Deck 29: Monetary Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/243
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 29: Monetary Policy
1
The Fed's duties include acting as a lender of last resort and supervising or regulating a variety of financial institutions.
True
2
A contractionary monetary policy decreases the money supply and the interest rate, which decreases investment and output.
False
3
The federal funds rate is the rate banks charge one another for overnight loans.
True
4
The difference between a standard and an inverted yield curve is that when the yield curve is inverted, the longer-term bond pays a lower interest rate than a short-term bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Monetary policy directly affects:
A)social spending.
B)tax rates.
C)the availability of credit.
D)the antitrust laws.
A)social spending.
B)tax rates.
C)the availability of credit.
D)the antitrust laws.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is the path through which contractionary monetary policy works?
A)Money down implies interest rate up implies investment down implies income down.
B)Money down implies interest rate down implies investment down implies income down.
C)Money down implies interest rate up implies investment up implies income down.
D)Money down implies interest rate down implies investment up implies income down.
A)Money down implies interest rate up implies investment down implies income down.
B)Money down implies interest rate down implies investment down implies income down.
C)Money down implies interest rate up implies investment up implies income down.
D)Money down implies interest rate down implies investment up implies income down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Monetary policy is one of the two main macroeconomic tools governments use to control the aggregate economy. The other is:
A)fiscal policy.
B)foreign policy.
C)trade policy.
D)immigration policy.
A)fiscal policy.
B)foreign policy.
C)trade policy.
D)immigration policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The Taylor Rule relates changes in the money supply to changes in interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The Federal Reserve controls the long-term interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Who determines U.S. monetary policy?
A)Congress
B)The president
C)The Internal Revenue Service
D)The Federal Reserve
A)Congress
B)The president
C)The Internal Revenue Service
D)The Federal Reserve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The art of monetary policy requires acting in accordance with the Taylor Rule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
According to the Taylor Rule, if current inflation is 2.5 percent, the target inflation rate is 2 percent, and output is 1 percent above potential, the Fed should target the federal funds rate at 5.25 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The three tools of monetary policy are open market operations, setting prices, and setting the velocity of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A decrease in the federal funds rate is an indication that monetary policy is expansionary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the short run, if the Fed undertakes expansionary monetary policy, the effect will be to shift the:
A)AD curve out to the right.
B)AD curve in to the left.
C)SAS curve up.
D)SAS curve down.
A)AD curve out to the right.
B)AD curve in to the left.
C)SAS curve up.
D)SAS curve down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the short run, if the Fed undertakes contractionary monetary policy, the effect will be to shift the:
A)AD curve out to the right.
B)AD curve in to the left.
C)SAS curve up.
D)SAS curve down.
A)AD curve out to the right.
B)AD curve in to the left.
C)SAS curve up.
D)SAS curve down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the AS/AD model, an increase in the money supply causes an increase in the interest rate and an increase in investment spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is not directly affected by monetary policy?
A)The money supply
B)The banking system
C)The availability of credit
D)The budget deficit
A)The money supply
B)The banking system
C)The availability of credit
D)The budget deficit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Expansionary monetary policy is always expected to increase:
A)nominal income but never real income.
B)real income but never nominal income.
C)nominal income.
D)real income.
A)nominal income but never real income.
B)real income but never nominal income.
C)nominal income.
D)real income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An increase in the federal funds rate is a signal that the Fed wants a tighter monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Assuming an economy is initially at potential output, in the long run, an expansionary monetary policy is expected:
A)not to affect output in the long run.
B)not to affect output in either the short run or the long run.
C)to affect output, but only in the long run.
D)to affect output in both the short run and the long run.
A)not to affect output in the long run.
B)not to affect output in either the short run or the long run.
C)to affect output, but only in the long run.
D)to affect output in both the short run and the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
With an upward sloping SAS curve, an expansionary monetary policy that affects the price level but not real output could be the result of a shift of:
A)both the AD and SAS curves.
B)only the AD curve.
C)only the SAS curve.
D)neither the SAS curve nor the AD curve.
A)both the AD and SAS curves.
B)only the AD curve.
C)only the SAS curve.
D)neither the SAS curve nor the AD curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A monetary policy that reduces both real and nominal income:
A)must be expansionary.
B)must be contractionary.
C)cannot be expansionary or contractionary.
D)could be expansionary or contractionary.
A)must be expansionary.
B)must be contractionary.
C)cannot be expansionary or contractionary.
D)could be expansionary or contractionary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the AS/AD model, a contractionary monetary policy:
A)reduces investment but increases aggregate demand.
B)increases both investment and aggregate demand.
C)reduces both investment and aggregate demand.
D)increases investment but reduces aggregate demand.
A)reduces investment but increases aggregate demand.
B)increases both investment and aggregate demand.
C)reduces both investment and aggregate demand.
D)increases investment but reduces aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If real income increases by 4 percent and the price level increases by 3 percent, nominal income must:
A)increase by 7 percent.
B)increase by 1 percent.
C)decrease by 1 percent.
D)decrease by 7 percent.
A)increase by 7 percent.
B)increase by 1 percent.
C)decrease by 1 percent.
D)decrease by 7 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Refer to the graph shown. Suppose the economy is initially at A but then the Fed adopts an expansionary monetary policy. The initial effect of this policy will be pressure to move the economy to: 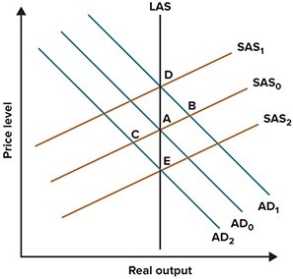
A)E.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

A)E.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Contractionary monetary policy is most likely to:
A)increases interest rates, raises investment, and increases income.
B)decreases interest rates, raises investment, and increases income.
C)increases interest rates, reduces investment, and decreases income.
D)decreases interest rates, reduces investment, and decreases income.
A)increases interest rates, raises investment, and increases income.
B)decreases interest rates, raises investment, and increases income.
C)increases interest rates, reduces investment, and decreases income.
D)decreases interest rates, reduces investment, and decreases income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If prices are inflexible, monetary policy:
A)affects both inflation and real output.
B)affects real output but not inflation.
C)affects inflation but not real output.
D)doesn't affect real output or inflation.
A)affects both inflation and real output.
B)affects real output but not inflation.
C)affects inflation but not real output.
D)doesn't affect real output or inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the AS/AD model, in the short run, monetary policy affects:
A)only inflation.
B)only real output.
C)both inflation and real output.
D)neither inflation nor real output.
A)only inflation.
B)only real output.
C)both inflation and real output.
D)neither inflation nor real output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If nominal income increases by 4 percent and the price level increases by 3 percent, real income must:
A)increase by 7 percent.
B)increase by 1 percent.
C)decrease by 1 percent.
D)decrease by 7 percent.
A)increase by 7 percent.
B)increase by 1 percent.
C)decrease by 1 percent.
D)decrease by 7 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Other things equal, a rise in interest rates can be expected to:
A)increase the quantity of investment.
B)decrease the quantity of investment.
C)have no effect upon the quantity of investment.
D)increase equilibrium income.
A)increase the quantity of investment.
B)decrease the quantity of investment.
C)have no effect upon the quantity of investment.
D)increase equilibrium income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Refer to the graph shown. Suppose the economy is initially at A but then the Fed adopts a contractionary monetary policy. Using the standard AS/AD model reasoning, this policy will cause the economy to move to: 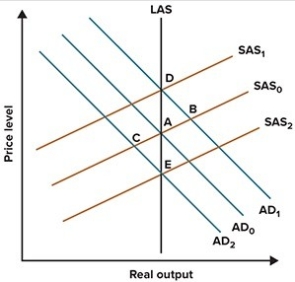
A)B in the short run and the long run.
B)A in the short run and the long run.
C)C in the short run and A in the long run.
D)C in the short run and E in the long run.

A)B in the short run and the long run.
B)A in the short run and the long run.
C)C in the short run and A in the long run.
D)C in the short run and E in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In the AS/AD model, an expansionary monetary policy has the greatest effect on the price level when it:
A)increases both nominal and real income.
B)increases real income but not nominal income.
C)increases nominal income but not real income.
D)doesn't increase real or nominal income.
A)increases both nominal and real income.
B)increases real income but not nominal income.
C)increases nominal income but not real income.
D)doesn't increase real or nominal income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Refer to the graph shown. Suppose the economy is initially at A but then the Fed adopts a contractionary monetary policy. The long-term effect of this policy will be to move the economy to: 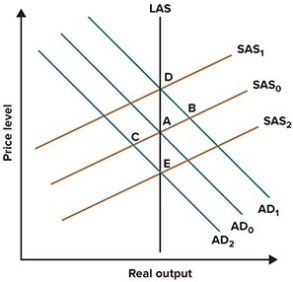
A)E.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

A)E.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An expansionary monetary policy is most likely to:
A)increases interest rates, raises investment, and increases income.
B)decreases interest rates, raises investment, and increases income.
C)increases interest rates, reduces investment, and decreases income.
D)decreases interest rates, reduces investment, and decreases income.
A)increases interest rates, raises investment, and increases income.
B)decreases interest rates, raises investment, and increases income.
C)increases interest rates, reduces investment, and decreases income.
D)decreases interest rates, reduces investment, and decreases income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If nominal income increases by 3 percent and real income increases by 4 percent, the price level must:
A)increase by 7 percent.
B)increase by 1 percent.
C)decrease by 1 percent.
D)decrease by 7 percent.
A)increase by 7 percent.
B)increase by 1 percent.
C)decrease by 1 percent.
D)decrease by 7 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If prices are inflexible, monetary policy:
A)affects both nominal and real income.
B)affects real income but not nominal income.
C)affects nominal income but not real income.
D)does not affect real or nominal income.
A)affects both nominal and real income.
B)affects real income but not nominal income.
C)affects nominal income but not real income.
D)does not affect real or nominal income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Refer to the graph shown. Monetary policy that shifts the AD curve from AD0 to AD2 is 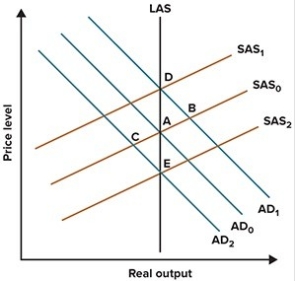
A)expansionary.
B)contractionary.
C)neither expansionary nor contractionary since it does not affect output.
D)neither expansionary nor contractionary since it does not affect inflation.

A)expansionary.
B)contractionary.
C)neither expansionary nor contractionary since it does not affect output.
D)neither expansionary nor contractionary since it does not affect inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If a contractionary monetary policy reduces nominal income in the short run, but not real income, it must be true that prices:
A)are perfectly flexible.
B)are at least partially flexible.
C)are completely inflexible.
D)have not fully adjusted to the change in aggregate demand.
A)are perfectly flexible.
B)are at least partially flexible.
C)are completely inflexible.
D)have not fully adjusted to the change in aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Refer to the graph shown. Monetary policy that shifts the AD curve from AD0 to AD1 and moves the economy from A to B: 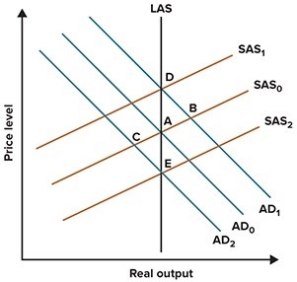
A)increases nominal output but not real output in the short run.
B)increases both real and nominal output in the short run.
C)increases real output but not nominal output in the short run.
D)doesn't increase real or nominal output in the short run.

A)increases nominal output but not real output in the short run.
B)increases both real and nominal output in the short run.
C)increases real output but not nominal output in the short run.
D)doesn't increase real or nominal output in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The body that directly oversees the 12 regional Federal Reserve banks is the:
A)Federal Open Market Committee.
B)Board of Governors.
C)U.S. Congress.
D)Federal Advisory Council.
A)Federal Open Market Committee.
B)Board of Governors.
C)U.S. Congress.
D)Federal Advisory Council.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Central banks are responsible for:
A)both monetary policy and fiscal policy.
B)monetary policy but not fiscal policy.
C)fiscal policy but not monetary policy.
D)neither monetary policy nor fiscal policy.
A)both monetary policy and fiscal policy.
B)monetary policy but not fiscal policy.
C)fiscal policy but not monetary policy.
D)neither monetary policy nor fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
One year, the lead sentence in a Wall Street Journal article read, "Tight job markets, rising wages, and the economy's continued strength put more pressure on the Federal Reserve to raise short-term interest rates." If the Fed responded to this pressure, it would adopt:
A)a contractionary monetary policy that reduces output.
B)a contractionary monetary policy that raises output.
C)an expansionary monetary policy that reduces output.
D)an expansionary monetary policy that raises output.
A)a contractionary monetary policy that reduces output.
B)a contractionary monetary policy that raises output.
C)an expansionary monetary policy that reduces output.
D)an expansionary monetary policy that raises output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The central bank of the United States is:
A)the Treasury.
B)the Fed.
C)the Bank of the United States.
D)Old Lady of Threadneedle Street.
A)the Treasury.
B)the Fed.
C)the Bank of the United States.
D)Old Lady of Threadneedle Street.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Fed watchers are:
A)financial advisers for the government, telling them when raising taxes will raise revenue and when it won't.
B)part of the Fed governor system and are given voting power on the FOMC.
C)individuals or organizations whose sole occupation is to follow the Fed's FOMC.
D)individuals or organizations whose sole occupation is to predict the future of the interest rates.
A)financial advisers for the government, telling them when raising taxes will raise revenue and when it won't.
B)part of the Fed governor system and are given voting power on the FOMC.
C)individuals or organizations whose sole occupation is to follow the Fed's FOMC.
D)individuals or organizations whose sole occupation is to predict the future of the interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When there are no vacancies, how many people serve on the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve system?
A)5
B)7
C)11
D)12
A)5
B)7
C)11
D)12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the United States monetary policy is:
A)also known as fiscal policy.
B)undertaken by the Treasury.
C)undertaken by the Fed.
D)also known as global policy.
A)also known as fiscal policy.
B)undertaken by the Treasury.
C)undertaken by the Fed.
D)also known as global policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The chairperson of the Federal Reserve's Board of Governors is:
A)elected by the public.
B)selected by commercial banks.
C)appointed by the president.
D)appointed by the Board of Governors.
A)elected by the public.
B)selected by commercial banks.
C)appointed by the president.
D)appointed by the Board of Governors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the AS/AD model, an effect of an expansionary monetary policy is to:
A)reduce investment spending.
B)shift the aggregate demand curve to the left.
C)raise interest rates.
D)lower interest rates.
A)reduce investment spending.
B)shift the aggregate demand curve to the left.
C)raise interest rates.
D)lower interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In the AS/AD model, higher interest rates are produced by:
A)an expansionary monetary policy.
B)an activist monetary policy.
C)a contractionary monetary policy.
D)a steady-as-you-go monetary policy.
A)an expansionary monetary policy.
B)an activist monetary policy.
C)a contractionary monetary policy.
D)a steady-as-you-go monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Unlike the practice in many other countries, in the United States:
A)only monetary policy is used to influence the economy, and fiscal policy is not allowed.
B)only fiscal policy is used to influence the economy, and monetary policy is not allowed.
C)the agency responsible for monetary policy is not directly controlled by the government.
D)the agency responsible for fiscal policy is not directly controlled by the government.
A)only monetary policy is used to influence the economy, and fiscal policy is not allowed.
B)only fiscal policy is used to influence the economy, and monetary policy is not allowed.
C)the agency responsible for monetary policy is not directly controlled by the government.
D)the agency responsible for fiscal policy is not directly controlled by the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
FOMC stands for:
A)Federal Open Money Committee.
B)Federal Open Market Committee.
C)Fixed Open Market Commitments.
D)Federation of Open Monies Committee.
A)Federal Open Money Committee.
B)Federal Open Market Committee.
C)Fixed Open Market Commitments.
D)Federation of Open Monies Committee.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Monetary policy that seeks to minimize the business cycle in the AS/AD model involves:
A)contractionary monetary policy throughout the business cycle.
B)expansionary monetary policy throughout the business cycle.
C)contractionary monetary policy when the economy is above trend growth and expansionary policy when the economy is below trend growth.
D)expansionary monetary policy when the economy is above trend growth and contractionary policy when the economy is below trend growth.
A)contractionary monetary policy throughout the business cycle.
B)expansionary monetary policy throughout the business cycle.
C)contractionary monetary policy when the economy is above trend growth and expansionary policy when the economy is below trend growth.
D)expansionary monetary policy when the economy is above trend growth and contractionary policy when the economy is below trend growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
One of the duties of the Fed is to:
A)change the demand for money.
B)set the market interest rate.
C)offer financial advising to the government.
D)offer financial advising to the public.
A)change the demand for money.
B)set the market interest rate.
C)offer financial advising to the government.
D)offer financial advising to the public.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The group that is comprised of five presidents of Fed regional banks and seven Fed governors that gathers around a table to discuss whether to increase interest rates is the:
A)Federal Open Market Committee.
B)Federal Depository Insurance Corporation.
C)Federal Advisory Council.
D)National Federal Reserve Bank.
A)Federal Open Market Committee.
B)Federal Depository Insurance Corporation.
C)Federal Advisory Council.
D)National Federal Reserve Bank.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
There are seven Governors of the Federal Reserve, who are appointed for terms of:
A)5 years.
B)10 years.
C)14 years.
D)17 years.
A)5 years.
B)10 years.
C)14 years.
D)17 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Most decisions about implementing monetary policy are made by the:
A)chairman of the Fed only.
B)president.
C)president and Congress.
D)Federal Open Market Committee.
A)chairman of the Fed only.
B)president.
C)president and Congress.
D)Federal Open Market Committee.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
How many regional banks are in the Federal Reserve System?
A)6
B)8
C)12
D)15
A)6
B)8
C)12
D)15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In the fall of 2008, the Federal Reserve lowered its target for the federal funds rate to nearly 0 percent. What is the name of the group within the Federal Reserve that made this decision?
A)Federal Advisory Committee
B)Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation
C)Federal Funds Operating Group
D)Federal Open Market Committee
A)Federal Advisory Committee
B)Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation
C)Federal Funds Operating Group
D)Federal Open Market Committee

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Expansionary monetary policy results in a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the right. The effect of the monetary policy on the aggregate demand is:
A)direct from the money supply to the aggregate demand.
B)indirect through the short-term and long-term interest rates.
C)direct from the money supply to the aggregate supply.
D)indirect through the government expenditures.
A)direct from the money supply to the aggregate demand.
B)indirect through the short-term and long-term interest rates.
C)direct from the money supply to the aggregate supply.
D)indirect through the government expenditures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Explicit functions of the Fed include all the following except:
A)conducting monetary policy.
B)conducting fiscal policy.
C)providing banking services to the U.S. government.
D)serving as a lender of last resort to financial institutions.
A)conducting monetary policy.
B)conducting fiscal policy.
C)providing banking services to the U.S. government.
D)serving as a lender of last resort to financial institutions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
By law, a commercial bank is allowed to lend out of all its:
A)deposits.
B)excess reserves.
C)required reserves.
D)demand (checkable)deposits.
A)deposits.
B)excess reserves.
C)required reserves.
D)demand (checkable)deposits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Open market operations are related to:
A)actions taken by the Fed to close or merge weakened banks.
B)changes in the reserve requirement.
C)changes in the discount rate.
D)the Fed's buying and selling of government securities.
A)actions taken by the Fed to close or merge weakened banks.
B)changes in the reserve requirement.
C)changes in the discount rate.
D)the Fed's buying and selling of government securities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
All of the following are components of the Federal Reserve system except the:
A)12 regional Federal Reserve banks.
B)Federal Open Market Committee.
C)Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation.
D)Board of Governors.
A)12 regional Federal Reserve banks.
B)Federal Open Market Committee.
C)Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation.
D)Board of Governors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which is not a function of the Fed?
A)Conducting monetary policy
B)Serving as a lender of last resort
C)Providing financial services such as check clearing to commercial banks
D)Directly financing U.S. budget deficits
A)Conducting monetary policy
B)Serving as a lender of last resort
C)Providing financial services such as check clearing to commercial banks
D)Directly financing U.S. budget deficits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The primary tool of monetary policy is:
A)the discount rate.
B)the reserve requirement.
C)the prime rate.
D)open market operations.
A)the discount rate.
B)the reserve requirement.
C)the prime rate.
D)open market operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following Fed actions increases the money supply?
A)Decreasing the amount of loans made to commercial banks
B)Buying government securities in the open market
C)Selling government securities in the open market
D)Increasing reserve requirements
A)Decreasing the amount of loans made to commercial banks
B)Buying government securities in the open market
C)Selling government securities in the open market
D)Increasing reserve requirements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following Fed policies would help the economy out of a recession?
A)Open market purchases of government securities
B)Open market sales of government securities
C)An increase in the discount rate
D)An increase in reserve requirements
A)Open market purchases of government securities
B)Open market sales of government securities
C)An increase in the discount rate
D)An increase in reserve requirements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The monetary base is comprised of:
A)currency held by the public.
B)vault cash.
C)commercial bank deposits at the Fed.
D)all of the options listed here.
A)currency held by the public.
B)vault cash.
C)commercial bank deposits at the Fed.
D)all of the options listed here.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The explicit functions given to the Fed by the Congress include all of the following except:
A)regulating financial institutions.
B)serving as a lender of last resort to financial institutions.
C)providing banking services to the U.S. government.
D)holding the nominal interest rate no more than 2 percent above the real interest rate.
A)regulating financial institutions.
B)serving as a lender of last resort to financial institutions.
C)providing banking services to the U.S. government.
D)holding the nominal interest rate no more than 2 percent above the real interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Suppose the money multiplier in the United States is 4. If the Fed wants to expand the money supply by 600 it should:
A)buy government securities worth 150.
B)buy government securities worth 600.
C)sell government securities worth 150.
D)sell government securities worth 600.
A)buy government securities worth 150.
B)buy government securities worth 600.
C)sell government securities worth 150.
D)sell government securities worth 600.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose the money multiplier in the United States is 2.5. If the Fed wants to reduce the money supply by 1,000 it should:
A)buy government securities worth 250.
B)buy government securities worth 400.
C)sell government securities worth 250.
D)sell government securities worth 400.
A)buy government securities worth 250.
B)buy government securities worth 400.
C)sell government securities worth 250.
D)sell government securities worth 400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If the Fed wants to increase the money supply, it can:
A)buy bonds.
B)sell bonds.
C)pass a law that interest rates rise.
D)pass a law that interest rates fall.
A)buy bonds.
B)sell bonds.
C)pass a law that interest rates rise.
D)pass a law that interest rates fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When the Fed sells bonds, the money supply:
A)expands.
B)contracts.
C)sometimes rises and sometimes falls.
D)Selling bonds does not affect the money supply.
A)expands.
B)contracts.
C)sometimes rises and sometimes falls.
D)Selling bonds does not affect the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Suppose the money multiplier in the United States is 2.5. If the Fed wants to reduce the money supply by 1,500 it should:
A)raise the required reserve ratio to 0.2.
B)raise the discount rate by 2 percentage points.
C)buy government securities worth 600.
D)sell government securities worth 600.
A)raise the required reserve ratio to 0.2.
B)raise the discount rate by 2 percentage points.
C)buy government securities worth 600.
D)sell government securities worth 600.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which is not something the Fed can do directly to conduct monetary policy?
A)Change the exchange rate
B)Change the reserve requirement
C)Change the discount rate
D)Execute open market operations
A)Change the exchange rate
B)Change the reserve requirement
C)Change the discount rate
D)Execute open market operations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The monetary base includes:
A)currency and coin in circulation plus checkable deposits.
B)currency and coin in circulation only.
C)vault cash plus checkable deposits.
D)currency and cash plus commercial bank deposits at the Fed.
A)currency and coin in circulation plus checkable deposits.
B)currency and coin in circulation only.
C)vault cash plus checkable deposits.
D)currency and cash plus commercial bank deposits at the Fed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The central bank in the United States does all the following except:
A)act as a financial adviser to the government.
B)loan money to corporations.
C)loan money to banks.
D)issue coin and currency.
A)act as a financial adviser to the government.
B)loan money to corporations.
C)loan money to banks.
D)issue coin and currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The reserve requirement is the:
A)maximum ratio of reserves to deposits that a bank can have.
B)minimum ratio of reserves to deposits that a bank can have.
C)maximum level of reserves a bank can have.
D)minimum level of reserves a bank can have.
A)maximum ratio of reserves to deposits that a bank can have.
B)minimum ratio of reserves to deposits that a bank can have.
C)maximum level of reserves a bank can have.
D)minimum level of reserves a bank can have.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Federal Reserve sales of government securities:
A)increase bank reserves and increase the money supply.
B)decrease bank reserves and decrease the money supply.
C)decrease bank reserves and increase the money supply.
D)increase bank reserves and decrease the money supply.
A)increase bank reserves and increase the money supply.
B)decrease bank reserves and decrease the money supply.
C)decrease bank reserves and increase the money supply.
D)increase bank reserves and decrease the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



