quickly determine the amount of radiation given off by a piece of radioactive material with which they are working
A)to measure their cumulative level of exposure to radiation
B)to measure the amount of time they spend in close proximity to radiation
C)to monitor the different types of radiation to which they are being exposed
D)to measure the radioactivity in their blood
E)to quickly determine the amount of radiation given off by a piece of radioactive material with which they are working

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
How many protons are contained in one alpha particle?
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)4
E)6
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)4
E)6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which nuclear particle is identical to an He2+ ion?
A)alpha
B)beta
C)gamma
D)proton
E)electron
A)alpha
B)beta
C)gamma
D)proton
E)electron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the charge of an alpha particle?
A)0
B)-1
C)1
D)2
E)4
A)0
B)-1
C)1
D)2
E)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the charge of a beta particle?
A)0
B)-1
C)1
D)-2
E)2
A)0
B)-1
C)1
D)-2
E)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which type of radiation emitted by radioactive nuclei is the slowest moving and least penetrating?
A)alpha
B)beta
C)gamma
D)positron
E)None of the choices are correct.
A)alpha
B)beta
C)gamma
D)positron
E)None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which statement concerning nuclear reactions and chemical reactions is FALSE?
A)Nuclear reactions involve changes in the protons or neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
B)Chemical reactions involve changes in the valence electrons of an atom.
C)Nuclear reactions usually result in a change in the identity of the radioactive isotope.
D)Nuclear reactions are capable of producing more energy than chemical reactions.
E)Chemical reactions always occur much faster than nuclear reactions.
A)Nuclear reactions involve changes in the protons or neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
B)Chemical reactions involve changes in the valence electrons of an atom.
C)Nuclear reactions usually result in a change in the identity of the radioactive isotope.
D)Nuclear reactions are capable of producing more energy than chemical reactions.
E)Chemical reactions always occur much faster than nuclear reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In the general symbol 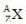 for a nucleus, how is the number of neutrons calculated?
for a nucleus, how is the number of neutrons calculated?
A)A + Z
B)A Z
C)Z A
D)2Z A
E)2Z + A
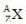 for a nucleus, how is the number of neutrons calculated?
for a nucleus, how is the number of neutrons calculated?A)A + Z
B)A Z
C)Z A
D)2Z A
E)2Z + A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following best describes the sequence with which nuclear power plants generate energy?
A)nuclear energy → mechanical energy → electrical energy → heat energy
B)nuclear energy → heat energy → mechanical energy → electrical energy
C)electrical energy → mechanical energy → heat energy → nuclear energy
D)mechanical energy → nuclear energy → heat energy → electrical energy
E)heat energy → mechanical energy → electrical energy → nuclear energy
A)nuclear energy → mechanical energy → electrical energy → heat energy
B)nuclear energy → heat energy → mechanical energy → electrical energy
C)electrical energy → mechanical energy → heat energy → nuclear energy
D)mechanical energy → nuclear energy → heat energy → electrical energy
E)heat energy → mechanical energy → electrical energy → nuclear energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The isotope 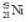 decays to
decays to 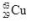 by emitting radiation.What type of radiation is emitted?
by emitting radiation.What type of radiation is emitted?
A)alpha
B)beta
C)gamma
D)positron
E)None of the choices are correct.
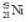 decays to
decays to 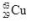 by emitting radiation.What type of radiation is emitted?
by emitting radiation.What type of radiation is emitted?A)alpha
B)beta
C)gamma
D)positron
E)None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The term LD50 represents which of the following?
A)the dosage of toxic material needed to kill 50% of the exposed population in 30 days
B)the number of people killed by 1 mg of a toxic material in one day
C)the number of people killed by 1 mg of a toxic material in 30 days
D)the percentage of people that will die when exposed to 50 mg of a toxic substance
E)the amount of radiation absorbed by the body when standing 50 m from a radioactive substance
A)the dosage of toxic material needed to kill 50% of the exposed population in 30 days
B)the number of people killed by 1 mg of a toxic material in one day
C)the number of people killed by 1 mg of a toxic material in 30 days
D)the percentage of people that will die when exposed to 50 mg of a toxic substance
E)the amount of radiation absorbed by the body when standing 50 m from a radioactive substance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The isotope 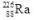 decays to
decays to 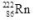 by emitting radiation.What type of radiation is emitted?
by emitting radiation.What type of radiation is emitted?
A)alpha
B)beta
C)gamma
D)positron
E)None of the choices are correct.
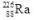 decays to
decays to 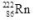 by emitting radiation.What type of radiation is emitted?
by emitting radiation.What type of radiation is emitted?A)alpha
B)beta
C)gamma
D)positron
E)None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
How many electrons are contained in an alpha particle?
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)4
E)6
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)4
E)6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Americium-241 is a radioactive isotope used in smoke detectors.If the symbol for this isotope is 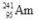 , which of the following correctly describes its subatomic composition?
, which of the following correctly describes its subatomic composition?
A)241 protons, 241 electrons, 95 neutrons
B)95 neutrons, 241 protons, 146 electrons
C)95 protons, 95 electrons, 51 neutrons
D)146 neutrons, 95 protons, 51 electrons
E)95 protons, 95 electrons, 146 neutrons
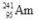 , which of the following correctly describes its subatomic composition?
, which of the following correctly describes its subatomic composition?A)241 protons, 241 electrons, 95 neutrons
B)95 neutrons, 241 protons, 146 electrons
C)95 protons, 95 electrons, 51 neutrons
D)146 neutrons, 95 protons, 51 electrons
E)95 protons, 95 electrons, 146 neutrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which radioactive emission can be stopped by a few sheets of paper?
A)alpha
B)beta
C)gamma
D)proton
E)electron
A)alpha
B)beta
C)gamma
D)proton
E)electron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How many half-lives are needed for a 400.0 ng sample of a radioactive isotope to decay to 12.5 ng?
A)4
B)5
C)10
D)16
E)32
A)4
B)5
C)10
D)16
E)32

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What does the symbol 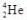 represent?
represent?
A)an alpha particle
B)a beta particle
C)a gamma ray
D)a positron
E)a deuteron
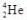 represent?
represent?A)an alpha particle
B)a beta particle
C)a gamma ray
D)a positron
E)a deuteron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What does the symbol 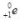 represent?
represent?
A)an alpha particle
B)a beta particle
C)a gamma ray
D)a positron
E)a deuteron
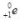 represent?
represent?A)an alpha particle
B)a beta particle
C)a gamma ray
D)a positron
E)a deuteron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following particles or rays requires barriers of lead and/or concrete for adequate protection?
A)alpha
B)beta
C)gamma
D)proton
E)electron
A)alpha
B)beta
C)gamma
D)proton
E)electron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When a nuclear reaction is balanced, which of the following is TRUE?
A)The number of atoms of each element is the same on either side of the reaction arrow.
B)The sum of the mass numbers is the same on either side of the reaction arrow.
C)The sum of the atomic numbers is the same on either side of the reaction arrow.
D)All of the choices are true.
E)Only the sum of the mass numbers is the same on either side of the reaction arrow and the sum of the atomic numbers is the same on either side of the reaction arrow are true.
A)The number of atoms of each element is the same on either side of the reaction arrow.
B)The sum of the mass numbers is the same on either side of the reaction arrow.
C)The sum of the atomic numbers is the same on either side of the reaction arrow.
D)All of the choices are true.
E)Only the sum of the mass numbers is the same on either side of the reaction arrow and the sum of the atomic numbers is the same on either side of the reaction arrow are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) depends on the presence of what type of particles in body tissue?
A)carbon atoms
B)hydrogen atoms
C)water molecules
D)radioactive isotopes
E)magnetic particles
A)carbon atoms
B)hydrogen atoms
C)water molecules
D)radioactive isotopes
E)magnetic particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A 200.0-ng sample of sodium-24 was stored in a lead-lined cabinet for 45 hours.The half-life of sodium-24 is 15 hours.How much sodium-24 remains?
A)100 ng
B)75 ng
C)50 ng
D)25 ng
E)13 ng
A)100 ng
B)75 ng
C)50 ng
D)25 ng
E)13 ng

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What nuclear process involves heavy nuclei splitting into lighter nuclei?
A)gamma decay
B)beta decay
C)breeding
D)fission
E)fusion
A)gamma decay
B)beta decay
C)breeding
D)fission
E)fusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What information is conveyed by the "m" in 99mTc?
A)The mass of the isotope is 99.
B)The isotope is metastable.
C)The isotope is man-made.
D)There are multiple isotopes for this element.
E)This is the most abundant isotope for this element.
A)The mass of the isotope is 99.
B)The isotope is metastable.
C)The isotope is man-made.
D)There are multiple isotopes for this element.
E)This is the most abundant isotope for this element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What fraction of the initial amount of an isotope remains after five half-lives?
A)0.200
B)0.969
C)0.0100
D)0.0313
E)1.00 × 10-10
A)0.200
B)0.969
C)0.0100
D)0.0313
E)1.00 × 10-10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which one of the following radioactive isotopes is used to diagnose coronary disease?
A)thallium-201
B)iodine-131
C)xenon-133
D)uranium-238
E)carbon-14
A)thallium-201
B)iodine-131
C)xenon-133
D)uranium-238
E)carbon-14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When the isotope 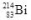 undergoes alpha decay, what isotope is formed?
undergoes alpha decay, what isotope is formed?
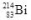 undergoes alpha decay, what isotope is formed?
undergoes alpha decay, what isotope is formed?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What is the process responsible for energy production in the sun?
A)chemical combustion
B)fissionoxidation-reduction
C)decomposition
D)fission
E)fusion
A)chemical combustion
B)fissionoxidation-reduction
C)decomposition
D)fission
E)fusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What fissionable isotope or element is produced from uranium-238 in a breeder reactor?
A)uranium-235
B)uranium-238m
C)plutonium-239
D)carbon-14
E)hydrogen-3
A)uranium-235
B)uranium-238m
C)plutonium-239
D)carbon-14
E)hydrogen-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What particle or nucleus X is needed to complete the following equation? 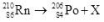
A)proton
B)uranium-235
C)alpha
D)beta
E)gamma
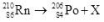
A)proton
B)uranium-235
C)alpha
D)beta
E)gamma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A 50-mg sample of iodine-131 was placed in a container 32.4 days ago.If its half-life is 8.1 days, how many milligrams of iodine-131 are now present?
A)47.3 mg
B)3.1 mg
C)3.24 mg
D)0.81 mg
E)6.2 mg
A)47.3 mg
B)3.1 mg
C)3.24 mg
D)0.81 mg
E)6.2 mg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When the isotope 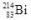 undergoes beta decay, what isotope is formed?
undergoes beta decay, what isotope is formed?
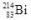 undergoes beta decay, what isotope is formed?
undergoes beta decay, what isotope is formed?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
From which of the following isotopes is carbon-14 formed by cosmic ray bombardment in the upper atmosphere?
A)Li-5
B)U-238
C)O-16
D)O-18
E)N-14
A)Li-5
B)U-238
C)O-16
D)O-18
E)N-14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Beta particles are a form of electromagnetic energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Positrons are produced when a proton is converted to a neutron in the nucleus of a radioactive isotope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The half-life of cobalt-60 is 5.3 years.What percent of a sample of cobalt-60 will remain after 21.2 years?
A)50%
B)40%
C)12.5%
D)10%
E)6.25%
A)50%
B)40%
C)12.5%
D)10%
E)6.25%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Gamma rays move at the speed of light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A radioactive sample will decay completely in two half-lives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The sun's source of energy is nuclear fission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Nuclei with 84 or more protons are unstable and radioactive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Commercial nuclear power plants use the fusion process to generate electrical energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When a molecule is hit by gamma radiation, it may become ionized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Compared to the energy of chemical bonds, nuclear binding energy is very weak.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A metastable isotope decays by emitting a gamma ray.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
After four half-lives, the fraction of a radioactive isotope remaining is one eighth of the initial amount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following is not a method used for detecting radiation?
A)Geiger counter
B)photographic imaging
C)film badges
D)computer imaging
E)radiocarbon dating
A)Geiger counter
B)photographic imaging
C)film badges
D)computer imaging
E)radiocarbon dating

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which statement concerning the stability of nuclei is TRUE?
A)Light elements are stable if their ratio of protons to neutrons is 2:1.
B)Nuclei with 36 or more protons are unstable.
C)Isotopes with even numbers of protons and neutrons are more stable than those with odd numbers of protons and neutrons.
D)All isotopes with more protons than neutrons are stable.
E)Naturally occurring isotopes containing 1, 3, 5, 7, 9…protons or neutrons are stable.
A)Light elements are stable if their ratio of protons to neutrons is 2:1.
B)Nuclei with 36 or more protons are unstable.
C)Isotopes with even numbers of protons and neutrons are more stable than those with odd numbers of protons and neutrons.
D)All isotopes with more protons than neutrons are stable.
E)Naturally occurring isotopes containing 1, 3, 5, 7, 9…protons or neutrons are stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Isotopes with even numbers of protons and neutrons are generally more stable than those with odd numbers of these particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What type of radioactive decay is illustrated by the following nuclear equation? 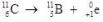
A)positron emission
B)alpha decay
C)beta decay
D)gamma production
E)helium emission
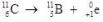
A)positron emission
B)alpha decay
C)beta decay
D)gamma production
E)helium emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The mass number of an alpha particle is 4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What type of radioactive decay is illustrated by the following nuclear equation? 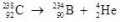
A)positron emission
B)alpha decay
C)beta decay
D)gamma production
E)helium emission
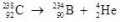
A)positron emission
B)alpha decay
C)beta decay
D)gamma production
E)helium emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What type of radioactive decay is illustrated by the following nuclear equation? 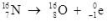
A)positron emission
B)alpha decay
C)beta decay
D)gamma production
E)helium emission
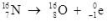
A)positron emission
B)alpha decay
C)beta decay
D)gamma production
E)helium emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Doubling the distance from a source of radioactivity will halve the radiation intensity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



